Step-by-step database synchronization method with autoincrement identifications
A database and self-incrementing technology, applied in database distribution/replication, electronic digital data processing, structured data retrieval, etc., can solve problems such as table uniqueness constraints, self-incrementing identification consistency problems, multi-source data updates, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example 1
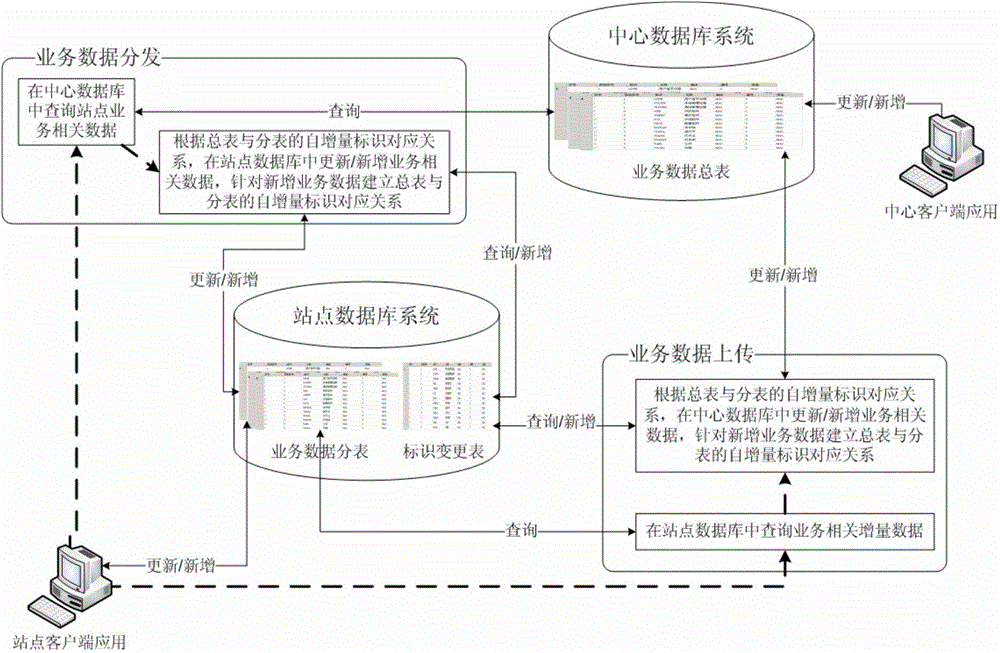
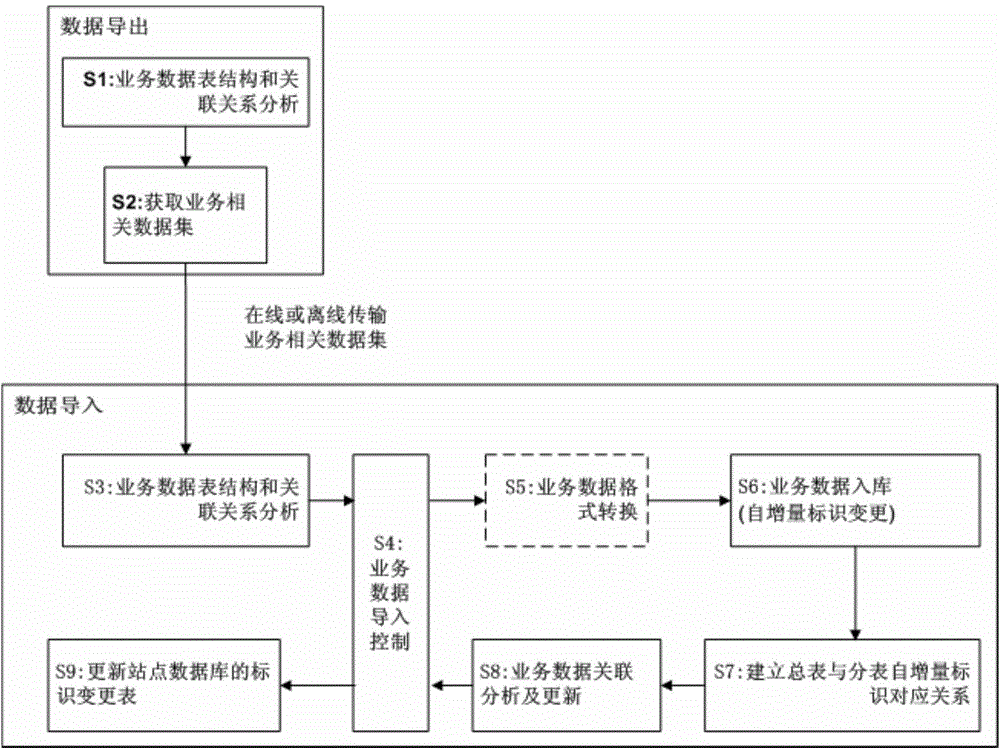
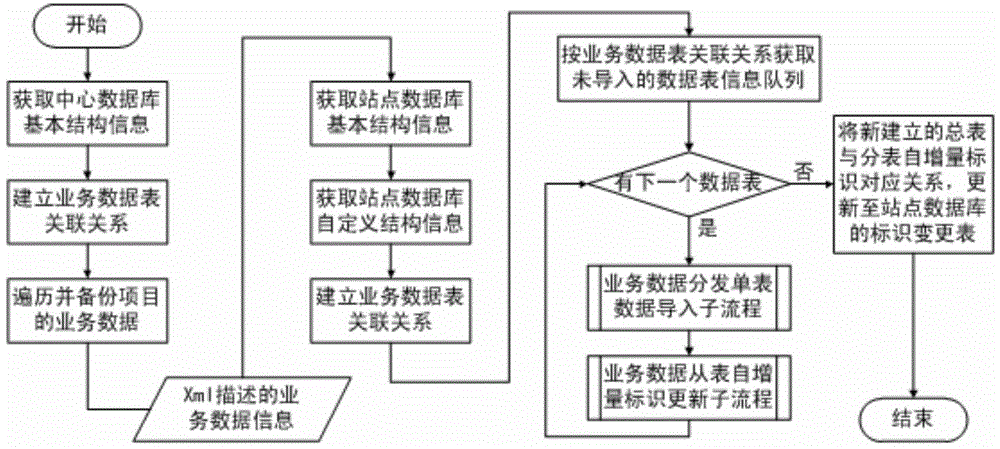
[0067] Taking a distributed database for project management as an example, the business data is centered on the project data table, and each business data table has a direct or multi-table cascaded relationship with the project data table. The business data of the central database and the site database The table structure is the same, and the process of distributing all business data of a project from the central database to the site database is as follows: image 3 As shown, the specific steps are as follows.
[0068] 1) Obtain the basic structure information of the central database. The basic structure information of the database includes information such as database type, table structure, column information of the table, primary key and foreign key of the table.
[0069] 2) According to the basic structural information of the central database, the business data table association relationship is established. The most important content in the association relationship of dat...
specific example 2
[0080] Taking a distributed database for project management as an example, the business data is centered on the project data table, and each business data table has a direct or multi-table cascaded relationship with the project data table. The business data of the central database and the site database The table structure is different. The process of uploading all business data of a project from the central database to the site database is as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the specific steps are as follows.
[0081] 1) Obtain the basic structure information of the site database. The basic structure information of the database includes information such as database type, table structure, column information of the table, primary key and foreign key of the table.
[0082] 2) According to the basic structural information of the site database, the business data table association relationship is established. The most important content in the association relationship of data tables is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com