The Method of Obtaining Power System Node Impedance Matrix Based on LDU Decomposition Based on Sparse Technology
A node impedance matrix, power system technology, applied in complex mathematical operations and other directions, can solve the problems of cumbersome access process, difficult triangular decomposition, unable to use element symmetry and sparsity, etc., to reduce calculation and reduce the amount of calculation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
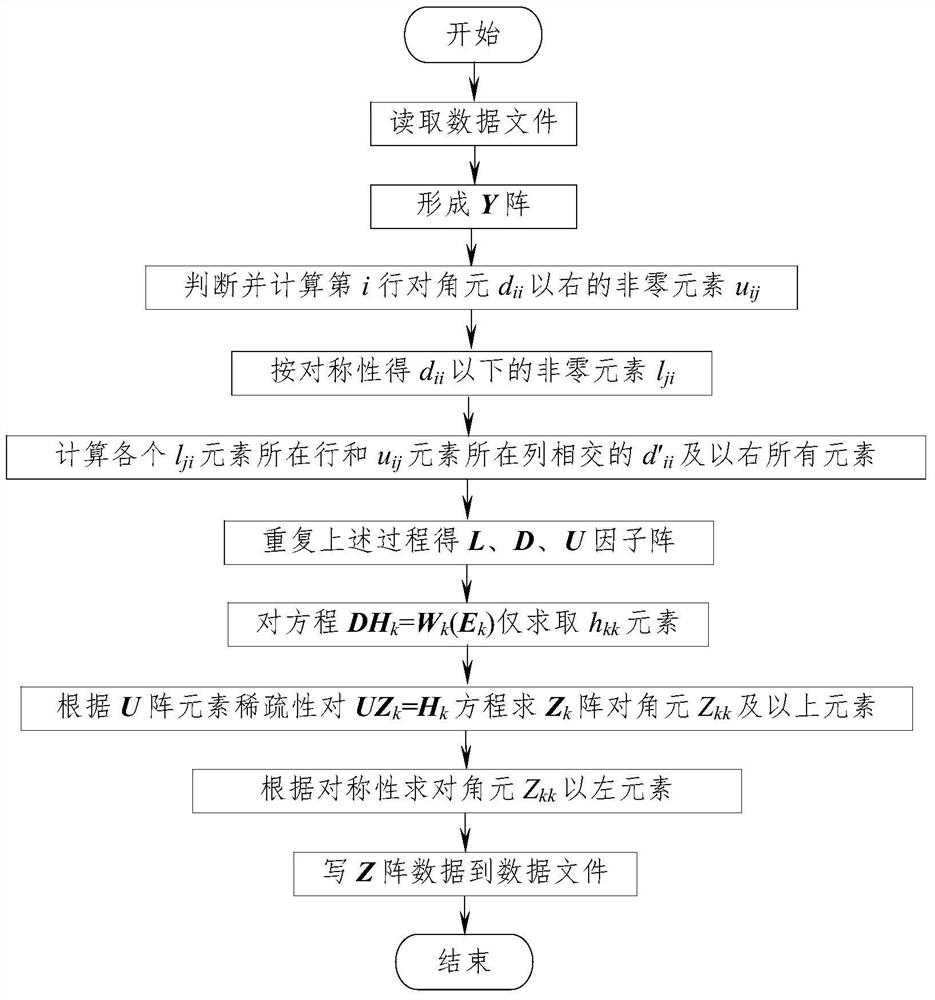
[0048] Taking Formula 1 as an example, the definition of elements in the method of the present invention and the application of the symmetric sparsity technology are illustrated.
[0049] assuming l 31 ≠0, then for d 11 l under the element 31 Element to be eliminated. first define d 11 elements are diagonal elements, d 11 all u on the right 1j elements are defined as cross elements, l 31 element is defined as an elimination element, then l 31 All elements to the right are defined as computed elements.
[0050] (1) If element sparsity is not considered in the process of element elimination, it is necessary to calculate l in steps 31 All computed elements to the right of the element l 32 、d 33 , u 34 .
[0051] (2) If sparsity technology is used, only step-by-step calculation of l 31 The line on the right side of the element and the non-zero u 1j All computed elements whose columns intersect, including l 32 、d 33 , u 34 Elements (need to consider l on the left o...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Taking the n×n order node system as an example, the difference between the traditional LDU triangular decomposition method and the method of the present invention for solving Z matrix elements is compared. The comparison results are shown in Table 1.
[0056] The comparison of the traditional LDU triangular decomposition method of table 1 and the method of the present invention for solving the Z matrix element process
[0057]
[0058] It can be seen from Table 1 that:
[0059] (1) When forming the factor array of traditional LDU by the formula method, all elements of the L, D, U arrays need to be solved, and the symmetry and sparseness of the elements themselves cannot be utilized; and the method of the present invention utilizes the symmetric sparse matrix technology, and only needs Solve a small number of non-zero elements of U array and D array elements, and a small amount of non-zero elements of L array can be obtained from U array elements according to symmetr...
Embodiment 3
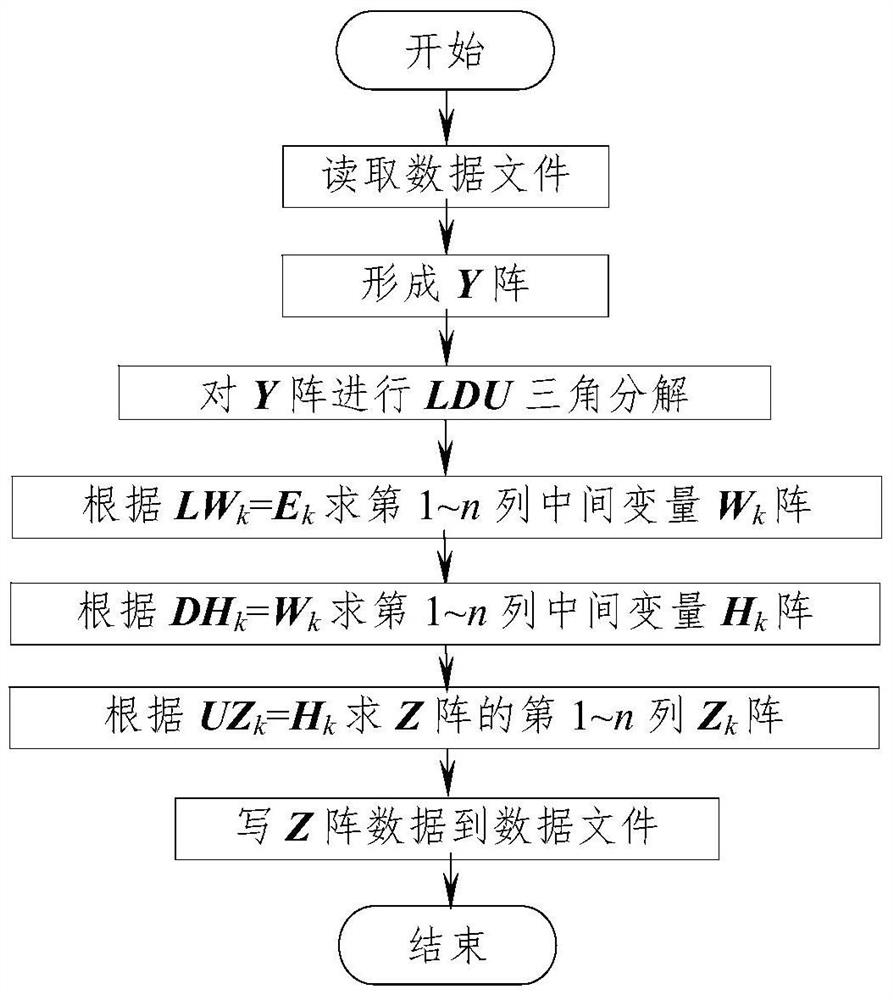
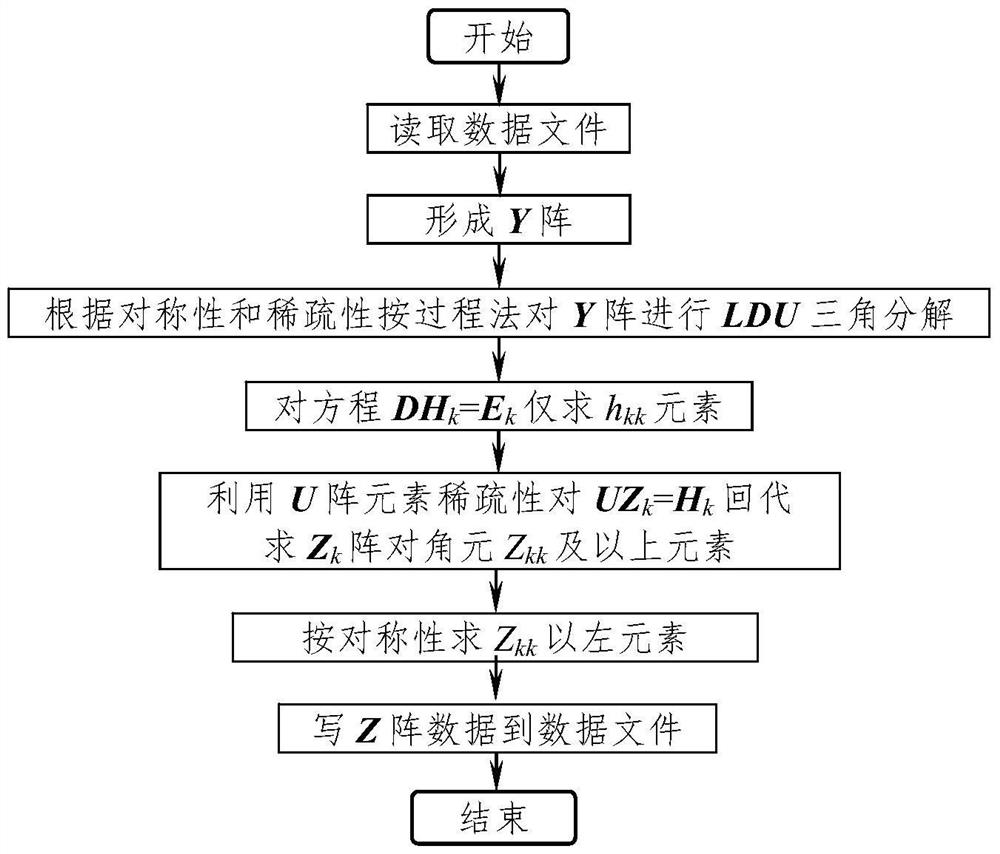
[0066] Using the traditional LDU triangular decomposition method ( figure 1 ), and the inventive method ( figure 2 ) Calculate the elements of the Z matrix for the Y matrix of the IEEE-30, -57, -118 node system, and compare the average calculation time of the processes of "decomposition", "regeneration" and "decomposition+regeneration". The calculation results are shown in Table 2.
[0067] Table 2 The traditional method and the method of the present invention are compared in the process time of "decomposition", "back generation" and "decomposition+back generation"
[0068]
[0069] (1) The average iteration time of the "decomposition" process:
[0070] T 1 : Traditional methods do not consider symmetric sparsity and do not use u ij = l ji properties, calculate all elements;
[0071] T 2 : the method of the present invention considers symmetric sparsity, only calculates D array elements and a small amount of U array non-zero elements, and records its position, utili...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com