A fault handling method and device in an operator shared network
A fault handling method and network sharing technology, applied in the field of fault handling methods and devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
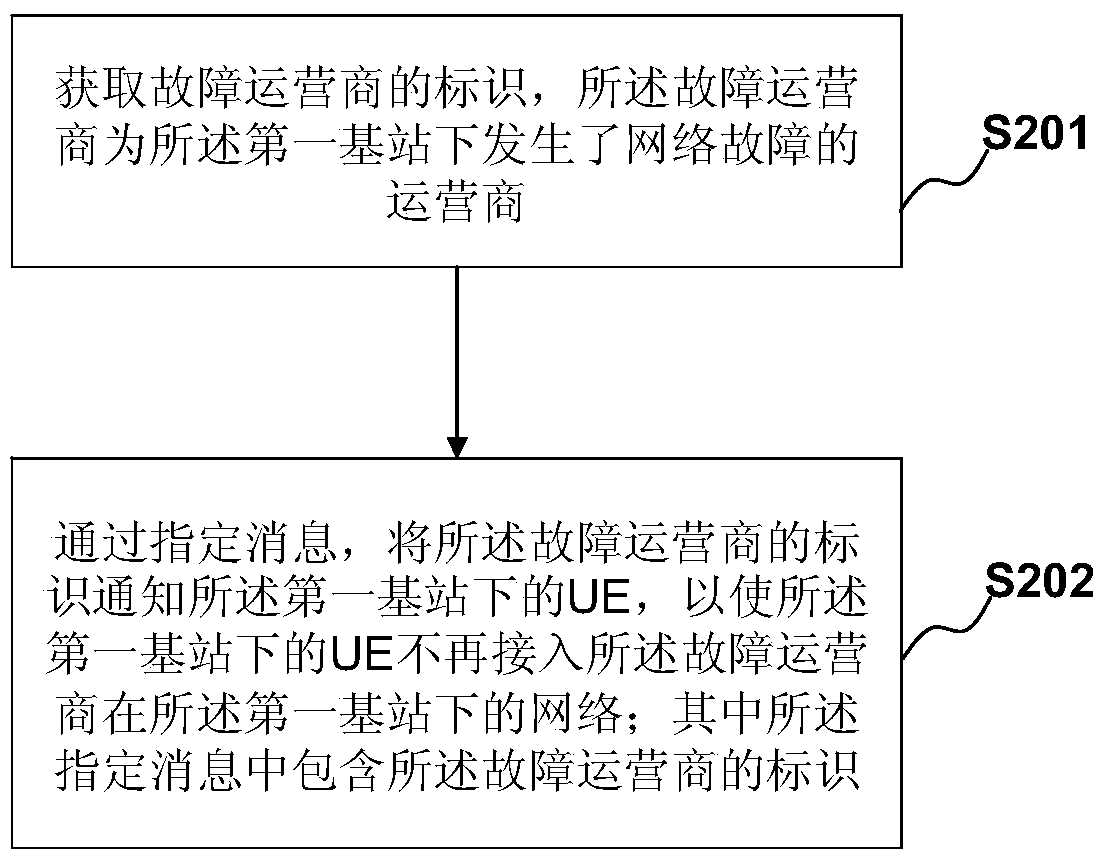
[0076] figure 2 It is an exemplary flow chart of a method in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In order to solve the above problems, this embodiment provides a fault handling method in an operator-shared network, which is used for a first base station, and multiple operators share a network under the first base station, and the method includes:
[0077] S201. Obtain an identifier of a faulty operator, where the faulty operator is an operator under the first base station where a network fault occurs;
[0078] S202. Notify the UE under the first base station of the identity of the faulty operator through a specified message, so that the UE under the first base station no longer accesses the faulty operator under the first base station network; wherein, the designated message includes the identification of the faulty operator.
[0079] In this embodiment, preferably, the designated message may be a SIB message, and the cell barred field of the SIB message includes a list ...
Embodiment 2
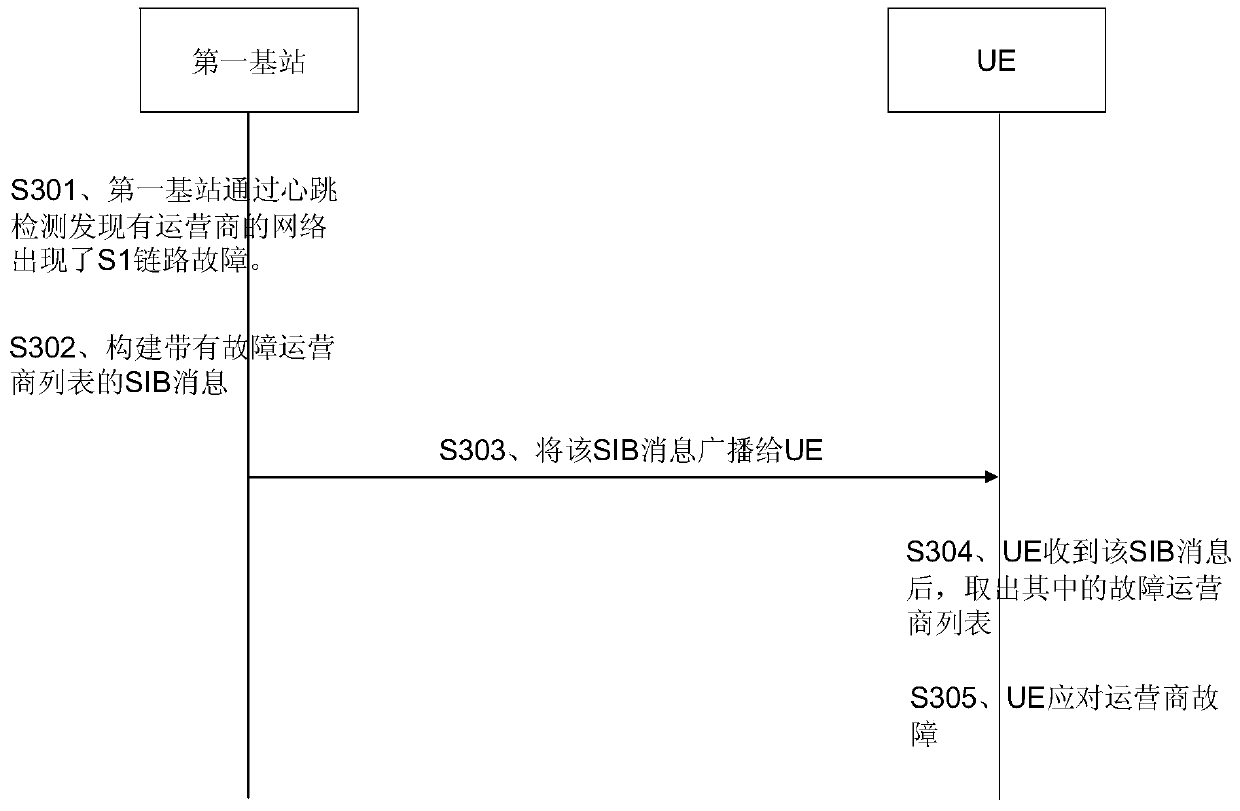
[0089] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of signaling of the method in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. This embodiment is based on the first embodiment and is a further refinement of the first embodiment.
[0090] In the prior art, some fields of the SIB message broadcast by the base station can be seen in Table 1 below, where the cellBarred (cell barred) field is used to indicate whether the current cell is barred from access. If the operator of the cell fails, the UE can no longer access according to the cellBarred field.
[0091] Table 1
[0092]
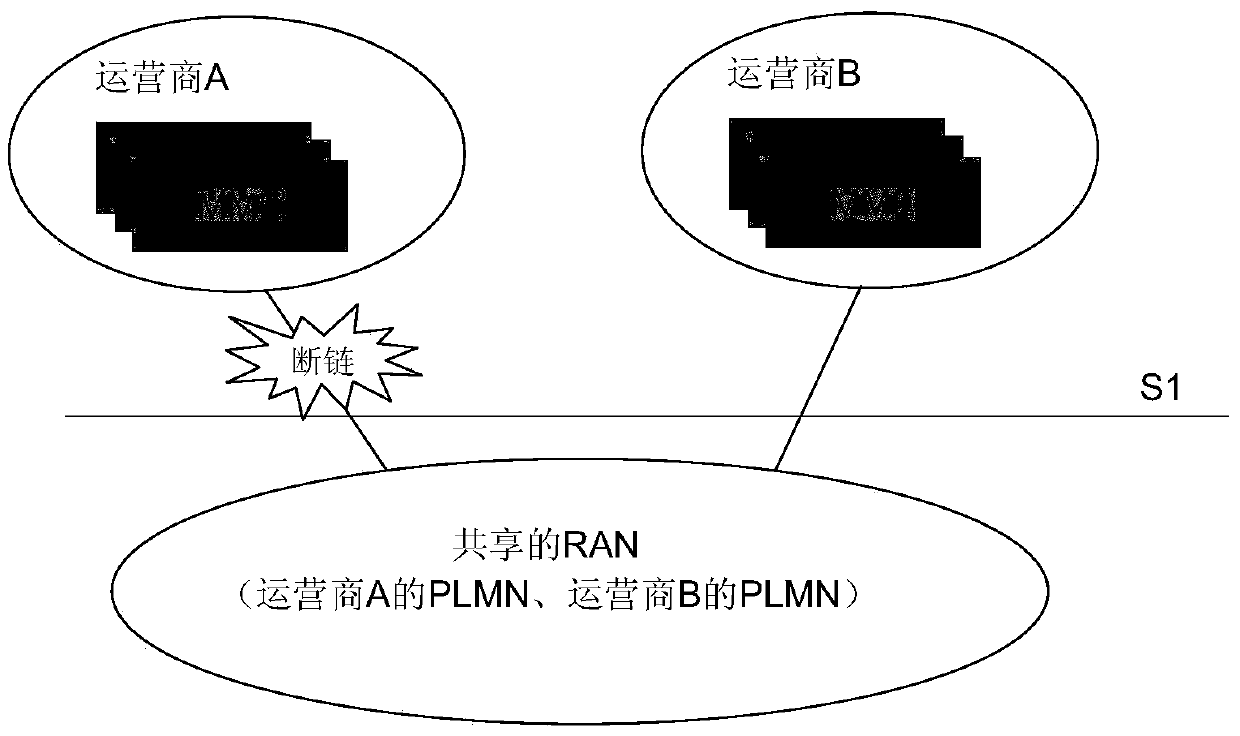
[0093] However, the inventor found in the process of implementing the present invention that the above method is applicable to only one operator under the first base station, because at this time, it can be deduced that the cell cannot be accessed if the operator fails. However, when the first base station When there are multiple operators, this method has limitations, because the failure of one operator does not me...
Embodiment 3
[0108] This embodiment is based on the foregoing embodiments, and is a further expansion and improvement of the foregoing embodiments. In the above embodiment, the first base station can inform the UEs in its cell which operators have link failures through the extended SIB message, thereby avoiding UE access errors and solving the basic problem when failures occur in the shared network of operators. question. In this embodiment, the faulty base station (that is, the first base station) can further notify the adjacent base station (that is, the second base station) of the operator's failure information, so that the adjacent base station can respond accordingly, so that the fault handling mechanism is more complete .
[0109] Specifically, in this embodiment, for the first base station, the method may further include:
[0110] After getting the id of the faulty operator:
[0111] Notifying the identity of the faulty operator to a second base station adjacent to the first base...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com