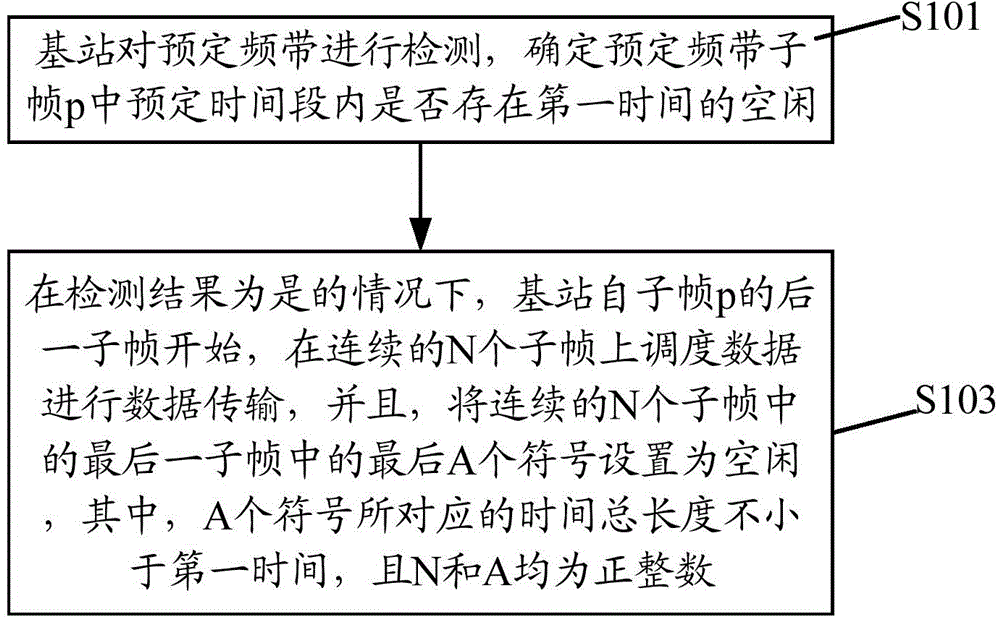
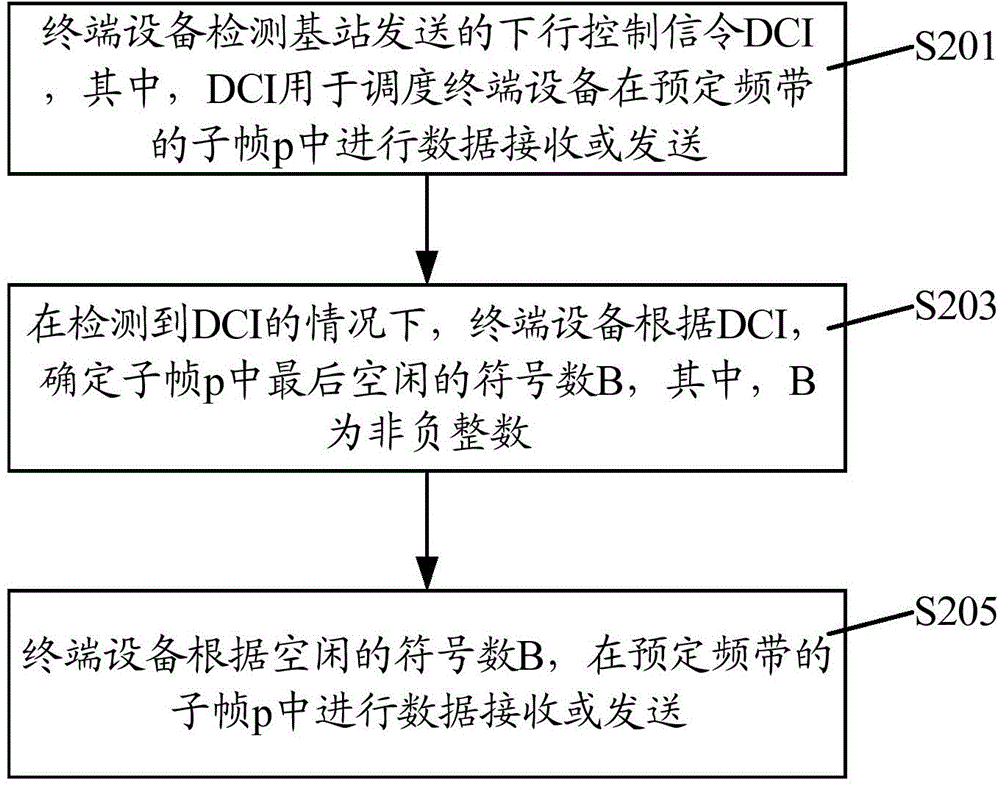
Data transmission method, base station and terminal equipment
A data transmission method and terminal equipment technology, which is applied in the field of data transmission methods, base stations and terminal equipment, and can solve problems such as ambiguity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
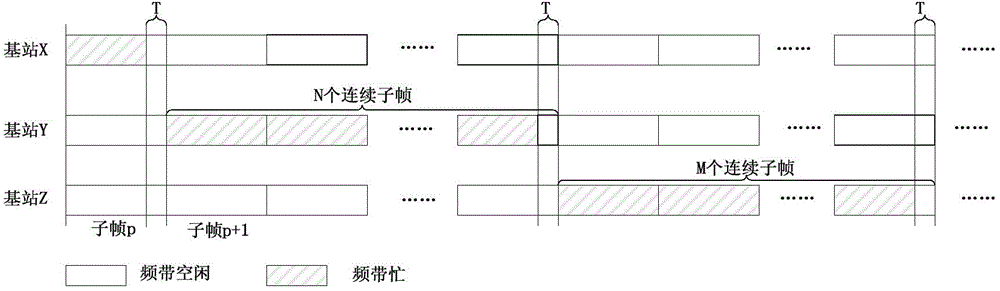
[0109] image 3 is a schematic diagram of the principle of the data transmission method in this embodiment, from image 3 It can be seen from the figure that LTE base station Y detects on the unlicensed frequency band. If it finds that the carrier is idle for at least T microseconds in a specific time period in any subframe p, it means that the carrier is currently idle. At this time, it can be in subframe p+1 Start to occupy consecutive N subframes for data transmission on the carrier.
[0110] In order to achieve fair and efficient use of unlicensed frequency band resources by multiple LTE base stations, base station Y can also idle the frequency band in the last part of the time period when it occupies unlicensed frequency band resources, so that other base stations can perform frequency band detection during this time period , once other base stations detect that the frequency band is free, they can immediately occupy the frequency band for data transmission in the next s...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of the principle of the data transmission method in this embodiment, from Figure 4 It can be seen from , that subframe p includes a first time period, a second time period, and a third time period. Base station Y does not schedule data transmission during the first time period of subframe p, and detects that the frequency band is idle during the second time period of subframe p, and then sends a PSS (Primary sync signal, Primary synchronization signal) / SSS (supplement sync signal, secondary synchronization signal) and measurement RS (Reference signal, reference signal), and continuously schedule N subframes for data transmission starting from subframe p+1, where N subframes can All are downlink subframes, or all are uplink subframes, or some downlink subframes, some uplink subframes, or some downlink subframes, some special subframes, or some downlink subframes, some special subframes, and some uplink subframes . Base station Y is id...
Embodiment 3
[0114] Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of the principle of the data transmission method in this embodiment, from Figure 5 It can be seen from , that subframe p includes a first time period, a second time period, and a third time period. Base station Y does not schedule data transmission in the first time period of subframe p, and detects the frequency band space in the second time period of subframe p, and then sends PSS / SSS and measurement RS in the third time period of subframe p , and starting from subframe p+1, N subframes are continuously scheduled for data transmission, wherein, all of the N subframes can be downlink subframes, or all can be uplink subframes, or part of downlink subframes, part of uplink subframes, or Some downlink subframes, some special subframes, or some downlink subframes, some special subframes, and some uplink subframes. Base station Y is idle for the second time period in subframe p+N. During this time period, all base stations and nodes (LTE,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com