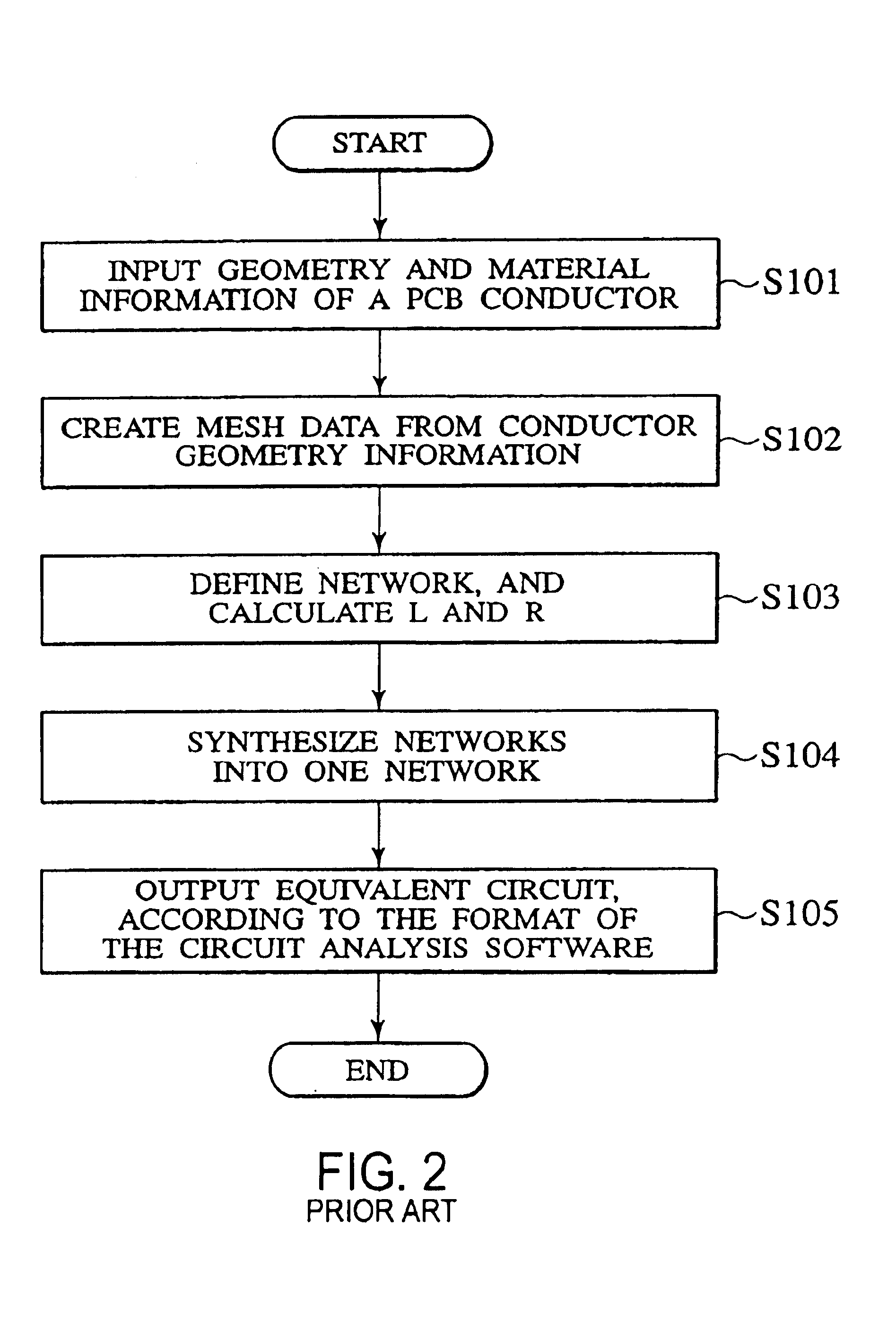
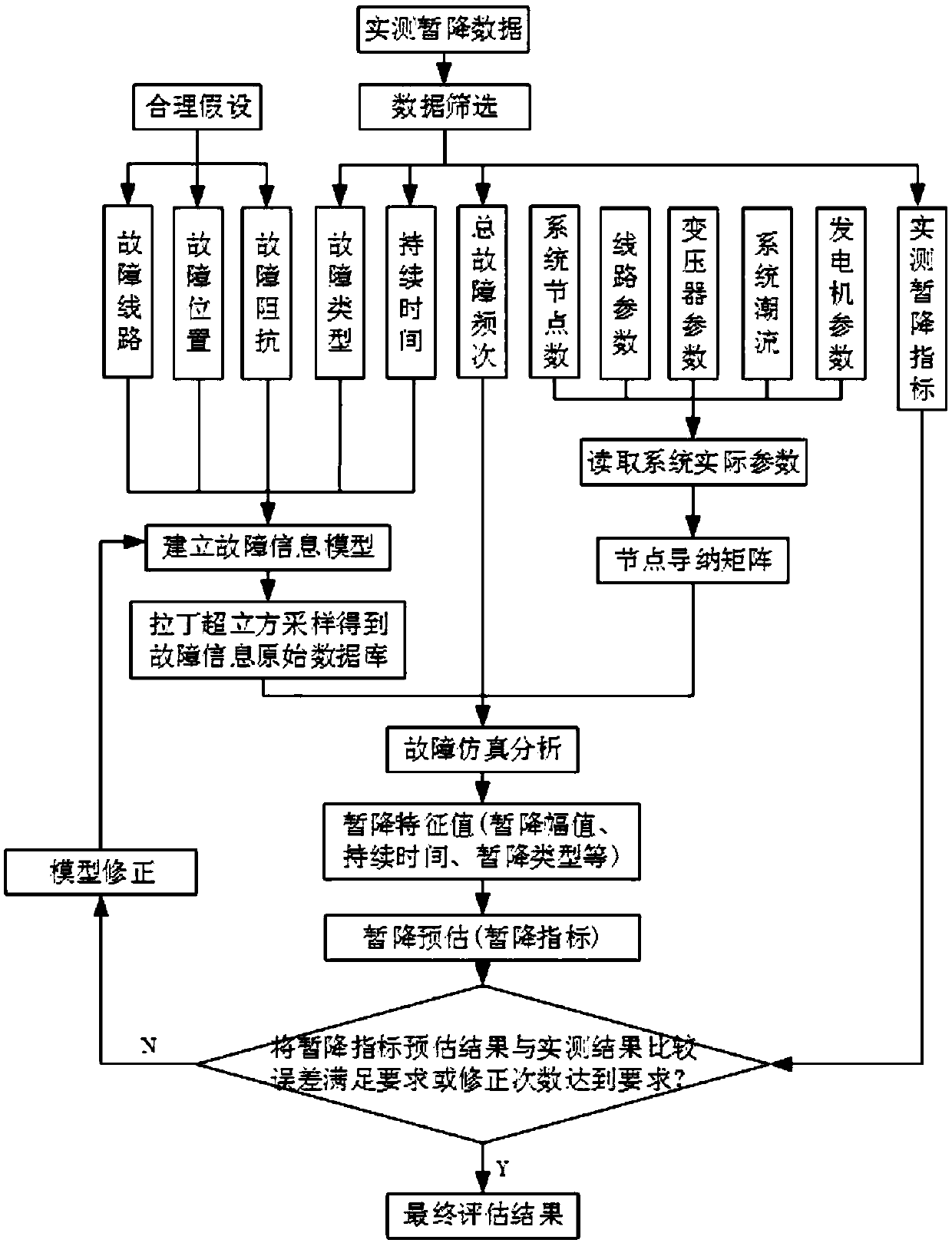
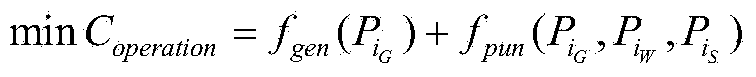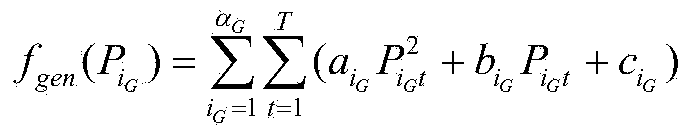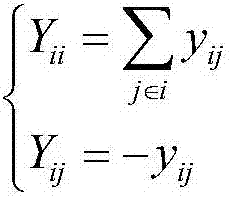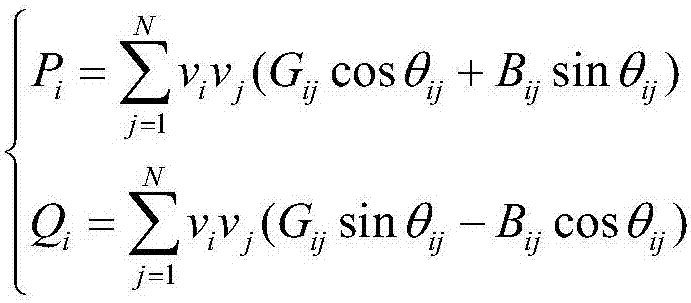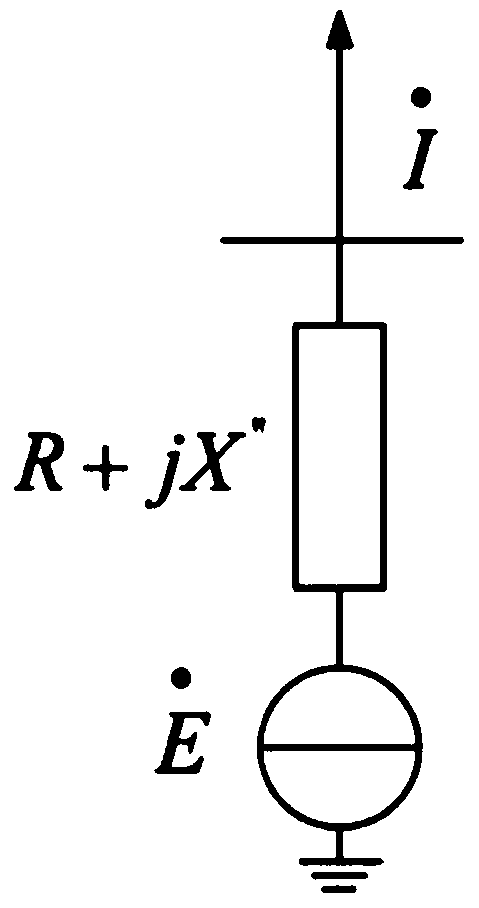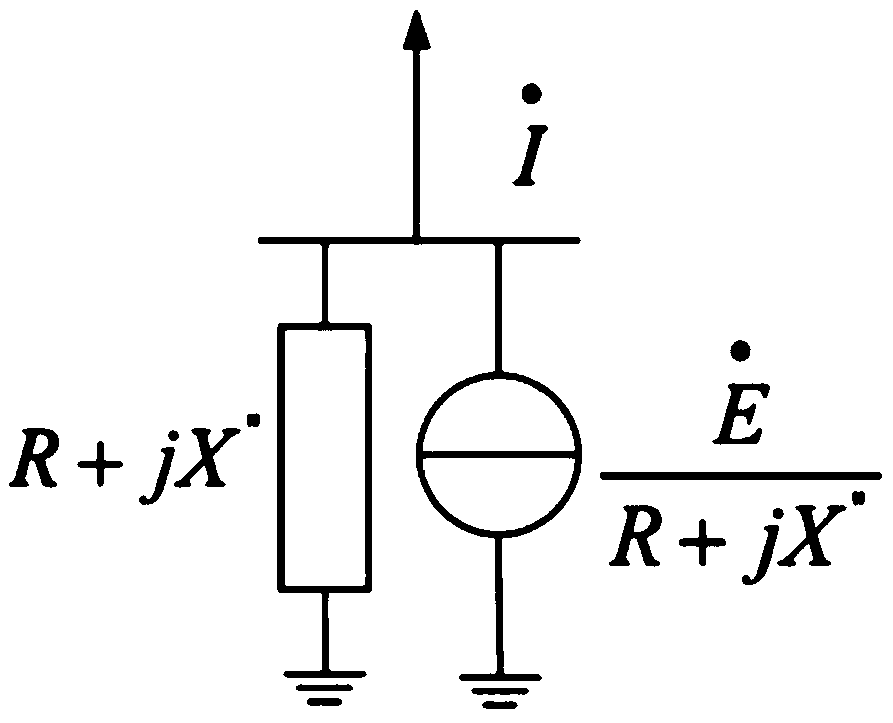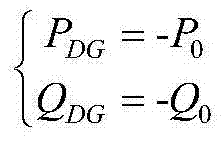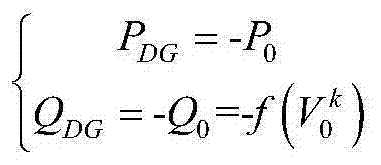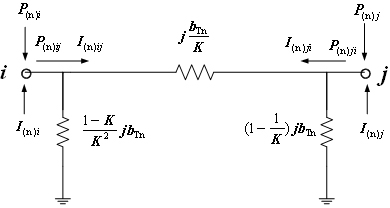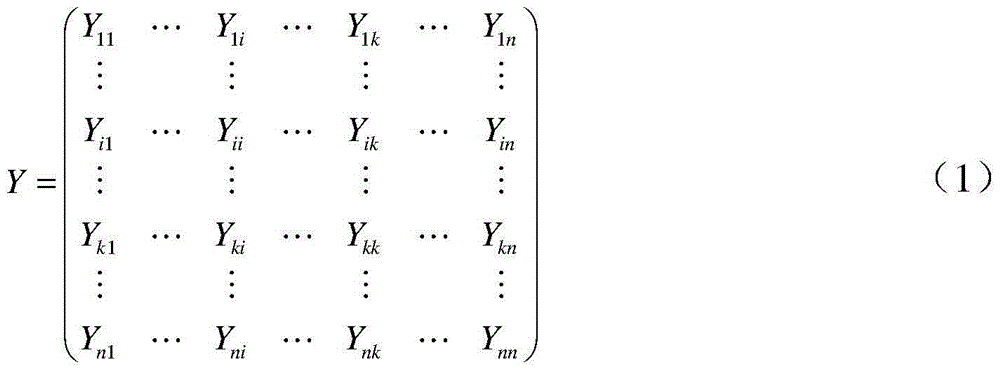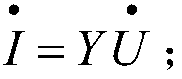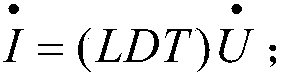Patents
Literature
138 results about "Nodal admittance matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
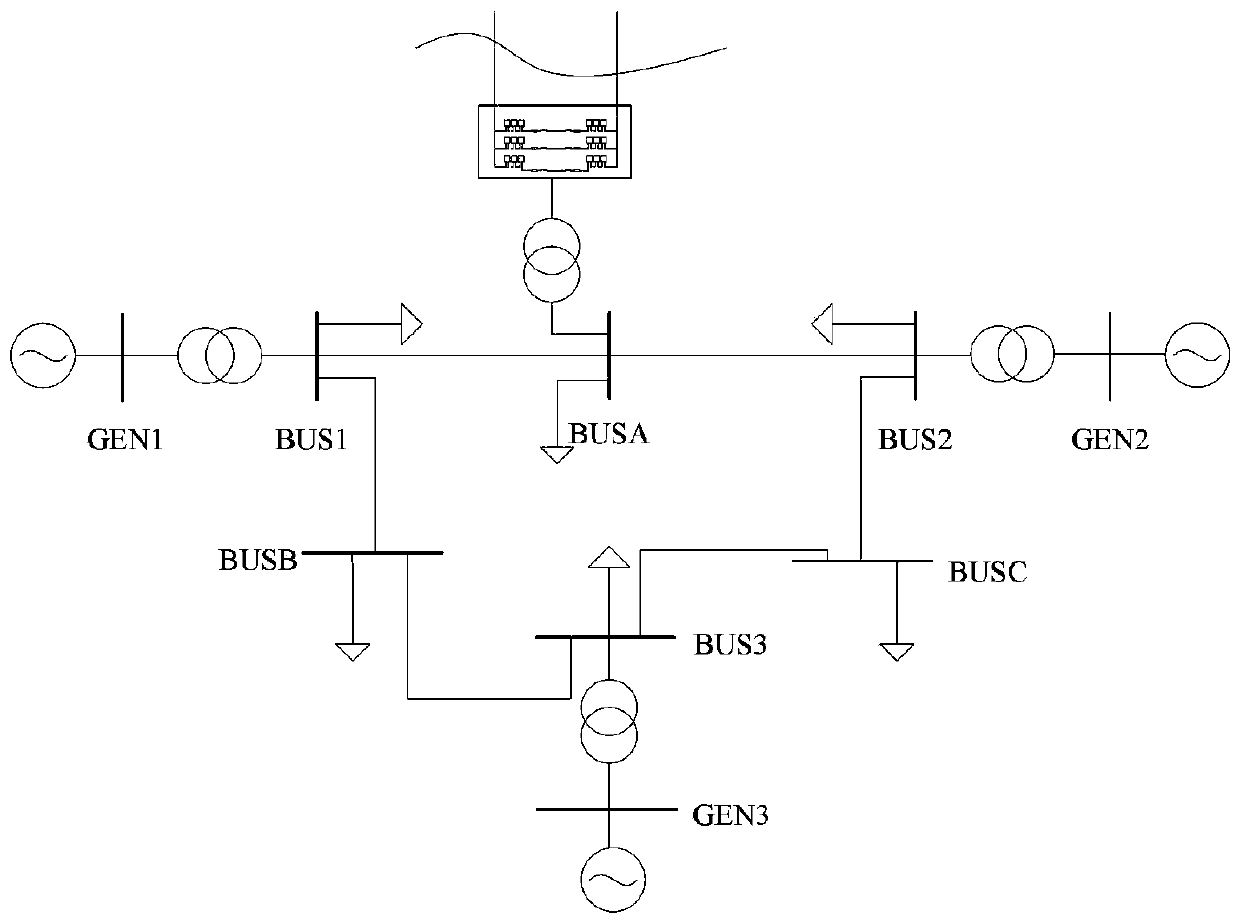
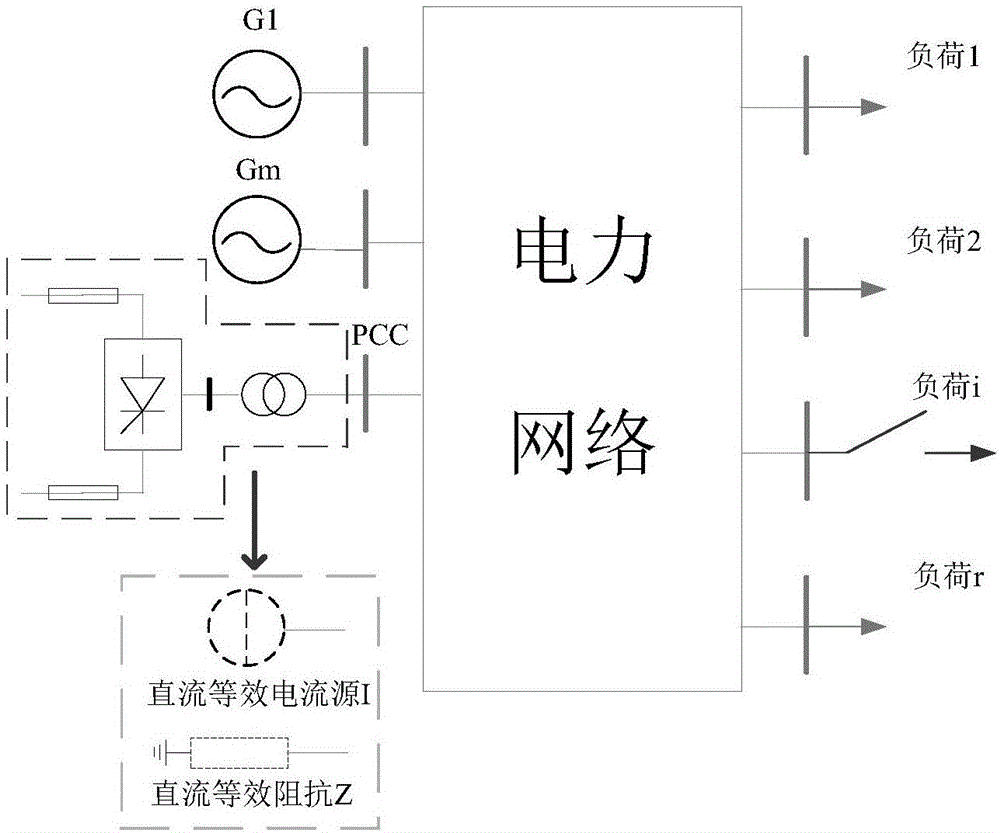
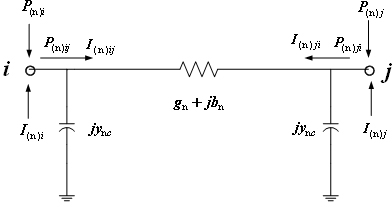
In power engineering, nodal admittance matrix (or just admittance matrix) or Y Matrix or Ybus is an N x N matrix describing a power system with N buses. It represents the nodal admittance of the buses in a power system. In realistic systems which contain thousands of buses, the Y matrix is quite sparse. Each bus in a real power system is usually connected to only a few other buses through the transmission lines. The Y Matrix is also one of the data requirements needed to formulate a power flow study.
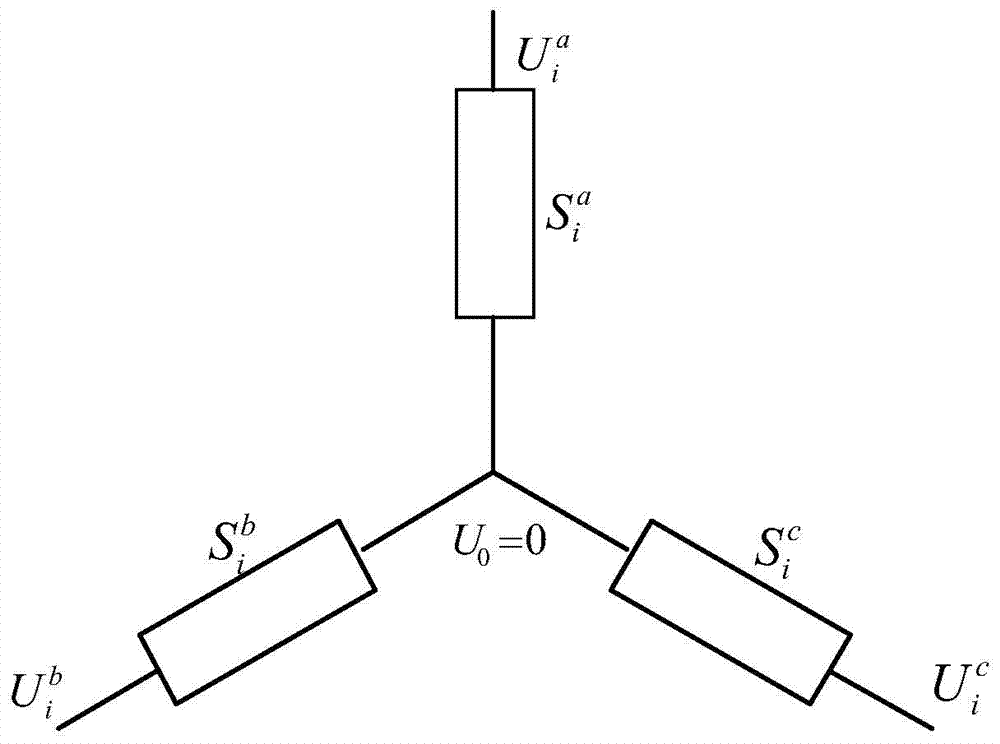
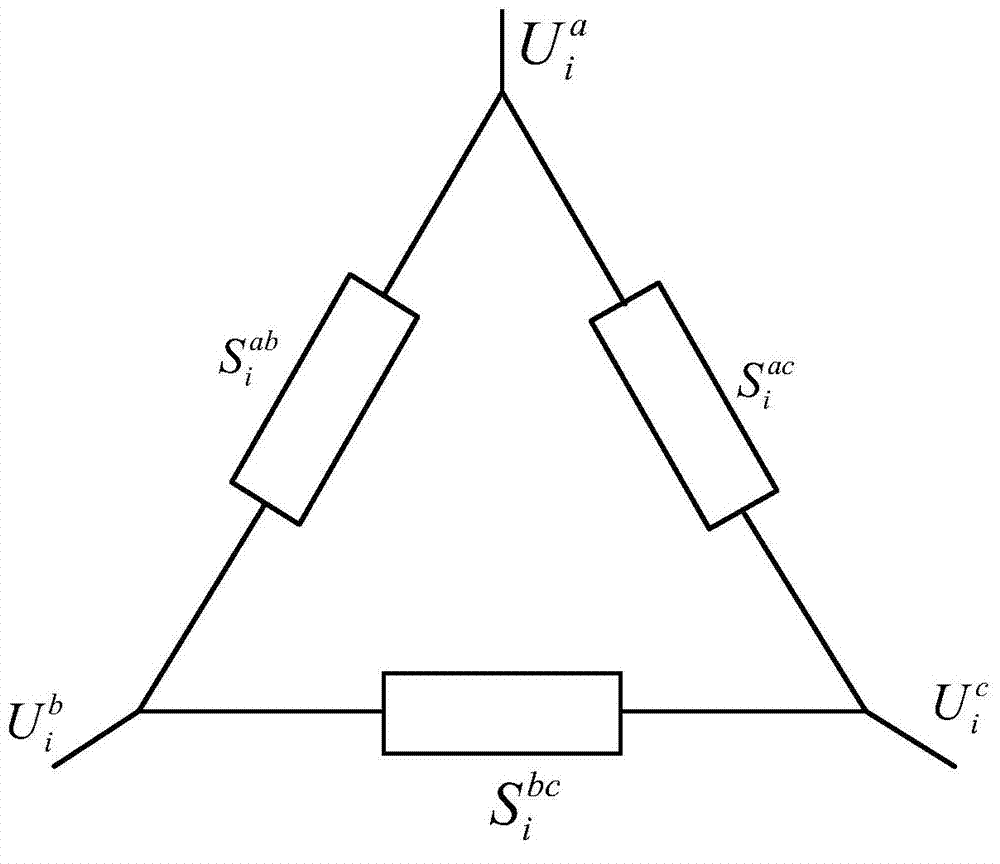
Three-phase imbalance three-phase imbalance method for power distribution network with distributed power supplies
ActiveCN103683284AEasy to implementRun fastPolyphase network asymmetry reductionSpecial data processing applicationsThree-phaseDistributed power
The invention provides a three-phase imbalance three-phase imbalance method for a power distribution network with distributed power supplies. The three-phase imbalance three-phase imbalance method for the power distribution network with distributed power supplies comprises: aiming at the complex power distribution network, on basis of the fundamental principle of the implicit Gaussian load flow calculation method.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
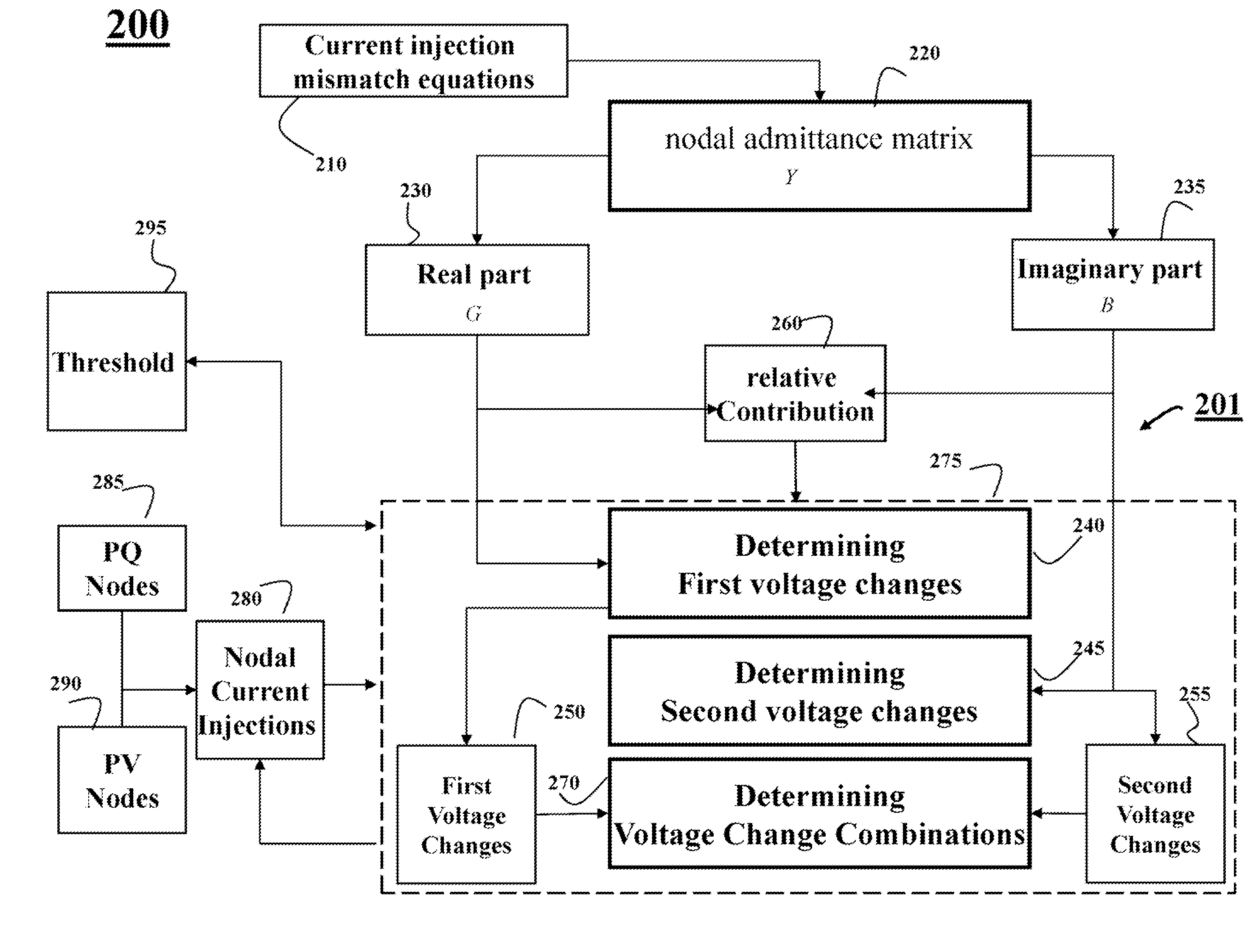
Decoupled Three-Phase Power Flow Analysis Method for Unbalanced Power Distribution Systems
ActiveUS20130226482A1Lighten the computational burdenImprove accuracyElectric devicesPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionPower flowDistribution power system
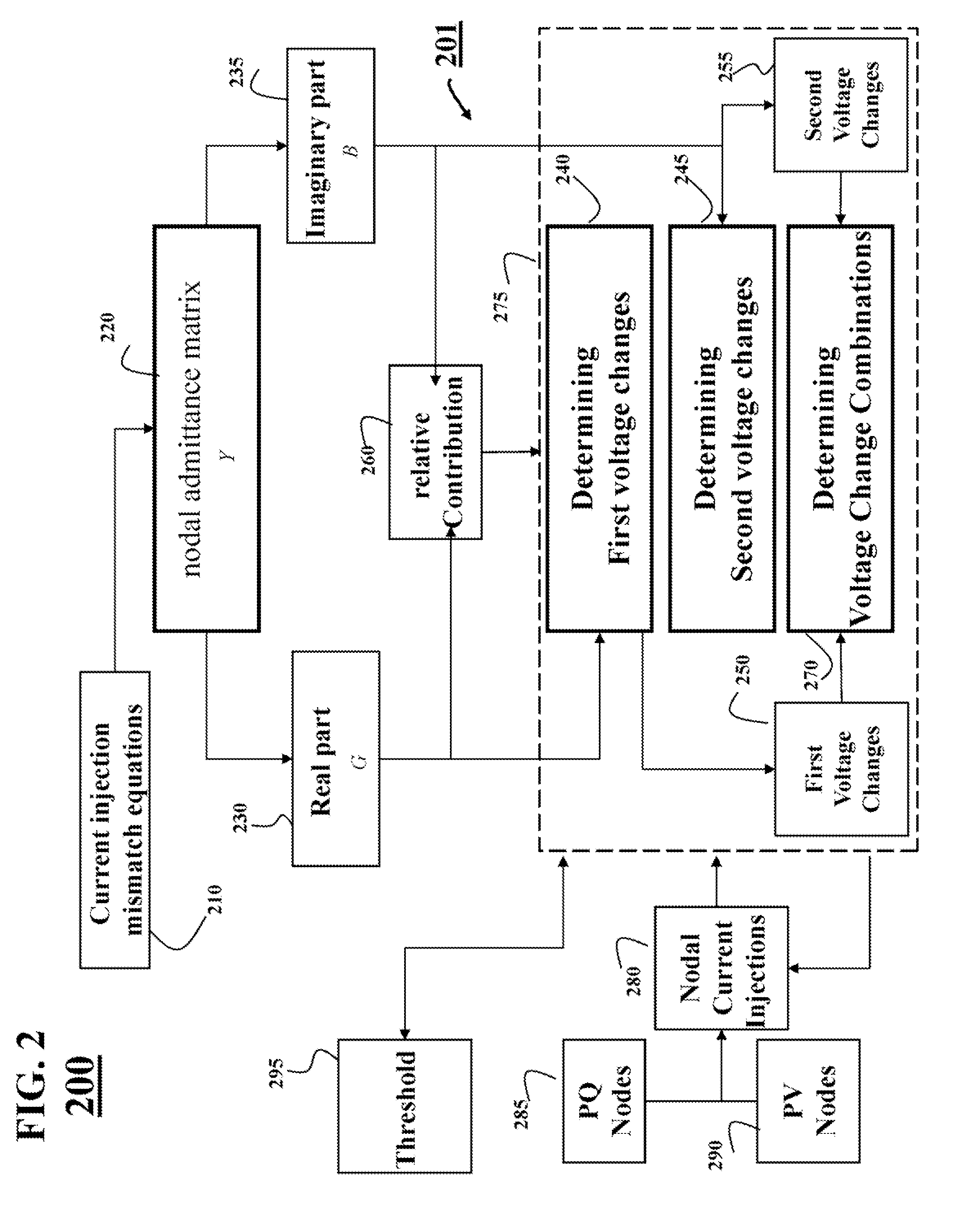
Three phase power flow analysis of an unbalanced power distribution system decouples voltage changes resulting from nodal admittance matrix into one contribution from a real part, conductance matrix, and other contribution from an imaginary part, and a susceptance matrix. A first voltage change and second voltage change resulting from conductance and susceptance matrices are determined respectively. The voltages of a node of the power distribution system are determined as a combination of first and second voltages.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for calculating harmonic wave impedance of alternating current system for direct current transmission
InactiveCN103544378AThe calculation result is accurateCalculation speedSpecial data processing applicationsBatch processingStatistical analysis
The invention provides a method for calculating harmonic wave impedance of an alternating current system for direct current transmission. The method includes the following steps that a node admittance matrix is formed according to a harmonic wave model of a transmission line, a transformer, a generator, a load and a parallel capacitor; nodes to be calculated are placed at the bottom line of the admittance matrix, the current value at the bottom line is set to be 1, and the current values at other lines are set to be 0; node optimizing numbering is conducted on the first n-1 nodes; the node admittance matrix is stored through a sparse technology; the node admittance matrix is solved, and the back substitution does not need to be conducted; a plurality of input files are simultaneously calculated through a parallel calculation method; statistic analysis is conducted according to the batch processing calculation result. According to the method, specific to the characteristic that multiple times of scanning needs to be conducted for calculating the harmonic wave impedance, the improved node optimizing numbering technology and the improved sparse technology are adopted, and therefore the workload for calculating the harmonic wave impedance is reduced, the calculating speed is greatly increased, burdens of operators are relieved, and precious time can be saved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD
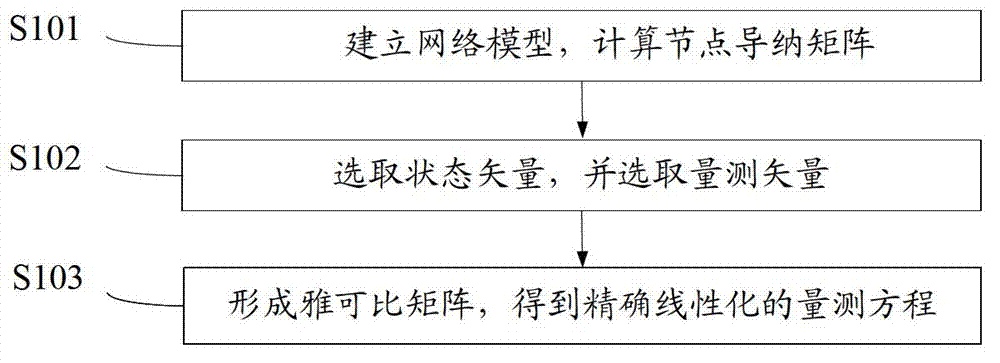
Accurate linearization method of measurement equation for electric power system state estimation
ActiveCN102831315AReduce complexityEasy to solveData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsElectric power systemEngineering
The invention provides an accurate linearization method of a measurement equation for electric power system state estimation. The accurate linearization method is characterized by including steps of establishing a network model and calculating a nodal admittance matrix; selecting state vectors and measurement vectors; and forming a jacobian matrix so as to get the accurately linearized measurement equation. The accurately linearized measurement equation is obtained by selecting the state vectors and the measurement vectors, and the state vectors can be solved by means of any types of existing state estimation according to the accurately linearized measurement equation, and estimation values such as all branch power and node injection power in the network can be acquired, so that complexity of the state estimation model is reduced greatly and the equation is easy to solve.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
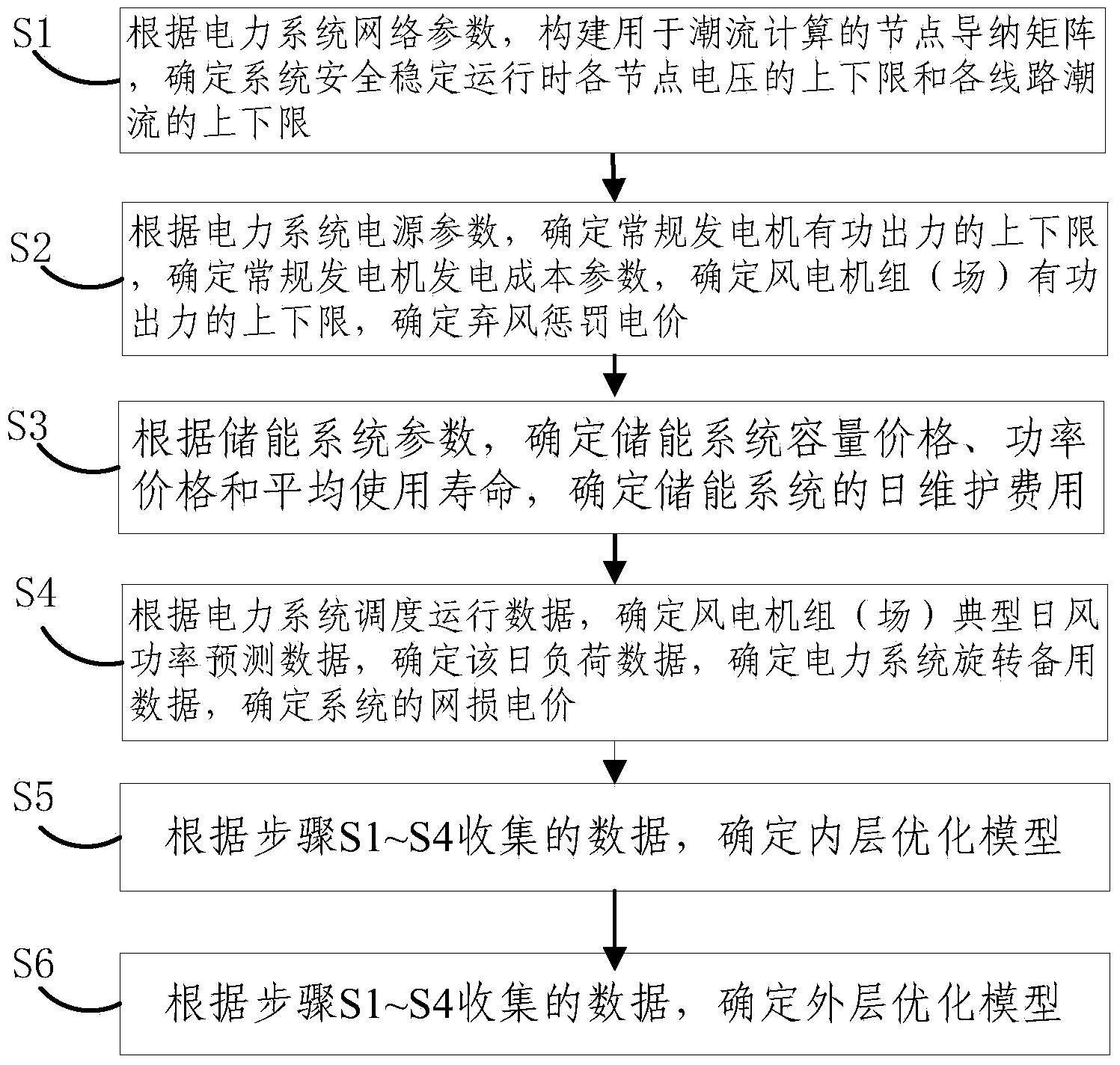
Method and system for comprehensively optimizing energy storing power station planning and operating
ActiveCN103475013AOptimal Power ConfigurationImprove access capabilitiesAc network load balancingSpecial data processing applicationsElectricity pricePower system scheduling
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively optimizing energy storing power station planning and operating. The method comprises the first step of constructing a real-part matrix G and a virtual matrix B of a node admittance matrix used for carrying out load flow calculation according to network parameters of an electric power system and determining the upper limit value and the lower limit value of voltage of all nodes and the upper limit value and the lower limit value of all line power flow when the electric power system operates safely and stably, the second step of determining the upper limit value and the lower limit value of work output of a common electric generator, determining generating cost parameters of the common electric generator, determining the upper limit value and the lower limit value of the work output of a wind turbine generator or a wind power motor field and determining the penalty electricity price for draught fan fault according to the power source parameters of the electric power system, the third step of determining the capacity price, the power price and the average service life of an energy storage system and daily maintenance charge according to parameters of the energy storage system, the fourth step of determining the typical day wind power predicted data of the wind turbine generator or the wind power motor field, determining the day load data, determining the backup data of rotating of the electric power system and determining the transmission loss price of the electric power system according to scheduling operating data of the electric power system, and the last step of determining an inner layer optimization model and an outer layer optimization model according to the data collected in the first step, the second step, the third step and the fourth step.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
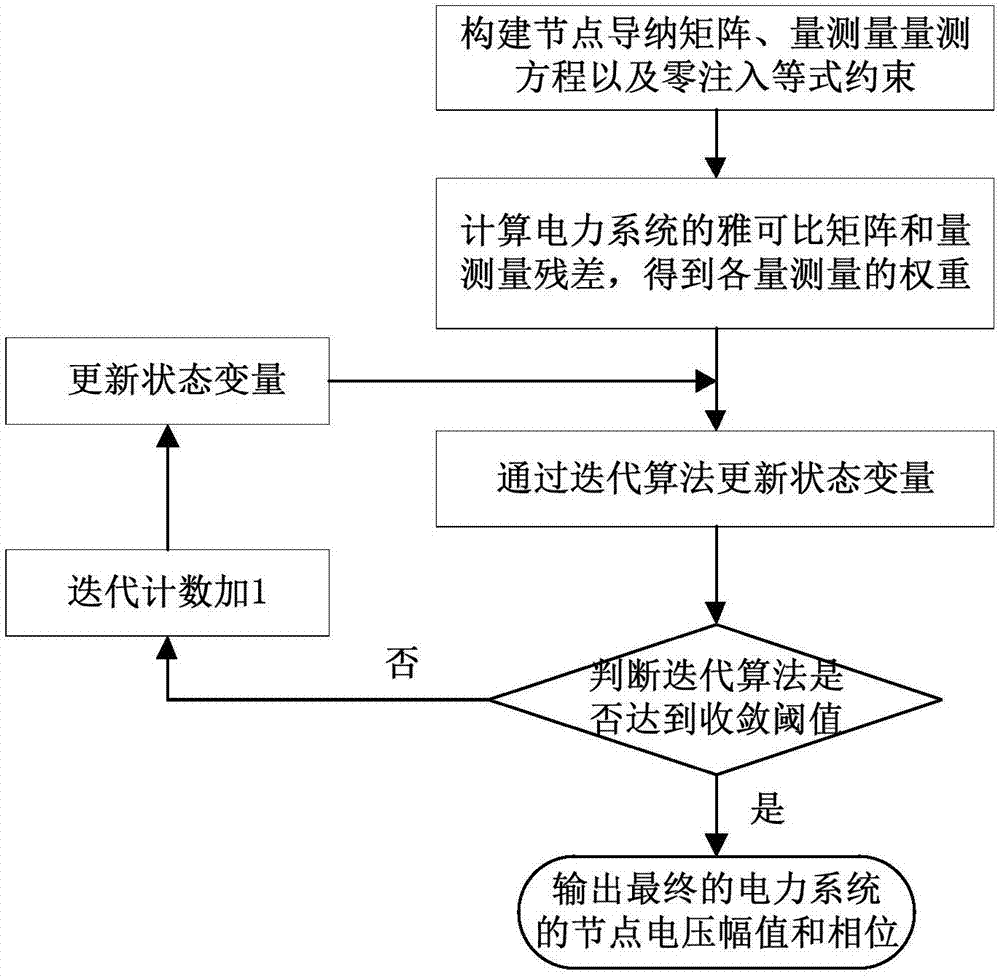
Electric-power-system robust state estimation method and apparatus thereof
PendingCN107016489ALose weightInhibition effectResourcesAc network circuit arrangementsVoltage amplitudeState variable
An embodiment of the invention provides an electric-power-system robust state estimation method based on a subsection nonlinear weight function and an apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps of constructing a node admittance matrix of an electric power system, a measurement amount measurement equation and a zero injection equality constraint; calculating a jacobian matrix and a measurement-amount residual error of the electric power system and acquiring a weight of each measurement amount; and updating a state variable, determining whether an iteration algorithm reaches a convergence threshold, and if the iteration algorithm reaches the convergence threshold, acquiring a final node voltage amplitude and a phase position of the electric power system. In the invention, bad data detection and identification, and state estimation are simultaneously performed; state estimation calculating is performed, and simultaneously a measurement amount weight can be changed; a bad data weight in iteration is continuously reduced and an influence brought by the bad data is restrained; a calculation amount is effectively reduced and work efficiency is increased; a residual error of the measurement amount is directly introduced into a subsection nonlinear weight function, and standardized residual error calculating is avoided so that a calculating speed can be greatly increased and calculating time is saved; and the method and the apparatus are suitable for an engineering application.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
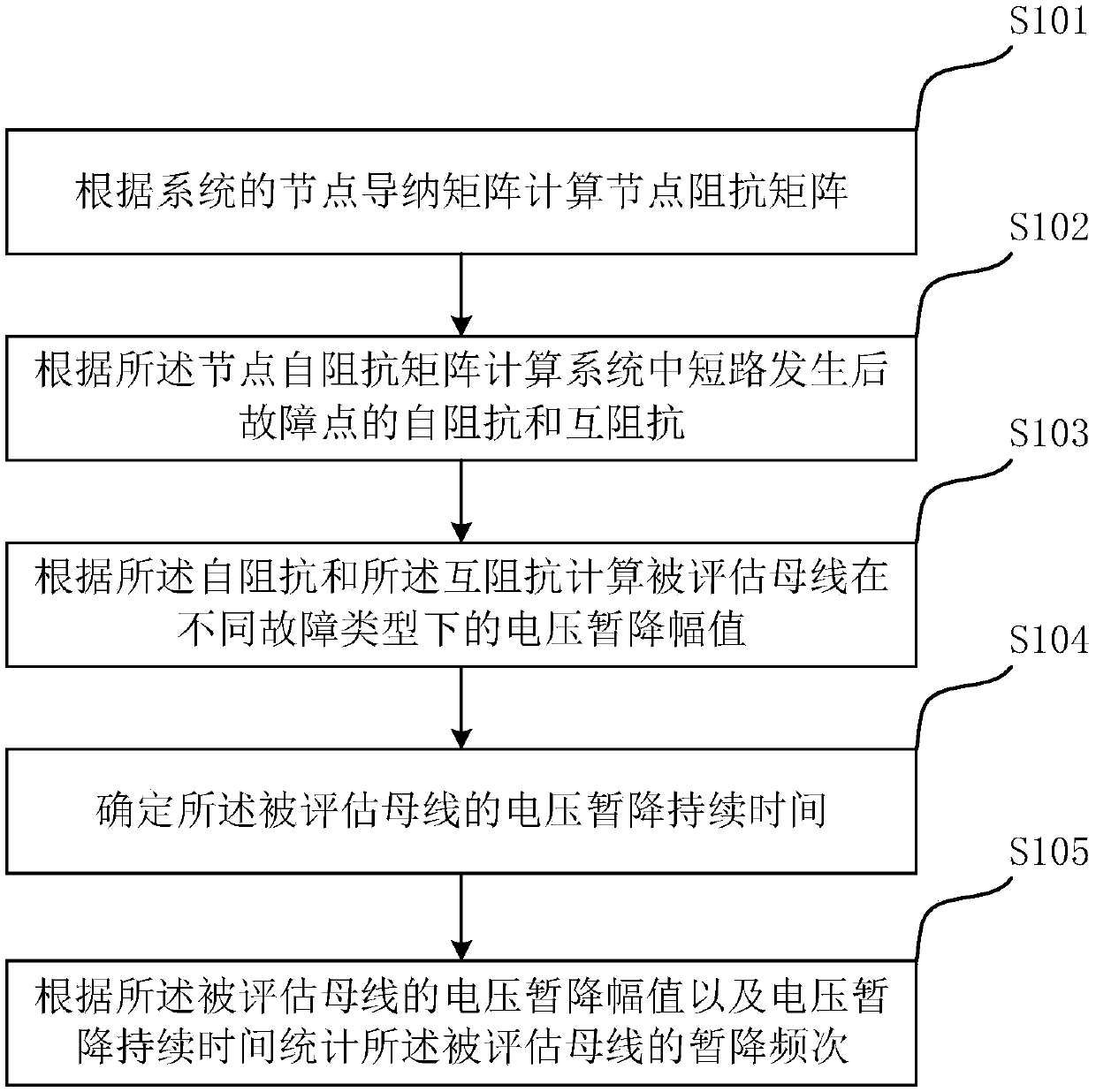
Network voltage sag frequency estimation method and device with distributed power supply
The invention relates to a network voltage sag frequency estimation method and device with a distributed power supply. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a node impedance matrix according to a node admittance matrix of the system; calculating the self-impedance and mutual impedance at the fault point after short circuit occurs in the system; calculating the voltage sag amplitudeof the estimated busbar under different fault types; determining the voltage sag duration of the estimated busbar; performing statistics of the sag frequency of the estimated busbar according to thevoltage sag amplitude and the voltage sag duration of the estimated busbar. According to the method and device provided by the invention, the estimation accuracy of the voltage sag with a distributedpower supply system is improved; by adopting kernel density estimation, the distribution law of the fault occurrence positions better conforms to the practical situation according to the history faultinformation, thus the estimation result of voltage sag is more accurate and conforms to the practice.
Owner:GUANGZHOU POWER SUPPLY BUREAU GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD
Improved modal analysis method of power distribution network harmonic resonance
ActiveCN106896267APrecise positioningAccurately determineFrequency analysisFeature vectorFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an improved modal analysis method of power distribution network harmonic resonance. The improved modal analysis method comprises the following steps that: a resonant frequency is determined through using a spectrum analysis method; the eigenvalue matrix of a node admittance matrix under the resonant frequency is obtained; the eigenvalues of the node admittance matrix are sequenced according to an ascending order, and the locations of the eigenvalues are recorded; and the first m minimum eigenvalues are selected as the feasible solutions of critical modes under the resonant frequency, critical right eigenvectors corresponding to each feasible solution are determined, the maximum right eigenvalues and the positions thereof of the critical right eigenvector feasible solutions can be obtained, and the positions are the feasible solutions of a highest excitation node. The improved modal analysis method of the invention has the advantages of high computational efficiency and accurate positioning of the highest excitation node, and the like, and is more suitable for the harmonic resonance analysis of a power distribution network.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Rectangular coordinate Newton load flow calculation method
InactiveCN101621200ASolving Convergence ProblemsConvergent and reliableAc network circuit arrangementsInternal memoryRectangular coordinates
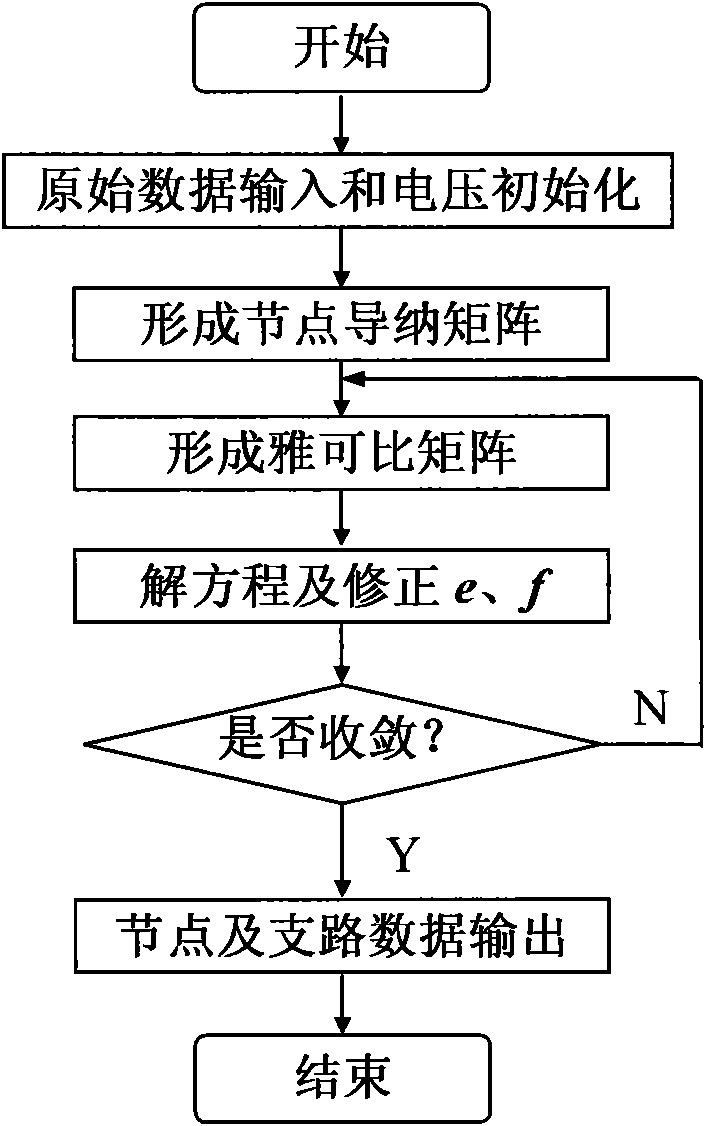
The invention discloses a rectangular coordinate Newton load flow calculation method; from the basic principle of rectangular coordinate Newton load flow calculation, the invention provides a composition method of Jacobimatrix calculated by rectangular coordinate Newton load flow calculation to improve the convergence of load flow calculation on the basis of analyzing the characteristics of basic modified equation. The method comprises the following steps: inputting original data and initializing voltage; forming nodal admittance matrix; forming Jacobimatrix J; solving the equation and correcting the real part e and the imaginary part f of voltage; and outputting nodal and subcircuit data. The invention corrects partial diagonal element calculation formula of Jacobimatrix J, solving the problem of convergency of rectangular coordinate Newton load flow calculation method when analyzing a subcircuit system containing low impedance; the iterations, possession of the amount of internal memory and arithmetic speed in the invention are all equivalent to conventional rectangular coordinate Newton load flow calculation method when treating system with no low impedance, so the calculated amount is not increased, but is slightly reduced on the contrary.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
General method for calculating tide of positive power distribution networks
ActiveCN103971026AFast convergenceImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsElectric distribution networkNodal admittance matrix
The invention provides a general method for calculating the tide of positive power distribution networks. The general method comprises the step of establishing various distributed generation (DG) tide calculation models to obtain a PV node sensitivity reactance matrix BPV of nPV PV type DG positive power distribution networks so as to calculate the tide of the positive power distribution networks. The general method is high in universality, can be used by power distribution networks with various wiring modes and operating modes, and also can be used for calculating the tide of power distribution networks at disconnected areas; the topological analysis of the power distribution networks is not needed, various path matrixes do not need to be calculated, and a node admittance matrix can be directly figured out according to node information and branch information, so that the general method is simple and is easy in implementation; the accurate PV node sensitivity reactance matrix is adopted, so that the convergence speed of reactive power output of the PV node type DG is enhanced; on the basis of a Zbus method, the calculation of the whole convergence speed is fast, and the stability is good; the generable method can be expanded to calculation of three-phase tides.
Owner:永春县产品质量检验所福建省香产品质量检验中心国家燃香类产品质量监督检验中心福建
Method of deducing equivalent circuit and system for the same
InactiveUS6871334B2Guaranteed accuracyReduce in quantityResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementElectricityDielectric
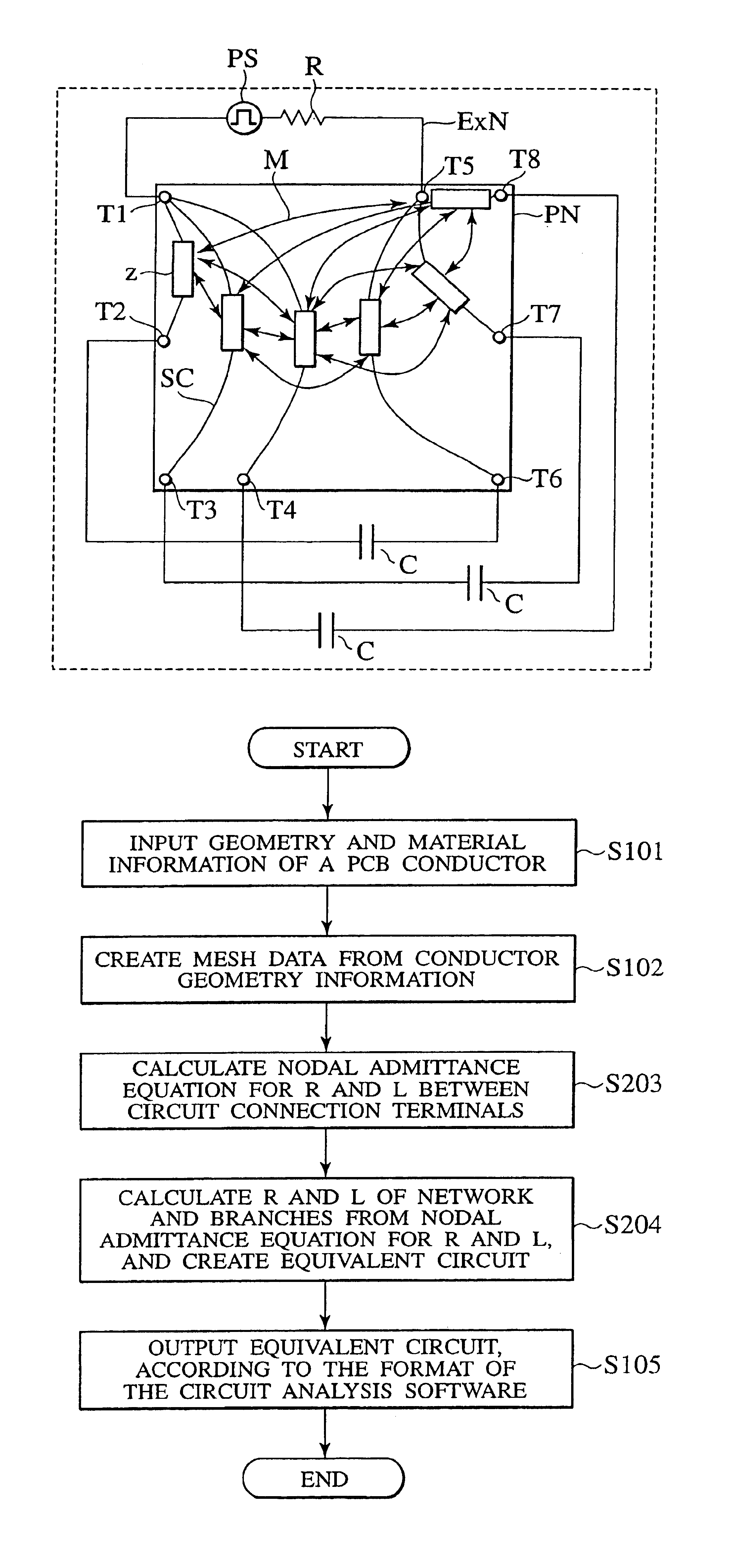
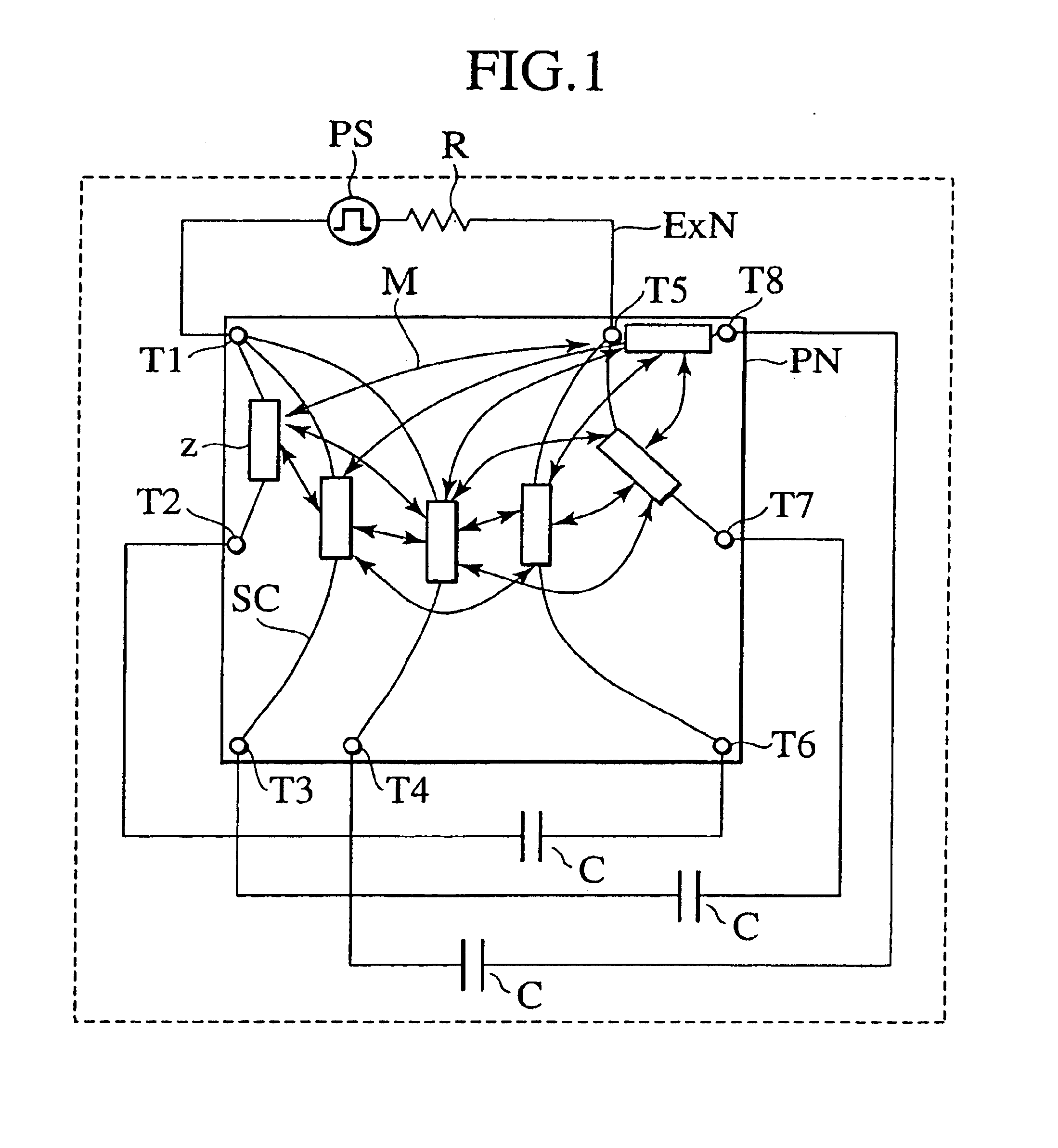
The invention provides a method of calculating an equivalent circuit, which reduces the number of elements constituting a network to a large extent with a target accuracy secured. The method of the invention calculates an equivalent circuit by a computer, with regard to an object that has a conductor, a dielectric to support the conductor, and plural input / output terminals to the outside. Step 1 in the method receives inputs of geometry information to specify a shape of a conductor in a circuit board being the object of determining the equivalent circuit, and material information to specify a material of the circuit board; Step 2 partitions the shape of the objective conductor into meshes on the basis of the geometry information received, and creates mesh data to be expressed; Step 3 calculates a nodal admittance matrix from the mesh data, and stores the result; step 4 calculates the number of nodes and the number of independent networks on the basis of the mesh data, determines an incidence matrix, and determines the structure of an equivalent network by means of the calculated nodal admittance matrix and incidence matrix; and Step 5 determines the values of elements of the equivalent network.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
A voltage sag random prediction method based on actual power network monitoring information
The invention discloses a voltage sag random prediction method based on actual power network monitoring information, belonging to the technical field of power quality analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: reading actual power network parameters to obtain node admittance matrix; processing the measured sag data of each node and obtaining the probabilistic model of fault type and fault duration; establishing a system fault information model; generating fault information by Latin hypercube sampling, and forming the original database of fault information; carrying out fault simulation to calculate the error between the predicted result and the measured result. According to whether the error meets the requirement, the fault information model is corrected until the error meets the requirement or reaches the preset correction times, and the final predicted result is obtained. The present invention can effectively avoid the problems of poor stability, slow convergence, long time consuming, large error of prediction result and the like in the existing prediction method, and the prediction result is more accurate.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST STATE GRID SHANXI ELECTRIC POWER +1
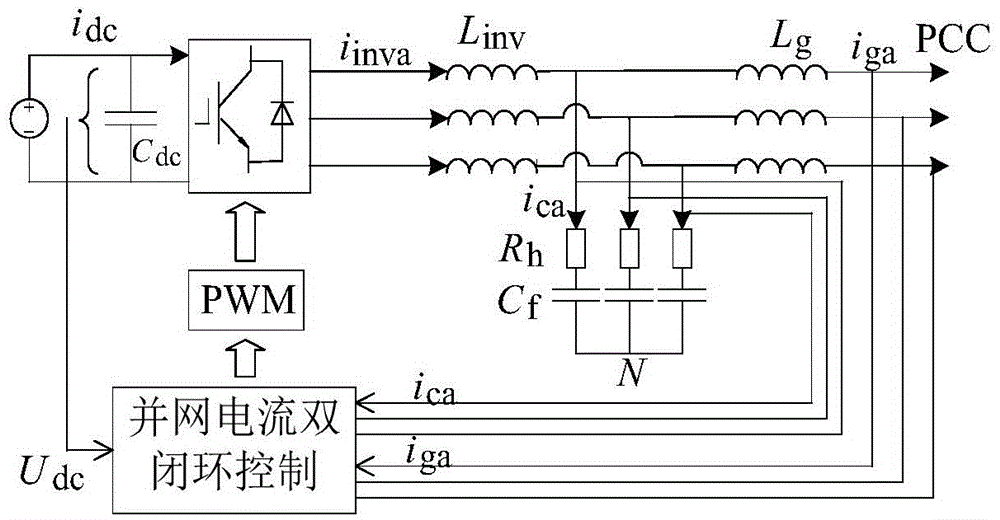
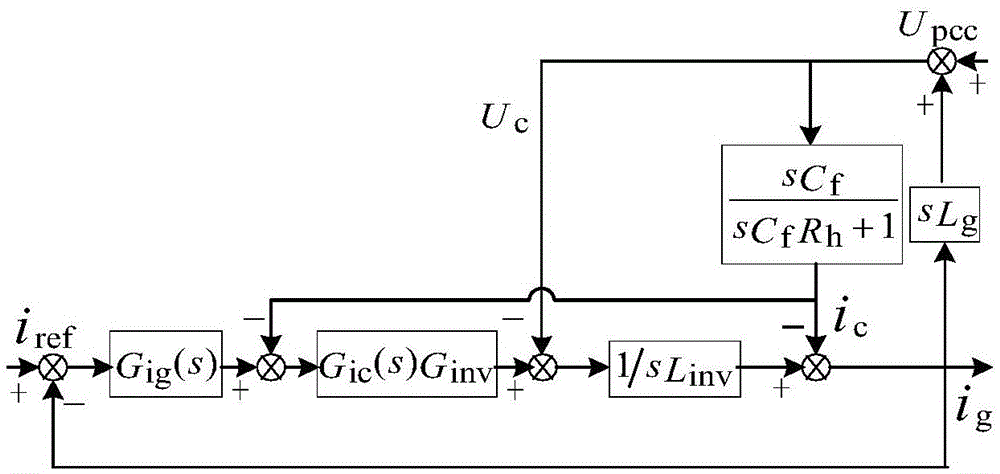
Long-line wind farm grid-connected resonance information extraction method
InactiveCN105676022AGood resonance characteristicsAccurately determine the resonance frequencyElectrical testingNODALAlgorithm
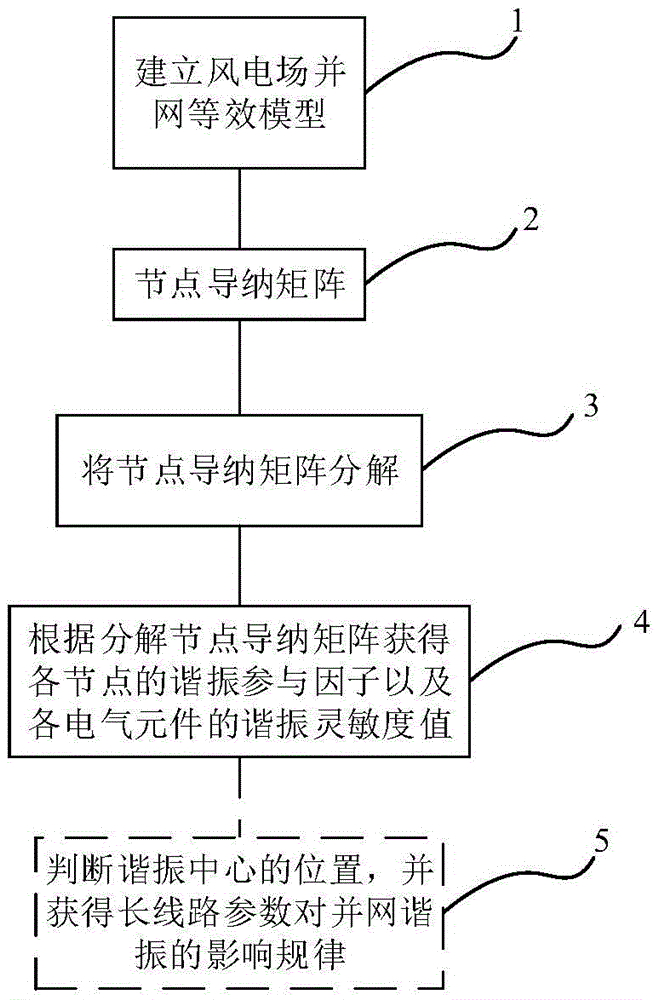
The invention relates to a method for extracting resonance information of a long-line wind farm grid connection, comprising the following steps: 1) establishing an equivalent model of a wind farm grid connection; 2) obtaining the wind farm grid connection system according to the wind farm grid connection equivalent model Nodal admittance matrix; 3) decompose said nodal admittance matrix into expressions about eigenvalues: Y f = LΛT; 4) According to step 3), the resonance participation factor of each node and the resonance sensitivity value of each electrical component are obtained when the long-line wind farm grid-connected resonance phenomenon occurs. Compared with the prior art, the present invention is based on the equivalent model of wind farm grid connection, and uses modal analysis method to analyze the resonance participation factors of each node of the system and the modal sensitivity of components, thereby giving detailed wind power grid connection resonance information, providing wind power It provides theoretical guidance for field construction planning, and has the advantages of accurate and reliable information extraction results.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
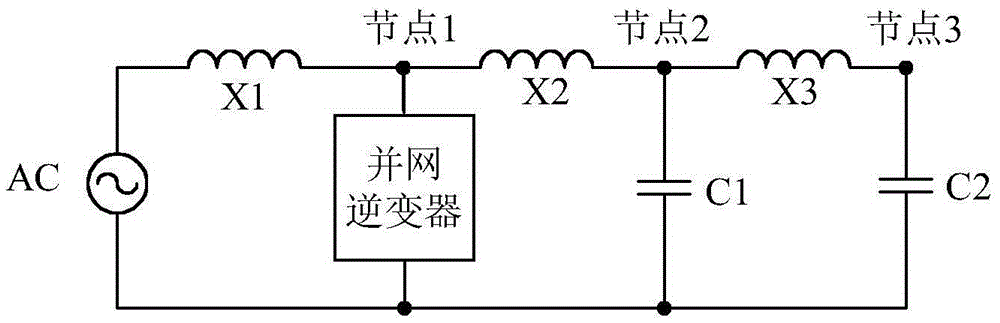
Node admittance matrix eigenvalue analysis method applied to grid-connected-inverter-included parallel resonance situation
InactiveCN105529727ABest Incentive PositionBest observation positionPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectric power systemResonance analysis
The invention provides a node admittance matrix eigenvalue analysis method applied to a grid-connected-inverter-included parallel resonance situation, which belongs to the field of inverter-included grid-connected resonance analysis and detection and solves a problem that the resonance generation and the resonance generation frequency can be obtained when the existing resonance detection method analyzes resonance waves, but an optimal observation position and an optimal excitation position in a resonance generation process cannot be determined. When a parallel resonance situation is analyzed in a grid-connected-inverter-included system, the system is subjected to equivalence, a branch of a three-bus system for analyzing the resonance situation of a traditional electric power system is changed into an inverter to perform analysis, thereby obtaining a node admittance matrix of the system, wherein a matrix eigenvalue and left and right eigenvectors are calculated; by analyzing the eigenvalue under every frequency, the eigenvalue under a certain frequency occurs a maximum value, so that the resonance occurs under the frequency; by analyzing left and right eigenmatrixes, the optimal observation position and an optimal excitation position are obtained. The node admittance matrix eigenvalue analysis method provided by the invention is applied to a grid-connected-inverter-included power distribution system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
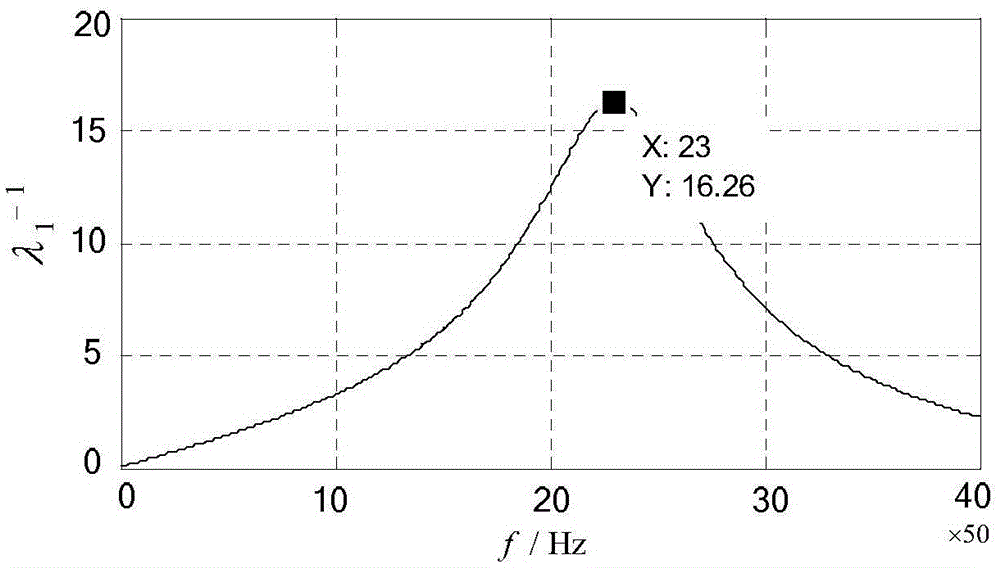
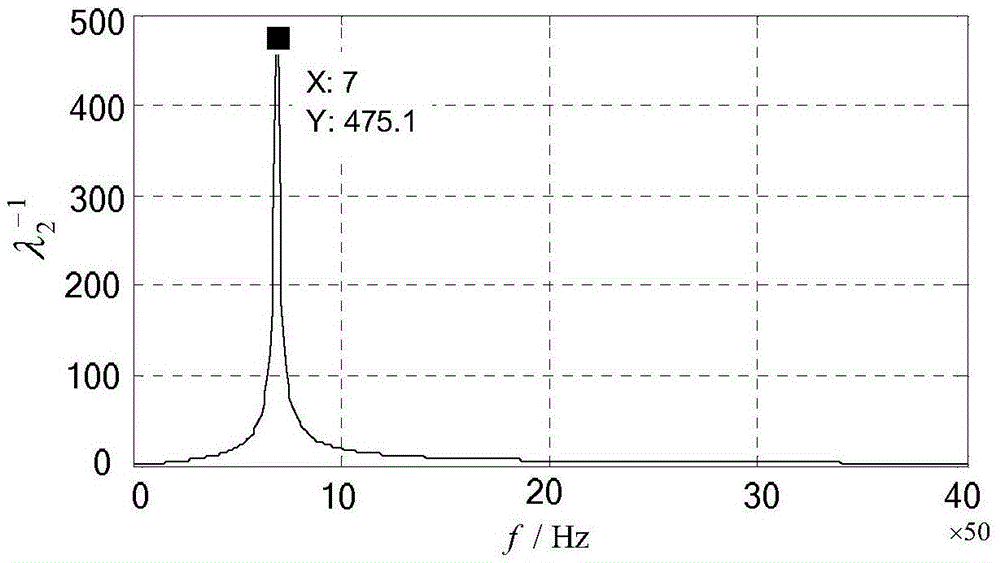
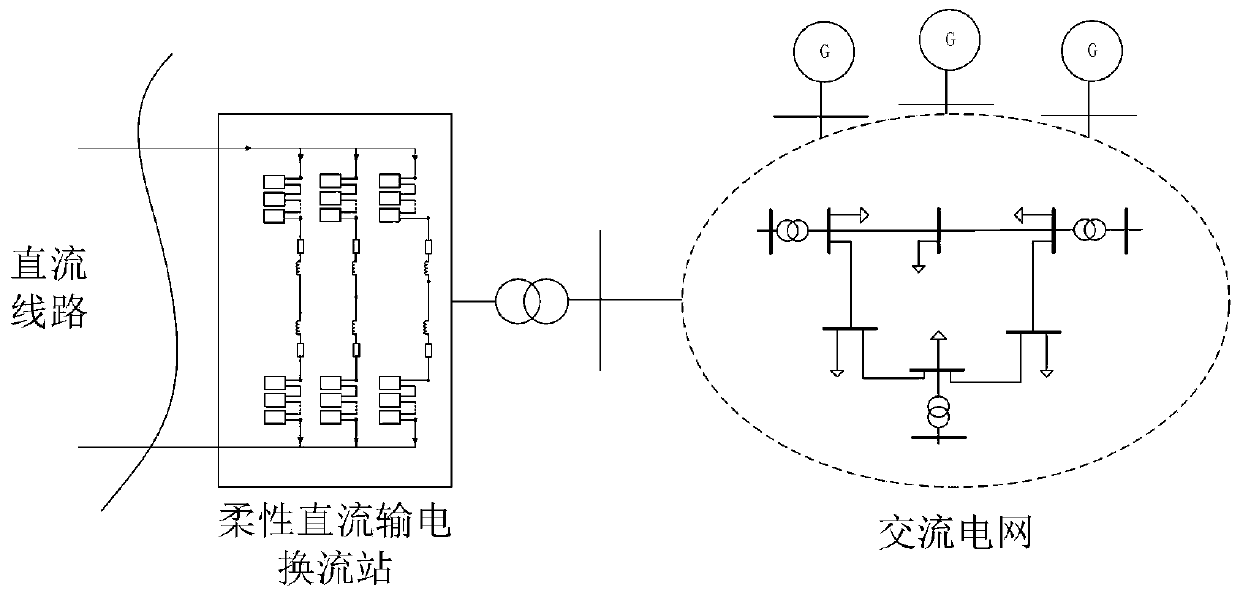
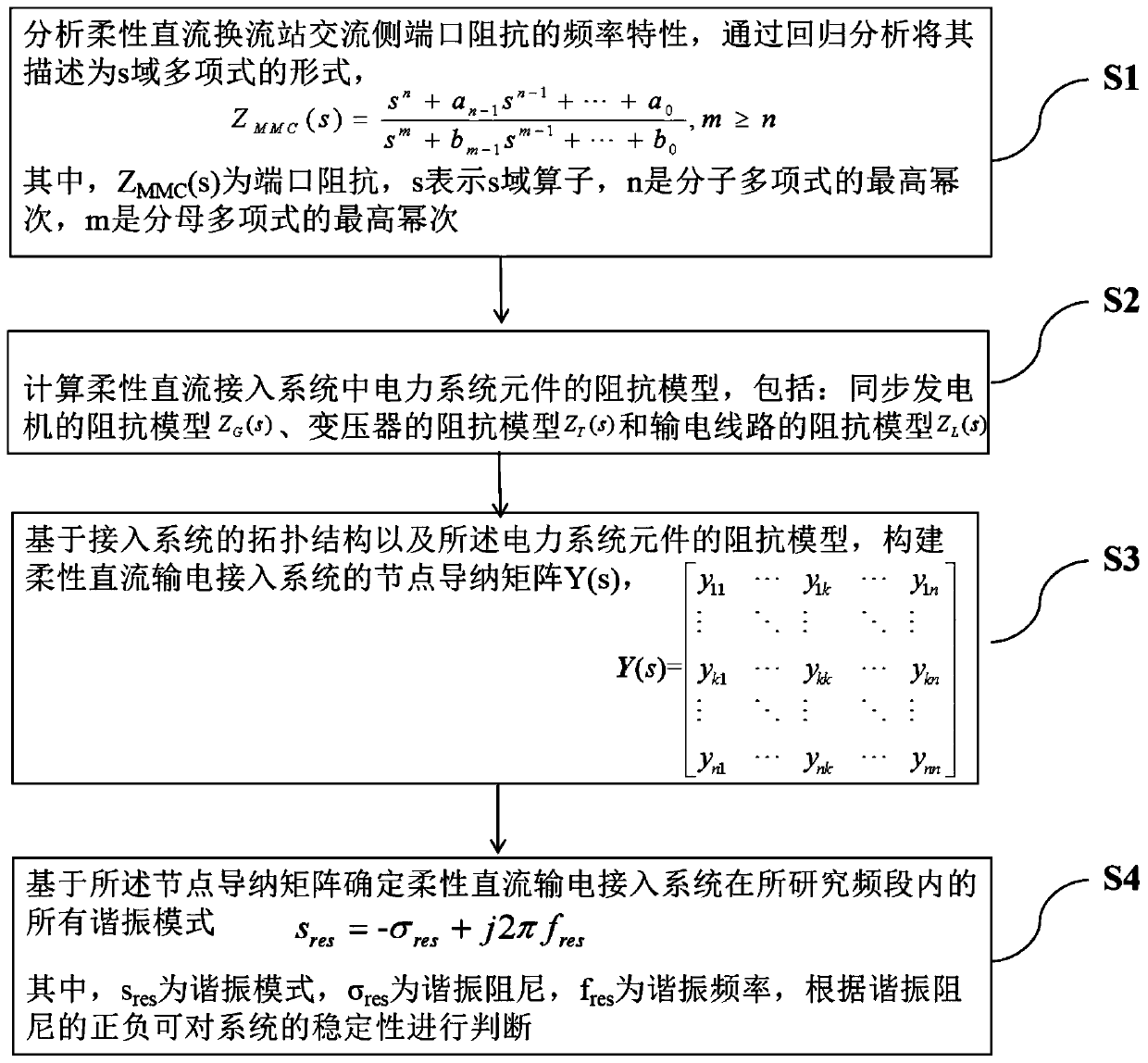
Method of analyzing resonance stability of flexible DC transmission access system
ActiveCN109802406AOvercome workloadOvercome the difficulty of unknown parametersElectric power transfer ac networkPower oscillations reduction/preventionResonanceState space
The invention provides a method of analyzing the resonance stability of a flexible DC transmission access system. A node admittance matrix of the flexible DC transmission access system is analyzed, the resonance mode of the system is determined, and the stability of the system is further judged. In view of the application scene of analyzing the resonance stability problem of the flexible DC transmission access system, the flexible DC transmission access system resonance stability analyzing method can comprehensively analyze the resonance mode existing in the flexible DC transmission access system, and the stability of the system is judged. The resonance stability judgment method overcomes the problems of a large workload and unknown parameters of a state space method, and in comparison with an impedance analysis method, the scanned resonance mode is more complete, the stability of the whole system is more accurately judged, and some reference and guidance are provided for actual engineering planning and construction of the flexible DC transmission engineer.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID
Nonlinearity-considered electromagnetic transient real-time simulation method of transformer substation
InactiveCN104298822AGood simulation accuracyGuaranteed real-timeData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsNODALTransformer
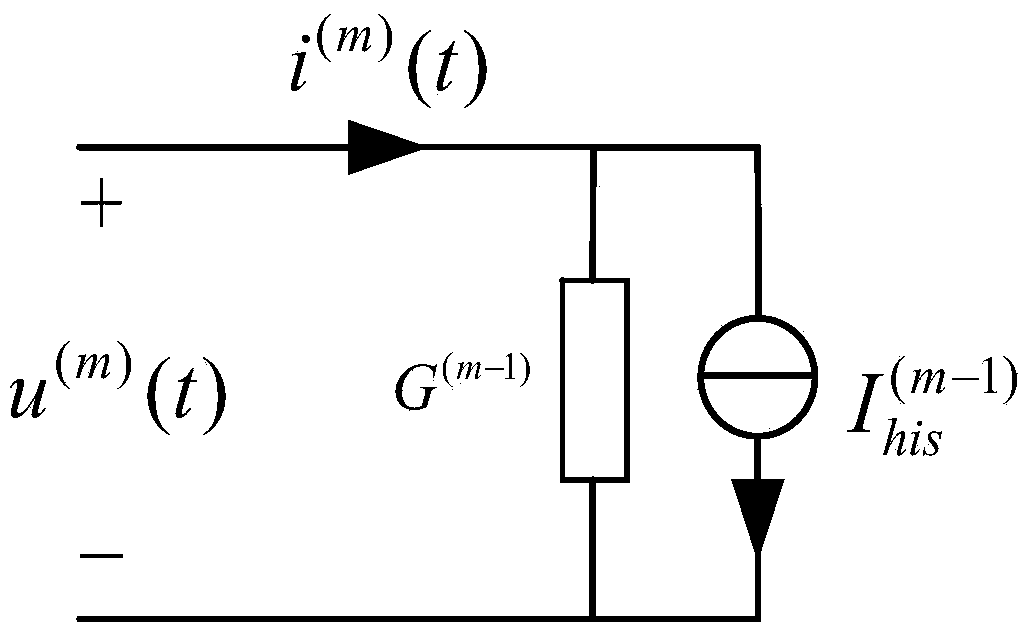
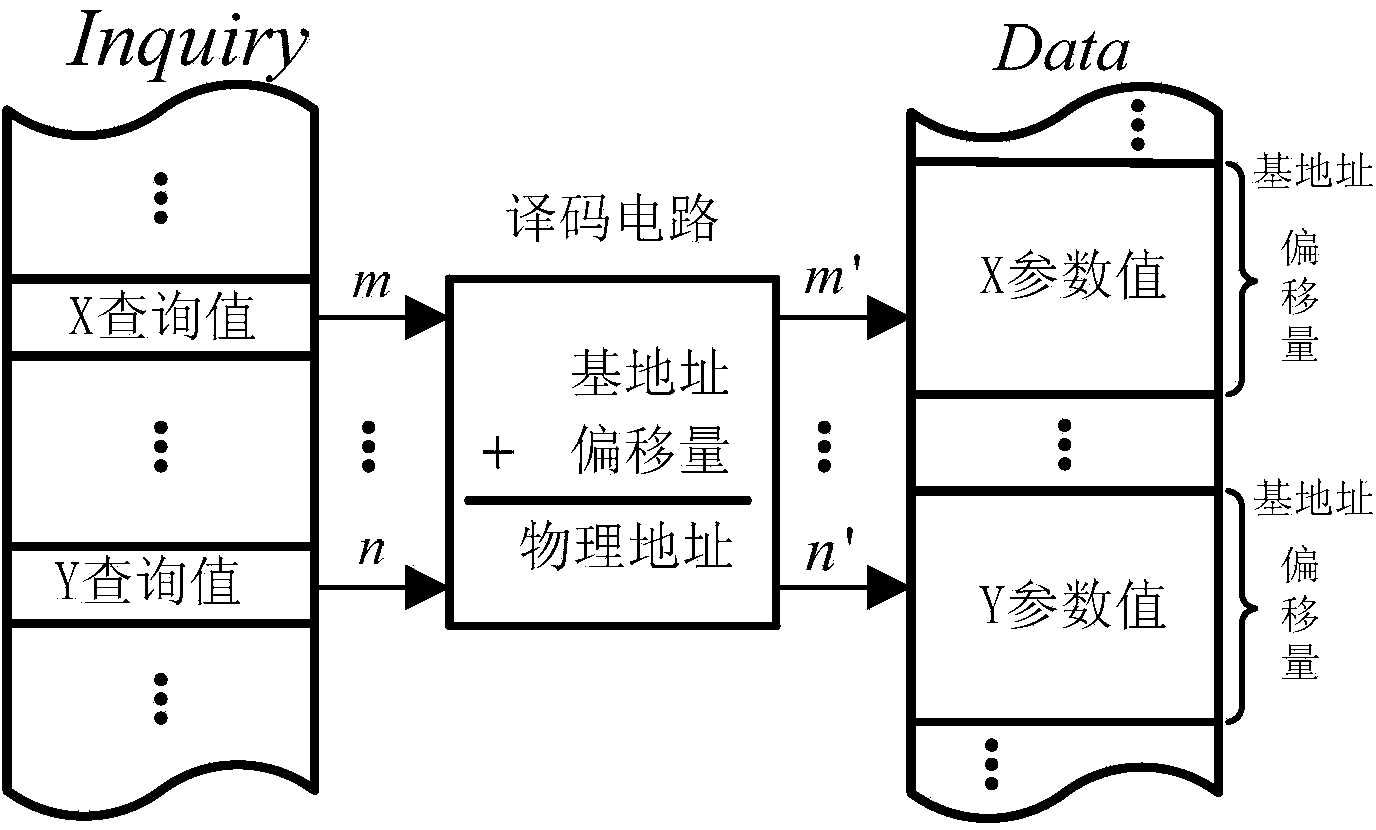
The invention provides a nonlinearity-considered electromagnetic transient real-time simulation method of a transformer substation. The method comprises the following steps: preparing for simulation off line; differencing transformer substation elements according to the selection of simulation step size delta t; converting electric network of the transformer substation elements into corresponding an adjoint network through an adjoint circuit; reordering a differenced nodal admittance matrix according to the nonlinear local iterating principle and the minimum degree independent set method; arranging instructions performed by an arithmetical unit according to the idea of solving a nodal voltage equation by the gauss elimination; calculating real-time simulation on line, wherein the online calculation specifically includes the historical current source calculation of the adjoint circuit, the nodal injection current of the adjoint network, the order elimination of the nodal voltage equation, reversed order back substitution of the nodal voltage equation, branch voltage calculation and branch current calculation which are processed in parallel through a plurality of arithmetical units; quickly simulating parameter read-write interaction between the arithmetical units and a data storage space by the simulation parameter decoding query method. With the adoption of the method, the real-time performance of electromagnetic transient real-time simulation of the transformer substation can be ensured.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
WARD equivalence-based alternating current direct current system equivalence method
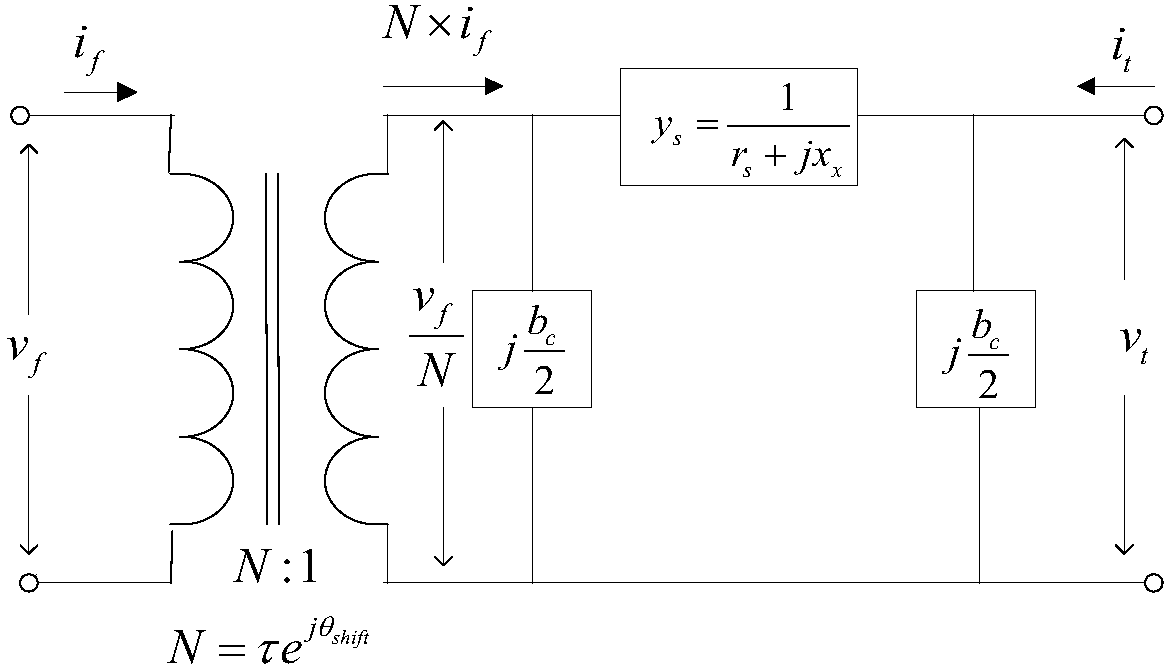
ActiveCN107681682ASmall tidal current errorEliminate the influenceElectric power transfer ac networkCapacitanceElement model
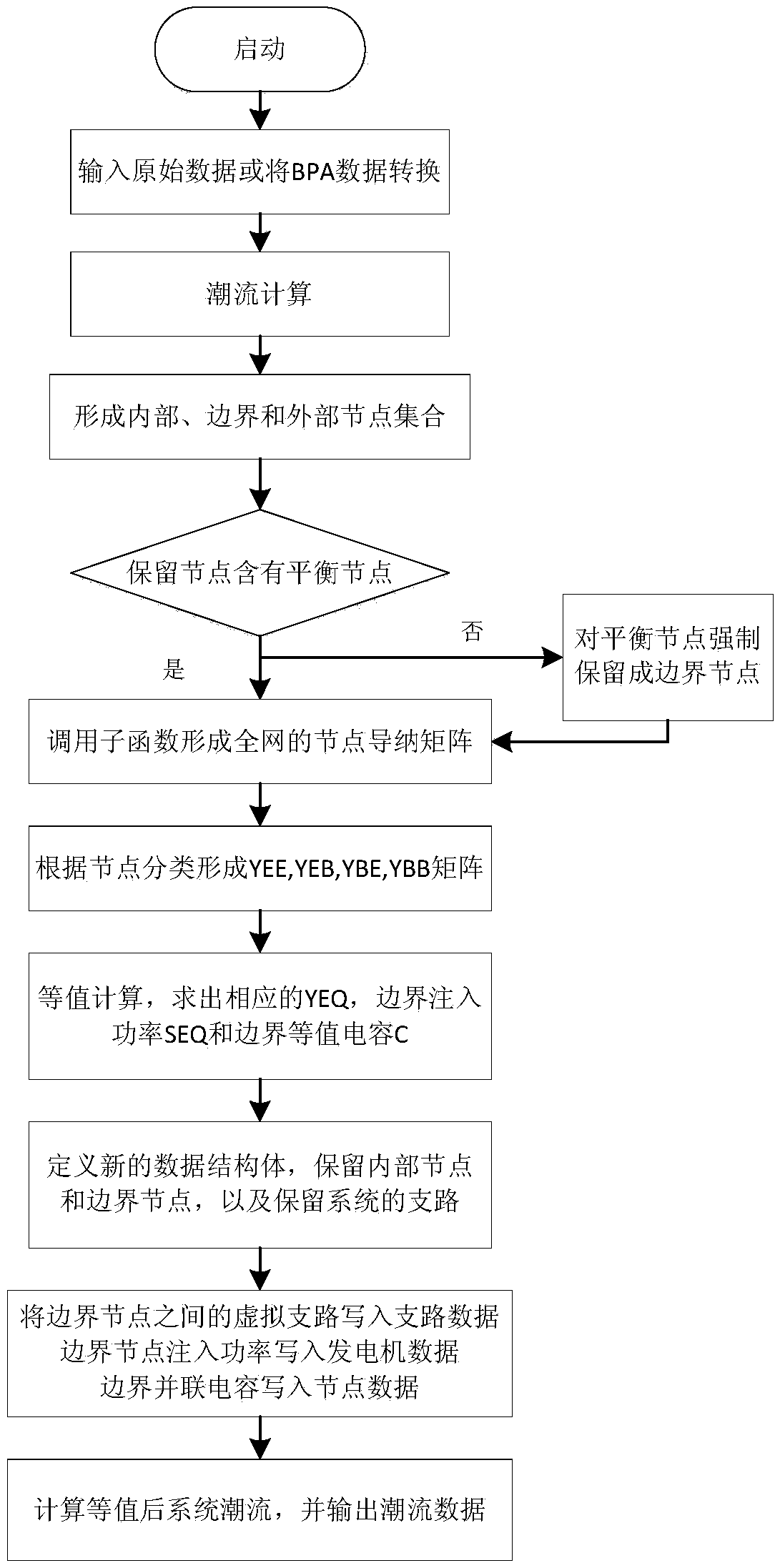
The invention relates to a WARD equivalence-based alternating current direct current system equivalence method. The alternating current direct current system equivalence method comprises the steps ofestablishing each basic element model, obtaining nodes in the whole network to be used as basic data, and determining the data format; performing power flow calculation on the whole network and obtaining the power flow solution of the whole network; dividing the nodes into an internal node set, a boundary node set and an external node set, wherein the elements in each set are arranged from small to big based on node numbers; forming a node admittance matrix of the whole network, and forming partitioned node admittance matrixes used for equivalence calculation according to the divided node sets; calculating an equivalence matrix, a boundary equivalence capacitor and a boundary equivalent injection power; forming a new structural data body, and storing the basic data of the system after equivalence to be defined as R<empc>; and performing power flow calculation on the system after equivalence, making comparison on the power flow results of the retained branch and the nodes before and after equivalence, and selectively outputting the power flow results. By virtue of the alternating current direct current system equivalence method, it is effectively ensured that the power flow error ofthe retained system before and after equivalence can be in the minimum, so that the method can be applied to an extra-high voltage direct current layering system.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
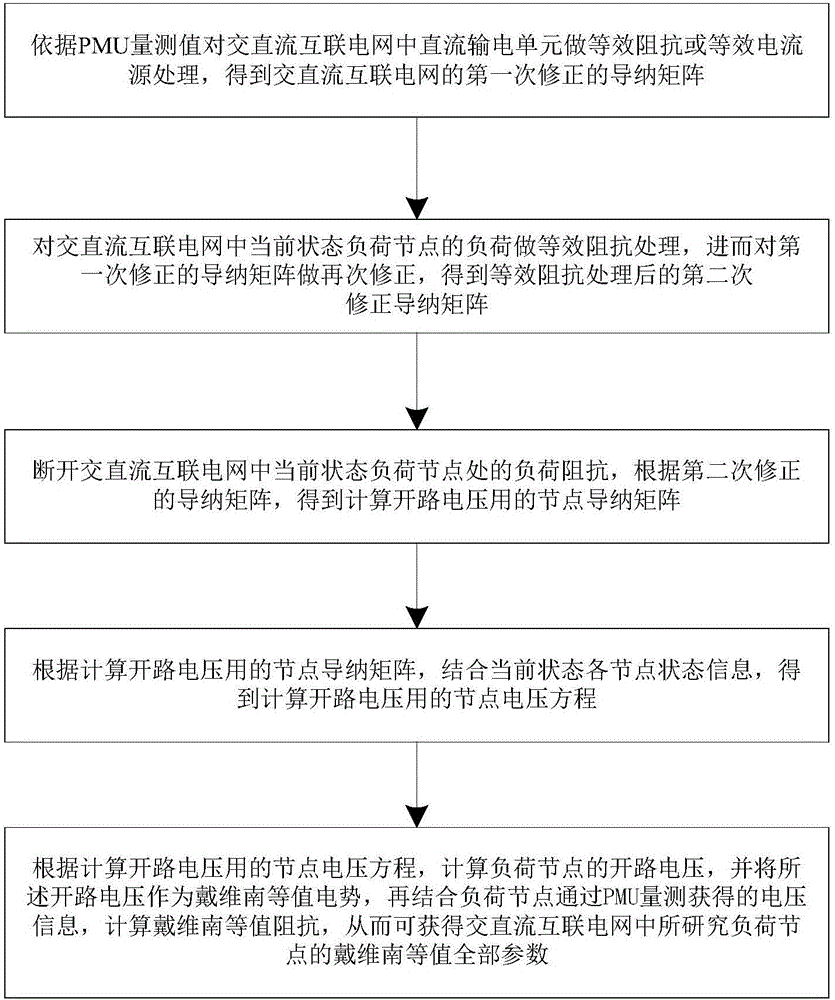
Alternating-current and direct-current interconnected power grid Thevenin equivalent parameter online calculation method
ActiveCN106295160AFull potentialHigh equivalence accuracySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsPower gridAlternating current
The invention discloses an alternating-current and direct-current interconnected power grid Thevenin equivalent parameter online calculation method. The method includes the steps that equivalent impedance or equivalent current source processing is conducted on a direct-current power transmission unit in an alternating-current and direct-current interconnected power grid according to PMU measurement values to obtain a primary correction admittance matrix; equivalent impedance processing is conducted on the load of current state load nodes in the alternating-current and direct-current interconnected power grid to obtain a secondary correction admittance matrix after equivalent impedance processing; load impedance at the current state load node in the alternating-current and direct-current interconnected power grid is cut off, and a node admittance matrix for open-circuit voltage is calculated according to the secondary correction admittance matrix; according to the node admittance matrix for open-circuit voltage and node state information of all nodes in the current state, a node voltage equation for open-circuit voltage is calculated; Thevenin equivalent impedance is calculated, and accordingly all Thevenin equivalent parameters of researched load nodes in the alternating-current and direct-current interconnected power grid can be obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
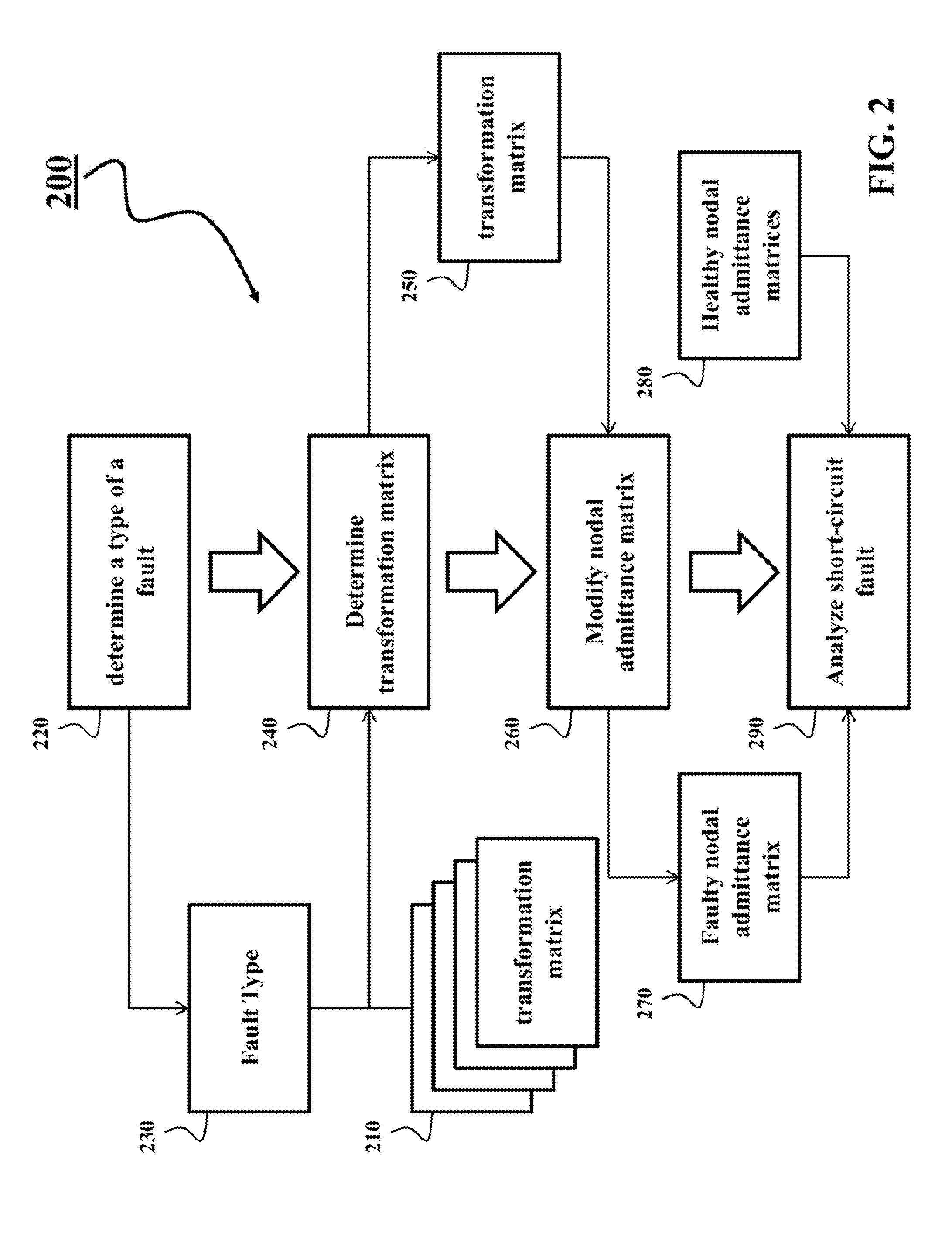
Method for Analyzing Faults in Ungrounded Power Distribution Systems
ActiveUS20140309952A1Efficient and accurateAccurate methodCircuit arrangementsFault location by conductor typesNODALElectric power distribution
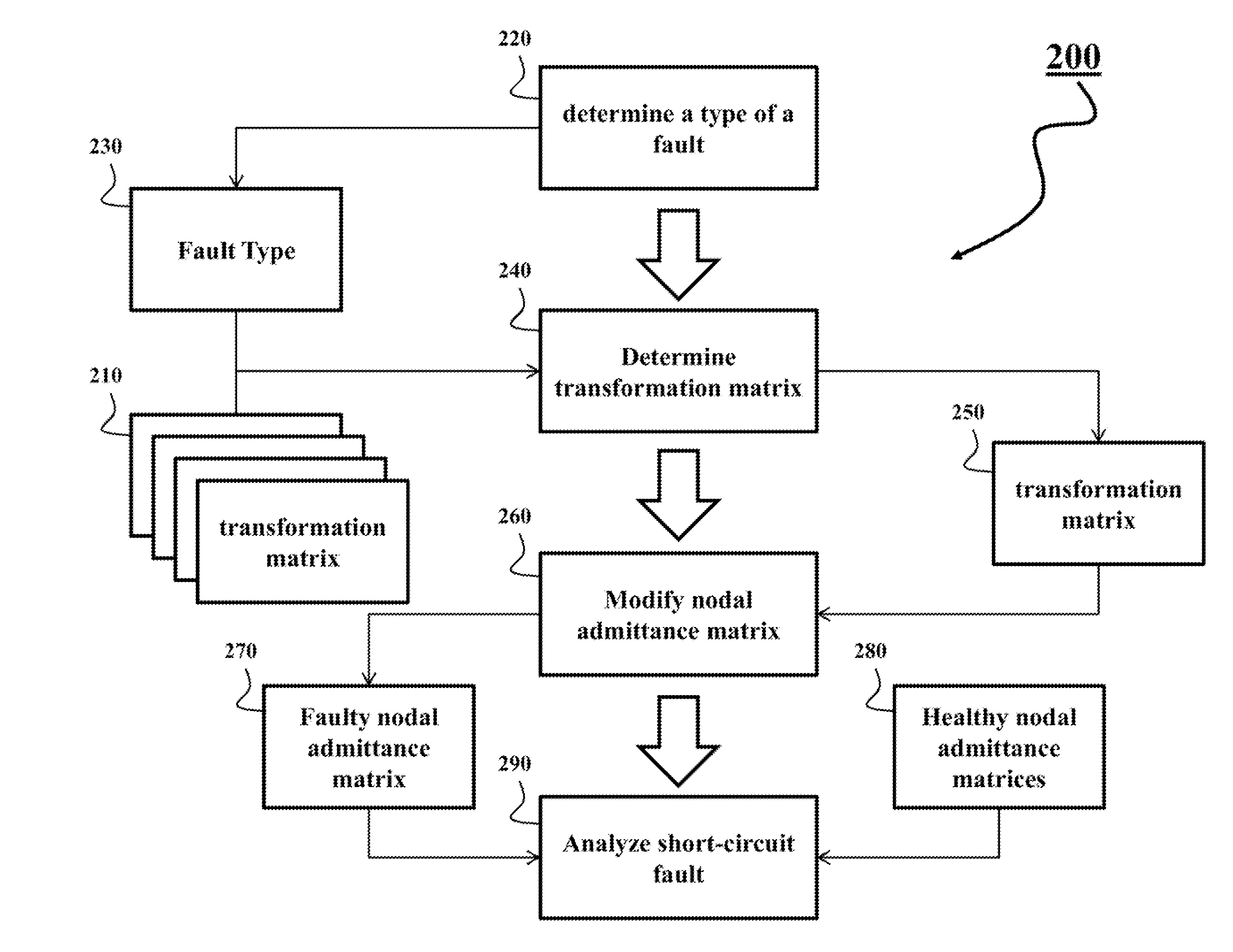
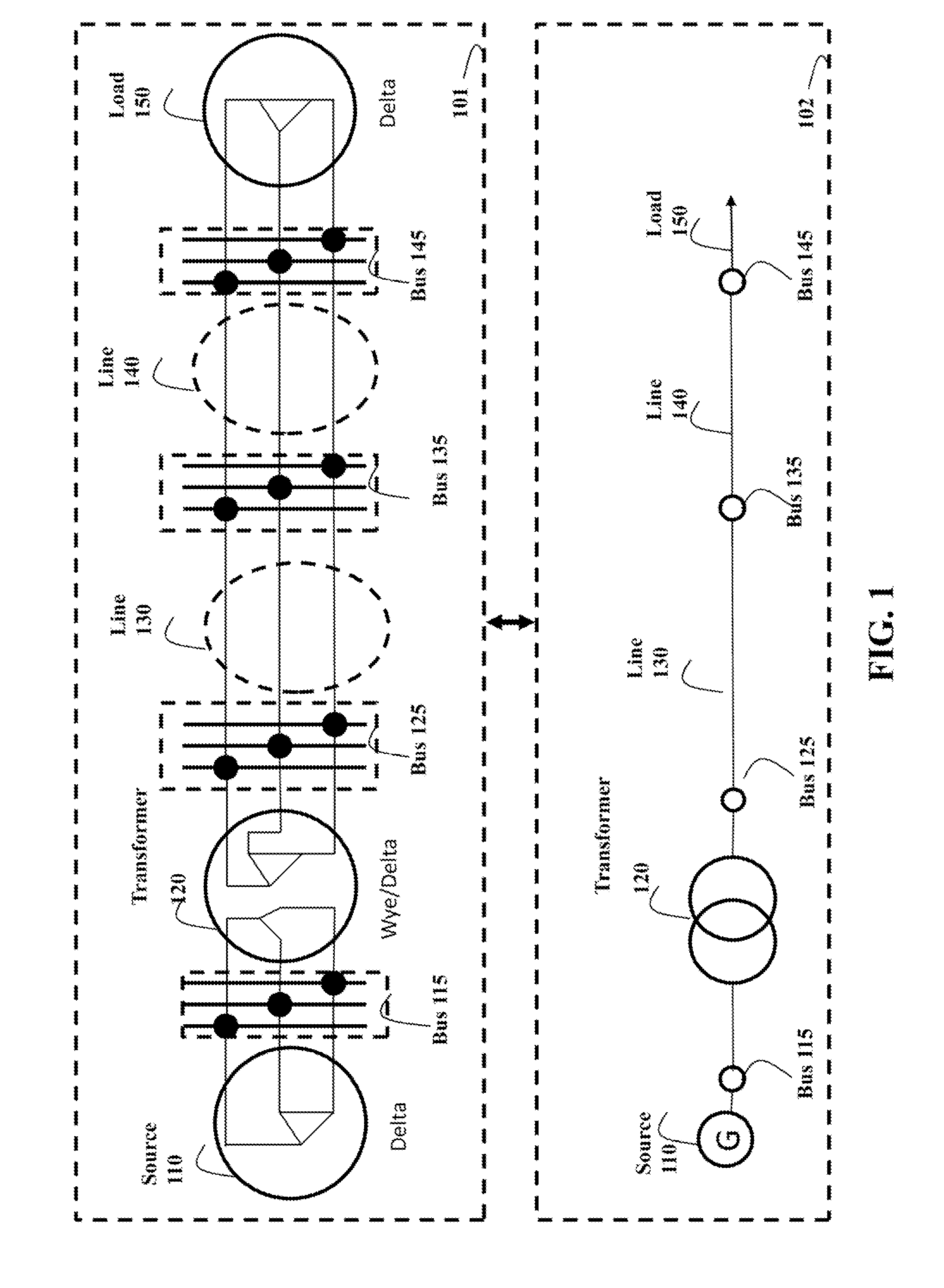
A method analyzes a fault of an ungrounded power distribution system. The method determines a type of a fault in a line segment of the ungrounded power distribution system, and modifies a nodal admittance matrix of the line segment determined before the fault using a transformation matrix corresponding to the type of the fault to produce a faulty nodal admittance matrix of the line segment after the fault. The ungrounded power distribution system is analyzed using the faulty nodal admittance matrix and nodal admittance matrices of functional branches or line segments of the power distribution system.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
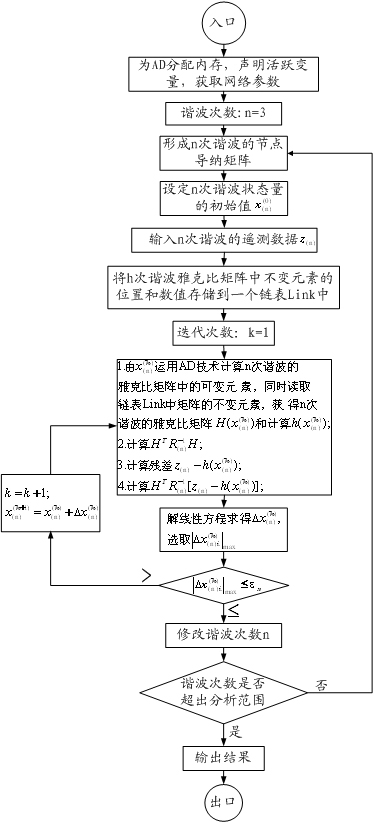
Power system harmonic state estimation method based on automatic differentiation
InactiveCN102624000AImprove development efficiencyImprove computing efficiencyHarmonic reduction arrangementAc network to reduce harmonics/ripplesCode writingNODAL
The invention discloses a power system harmonic state estimation method based on an automatic differentiation. The automatic differentiation (AD) technology is applied to the power system harmonic state estimation. The method includes that firstly storage allocation is performed for the AD, live variables are described, a network parameter is obtained, a harmonic number is set, and a node admittance matrix of a harmonic is formed; then before iteration, positions and values of invariant elements in a jacobian matrix are stored in a linked list; and the iteration starts, the AD tool is used to calculate variable elements in the jacobian matrix, and simultaneously the invariant elements of the jacobian matrix in the linked list are read to obtain the jacobian matrix required by the harmonic state estimation. According to the power system harmonic state estimation method based on the automatic differentiation, traditional manual differential code writing is replaced by the AD to calculate the jacobian matrix, thereby handwritten code quantity is reduced, development efficiency of programs is increased, truncation error is effectively avoided, computational efficiency of algorithm is improved, and the power system harmonic state estimation method based on the automatic differentiation is convenient to implement on an existing state estimation software.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method and device for acquiring harmonic characteristics of power grid containing new energy stations
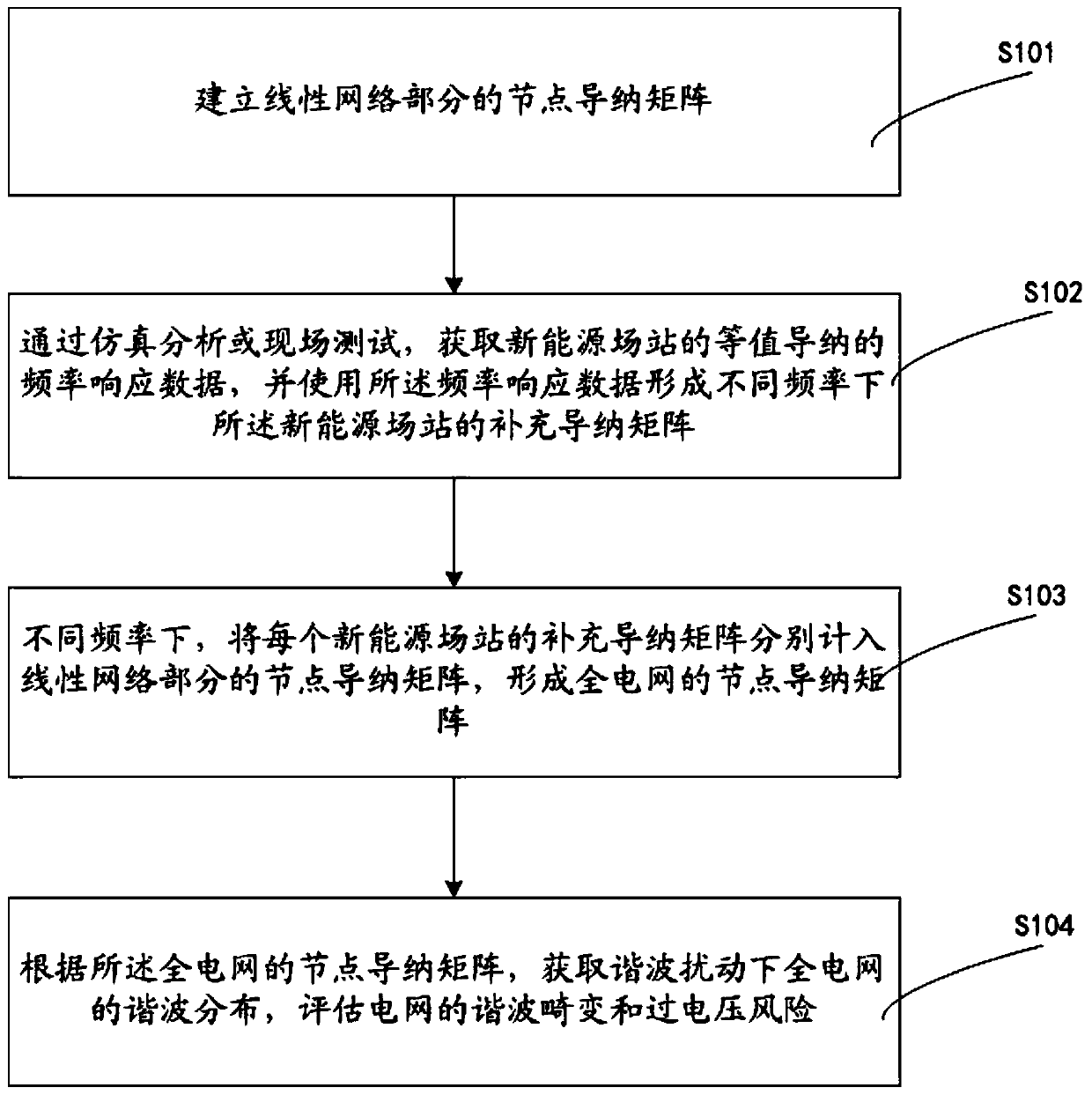
The invention discloses a method for acquiring the harmonic characteristics of a power grid containing new energy stations, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: establishing a node admittance matrix of a linear network part; acquiring frequency response data of equivalent admittance of new energy stations by simulation or field test, and using the frequency response data to form supplementary admittance matrixes of the new energy stations at different frequencies; including the supplementary admittance matrix of each new energy station in the node admittance matrix of thelinear network part to form a node admittance matrix of the whole power grid; and acquiring the harmonic distribution of the whole power grid under harmonic disturbance according to the node admittance matrix of the whole power grid, and evaluating the harmonic distortion and overvoltage risk of the power grid. The need for harmonic characteristic analysis is satisfied.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
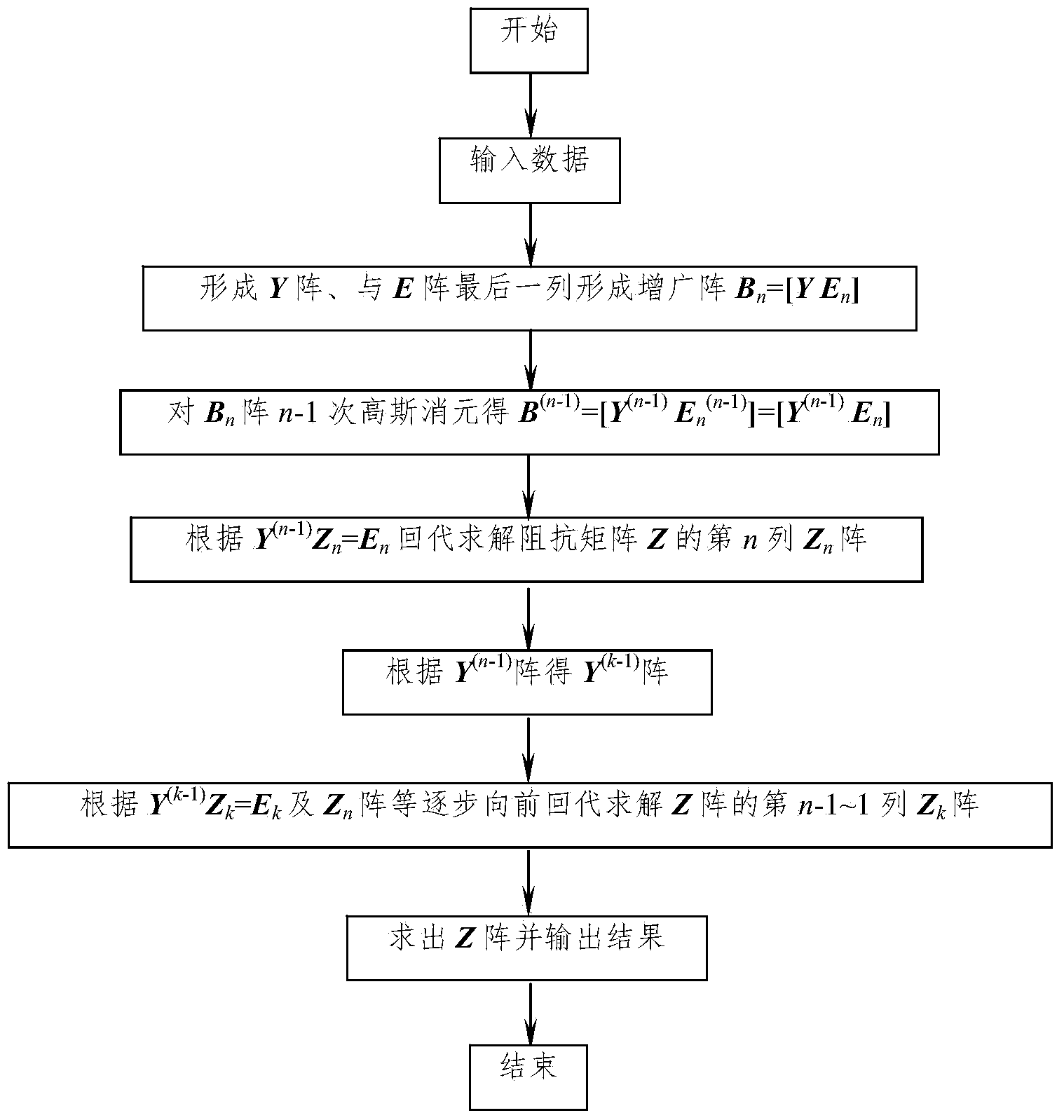
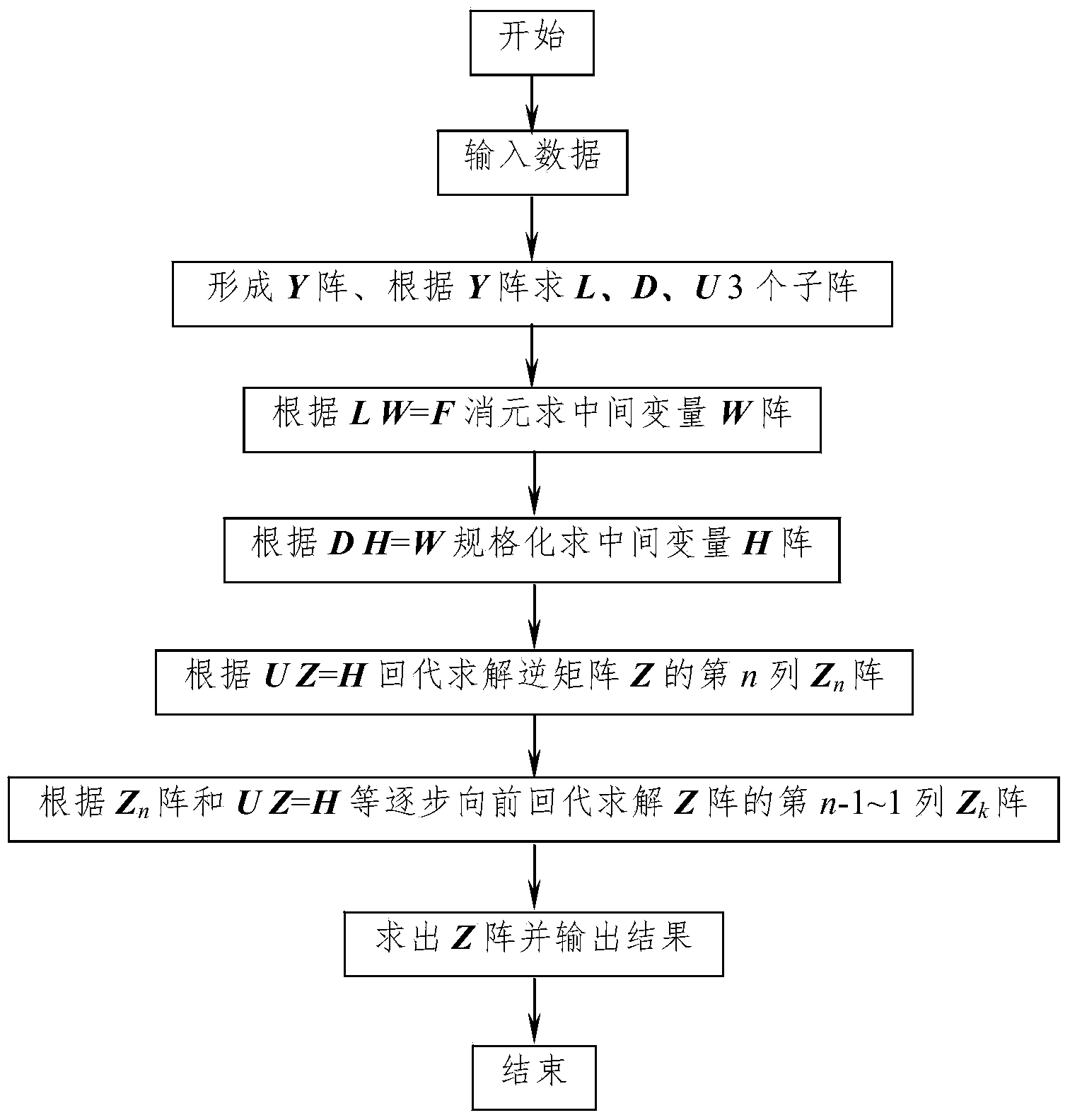
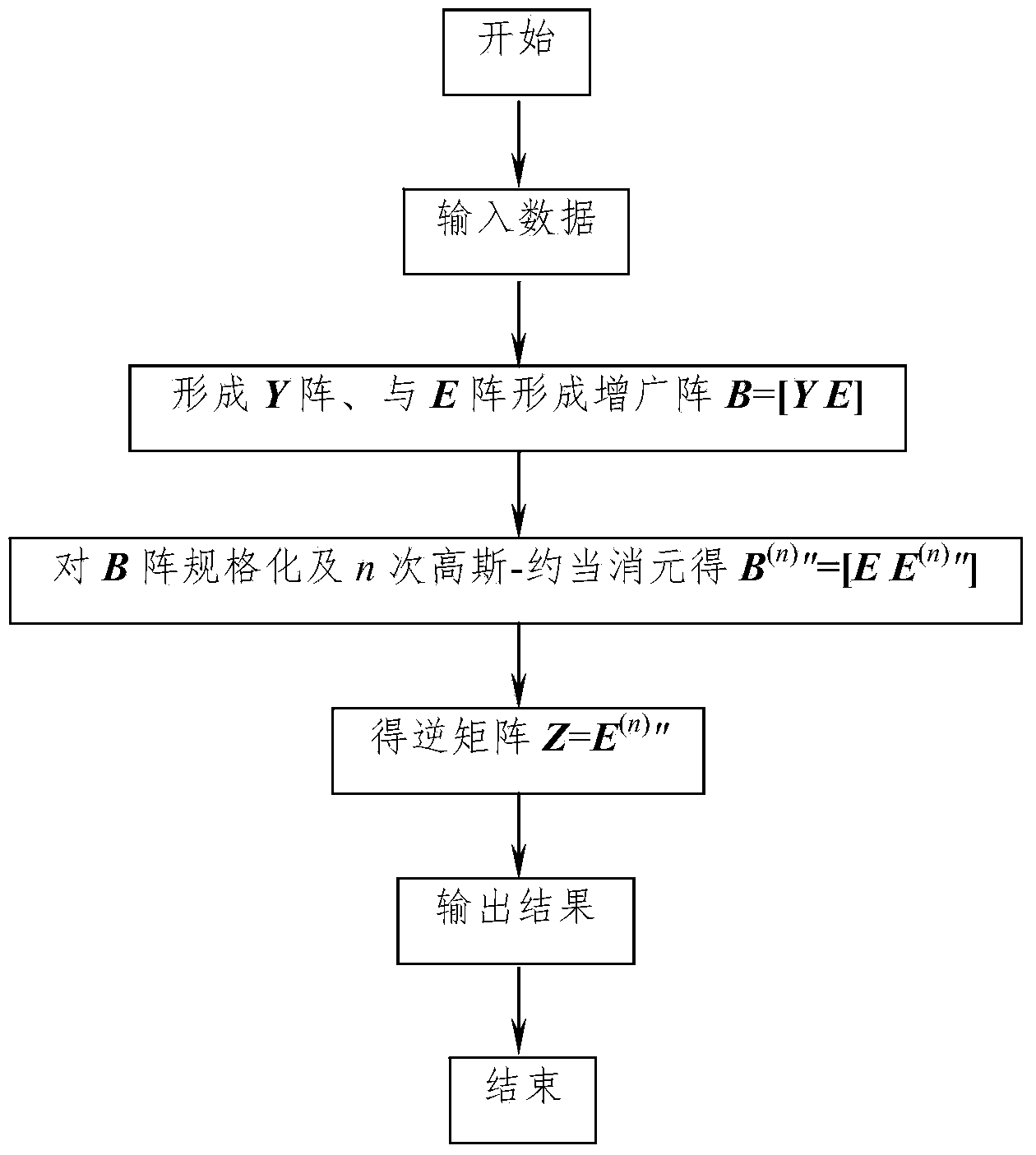
Method for quickly solving nodal impedance matrix of power system
The invention provides a method for quickly solving a nodal impedance matrix of a power system, and relates to the field of analytical computation of the power system. The method mainly comprises the following steps of inputting data of a nodal admittance matrix Y; establishing an augmented matrix B by the nodal admittance matrix Y and an identity matrix E together; normalizing the augmented matrix B and carrying out a Gauss-Jordan elimination method on the augmented matrix B for n times; obtaining an inverse matrix Z. At present, traditional methods for solving the nodal impedance matrix comprise an LDU (Logic Data Unit) triangular decomposition method and a Gauss elimination method, and compared with the two traditional methods, the novel method for quickly solving the nodal impedance matrix by utilizing the Gauss-Jordan elimination method, provided by the invention, has the advantages that the principle is simple and easy to understand, the computation time is reduced, the programming is convenient, and the like; compared with the traditional LDU triangular decomposition method and the Gauss elimination method, by utilizing the method for verifying systems such as an IEEE-57 node, an IEEE-118 node and an IEEE-300 node, the computation speeds can be respectively increased by about 25%-50%.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
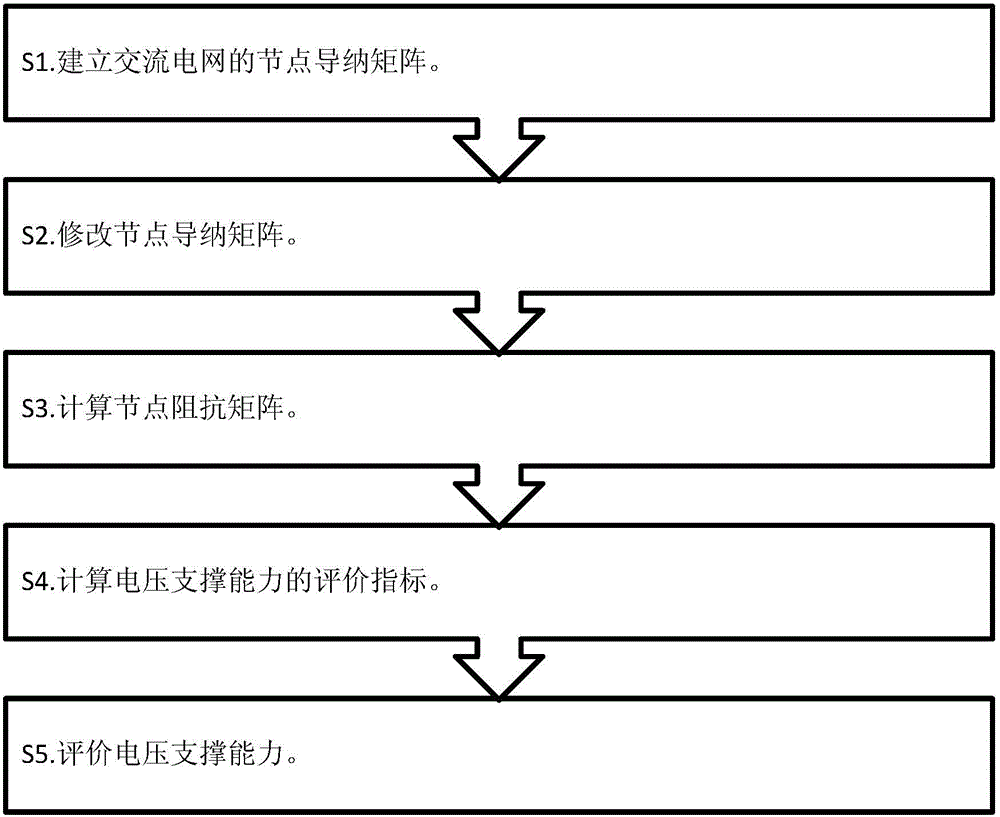
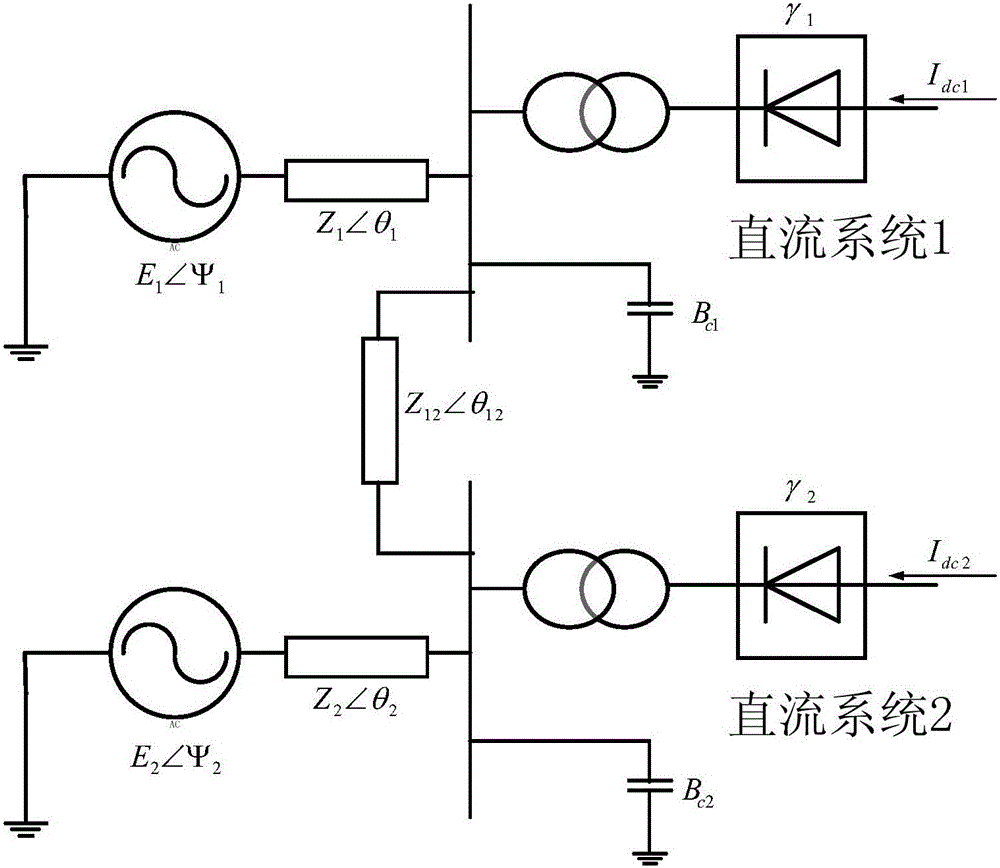
Method for evaluating voltage supporting ability of multi-direct current feed alternating current power grid provided with dynamic reactive power compensation device
ActiveCN104410080ACorrectly reflect the voltage support capabilityLoad forecast in ac networkElectric power transfer ac networkPower compensationPower grid
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the voltage supporting ability of a multi-direct current feed alternating current power grid provided with a dynamic reactive power compensation device. The method includes the following steps that: S1, a node admittance matrix of the alternating current power grid is established; S2, the node admittance matrix of the alternating current power grid is modified, so that a node admittance correction matrix can be obtained; S3, a node impedance matrix which is included into the influence of the dynamic reactive power compensation device is calculated; S4, voltage supporting ability evaluation indexes at direct current transmission system feed nodes to be investigated are calculated according to the node impedance matrix which is included into the influence of the dynamic reactive power compensation device; and S5, the voltage supporting ability at the direct current transmission system nodes to be investigated is evaluated according to the voltage supporting ability evaluation indexes and based on evaluation threshold values. With the method of the invention adopted, the node impedance matrix which is included into the influence of the dynamic reactive power compensation device is calculated, and therefore, the voltage supporting ability of the existing alternating current power grid which is provided with the dynamic reactive power compensation device can be reflected correctly, and decision-making support can be provided for the planning and operation of the power grid.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
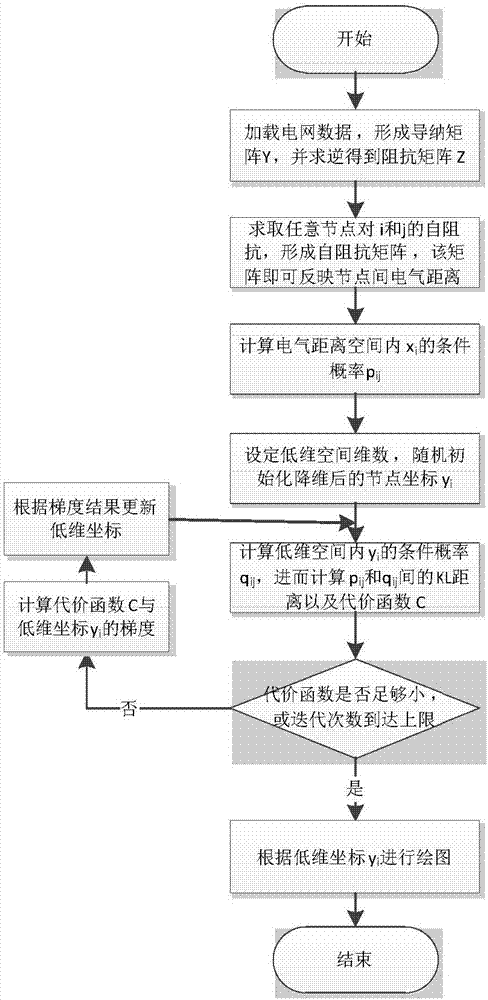
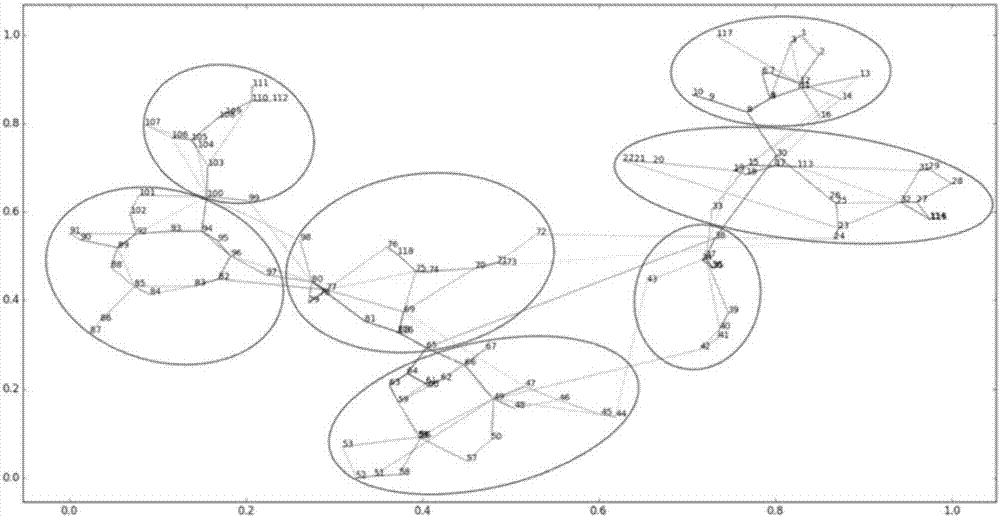
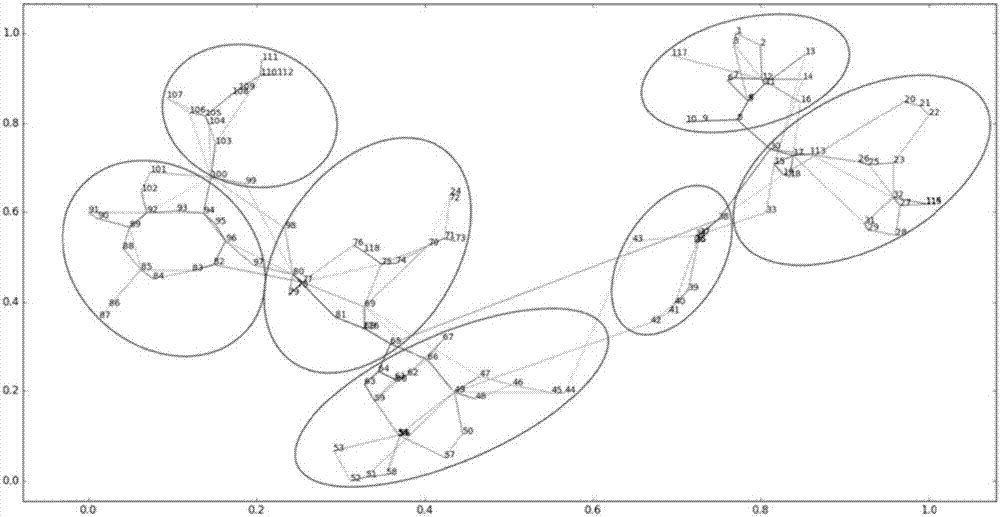
Visualization method and device for electrical distance of power system
The invention provides a visualization method and device for electrical distance of a power system. The method comprises the steps of calculating a self-impedance matrix of a node according to a power grid topology and a running parameter, which are acquired in advance, of the power system by a node admittance matrix inversion method; mapping high-dimensional space data to a low-dimensional space by a t-SNE algorithm according to the self-impedance matrix to calculate the electrical distance; and drawing a pattern relevant to the electrical distance of the power system according to node coordinates obtained by calculation of the low-dimensional space. The device comprises a matrix building unit, a dimension reduction unit and a drawing unit. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, the tightness degree among different equipment can be fully displayed, and an intuitive object can be given to an operator.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Design method of real-time simulation solver of active power distribution network on basis of FPGA
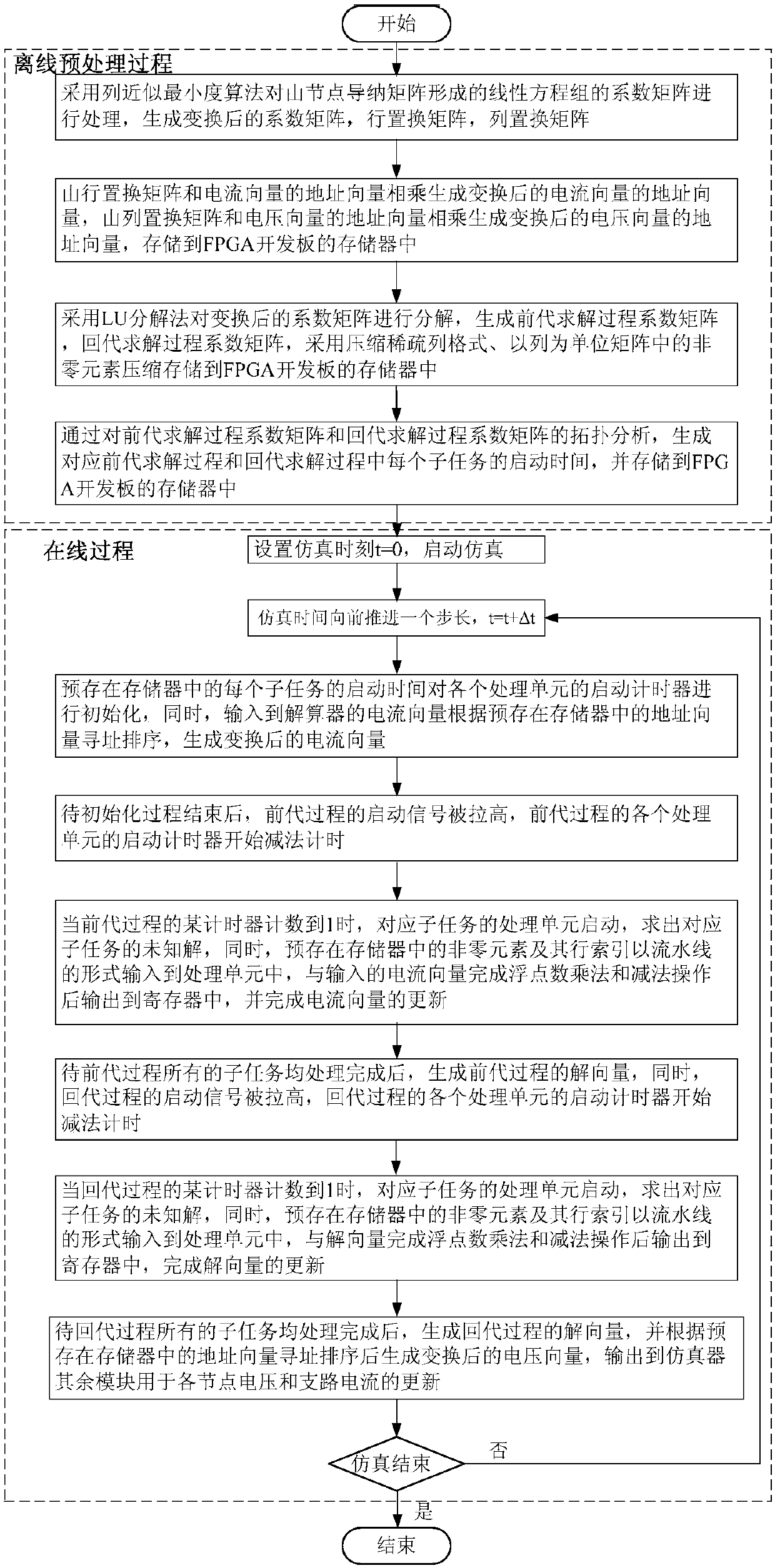
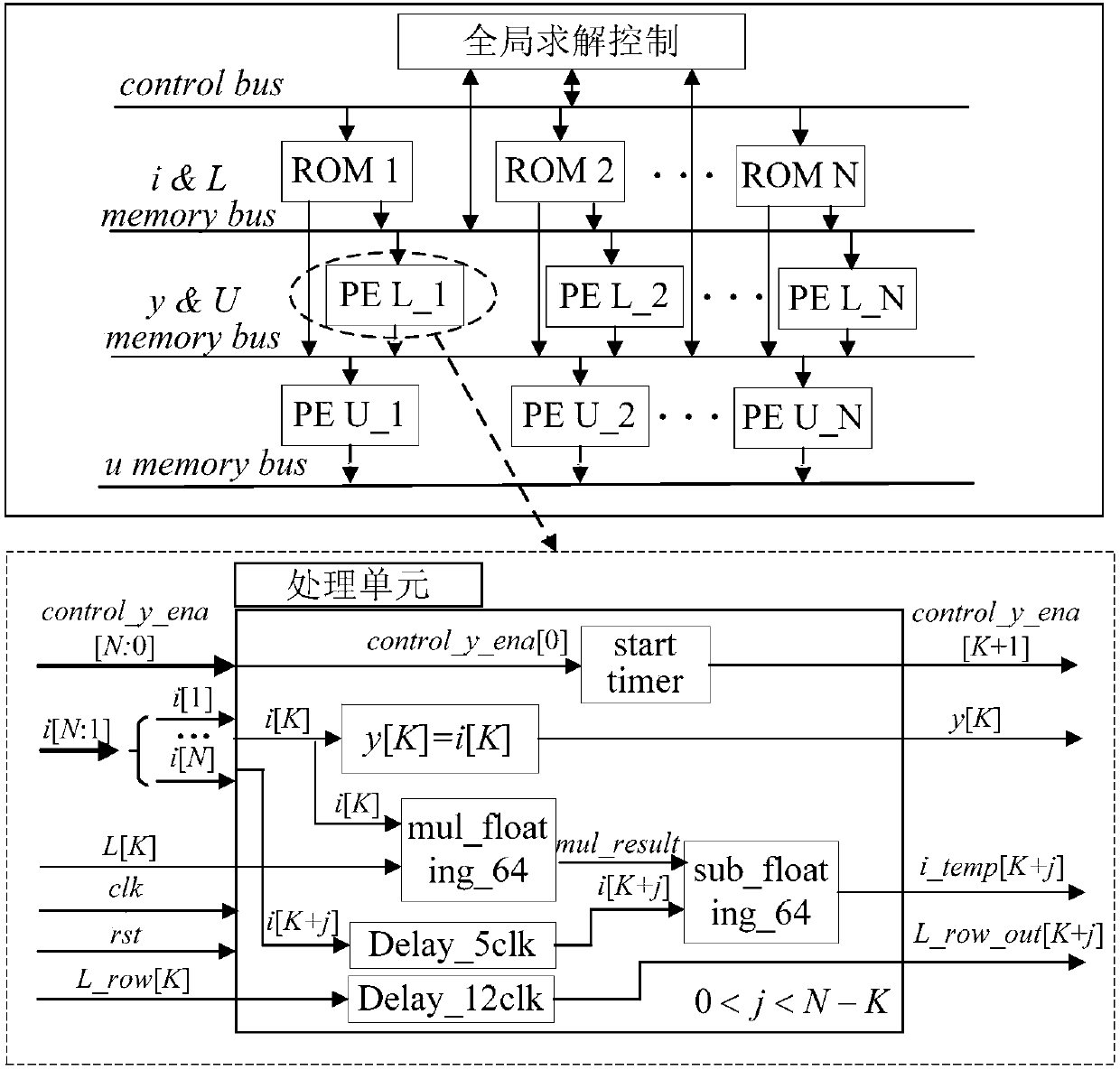
InactiveCN107784158AGuaranteed solution accuracyGuaranteed solution speedDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsStart timeAlgorithm
Disclosed is a design method of a real-time simulation solver of an active power distribution network on basis of an FPGA. The method comprises the steps of offline preprocessing and online solving. During offline preprocessing, a column approximate minimum degree algorithm is adopted for processing a node admittance matrix; the address vectors of current and the address vectors of current voltageare prestored; an LU decomposition method is adopted for decomposing the node admittance matrix; the starting time of each sub-task in the previous substitution process and the back substitution process is prestored. During online solving, the simulation starting time is set; the simulation time is advanced by one step length; information initialization of each sub-task and addressing sorting ofthe current vectors are completed; when solving begins, a starting timer of each processing unit is initialized according to the prestored starting time of the corresponding sub-task; solving in the previous substitution process is completed, and an intermediate solution vector is generated; solving in the back substitution process is completed, and a final solution vector is generated after addressing sorting; whether or not the simulation time reaches the final simulation moment is determined. By means of the method, while the solving precision and speed are ensured, sparse linear equationsare solved accurately and efficiently.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +2
Multi-principal component modal analysis method for electric power network node harmonic characteristic analysis
ActiveCN108268999AHighly affected by harmonicsThe influence of harmonics is largeResourcesNODALDecomposition
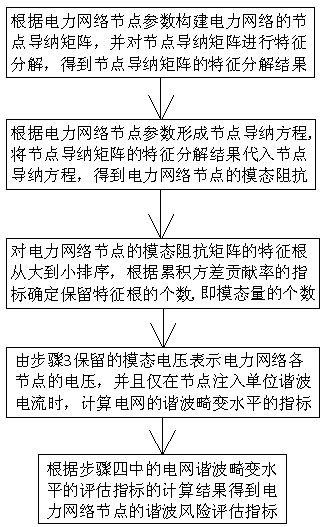
The present invention provides a multi-principal component modal analysis method for electric power network node harmonic characteristic analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, constructing a node admittance matrix of an electric power network, and performing characteristic decomposition of the node admittance matrix; 2, constructing a node admittance equation of the electric power network, and obtaining modal impedance of the nodes of the electric power network; 3, performing ordering of characteristic roots of a modal impedance matrix, and determining the number of reservedcharacteristic roots according to an index of a cumulative variance contribution rate; 4, calculating an index of a harmonic distortion level of the power grid; and 5, calculating harmonic risk evaluation indexes of the nodes of the electric power network. On the basis of a traditional modal analysis method, the index of the cumulative variance contribution rate is employed to determine the number of the reserved characteristic roots to avoid the problem that rich harmonic components injected into the electric power network comprise harmonic waves with unresonance frequencies and a conditionthat single modal quantity takes the lead is destroyed to cause that the analysis precision of the harmonic characteristics of the nodes of the electric power network cannot reach the requirement.
Owner:STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST +2
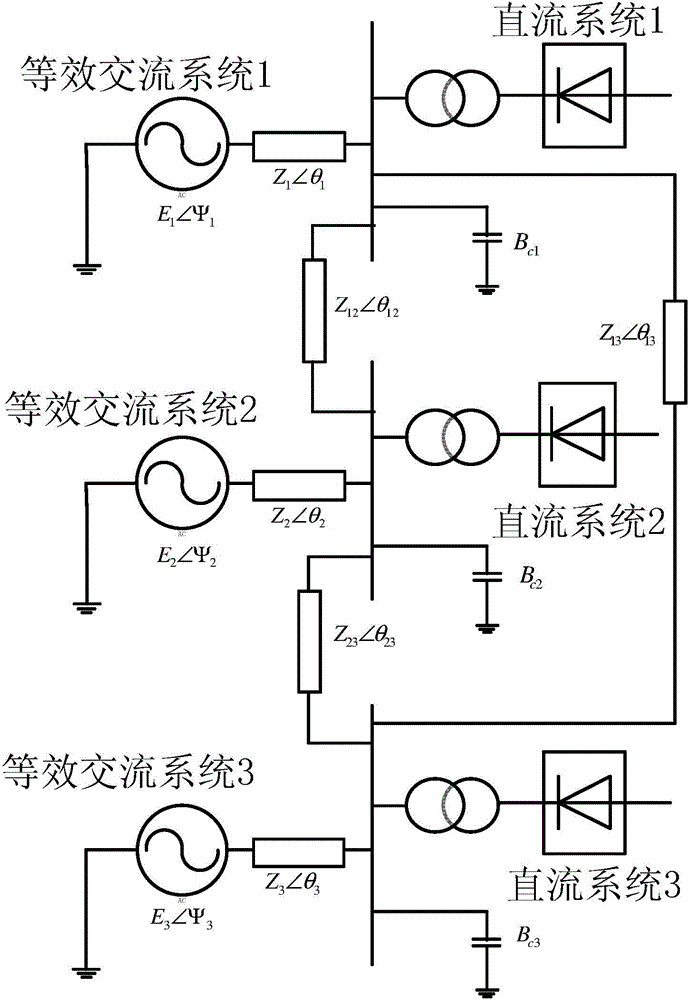
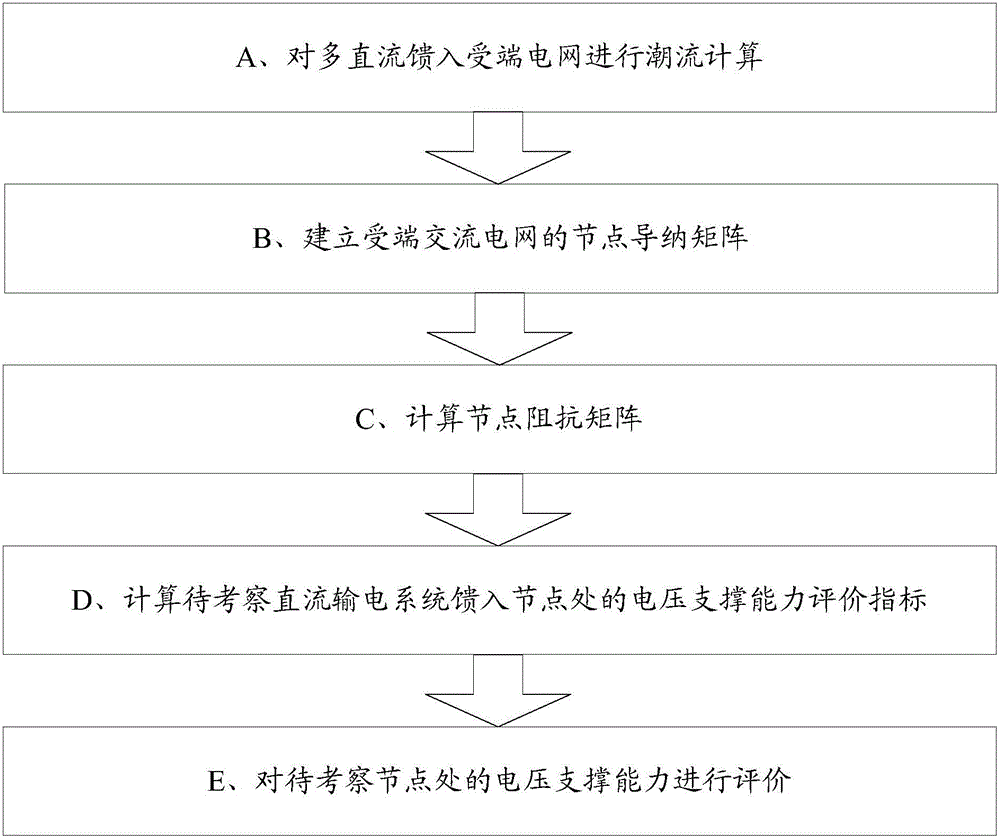
Flow-based voltage supporting ability evaluation method of multi-infeed direct-current receiving-end power grid
InactiveCN105140911ASolve the problem of voltage support ability evaluation methodSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsNODALPower grid
The invention provides a flow-based voltage supporting ability evaluation method of a multi-infeed direct-current receiving-end power grid. The method comprises the following steps: (A) calculating flow of the multi-infeed direct-current receiving-end power grid; (B) constructing a nodal-admittance matrix Y of a receiving-end alternating-current power grid; (C) calculating a nodal-impedance matrix Z, which is an inverse matrix of the nodal-admittance matrix Y; (D) calculating voltage supporting ability evaluation indexes of a to-be-inspected direct-current power transmission system feed node; and (E) evaluating the voltage supporting ability of the to-be-inspected node. According to the flow-based voltage supporting ability evaluation method, the problem of no voltage supporting ability evaluation method suitable for a general multi-infeed direct-current receiving-end power grid at present is solved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Power grid robust state prediction method based on multi-dimensional state matrix sliding matching
ActiveCN109818349AAccurate removalGood predictive robustnessSystems intergating technologiesInformation technology support systemState predictionAlgorithm
The invention provides a power grid robust state prediction method based on multi-dimensional state matrix sliding matching. The power grid robust state prediction method comprises the steps of obtaining a node admittance matrix; acquiring SCADA instrument quantity measurement and PMU device quantity measurement, and constructing a state quantity set based on mixed state estimation; forming a historical state quantity database; predicting the future state of the nodes of the smart power grid by using a multi-dimensional state matrix sliding matching method to obtain a prediction result; adopting an improved power balance equation detection method to detect whether abnormal data exists in a current system or not, if yes, a residual distribution deviation degree detection method is adopted to judge whether the abnormality is caused by abrupt change of quantity measurement, if yes, correction is carried out, bad data are removed, and reliable data support is provided for state predictionin future. The method has better prediction robustness, information in a historical database can be effectively utilized, and the safety and reliability of the intelligent power grid and the capability of resisting malignant data and bad data are improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Power system broken line impedance scanning method and device
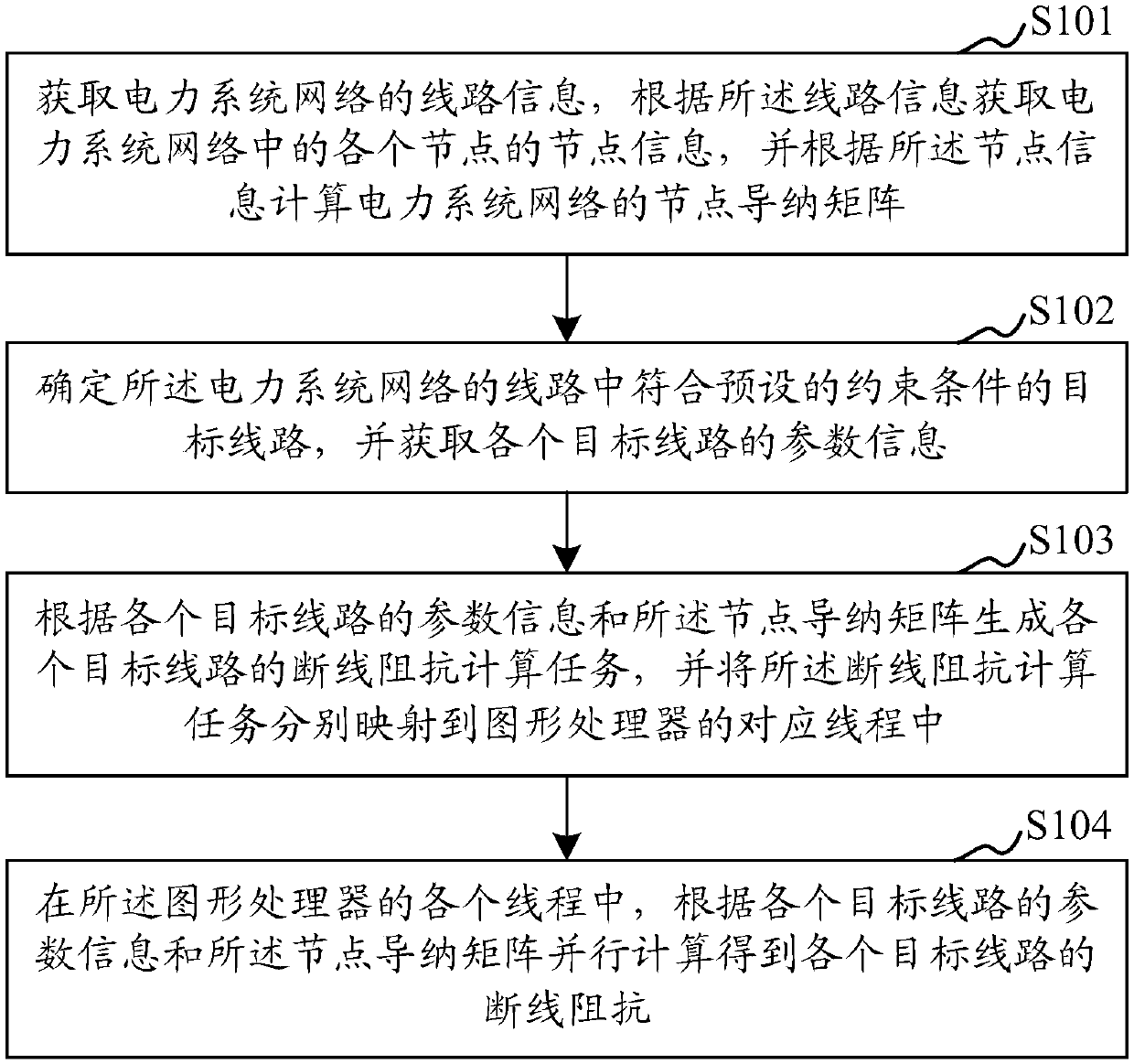
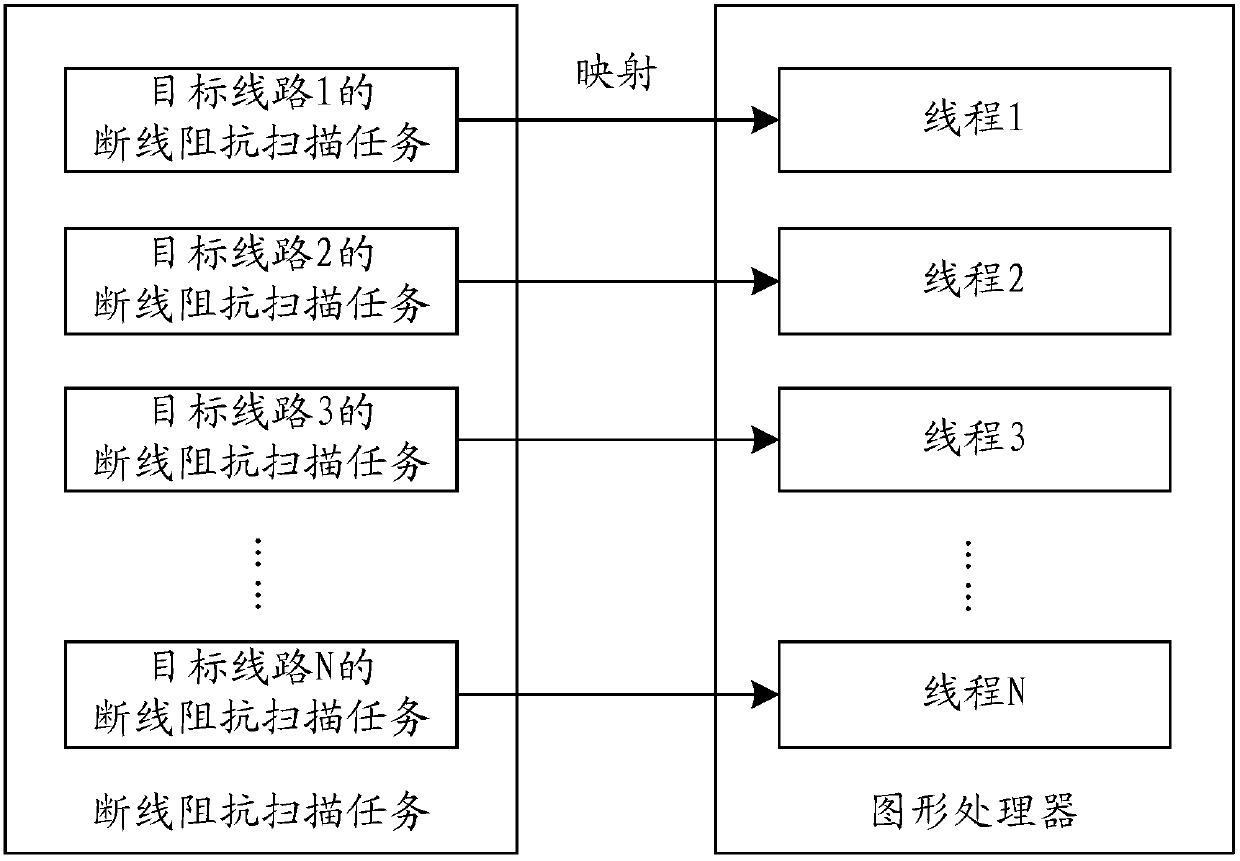
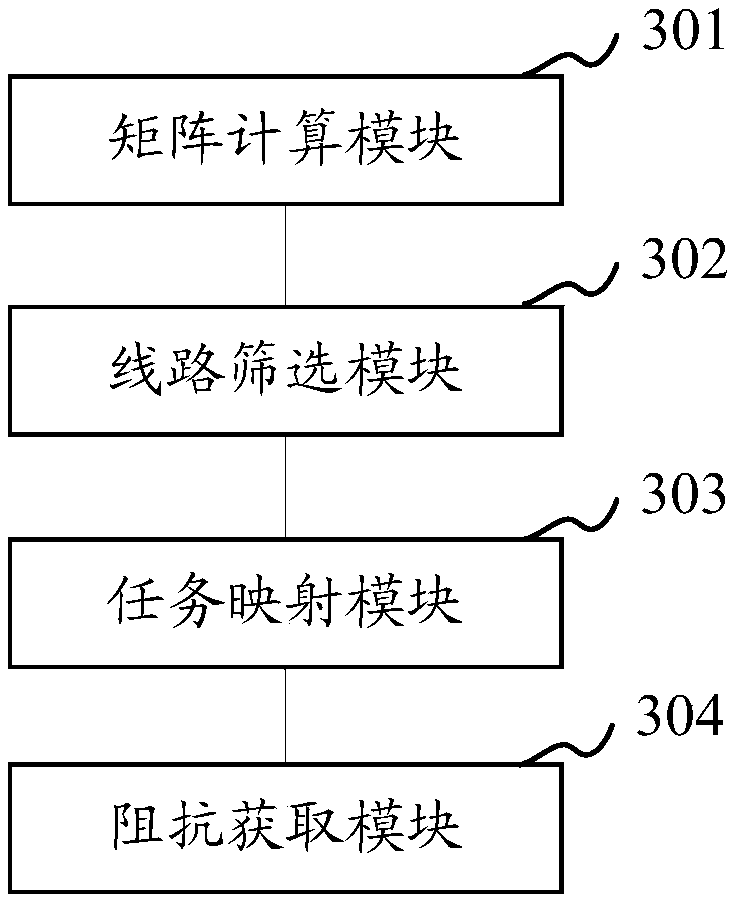
ActiveCN107741528AFast acquisition of disconnection impedanceFast operationResistance/reactance/impedenceGraphicsElectric power system
The invention relates to a power system broken line impedance scanning method and device. The method comprises the following steps that line information of a power system network is obtained, node information of all nodes in the power system network is obtained according to the line information, and a node admittance matrix of the power system network is calculated according to the node information; target lines, meeting preset constraint conditions, in lines of the power system network are determined, and parameter information of all the target lines is obtained; broken line impedance computing tasks of all the target lines are generated according to the parameter information of all the target lines and the node admittance matrix, and the tasks are mapped to corresponding threads of a graphics processor; in all the threads of the graphics processor, broken line impedance of all the target lines is obtained through parallel computing. According to the technical scheme, when broken lineimpedance scanning of the multiple target lines and particularly large power network lines complex in structure is conducted, the operating rate can be significantly increased, and the broken line impedance of the target lines of the power system network is obtained rapidly.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD
Weight function least square state estimation method based on residual normalization
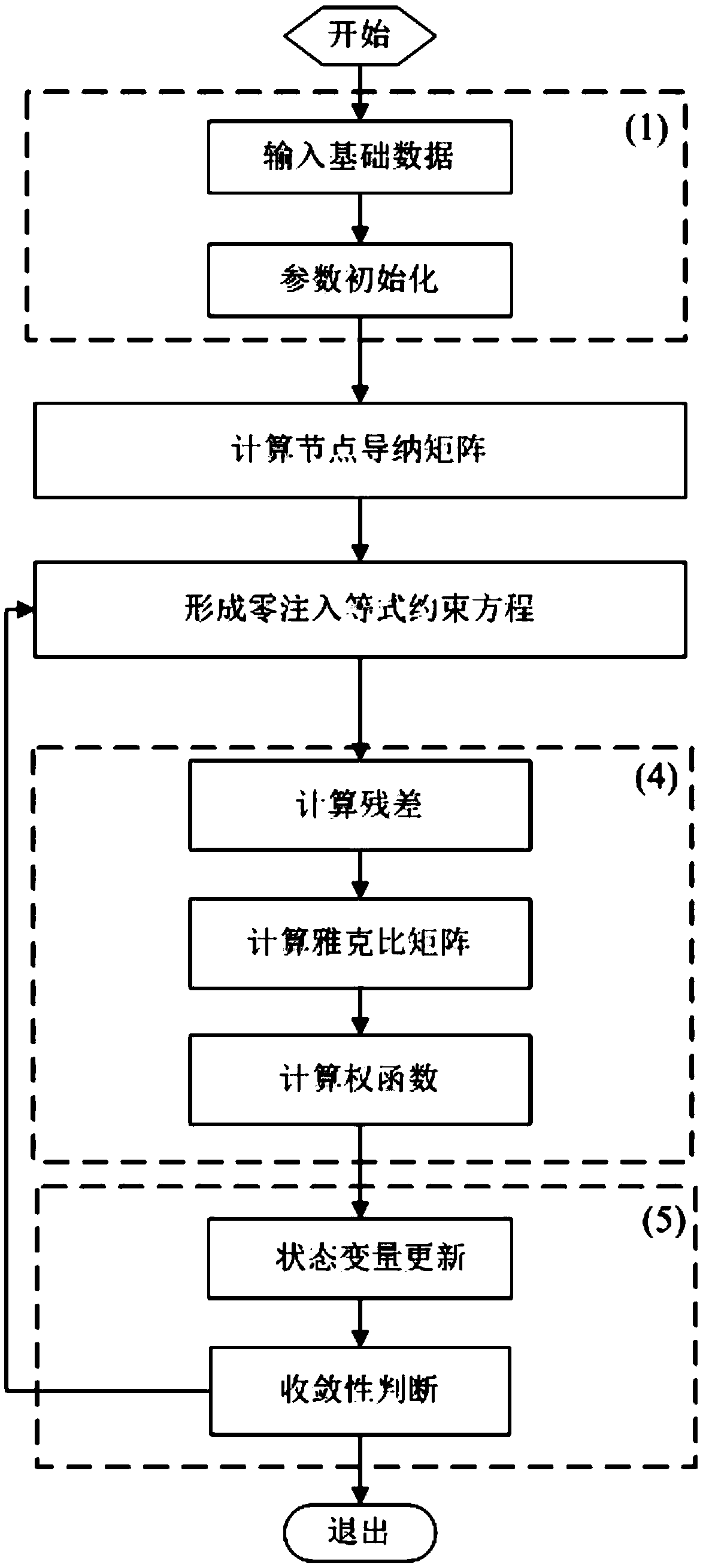
ActiveCN105512502AAutomatic elimination of influenceInhibit bad effectsInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsVoltage amplitudePower system scheduling
The invention discloses a weight function least square state estimation method based on residual normalization, and belongs to the field of electric power system dispatching automation. The method comprises the steps that SCADA data, collected by a data terminal, of any time section, a network structure and parameter information are input firstly through a computer and a program and initialized; a node admittance matrix of a network is calculated, a zero-injection equality constraint equation is formed, and then a corresponding residual, a jacobian matrix and a weight function are calculated by comprehensively considering a voltage amplitude value measuring equation, an injection power measuring equation and a branch circuit power measuring equation and taking the node voltage amplitude value and phase angle as state variables; finally, the state variables are updated, convergence judgment is conducted, and the state estimation of a power grid is achieved. By means of the weight function least square state estimation method based on residual normalization, bad lever measurement can be effectively restrained, high robustness and good convergence are achieved, the computational efficiency is very high, and a good engineering application prospect is achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com