Heuristic spanning method and system for link state routing
A free and node-based technology, applied in the transmission system, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to generate trees, not taking into account the network status, and lack of information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
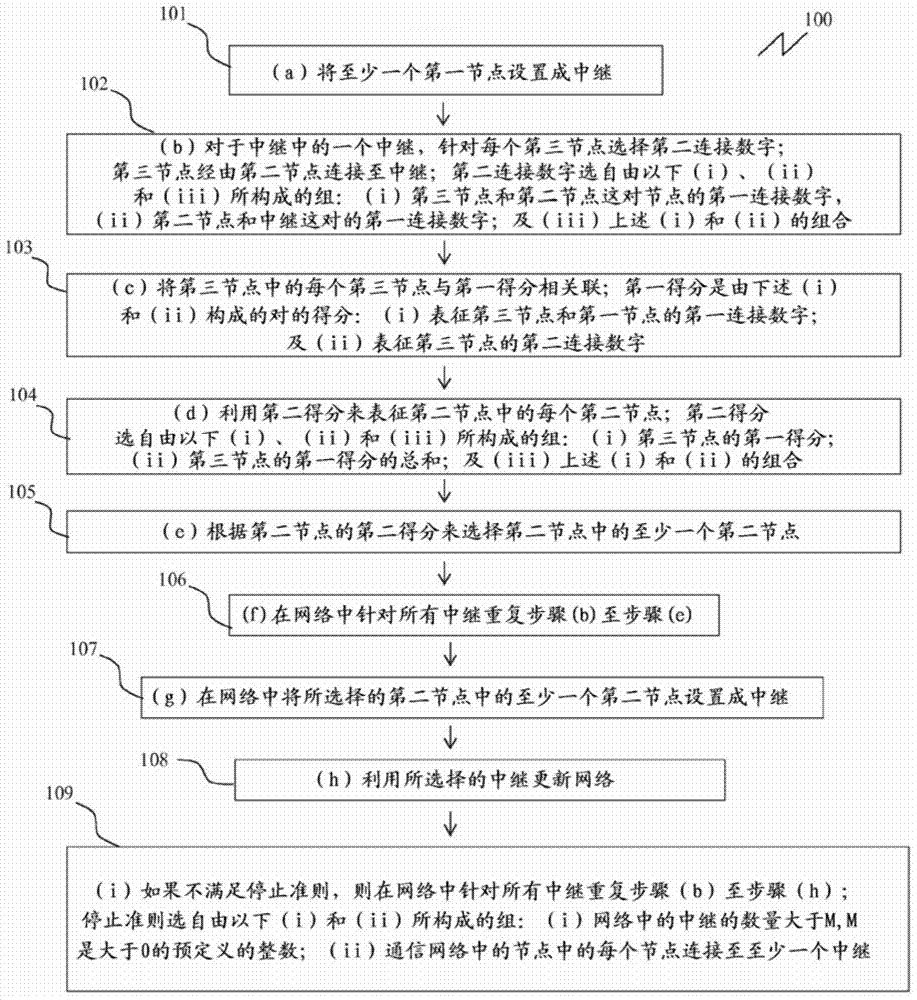
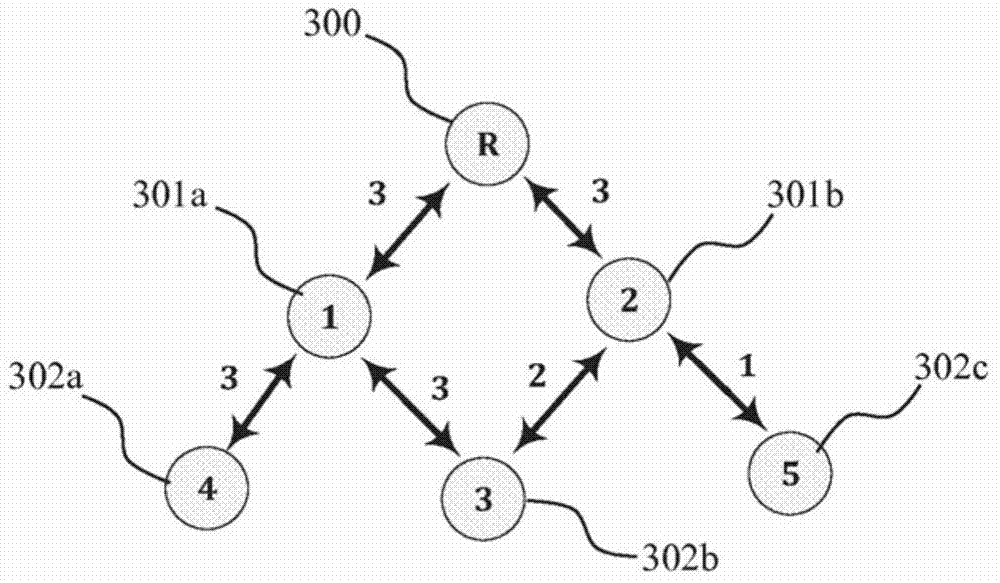
[0108] This example is provided in a non-limiting manner to illustrate a scope of the invention, wherein in a method for selecting at least one relay in a communication network, the network comprising a plurality of nodes; each of the nodes comprising At least one processing unit; each pair of nodes is characterized by an integer between 0 and 3, where 0 means that the two nodes are not connected, and any number between 1 and 3 means that the nodes are connected and the strength. From image 3 As can be seen from , the relay 300 is connected to two nodes with the first connection number 3 and the first connection number 3, namely the second node 1301a and the second node 2301b. Node 1301a is connected with first connection number 3 and first connection number 3 to third node 4302a and third node 3302b. Node 2301b is connected to third node 5302c and third node 3302b with first connection number 1 and first connection number 2, respectively. The relay is not connected to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com