Splicing seam brightness compensation and adjustment method for high-density LED display screen
A technology of LED display and brightness compensation, which is applied to static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as increasing display manufacturing costs, uneven brightness distribution, and affecting screen display effects, so as to improve display effects, avoid errors, and improve Effect of Positioning Accuracy and Efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
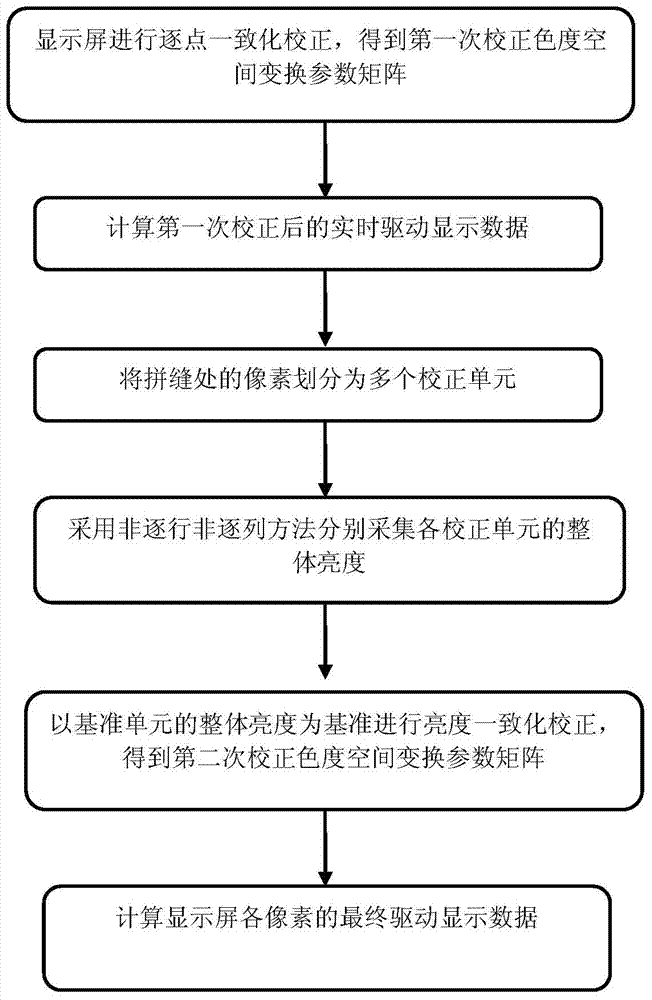
[0046] Such as figure 2 As shown, the high-density LED display screen of the present invention is an integrated display screen with a dot pitch d=2.5 mm. The process flow of the high-density LED display patchwork brightness compensation adjustment method is as follows:
[0047]Firstly, perform point-by-point lighting and uniform color correction on the display to obtain the first-time corrected chromaticity space transformation parameter matrix for each pixel;
[0048] N [ m , n ] [ i , j ] _ 1 = C [ m , n ] ...
Embodiment 2
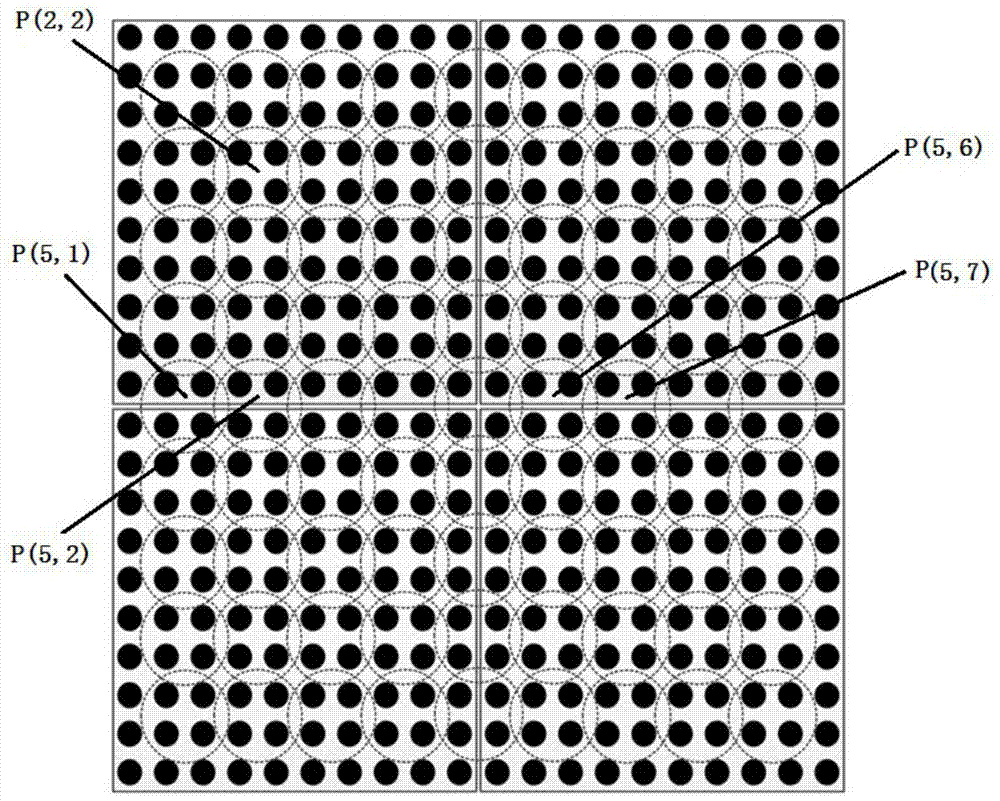
[0058] Such as image 3 As shown, the high-density LED display screen of the present invention is an integrated display screen with a dot pitch d=1.875 mm. The process flow of the high-density LED display patchwork brightness compensation adjustment method is as follows:
[0059] Firstly, perform point-by-point lighting and uniform color correction on the display to obtain the first-time corrected chromaticity space transformation parameter matrix for each pixel;
[0060] N [ m , n ] [ i , j ] _ 1 = C [ m , n ] ...
Embodiment 3
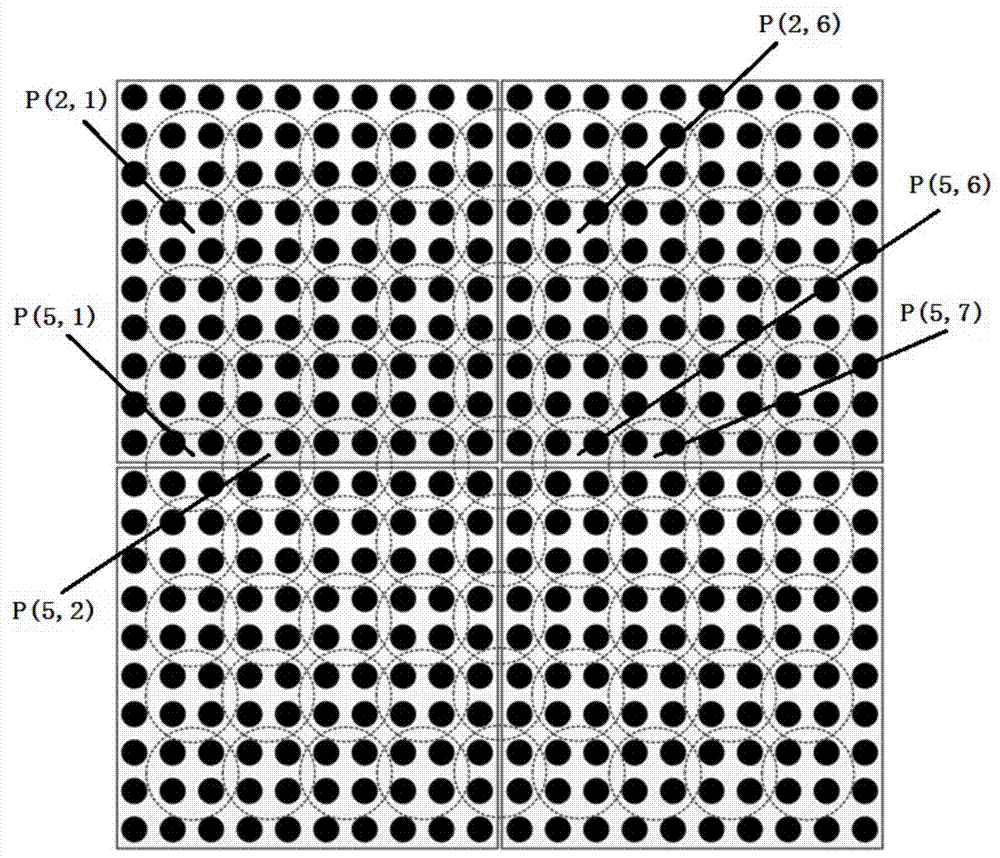
[0070] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the high-density LED display screen of the present invention is an integrated display screen with a dot pitch d=1.25 mm. The process flow of the high-density LED display patchwork brightness compensation adjustment method is as follows:
[0071] Firstly, perform point-by-point lighting and uniform color correction on the display to obtain the first-time corrected chromaticity space transformation parameter matrix for each pixel;
[0072] N [ m , n ] [ i , j ] _ 1 = C [ m , n ] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com