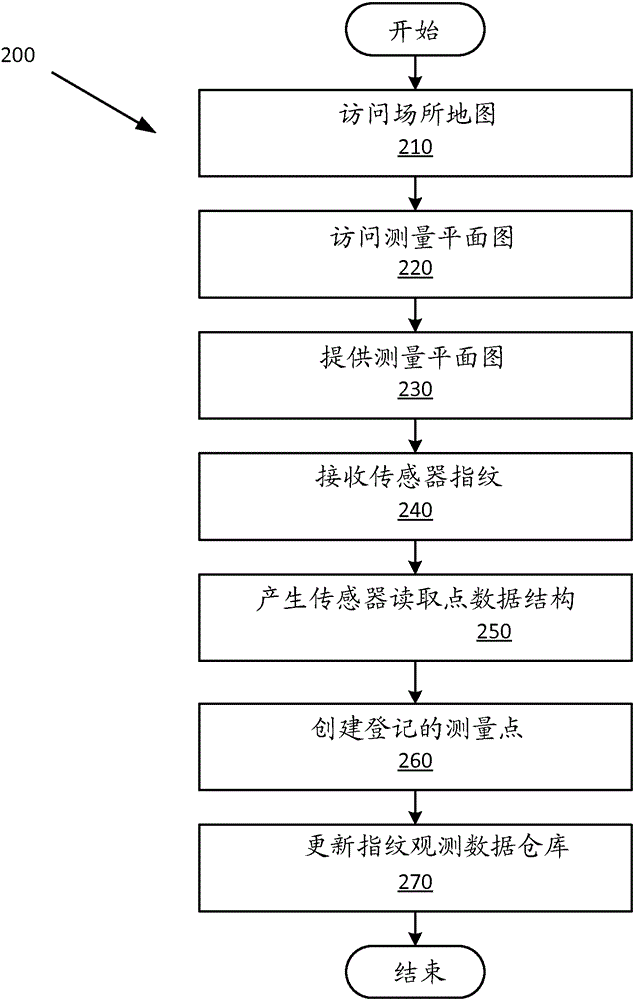
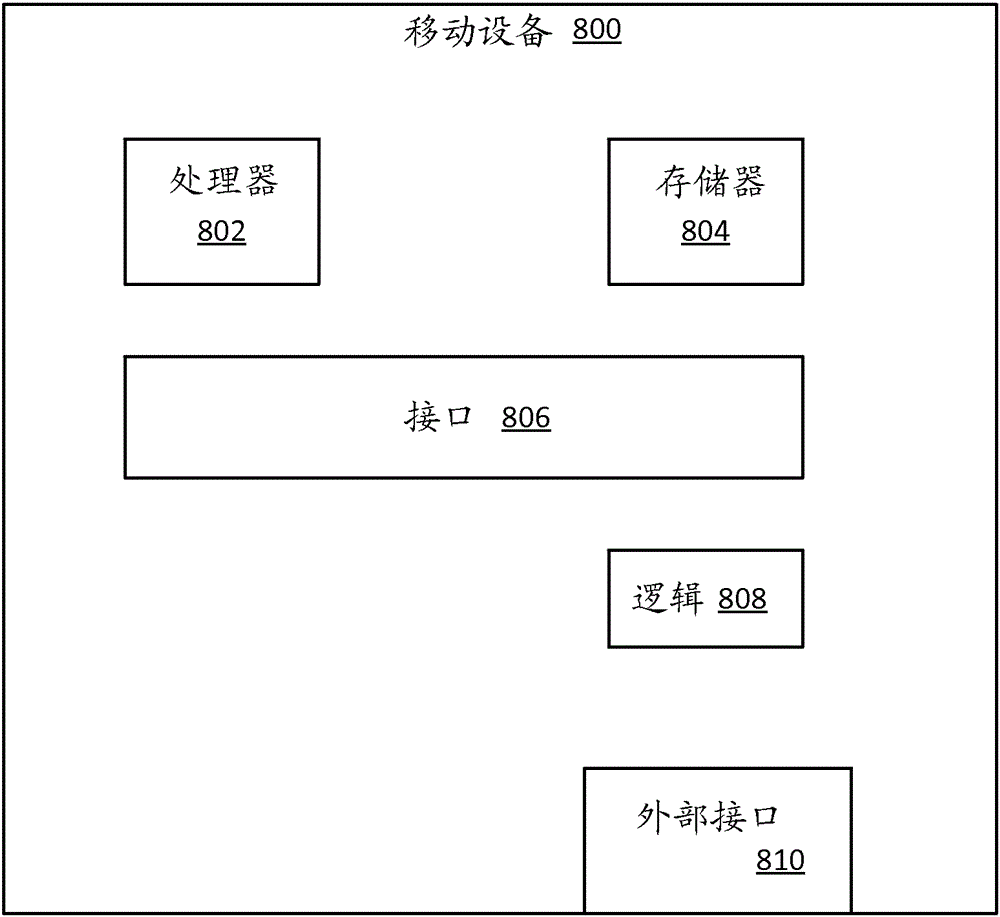
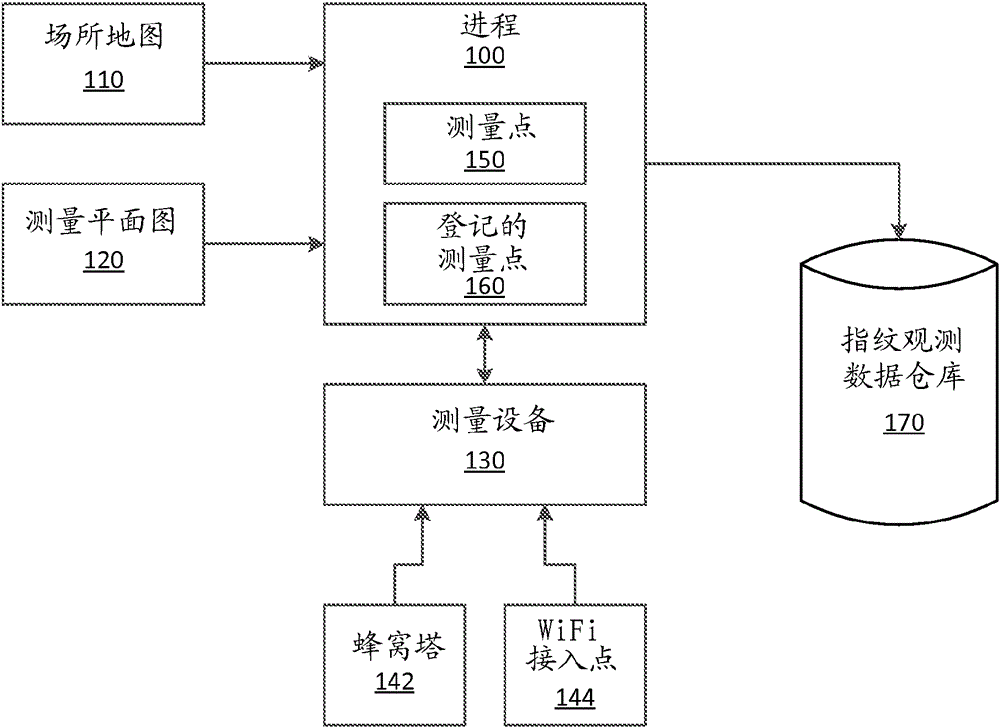
Sensor data collection
A sensor and place technology, applied in the field of sensor data collection, which can solve problems such as GPS positioning of surveyors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] People want to have maps so they know where they are, so they know where they've been, so they'll know how to get from where they are to where they want to go, and for other reasons consideration. For example, when in a mall, a shopper may want to know how to get from one store to another. Similarly, in a large office building, someone in the mail room may want to know how to get to a particular worker's desk so that mail can be delivered. Likewise, in a maze of underground sewer pipes, a worker may want to know how to get to a specific cleaning valve. Unfortunately, the map about the location will change. For example, for a place, there may be two, three, or twelve map revisions.
[0018] Additionally, the physical configuration of a mall, office building, or underground pipeline network may vary. More generally, the physical reality of the physical geography may change or the mapping of locations may change. These changes can occur so rapidly that maps quickly be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com