A Fast Fault Detection Method Based on Random Projection and k-Nearest Neighbors
A technology of random projection and fault detection, applied in electrical testing/monitoring, testing/monitoring control systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as high computational complexity, missed reports, and inability to guarantee sample distances, to ensure detection performance, effective Monitoring the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0056] The effectiveness of the method of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with a specific semiconductor process example. The data of this process comes from three sets of experiments conducted by Texas Instruments in three months. There are 127 batches of available data, including 107 batches of normal data and 20 batches of fault data. The fault data is mainly obtained by artificially changing some Variations in variables such as power and pressure are caused. The sampling time points of each batch are 85, and a total of 17 non-set point process variables are selected for monitoring, as shown in Table 1.
[0057] Next, in conjunction with this specific process, the implementation steps of the present invention are described in detail:
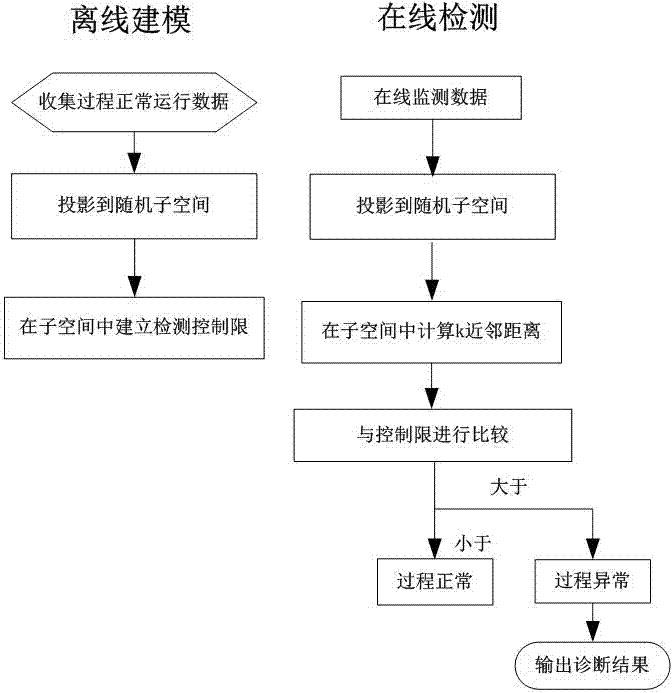
[0058] Step 1: Offline training
[0059] 1) Collect data on normal operating conditions of the process. The three-dimensional array of the batch process in this example is expanded by batch
[0060] 2) Get a tw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com