A method for establishing an n-glycosylation receptor protein model in Escherichia coli using the skeleton protein fn3
A skeleton protein, Escherichia coli technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low efficiency of recombinant protein, increased difficulty of recombinant oligosaccharide analysis, increased difficulty of separation and purification of glycoprotein, etc., and achieves improved solubility and high efficiency in vitro glycosylation modification. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
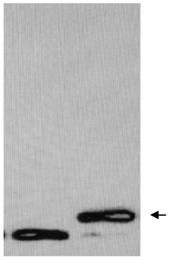
[0024] 1. In this example, the human scaffold protein fibronectin type III domain (Fn3) protein was used as the model gene (EMBL accession number AJ320527). At the 3' end of the gene, the nucleotide sequence encoding 6 histidine residues was introduced, and the nucleotide sequence encoding the glycosylation site DQNAT was introduced at the 3' end. For the structure of the fusion gene, see figure 1 . The gene was constructed into pIG6H by genetic recombination, see the vector structure figure 2 .
[0025] 2. After synthesizing the Fn3-Gly expression cassette sequence of the human fibronectin type III domain recombinant gene shown in the sequence table (Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), use EcoR V and HindIII to construct on the E. coli expression vector pIG6H , the recombinant vector pIG6H-Fn3-Gly was obtained.
[0026] 3. The constructed expression vector and pACYCpgl were electroporated into E. coli strain CLM37, and then the transformants were inoculated into L...
Embodiment 2
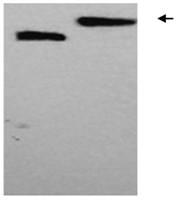
[0033] 1. In this example, the human scaffold protein fibronectin type III domain (Fn3) protein was used as the model gene (EMBL accession number AJ320527). At the 3' end of the gene, the nucleotide sequence encoding 6 histidine residues was introduced, and the nucleotide sequence encoding the glycosylation site DQNAT was introduced at the 3' end. For the structure of the fusion gene, see figure 1 . The gene was constructed into pIG6H by genetic recombination, see the vector structure figure 2 .
[0034] 2. After synthesizing the Fn3-Gly expression cassette sequence of the human fibronectin type III domain recombinant gene shown in the sequence table (Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), use EcoR V and HindIII to construct on the E. coli expression vector pIG6H , the recombinant vector pIG6H-Fn3-Gly was obtained.
[0035] 3. The constructed expression vector and pACYCpgl were electroporated into E. coli strain CLM37, and then the transformants were inoculated into L...
Embodiment 3
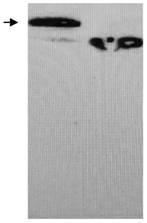
[0042] 1. In this example, the human scaffold protein fibronectin type III domain (Fn3) protein was used as the model gene (EMBL accession number AJ320527). At the 3' end of the gene, the nucleotide sequence encoding 6 histidine residues was introduced, and the nucleotide sequence encoding the glycosylation site DQNAT was introduced at the 3' end. For the structure of the fusion gene, see figure 1 . The gene was constructed into pIG6H by genetic recombination, see the vector structure figure 2 .
[0043] 2. After synthesizing the Fn3-Gly expression cassette sequence of the human fibronectin type III domain recombinant gene shown in the sequence table (Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), use EcoR V and HindIII to construct on the E. coli expression vector pIG6H , the recombinant vector pIG6H-Fn3-Gly was obtained.
[0044] 3. The constructed expression vector and pACYCpgl were electroporated into E. coli strain CLM37, and then the transformants were inoculated into L...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com