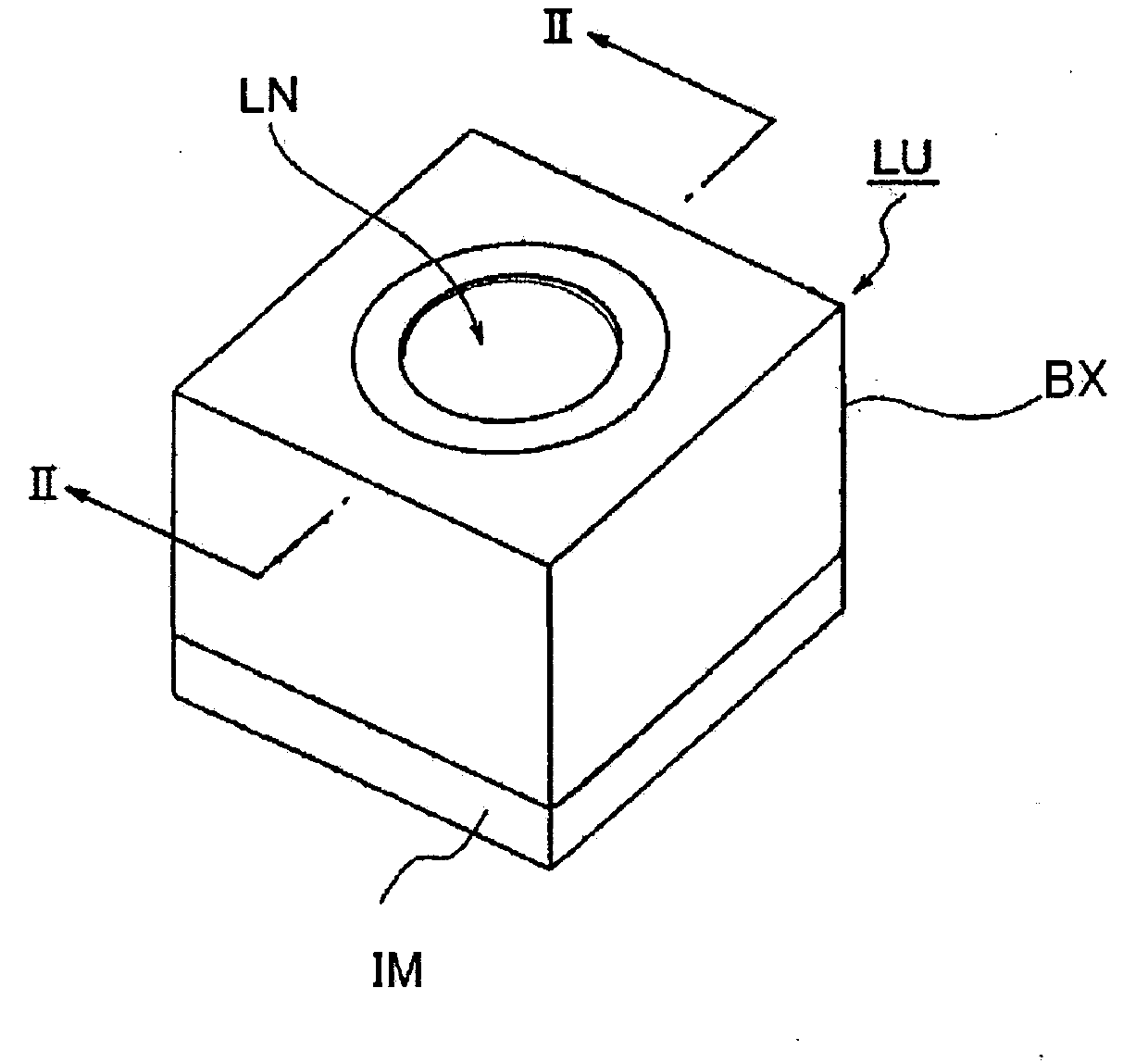
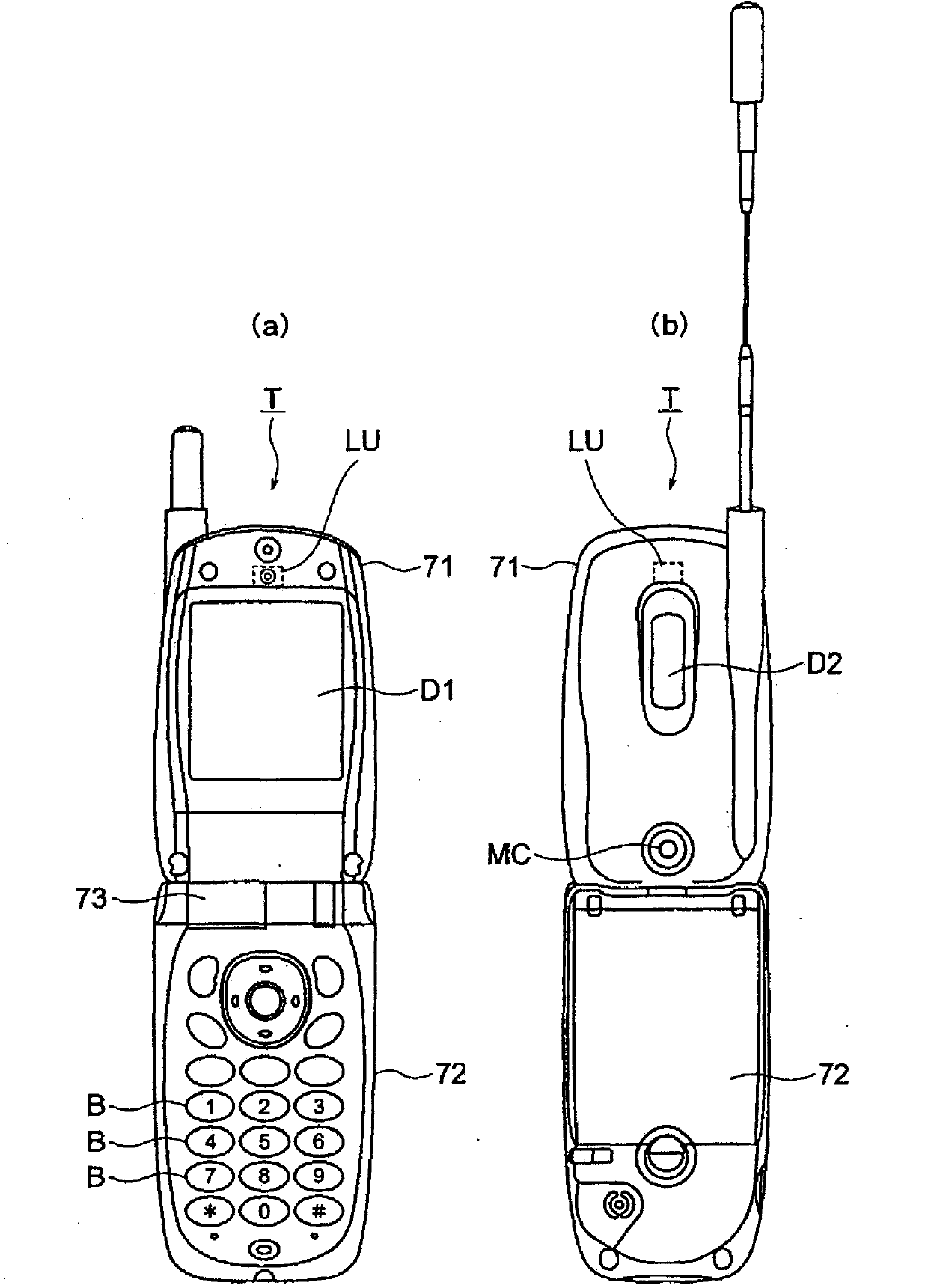
Image capture lens, image capture device, and portable terminal
A camera lens and lens technology, applied in optical components, instruments, optics, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in achieving high performance, performance degradation, and increase in elements, and achieve good telecentric characteristics and ensure the effect of back focal length.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
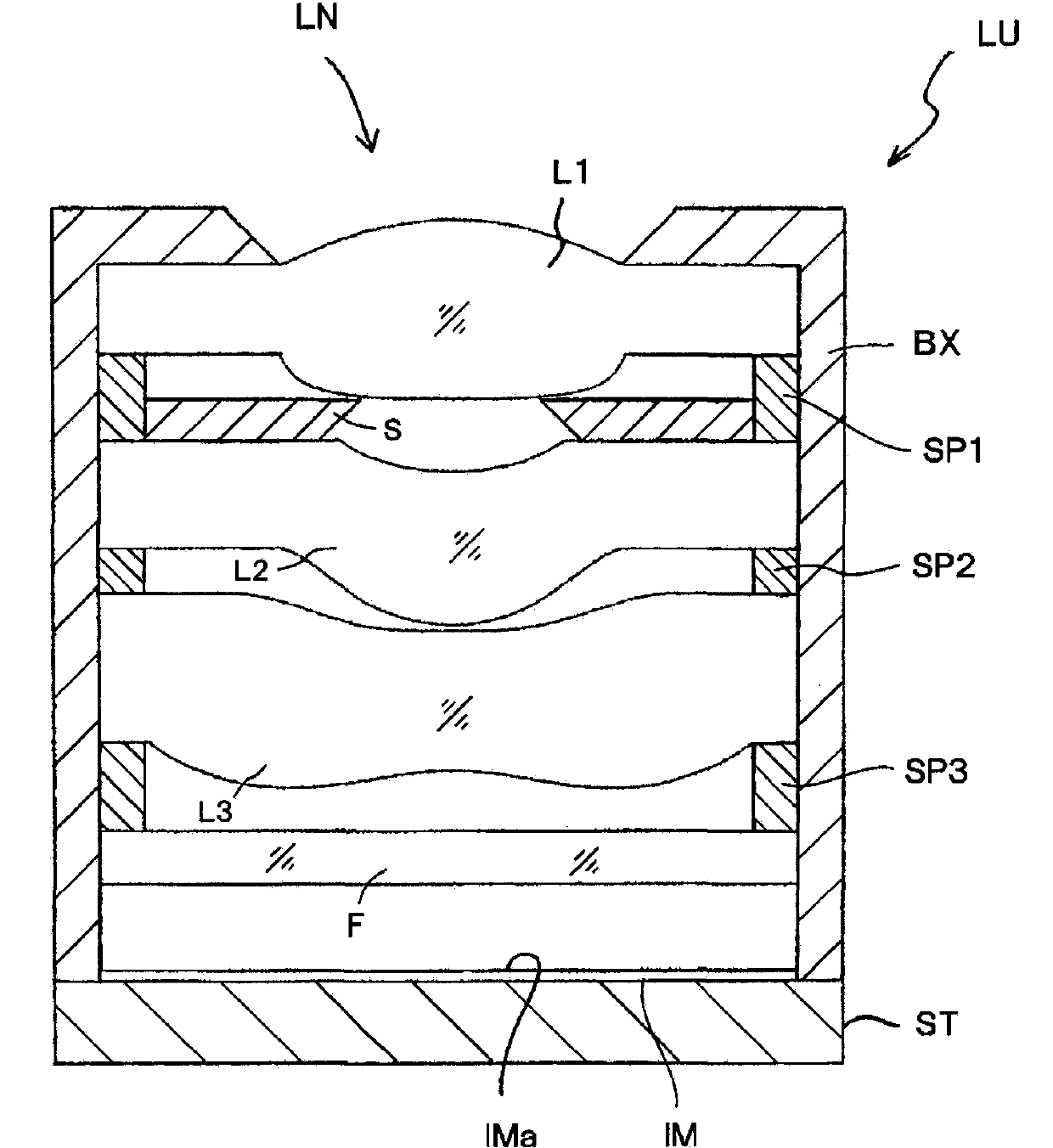
[0147] Table 1 shows lens data in Example 1. Figure 4 It is a sectional view of the lens of Example 1. The imaging lens of Embodiment 1 includes a first lens L1, an aperture stop S, a second lens L2, and a third lens L3 in sequence from the object side. The first lens L1 is a positive lens with a convex surface on the side of the object, and the second lens L2 is a convex lens on the object side. The third lens L3 is a positive meniscus lens with a concave surface, and the third lens L3 is a negative lens with an aspheric surface that is concave near the optical axis and has an inflection point within the effective diameter, and convex around the lens. CG is a parallel plate in which a cover glass or an IR cut filter is assumed, and IM is an imaging surface of a solid-state imaging element.
[0148] [Table 1]
[0149] [Example 1]
[0150] Reference wavelength = 587.56nm
[0151] Unit: mm
[0152]
[0153] Aspheric coefficient
[0154]
[0155]
[0156]
[01...
Embodiment 2
[0159] Table 2 shows lens data in Example 2. Figure 6 It is a sectional view of the lens of Example 2. The imaging lens of Embodiment 2 includes a first lens L1, an aperture stop S, a second lens L2, and a third lens L3 in sequence from the object side. The first lens L1 is a positive lens with a convex surface on the side of the object, and the second lens L2 is a convex lens on the object side. The third lens L3 is a positive meniscus lens with a concave surface, and the third lens L3 is a negative lens with an aspheric surface that is concave near the optical axis and has an inflection point within the effective diameter, and convex around the lens. CG is a parallel plate in which a cover glass or an IR cut filter is assumed, and IM is an imaging surface of a solid-state imaging element.
[0160] [Table 2]
[0161] [Example 2]
[0162] Reference wavelength = 587.56nm
[0163] Unit: mm
[0164]
[0165]
[0166] Aspheric coefficient
[0167]
[0168]
[0169...
Embodiment 3
[0172] Table 3 shows lens data in Example 3. Figure 8 It is a sectional view of the lens of Example 3. The imaging lens of Embodiment 3 includes a first lens L1, an aperture stop S, a second lens L2, and a third lens L3 in order from the object side. The first lens L1 is a positive lens with a convex surface on the side of the object, and the second lens L2 is a convex lens on the object side. The third lens L3 is a positive meniscus lens with a concave surface, and the third lens L3 is a negative lens with an aspheric surface that is concave near the optical axis and has an inflection point within the effective diameter, and convex around the lens. CG is a parallel plate in which a cover glass or an IR cut filter is assumed, and IM is an imaging surface of a solid-state imaging element.
[0173] [table 3]
[0174] [Example 3]
[0175] Reference wavelength = 587.56nm
[0176] Unit: mm
[0177]
[0178]
[0179] Aspheric coefficient
[0180]
[0181]
[0182]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com