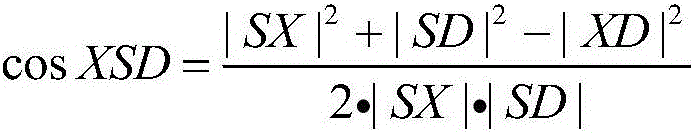Path Planning Algorithm Based on Target Direction Constraint
A path planning and target direction technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control and other directions, can solve the problems of a large number of reserved nodes, low search efficiency, and large memory resources, so as to reduce the search scale, improve search efficiency, reduce The effect of memory resource occupancy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] The technical scheme of the present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the drawings.
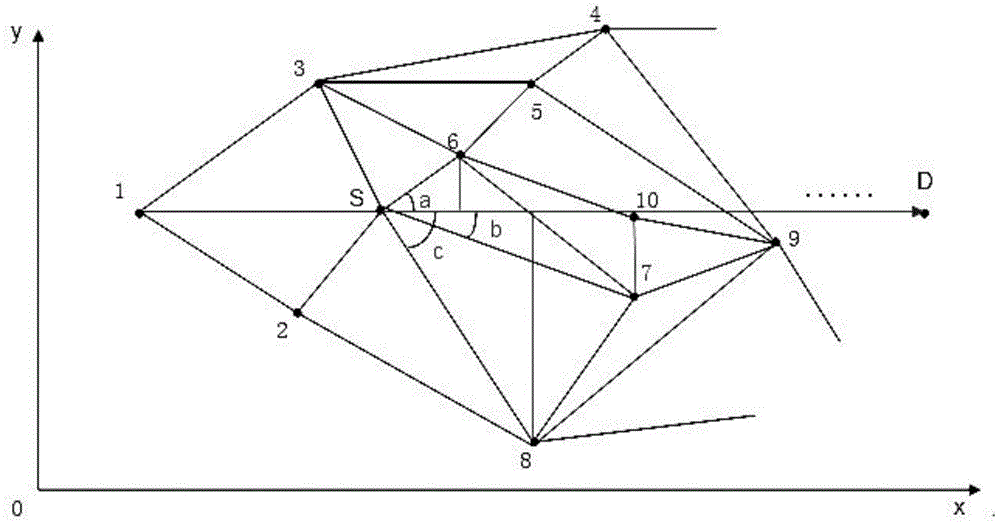
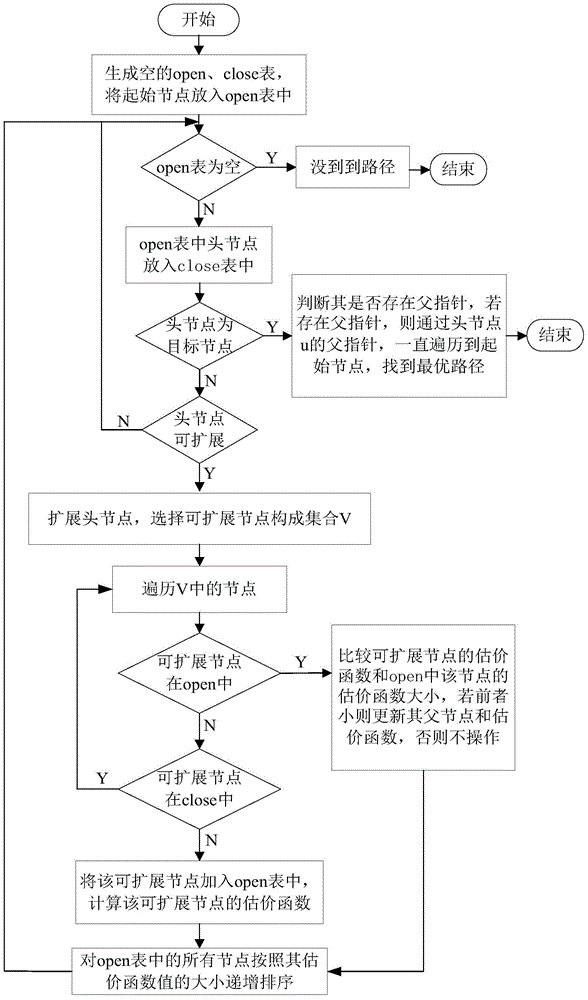
[0039] The path planning algorithm based on the target direction constraint, its algorithm principle is: in the path search process, only keep the current node (the starting node is the first current node) and the target node in the same direction as the expandable nodes, and combine these The scalable node is added to the state space of the scalable node, and each scalable node in the state space is evaluated, and the scalable node with the smallest evaluation function value is obtained as the next current node (the node as the current node is no longer in the state space ), the path search is repeated until the scalable node with the smallest value of the evaluation function in the state space is the target node, and the optimal path is obtained.
[0040] According to geometry, the straight-line distance between two points is the shortest, so when path planning...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com