A method for efficiently degrading azoxystrobin by using Pallidum pallidus
A technology of Bacillus pallidum and azoxystrobin, which is applied in the field of efficient degradation of azoxystrobin, can solve the problem of low efficiency of microbial degradation of azoxystrobin, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of experiments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1 single factor investigation experiment
[0030] Select temperature, pH value, strain inoculum amount, liquid loading amount, and shaking rate as the main factors affecting the degradation rate of azoxystrobin, and change the above-mentioned factors in turn to investigate the effect of the degrading bacteria Ochrobactrum anthropi SH14 on azoxystrobin. The results showed that the three factors of temperature, pH value and strain inoculum had a significant impact on the degradation rate of azoxystrobin.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Response surface optimization experiment
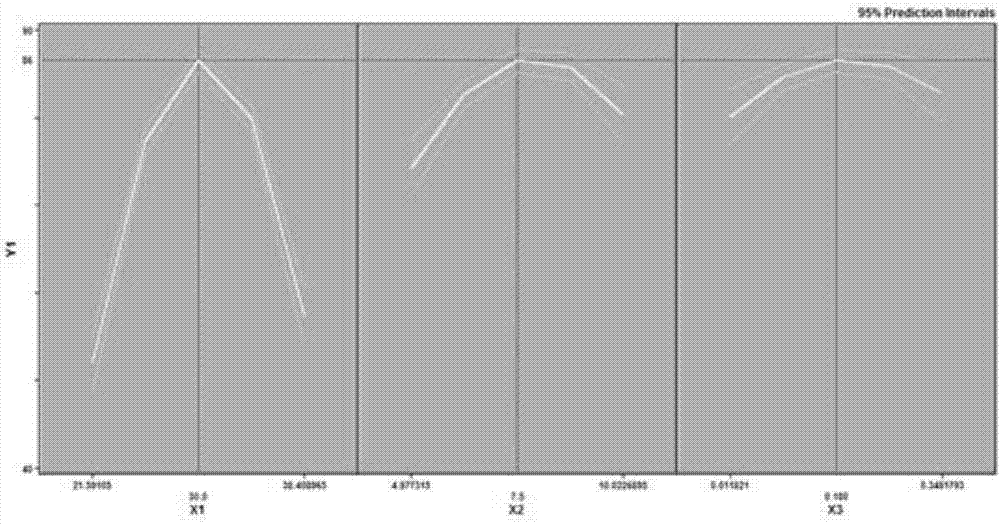
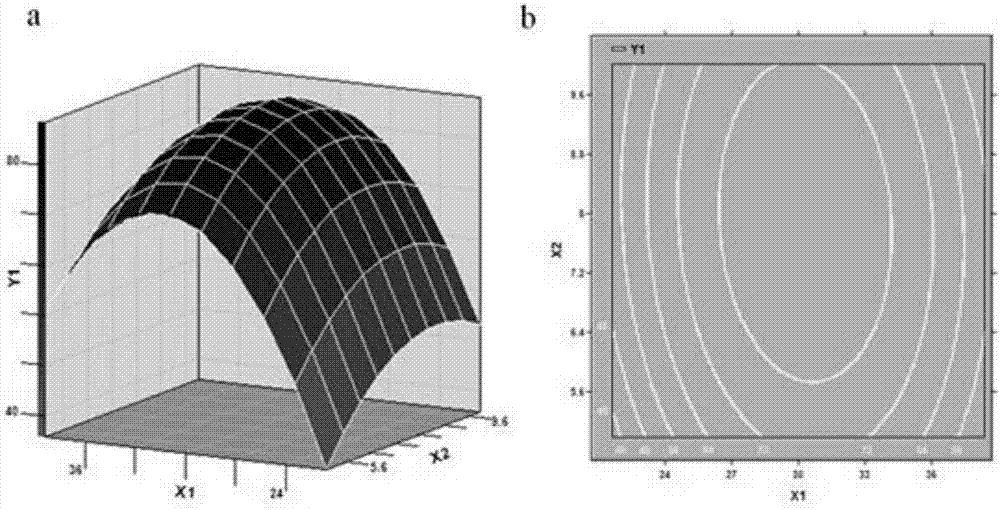
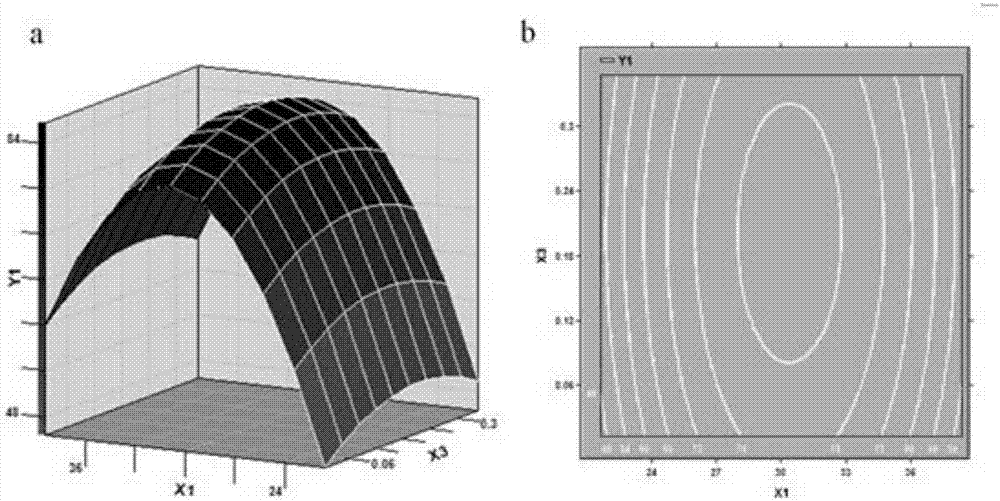
[0032] According to the results of the single factor experiment, the three factors of temperature, pH value and bacterial inoculum were selected for optimal design of the response surface, and the experimental design was carried out according to the principle of Central Composite Rotatable Design (CCRD) by using SAS 9.0 statistical software (Table 1 ), with temperature (X 1 ), pH value (X 2 ) and inoculum amount (X 3 ) as the independent variable, with the degradation rate of azoxystrobin as the response value (Y 1 ), to establish the multiple quadratic regression equation:
[0033] Y 1 =86.49+1.39X 1 +2.05X 2 +1.0X 3 -11.22X 1 2 -1.2X 1 x 2 -0.13X 1 x 3 -3.23X 2 2 -0.53X 2 x 3 -1.78X 3 2
[0034] Table 1 Response surface central composite rotation design (CCRD) experiment
[0035]
[0036] The statistical analysis results are shown in Tables 2-4. The statistical analysis results show that the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com