Switches capable of suppressing arcs
A technology for suppressing arcs and switches, applied in electrical components and other directions, can solve problems such as reducing switch life, causing accidents, affecting switch feel, etc., and achieves the effects of low manufacturing cost, simple structure, and improved service life and reliability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: This embodiment is a switch with a current of 10A and below,
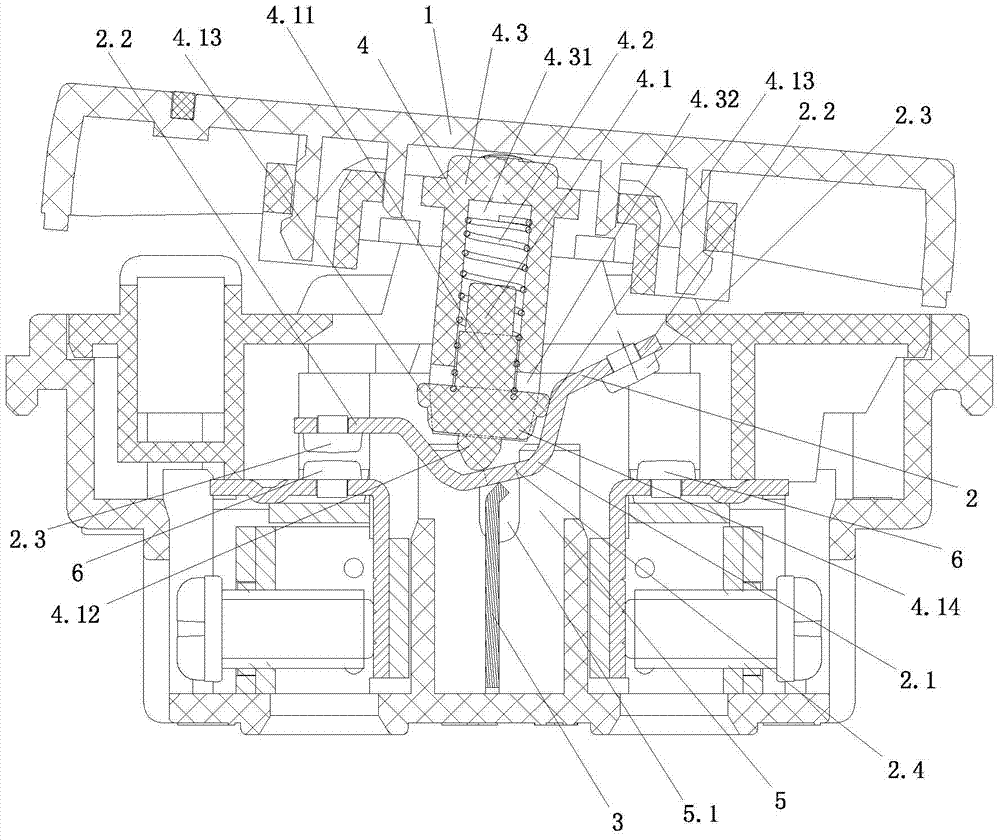
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention includes a switch button 1, a seesaw assembly 2, an incoming line terminal 3, a drive unit 4, a seesaw positioning member 5, and a static contact 6;
[0028] The rocker assembly 2 includes a rocker body 2.1. The middle part of the rocker body is U-shaped. The two side walls of the U-shape in the middle of the rocker body are respectively folded outward to form a rocker flange 2.2. The rocker flange is fixed with a movable contact. Head 2.3; the lower surface of the middle part of the rocker body is supported on the upper end of the incoming terminal 3, and the front and rear ends of the middle part of the rocker body 2.1 are provided with positioning protrusions 2.4; the positioning protrusions 2.4 extend on the positioning seat 5 of the rocker body inside the seesaw positioning groove 5.1;
[0029] The driver part 4 includes a drive rod...
Embodiment 2
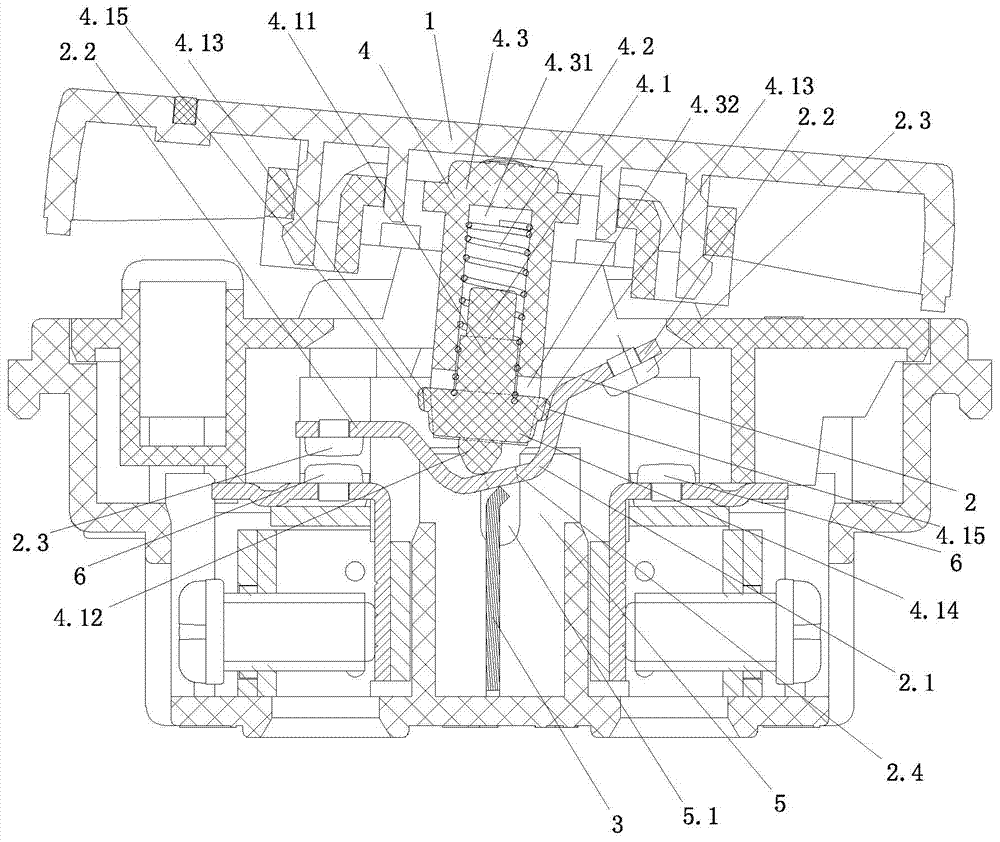
[0034] Such as figure 2 As shown, the difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that in the second embodiment, the end of the position-limiting protrusion 4.13 is fixed with an elastic element 4.15, and the elastic coefficient of the elastic element 4.15 is less than five times the elastic coefficient of the spring 4.2. One-third, in this embodiment, the elastic coefficient of the elastic element 4.15 is equal to one-sixth of the elastic coefficient of the spring 4.2, and the end surface of the elastic element 4.15 and the U-shaped side wall in the middle of the seesaw body are always in contact with each other.
Embodiment 3
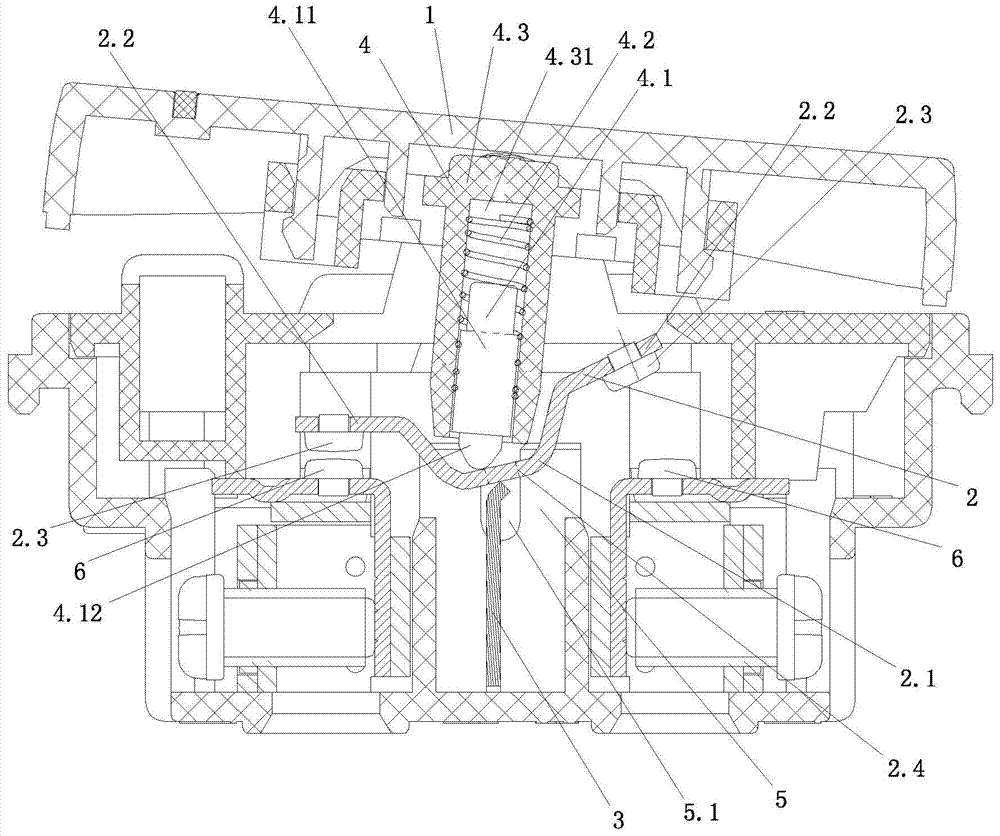
[0036] Such as image 3 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that before the switch is turned on or off, the U-shaped distance between the outer surface of the lower end of the transition piece 4.3 and the middle part of the seesaw body will be the same as that of the static contact 6. The side wall of the moving contact 2.3 that is touched is connected; that is, before the switch is turned on or off, the moving and static contacts that were originally in the state of contact are separated, and the other moving contact is connected to the other. The static contact approaches and finally connects with another static contact; during this period, the U-shaped side wall of the middle part of the seesaw body close to the side where the moving and static contacts are separated from each other is in contact with the transition piece 4.3, and the drive rod 4.1 The lower end of the U-shaped bottom in the middle of the rocker body slides toward the side c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com