A karst geology rotary-dig cast-in-place pile hole-forming technology
A cast-in-place pile and geology technology, applied in sheet pile walls, infrastructure engineering, construction, etc., can solve problems such as drill bit falling, drilling sticking, drilling deflection, etc. Avoid the effect of sticking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
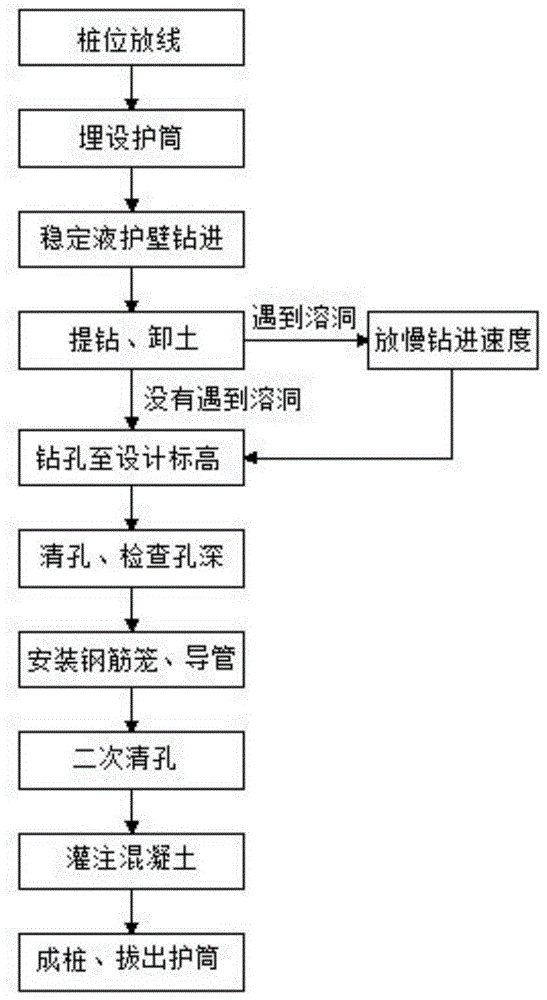
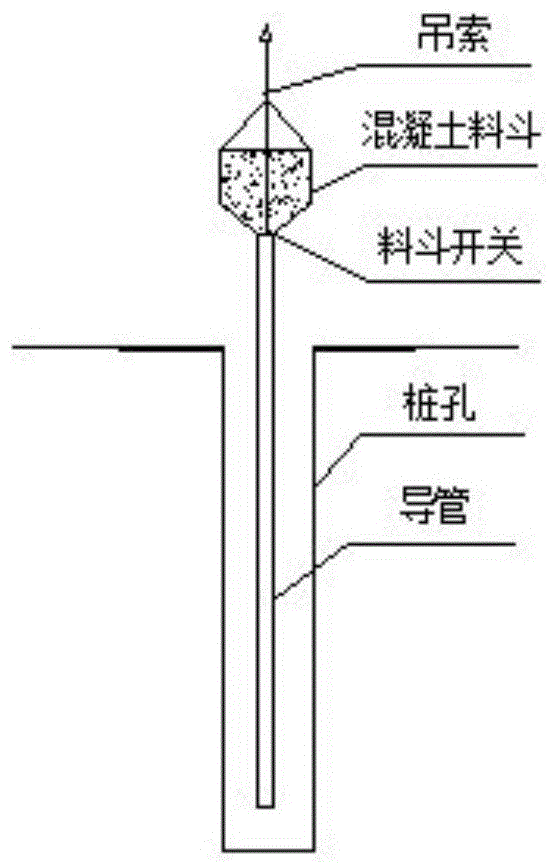
[0023] refer to figure 1 , the technical solution adopted by the present invention to solve its technical problems is: the construction process of the improved rotary-dug hole-forming cast-in-place pile in the karst area is: leveling the site→pile position setting-out→rotary drilling rig in place→burying casing→casing Supplement internal stabilization fluid → rotary digging to form a hole (slow down the drilling speed when encountering a karst cave, and drill to the design elevation when not encountering a karst cave) → clean the hole and check the depth of the hole → install steel cages and conduits → gas lift reverse circulation 2 Secondary hole cleaning → pouring underwater concrete (considering the existence of karst caves, it is necessary to prepare 30 to 40 cubic meters of concrete to prevent the break...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com