Node admittance matrix eigenvalue analysis method applied to grid-connected-inverter-included parallel resonance situation
A technology of node admittance matrix and admittance matrix, applied in AC network circuits, reducing/preventing power oscillation, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to determine the best observation position and the best excitation position of resonance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0038] Specific implementation mode 1: The eigenvalue analysis method of the node admittance matrix applied to the parallel resonance phenomenon of grid-connected inverters described in this implementation mode includes the following steps:
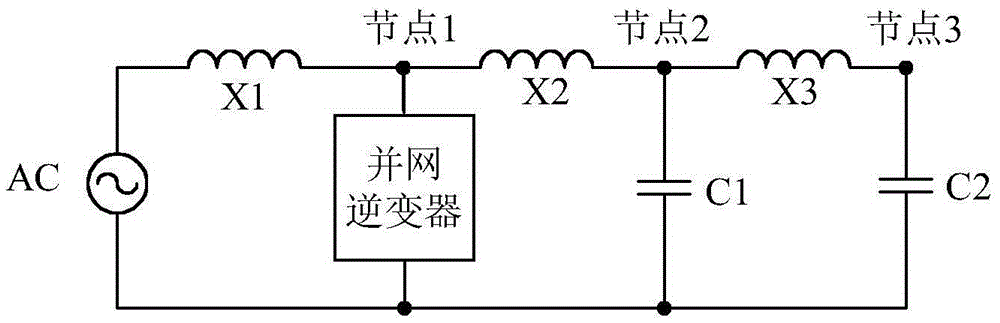
[0039] Step 1. Determine the harmonic characteristics of all components and equipment in the power distribution system including the grid-connected inverter, and judge whether there is a transformer in the power distribution system including the grid-connected inverter. Punitization, use the node method to establish a three-bus network model in the form of per unit value together with grid voltage, grid impedance, resistive, capacitive and inductive load elements, and if the judgment result is negative, use the node method to establish a three-bus network model;
[0040] Step 2. According to the node method, in the three-bus network model, establish the network node admittance matrix Y at the frequency f1 f1 The parametric equation of the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0074] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the eigenvalue analysis method of node admittance matrix applied to the parallel resonance phenomenon of grid-connected inverters described in Embodiment 1 is that in step 2, according to the node method, In the three-bus network model, the network node admittance matrix Y established at frequency f1 f1 The parametric equation for is:
[0075] Y f 1 = G 11 G 12 G 13 G 21 G 22 G ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
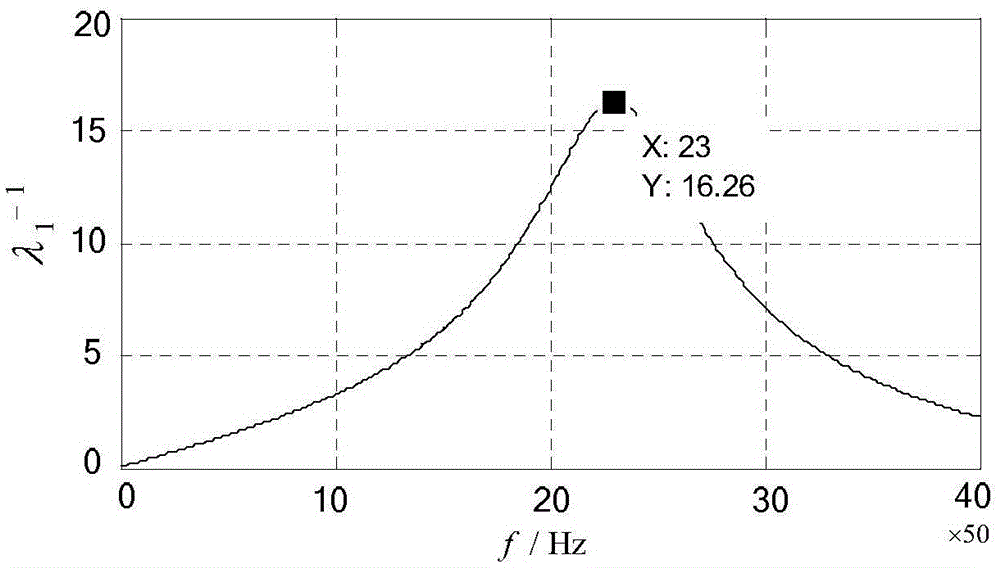
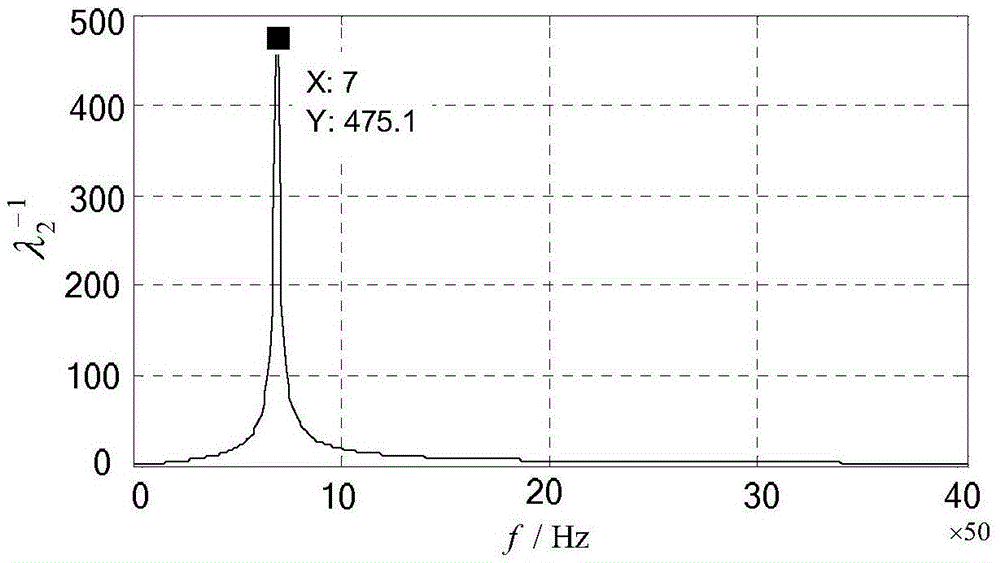
[0077] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the eigenvalue analysis method of the node admittance matrix applied to the parallel resonance phenomenon of grid-connected inverters described in Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in step 2, according to the node method, in the three-bus network model, the network node admittance matrix Y under the frequency f1 is established f1 The parametric equation of the network node admittance matrix Y f1 Solve the eigenvalues to get the eigenvalues λ k,f1 The specific process is:
[0078] At frequency f1, by the formula (Yf1-λ k,f1 E)=0, find the network node admittance matrix Y f1 The eigenvalue of , the eigenvalue λ can be obtained k,f1 ;
[0079] Among them, E represents the third-order identity matrix.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com