Cross Model Datum Access With Semantic Preservation For Universal Database
A technology for data and data storage, applied in database models, relational databases, object-oriented databases, etc., can solve problems such as missing data, inconsistencies between two databases, and data problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
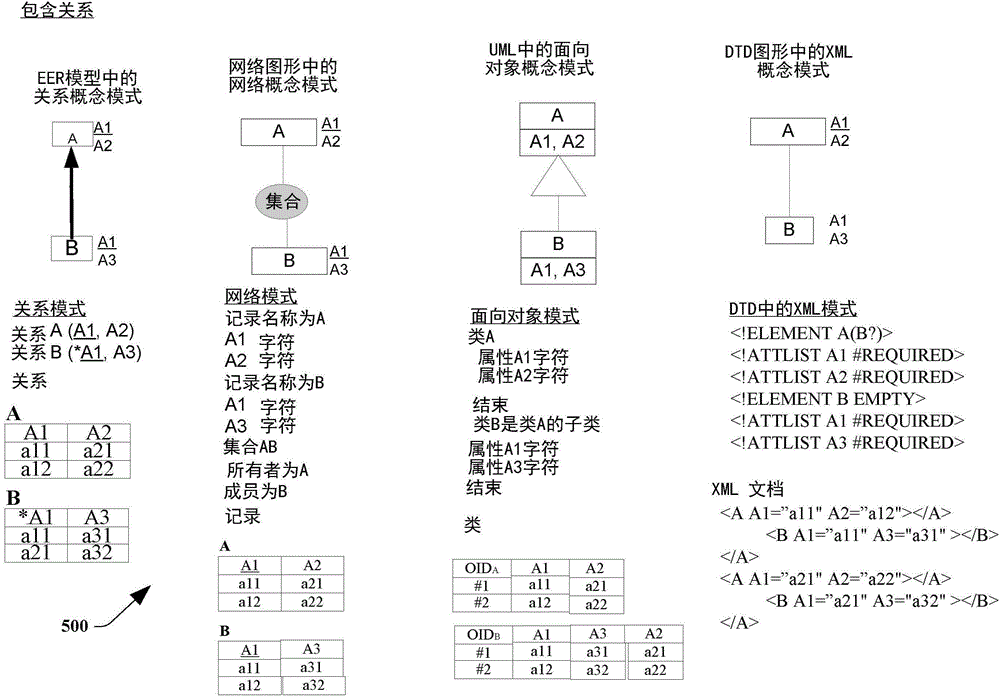
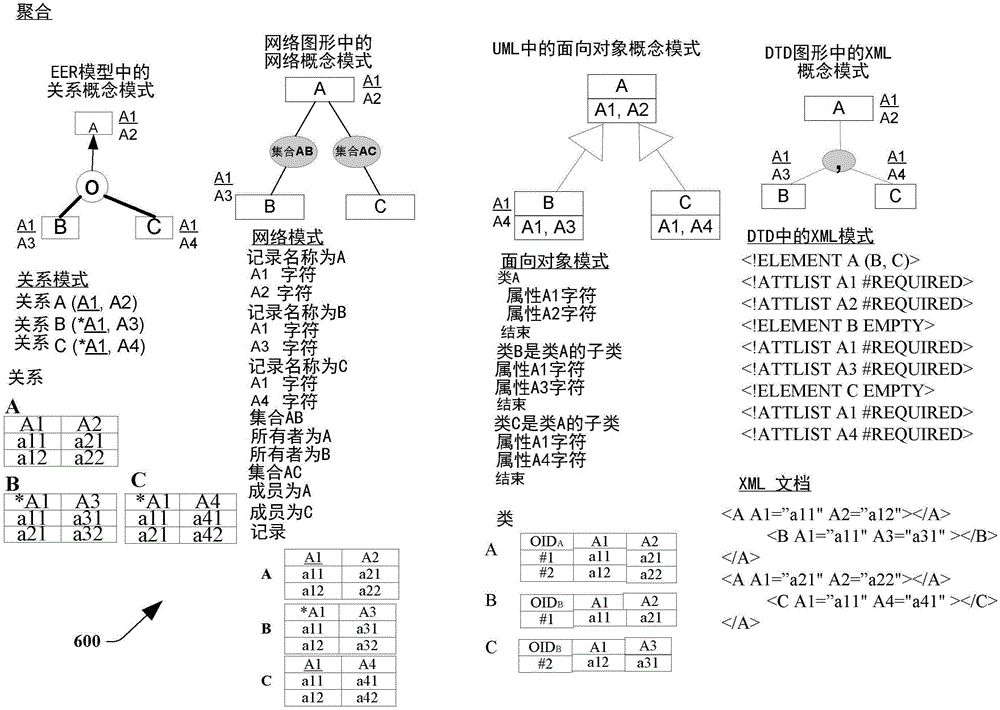
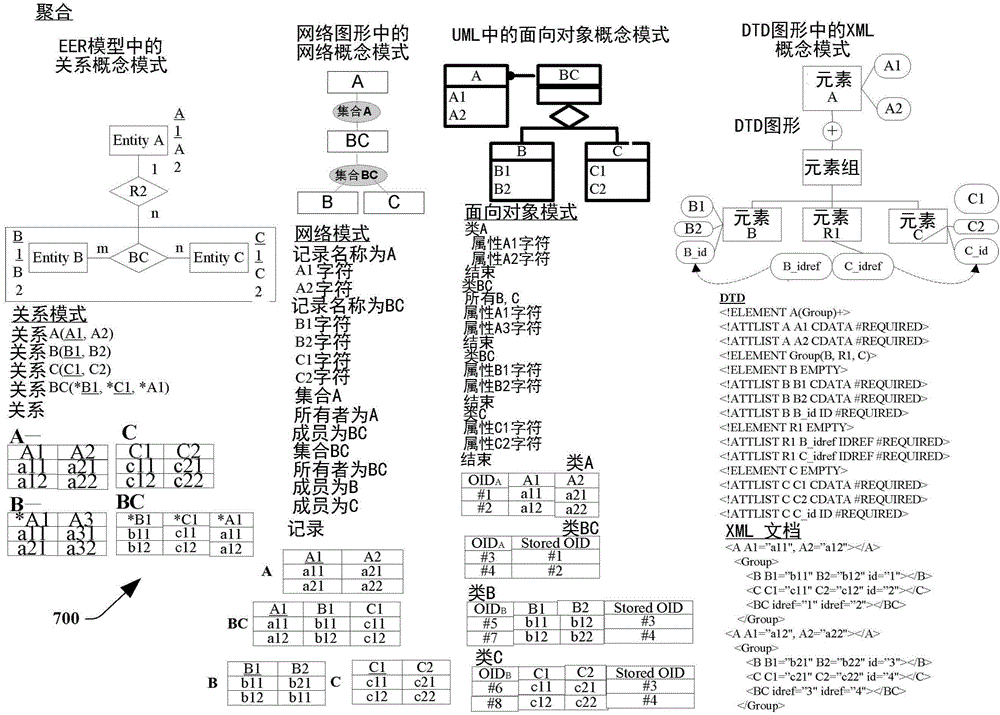
[0031] The disclosed subject matter provides cross-model data access with semantic preservation. In one approach, a traditional database can be associated with multiple database models (eg, database silos) that are often incompatible. Data stored in a database under a particular database model may often not be accessible or interoperable with data stored under another database model. Thus, a database management system (DBMS) associated with one database silo (e.g., data stored under a first database model) may be associated with another database silo (e.g., data stored under a second database model) It is not interoperable with another database management system (DBMS) associated with it. These approaches to conventional database environments, systems, and techniques can limit the exchange of information stored in databases. This constrains users of database management systems within legacy database silos. Sharing data between different database silos can be associated with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com