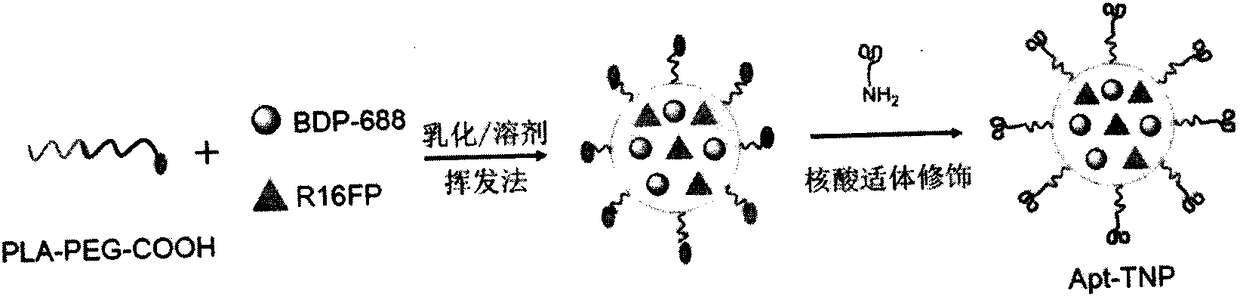
A kind of integrated nanoparticle for diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer and its preparation method
A nanoparticle, breast cancer technology, applied in preparations for in vivo experiments, wave energy or particle radiation treatment materials, pharmaceutical formulations, etc. Lack of targeting and other problems, to achieve the effect of large molar absorption coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: In vitro screening of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell-specific nucleic acid aptamers:
[0026] Using CELL-SELEX technology, the breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 was used as the target cell, and the normal breast epithelial cell MCF-10A was used as the anti-screening cell. After 15 rounds of screening, the nucleic acid aptamer of the breast cancer cell was obtained, and the nucleic acid was sequenced. Synthesis of aptamers.
Embodiment 2
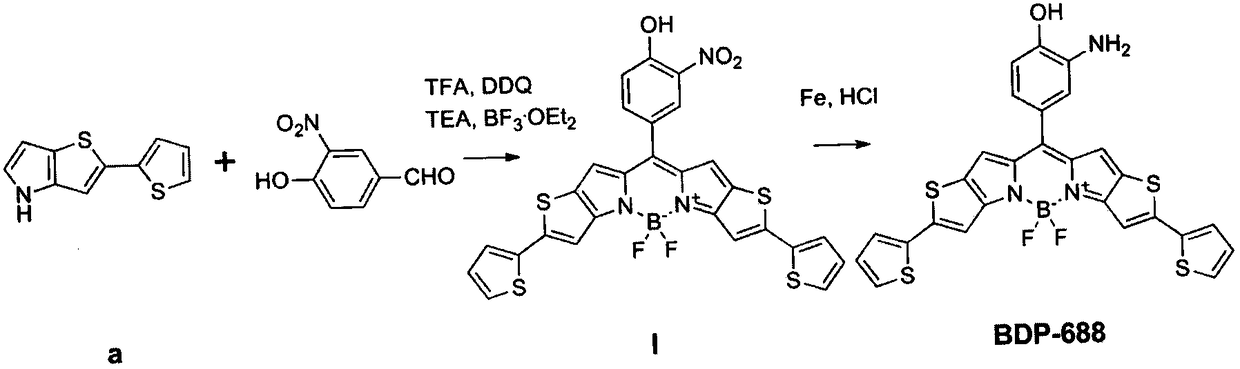
[0027] Example 2: Combining figure 2 , synthesis of acidic pH-triggered fluorescent probe BDP-688
[0028] 1) Synthesis of compound I: 100 mg of 2-(thiophene-2-yl)-4H-thiophene[3,2-b]pyrrole (compound a) was dissolved in 50 mL of dichloromethane under the protection of argon, and stirred to dissolve in the dark. Add 41 mg m-nitro-p-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 1 drop of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) to solution a, and stir at room temperature for 12 hours. Add 55 mg of 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (DDQ), continue stirring for 1 hour, then add 3 mL of triethylamine (TEA) and 3 mL of boron trifluoride diethyl ether (BF 3 ·Et 2 O), stirred for 3 hours. Add an appropriate amount of distilled water to quench the reaction, filter, collect the filtrate, extract with chloroform, wash with distilled water, and wash the organic layer with anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 After drying, the organic solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure and separated by column chromatography to ob...
Embodiment 3
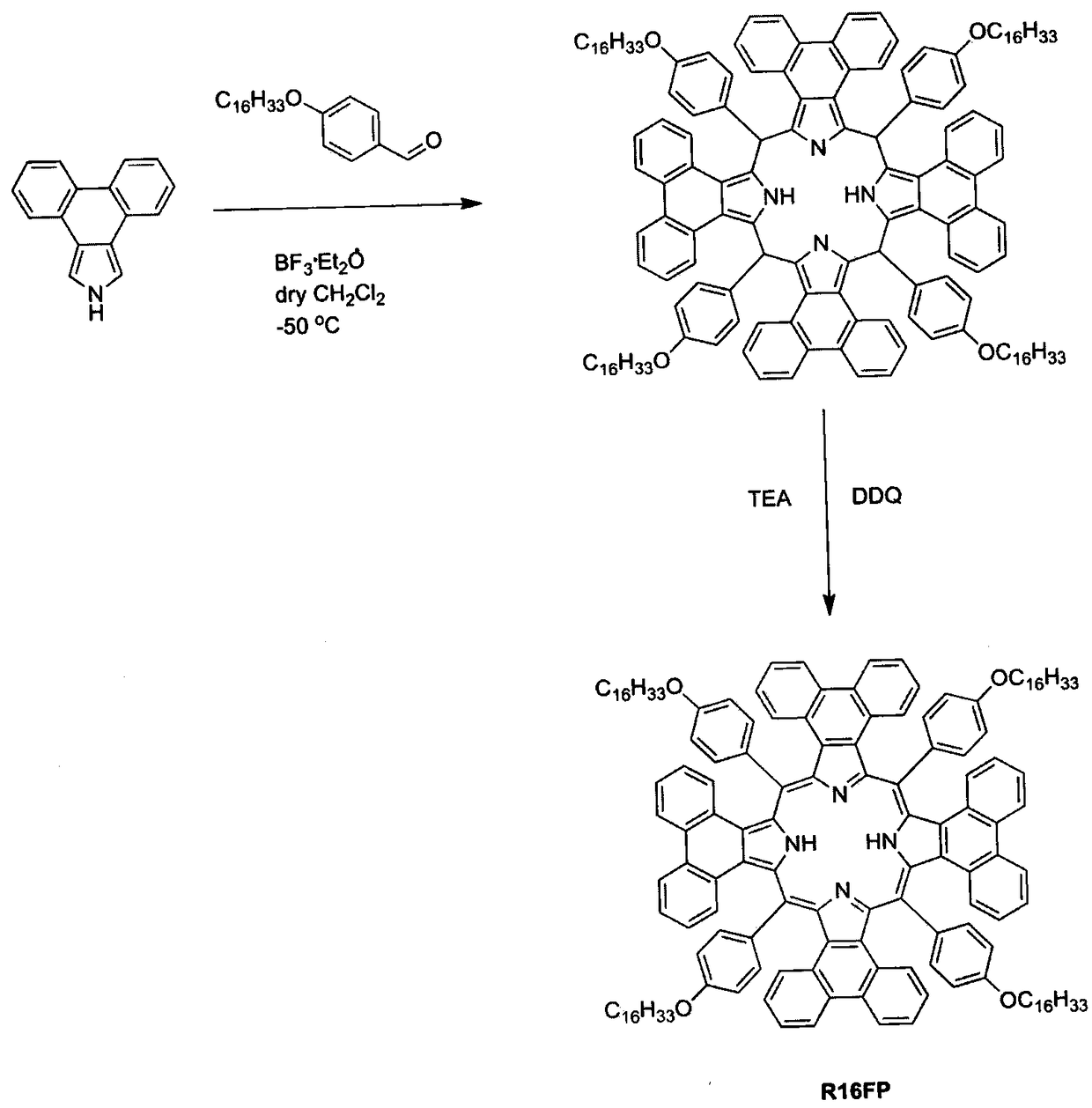
[0030] Example 3: Binding image 3 , synthesis of near-infrared light-activated photosensitizer R16FP
[0031] 217 mg of phenanthrene[9,10-c]pyrrole was dissolved in 350 mL of dry dichloromethane under the protection of argon, and stirred to dissolve. The reaction system was protected from light and cooled to -50°C, 346 mg of 4-hexadecyloxybenzaldehyde was added, and stirred overnight. Add 40mL boron trifluoride diethyl ether (BF 3 ·Et 2 (0), stirred and reacted for 2 hours, then the reaction system returned to room temperature, and continued to stir for 48 hours. Add 227 mg DDQ and 3 drops of triethylamine (TEA) to the solution, stir the reaction for 1 hour, remove the organic solvent under reduced pressure, and separate by column chromatography to obtain a dark red solid. Recrystallization from chloroform / methanol solution gave the dark red product R16FP with a yield of 13%. 1 H-NMR (500MHz, CD 2 C1 2 ) Analysis results: δ8.43(d, J=8.1Hz, 4H), 7.74-7.59(m, 8H), 7.35-7...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com