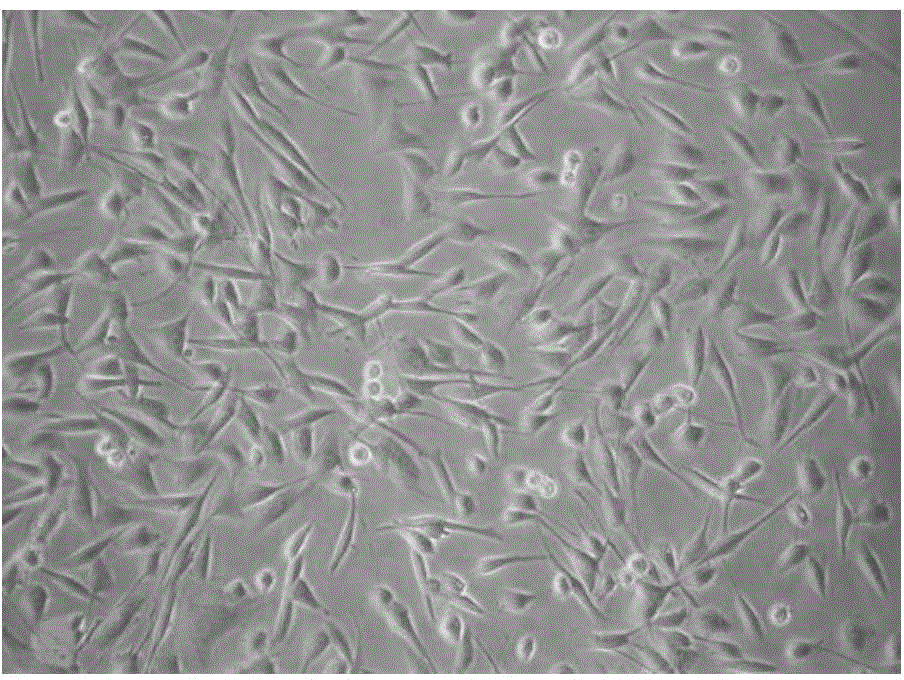
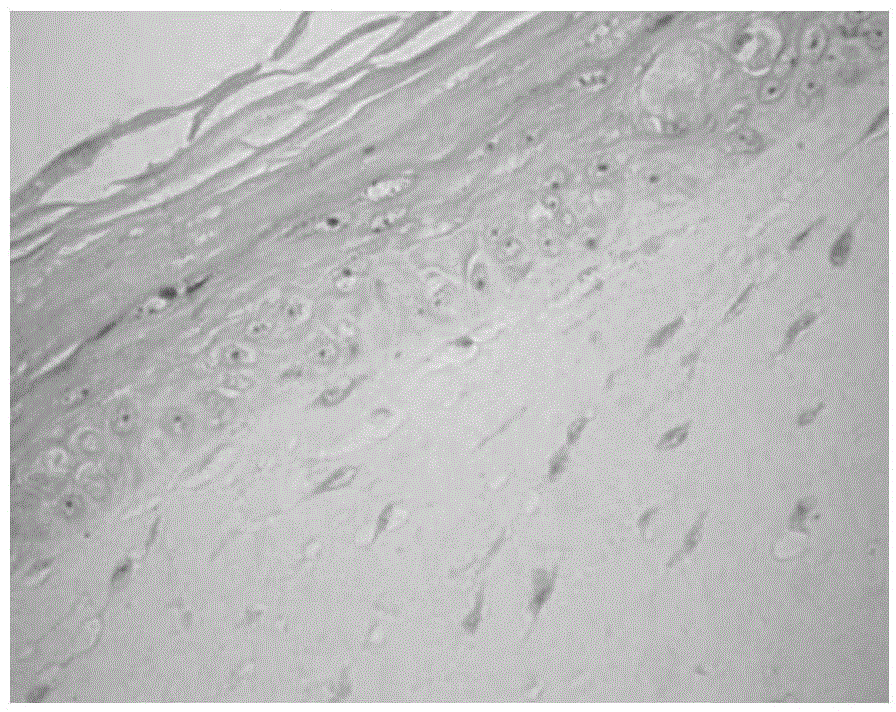
Method for differentiating epidermal stem cells to sweat gland-like epithelial cells
A technology of epidermal stem cells and epithelial cells, which is applied in the field of differentiation of epidermal stem cells into sweat gland-like epithelial cells, which can solve problems such as lack of skin attachments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1 : Preparation of rat tail collagen
[0067] The specific steps are as follows:
[0068] 1) Defrosting: Freeze 3 rat tails of about 300g, and thaw them in 75% alcohol solution for 1 hour;
[0069] 2) Take the tendon: remove the skin, rinse with D-Hanks solution 3 times, take out the tail tendon, cut it into mud, dissolve it in 250ml of sterile 1% glacial acetic acid, store at 4°C for more than 48 hours, and shake it repeatedly during the period;
[0070] 3) Centrifugation: Centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 1 hour and take the supernatant;
[0071] 4) Storage: The obtained level is milky white translucent viscous liquid, stored at 4°C for later use, and the measured concentration is 20mg / ml (wet weight).
Embodiment 2
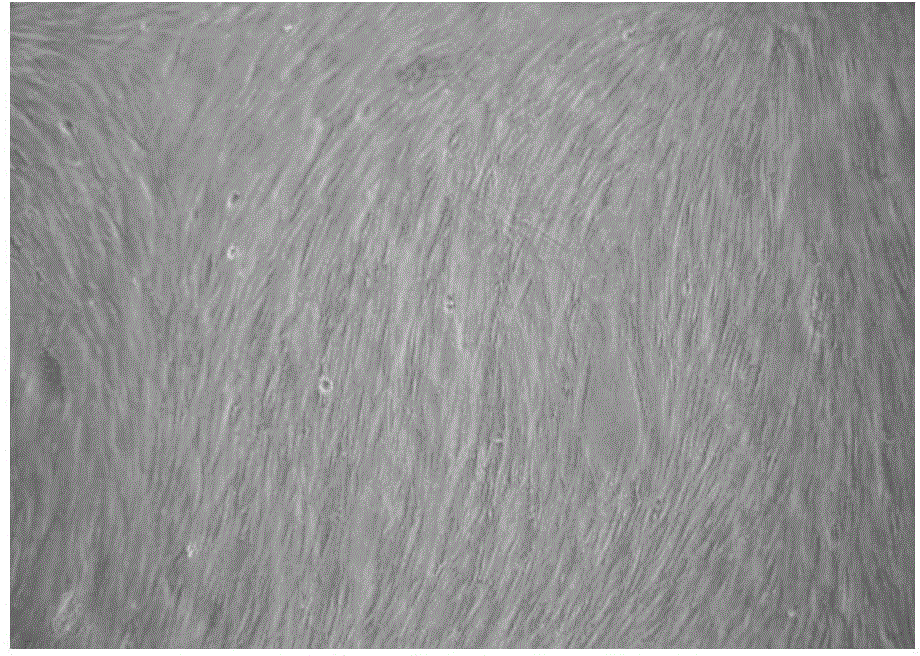
[0072] Example 2 Cultivation of human fibroblasts
[0073] Specific steps are as follows:
[0074] 1) The specimen is the foreskin of healthy adult circumcision (healthy foreskin, provided by the Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Third Military Medical University of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army and the Medical Beauty Center of the Third Affiliated Hospital of the Third Military Medical University of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, all patients are aware of And agree. The same below), after immersing and wiping in the clean bench with 75% alcohol for 5 minutes, rinse with PBS solution 3 times, each time for 3-5 minutes;
[0075] 2) Remove the subcutaneous tissue and dermal reticular layer as much as possible, cut the epidermis into a size of 2cm×0.3cm in another clean petri dish, transfer it into a glass vial containing 10-20ml of 0.25% separating enzyme, and place it with a cap Digestion at 4°C for 18-20 hours;
[0076] 3) Take out the skin pi...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Example 3 Cultivation of epidermal stem cells
[0086] 1. Primary isolation and culture of human epidermal stem cells
[0087] The specimen was taken from a healthy foreskin.
[0088] After removing the specimen, soak it in PBS balanced salt solution and store in a refrigerator at 4°C. Follow the steps below:
[0089] 1) After soaking in alcohol for 5 minutes, place it on a clean bench and gently wipe the specimen three times with an alcohol cotton ball;
[0090] 2) Move the specimen to a petri dish, rinse the specimen 3 times with PBS balanced salt solution, and rinse every corner, not less than 5 minutes each time, until the specimen becomes whitish and swollen;
[0091] 3) Cut the subcutaneous tissue with surgical scissors in a petri dish, and cut the specimen into a leather strip of 0.3cm×2cm size;
[0092] 4) Put the leather strips in a petri dish, add 0.25% separating enzyme to submerge the tissue (the ratio of separating enzyme to specimen is 5:1);
[0093] 5) Digested overn...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap