Method for managing parent frogs in greenhouses
A management method and greenhouse technology, applied in the field of animal breeding, can solve the problems that the production situation has not been improved, cannot promote the boom of frog breeding, and the history of artificial breeding of frogs is not long. economic effect
Active Publication Date: 2015-09-23
蒙有恳
View PDF6 Cites 8 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0021] During the development of frog farming, a variety of farming methods have emerged, some are farming frogs in vegetable fields, some are raising frogs alone in ponds, some are raising frogs in paddy fields, and some are farming frogs in fish forests. , The development prospect of the frog breeding industry is very promising, but under the current situation, there are few researches on frog breeding skills, the history of artificial breeding of frogs is not long, the situation that scientific research lags behind production ha
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
 Login to View More
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
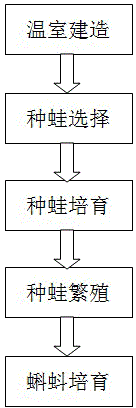
The invention provides a method for managing parent frogs in greenhouses. The method includes constructing culture ponds in selected leeward and sunny places with convenience in drainage and irrigation so as to construct the greenhouse; selecting physically large and strong young frogs with high growth speeds from young frogs hatched in a current year so as to select the parent frogs; breeding the parent frogs, to be more specific, starting breeding the parent frogs from the autumn, and feeding feed to the parent frogs twice on a daily basis; enabling the parent frogs to naturally reproduce tadpoles; feeding the tadpoles by the aid of artificial matched feed so as to breed the tadpoles in periods when the tadpoles are hatched and then grow into young frogs. Sufficient proteins, trace elements and vitamins in the feed for the parent frogs need to be guaranteed. The method has the advantages that every link in frog breeding procedures is managed, accordingly, the bred frogs are high in survival rate, excellent economic benefits can be generated, and income can be increased for frog farmers.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention relates to the technical field of animal breeding, in particular to a management method for growing frogs in a greenhouse. Background technique [0002] Frogs belong to amphibians belonging to the phylum Chordate, Amphibians, Anura, and Ranaidae. Adults have no tail, eggs are laid in water, fertilized in vitro, hatched into tadpoles, breathe with gills, and after mutation, adults mainly breathe with lungs , and use the skin to breathe. [0003] Most frogs reproduce through in vitro fertilization, and the fertilized eggs hatch into tadpoles outside the mother's body. Only 10 to 12 species of frogs in the world have evolved to internal fertilization, and some of them will expel fertilized eggs from the body to hatch into tadpoles. Frogs have always been considered oviparous, but scientists have discovered that a frog that lives in the rainforest of Sulawesi, Indonesia, can lay tadpoles. This frog is the only frog that can "tadpole" among...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): A01K67/02A23K1/18A23K1/04A23K1/10A23K1/14A23K1/175
CPCA01K67/02Y02A40/818Y02P60/87
Inventor 蒙有恳
Owner 蒙有恳
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com