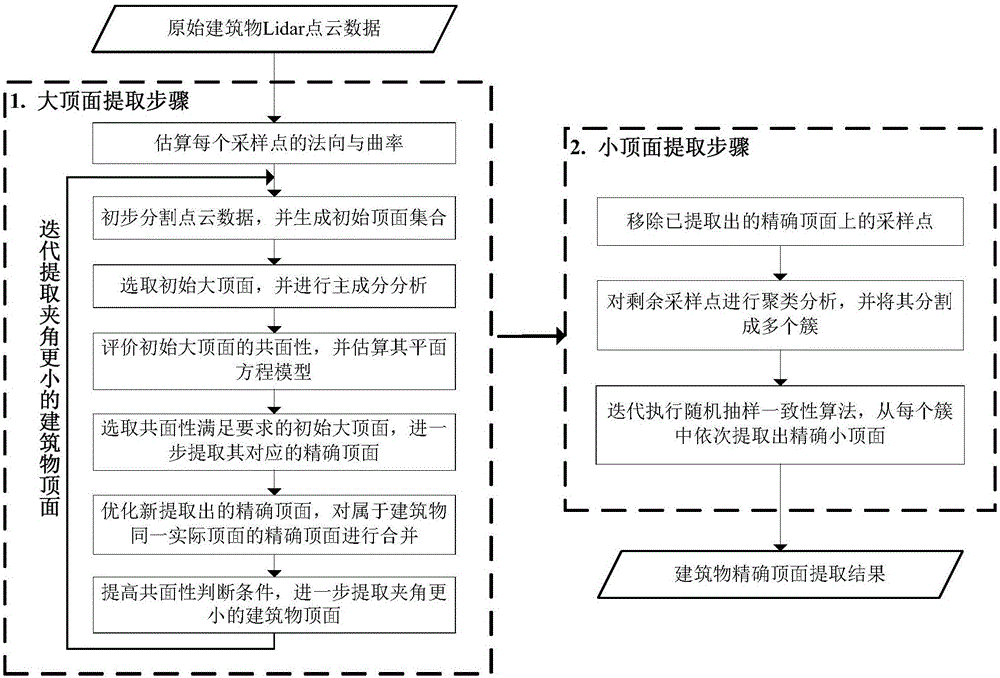
Airborne Lidar point cloud building top surface gradual extraction method based on classifying and laying
A progressive extraction and building technology, applied in image analysis, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as scattered point cloud data, difficult to get good results on the top of buildings, and slow algorithm efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
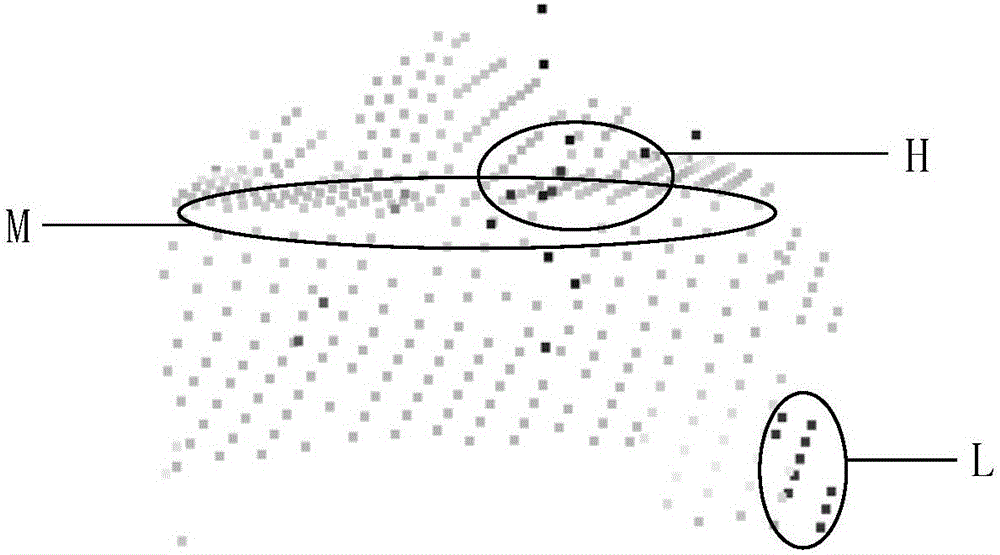
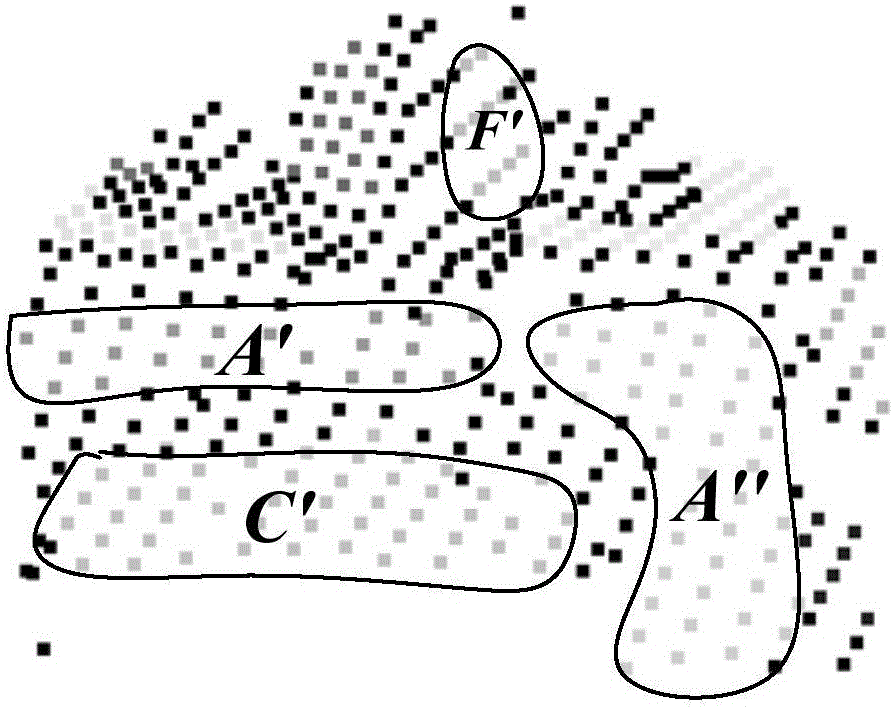
[0060] This example uses the Lidar point cloud data of a real building. The building contains 12 areas of varying sizes, including A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, L, and Q. The top surface, and the angle between the top surfaces also varies in size. For example, the four top surfaces of Q, L, I, and J have a small area (the number of sampling points on them is only 5, 6, 6, and 5), and the angle between the two top surfaces of D and C Very small. At the same time, there is an erect slender chimney above the building and two horizontal wires passing through it, which will cause the lidar point cloud data of the building to contain noise points.
[0061] The original lidar point cloud data of the building is as follows figure 2 As shown, it gives the original point cloud data of the building collected by the airborne Lidar system, where the dark black point in the L area is the point on the lowest top surface of the building; the dark black point in the H area is The point on the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com