Residual image elimination method, drive system and display device
A drive system and afterimage technology, applied to static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as limited afterimage elimination effect and failure to display normally, and achieve good elimination effect, image afterimage elimination, and precise shake control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
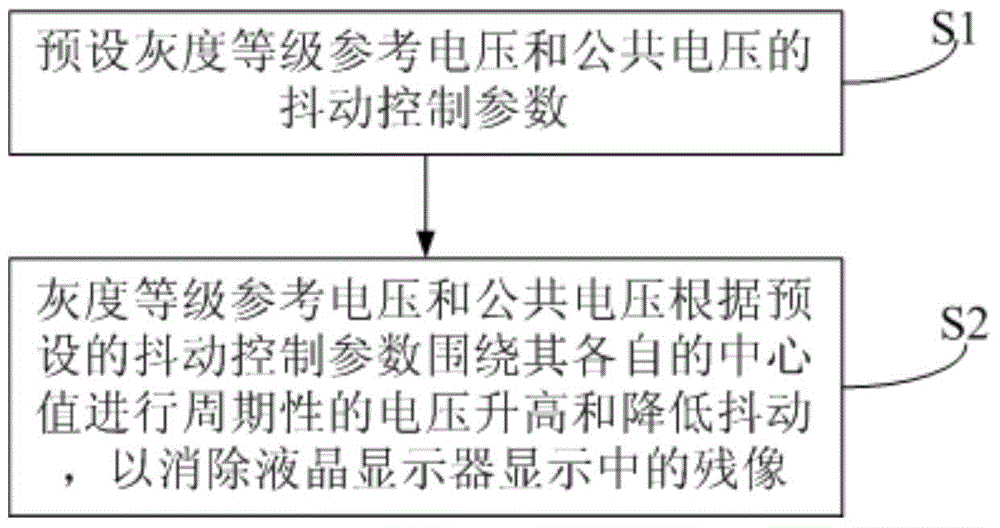
[0049] This embodiment provides a method for eliminating afterimages, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0050] Step S1: Presetting the dithering control parameters of the gray scale reference voltage and the common voltage.
[0051] In this step, the dithering control parameters of the preset gray scale reference voltage include: the center value of the preset gray scale reference voltage; the dithering period, dithering range, dithering amplitude and the gray scale to be dithered of the preset gray scale reference voltage; order. The jitter control parameters of the preset common voltage include: a central value of the preset common voltage; a jitter period, a jitter range and a jitter amplitude of the preset common voltage.
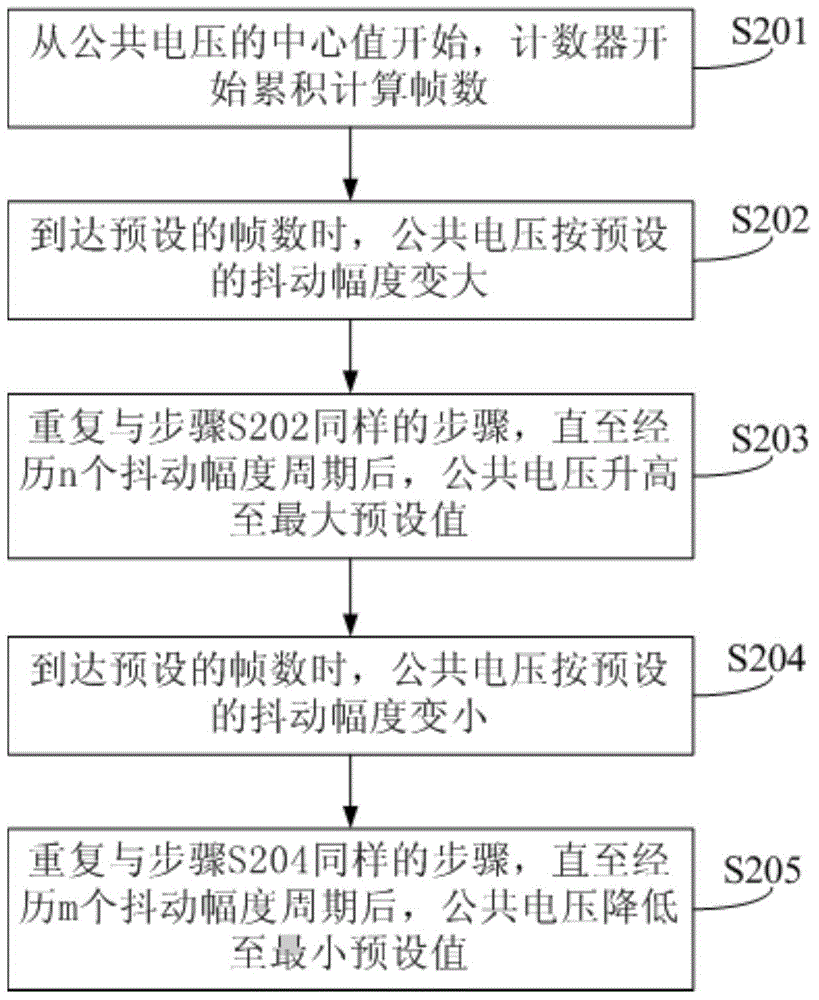
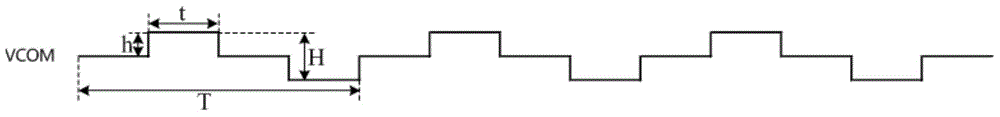
[0052] Wherein, the dithering period refers to the time taken for the gray scale reference voltage or the common voltage to return to the respective central value after the voltage rises and dithers from the respective central value. The dithering...
Embodiment 2
[0084] This embodiment provides a method for eliminating afterimages. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that, as Figure 7 shown, including:
[0085] Step S1': preset the dithering control parameters of the gray scale voltage.
[0086] This step includes: setting the grouping parameters of the gray-scale voltage; presetting the dithering period, dithering range, dithering amplitude and gray scales to be dithered of the gray-scale voltage.
[0087] Wherein, the dithering period refers to the time taken for the gray scale voltage to return to its central value after the voltage increases or decreases after dithering from the central value. The dithering range refers to the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of the gray scale voltage within one dithering period. The jitter amplitude refers to the variation amount of the voltage of two adjacent jitters of the gray scale voltage. The gray scale that needs to be dithered refers to the voltage value of th...
Embodiment 3
[0105] This embodiment provides a method for eliminating afterimages. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that Figure 11 As shown, it includes: step S1 ″: preset the dithering control parameters of the gray level reference voltage and the common voltage.
[0106] This step specifically includes:
[0107] Step S10: Pre-store a mapping table of different temperature ranges of the ambient temperature of the liquid crystal display and corresponding dithering control parameters of the gray scale reference voltage and the common voltage.
[0108] In this step, the different temperature ranges of the ambient temperature of the liquid crystal display correspond to a different grayscale reference voltage and the jitter control parameters of the common voltage, and the jitter control parameters of each grayscale reference voltage and common voltage correspond to control generation A set of grayscale reference voltages and a common voltage.
[0109] Step S2 ″: The gray level reference...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com