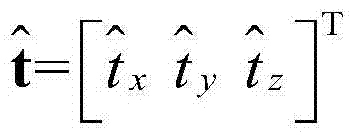Method of correcting positional accuracy of target space for artificial limb
A technology for spatial positioning and targeting, applied in the fields of prosthesis, medical science, manipulators, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable upper limb prosthesis on the target operation, affecting the operation effect of the upper limb prosthesis, affecting the target positioning accuracy, etc., to achieve good personalized service, The effect of low cost and strong practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
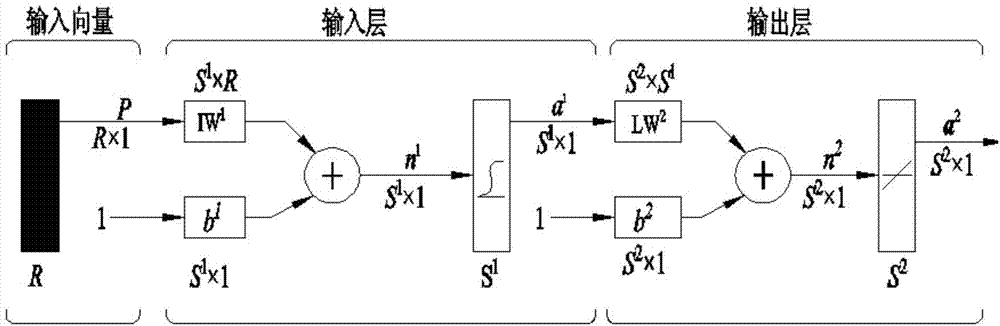
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
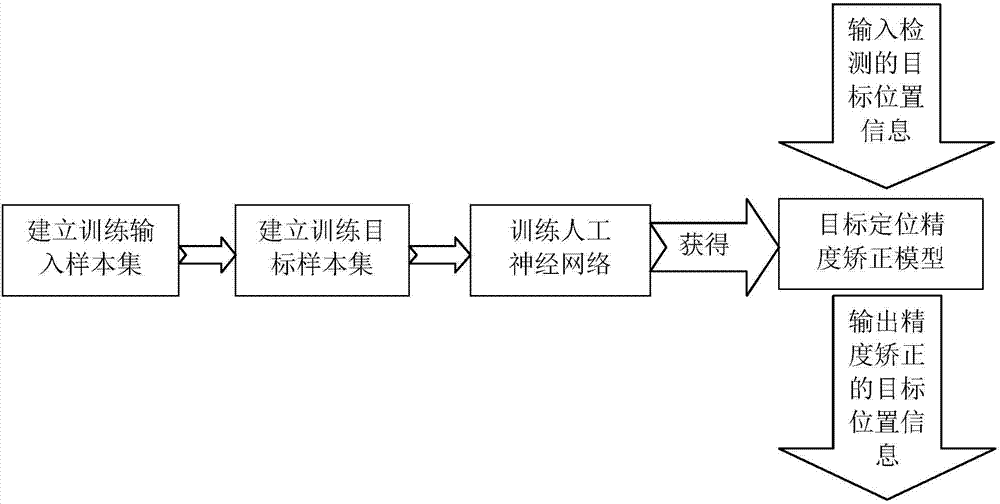
[0022] Accuracy correction method step of the present invention is as follows, see figure 1 :
[0023] 1. Establish training input sample set
[0024] When using the invention patent "Method for Realizing Spatial Positioning of Random Targets with Multi-Freedom Prosthesis" (ZL201010280508.3) to initially position a target, its three-dimensional coordinate value p=[p x p y p z ] T ;
[0025] When the three-dimensional coordinate values of a series of target points are collected and measured in the operating space of the upper limb prosthesis, the above p i (i=1,2...,n) set {P}, mark and save the position and order of the series of target points, and reserve the set {P} as the training input sample set of the artificial neural network;
[0026] 2. Establish training target sample set
[0027] The actual three-dimensional coordinate value of a target is accurately measured manually with the help of a three-dimensional coordinate measuring instrument, and the value is e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com