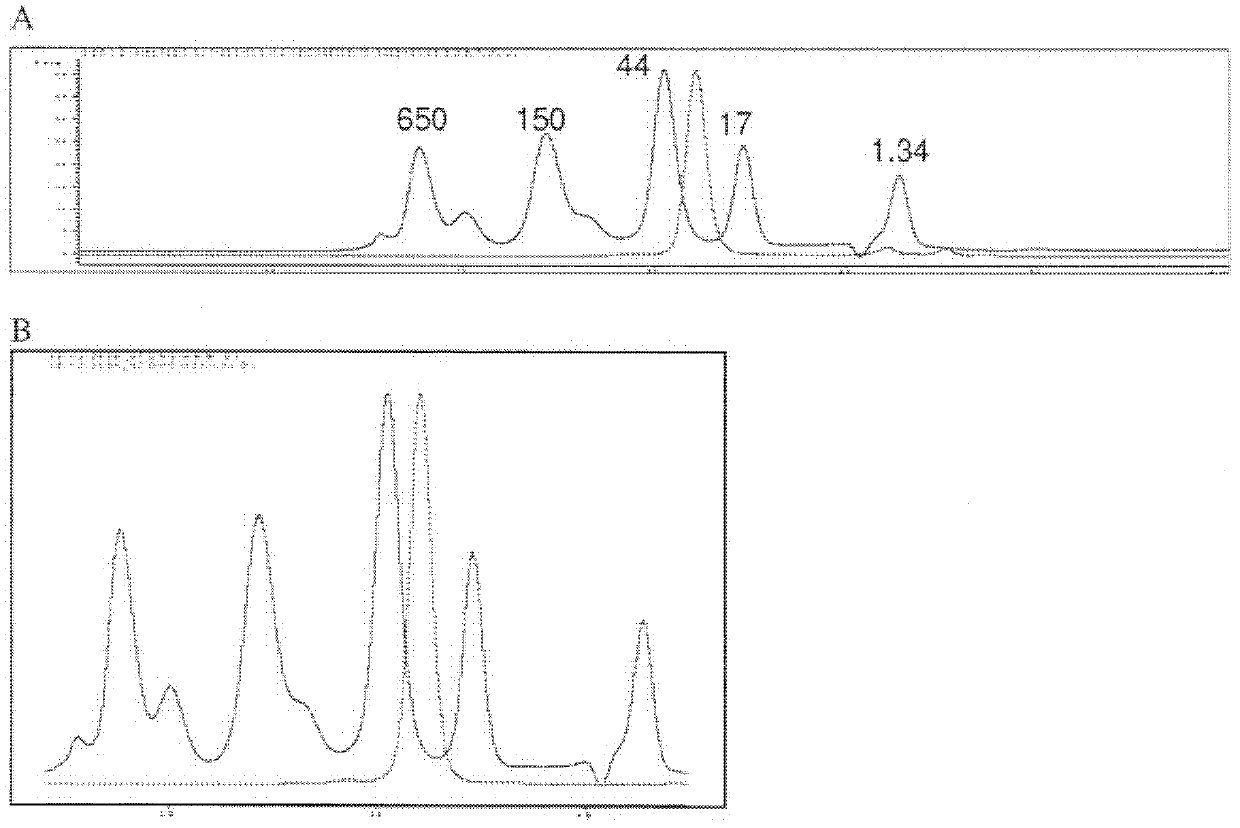
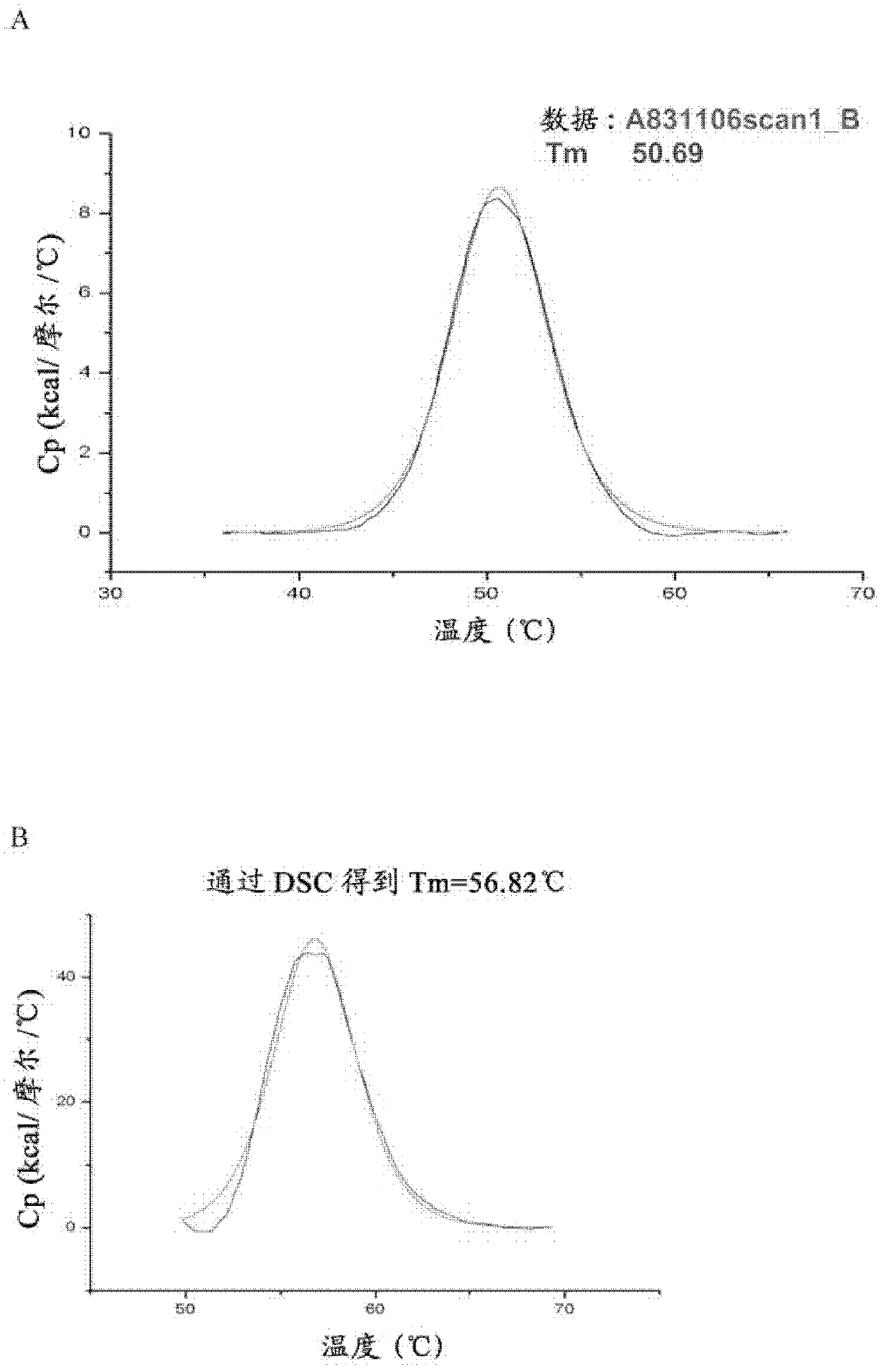
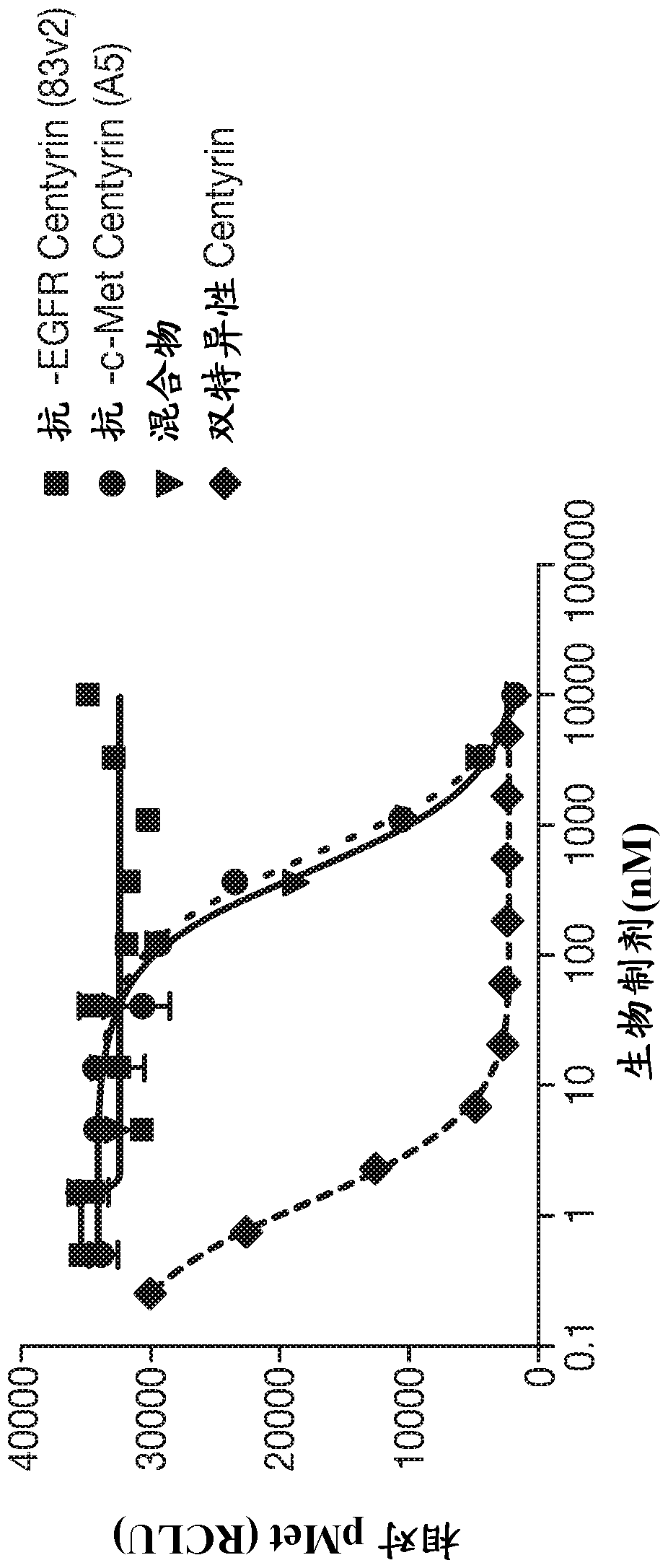
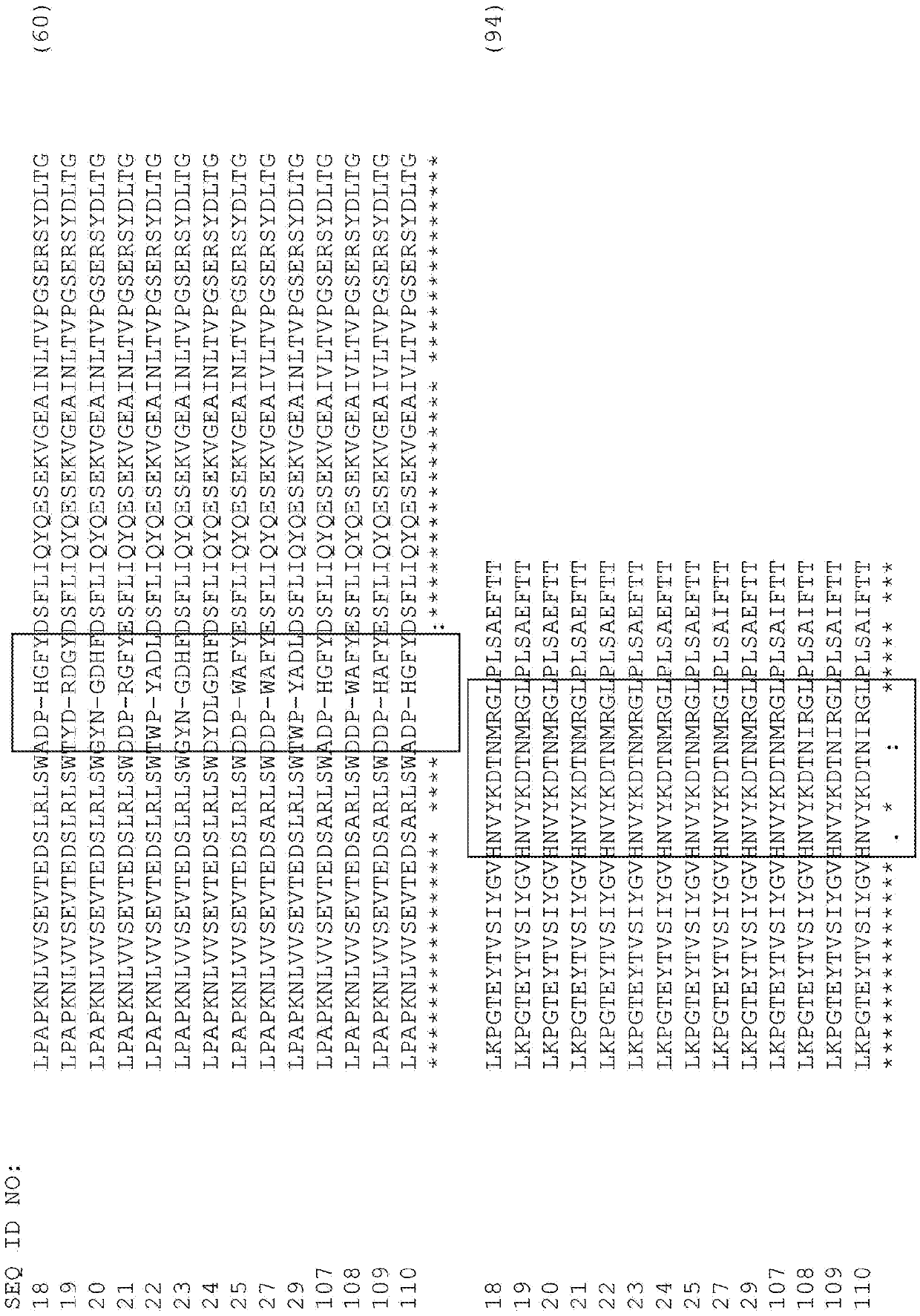
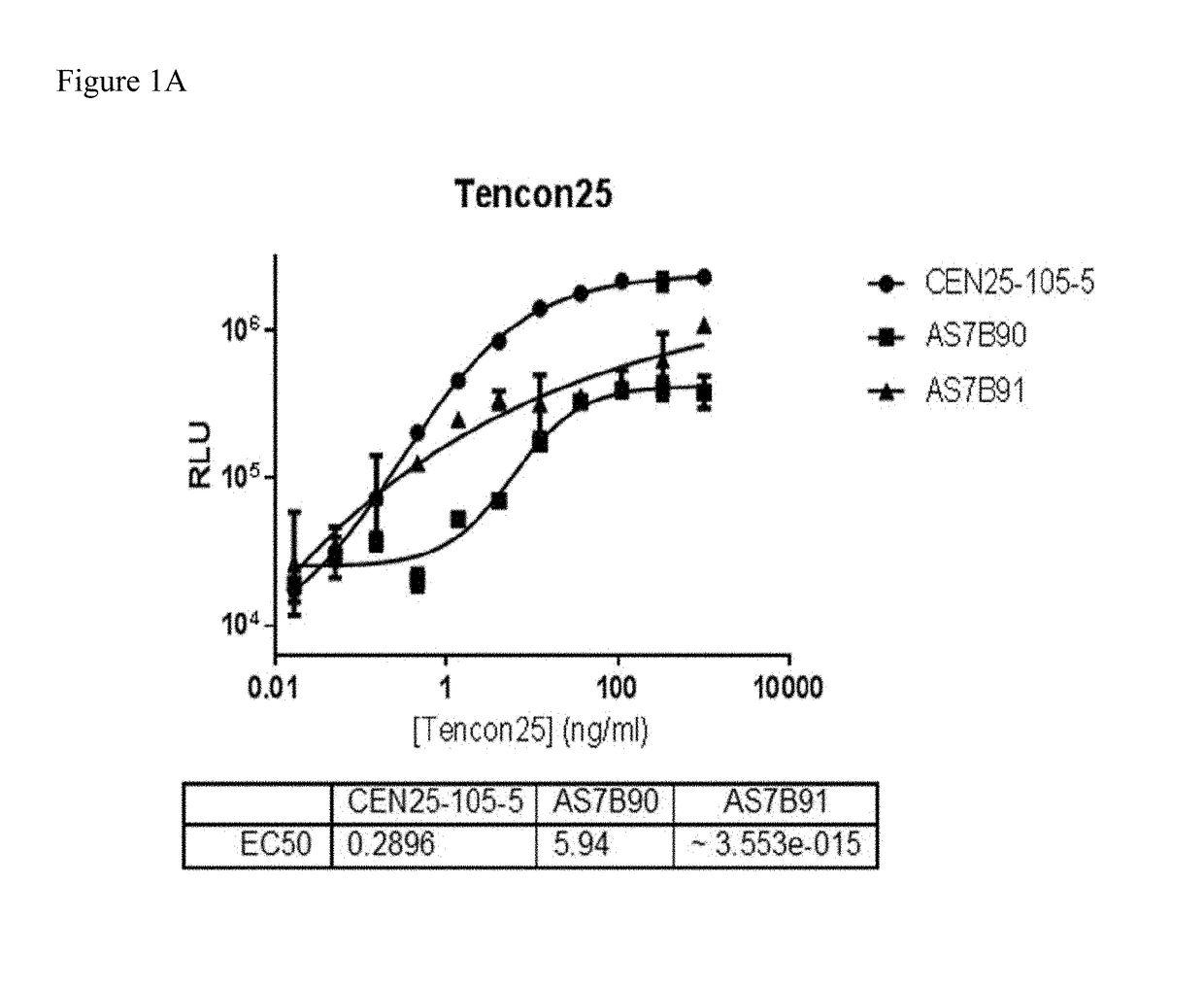
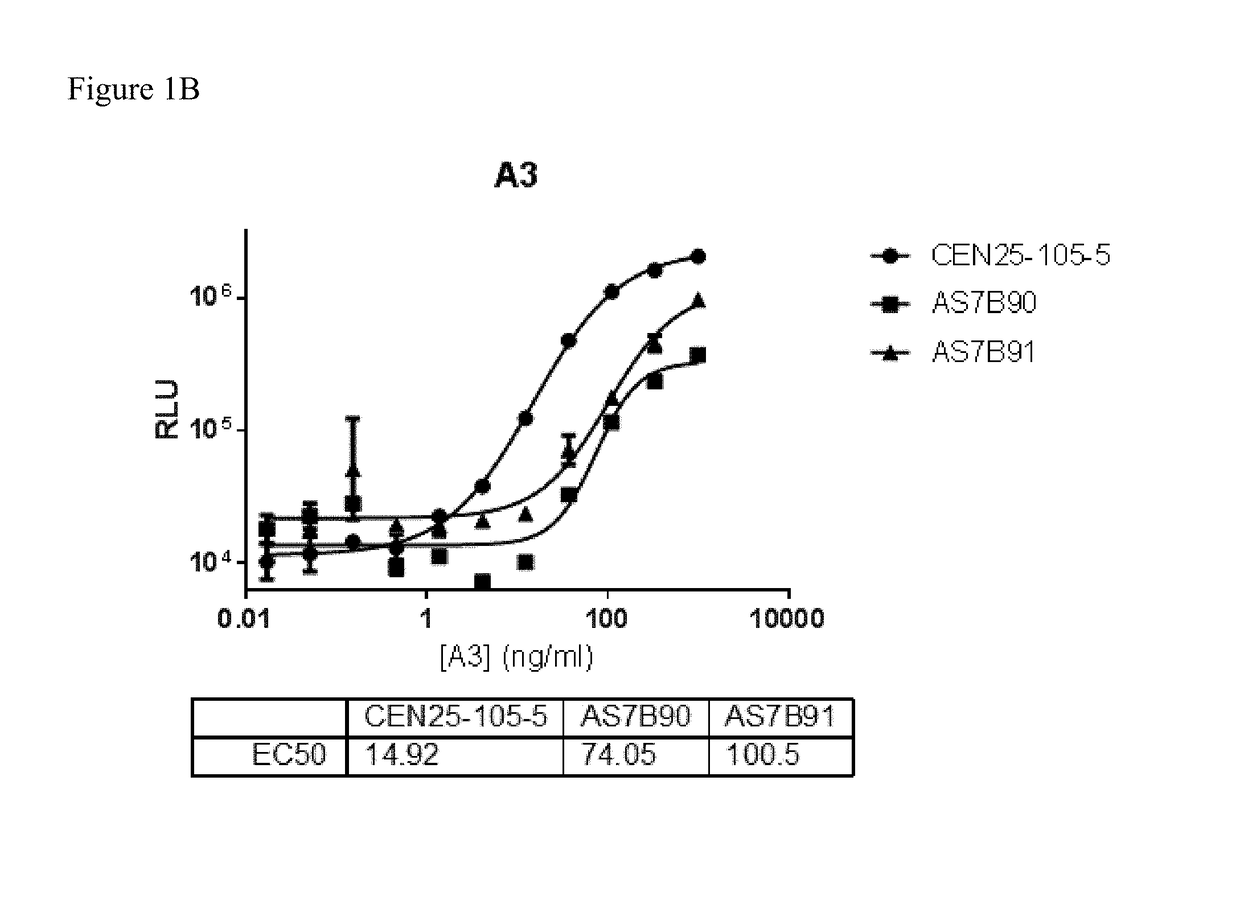
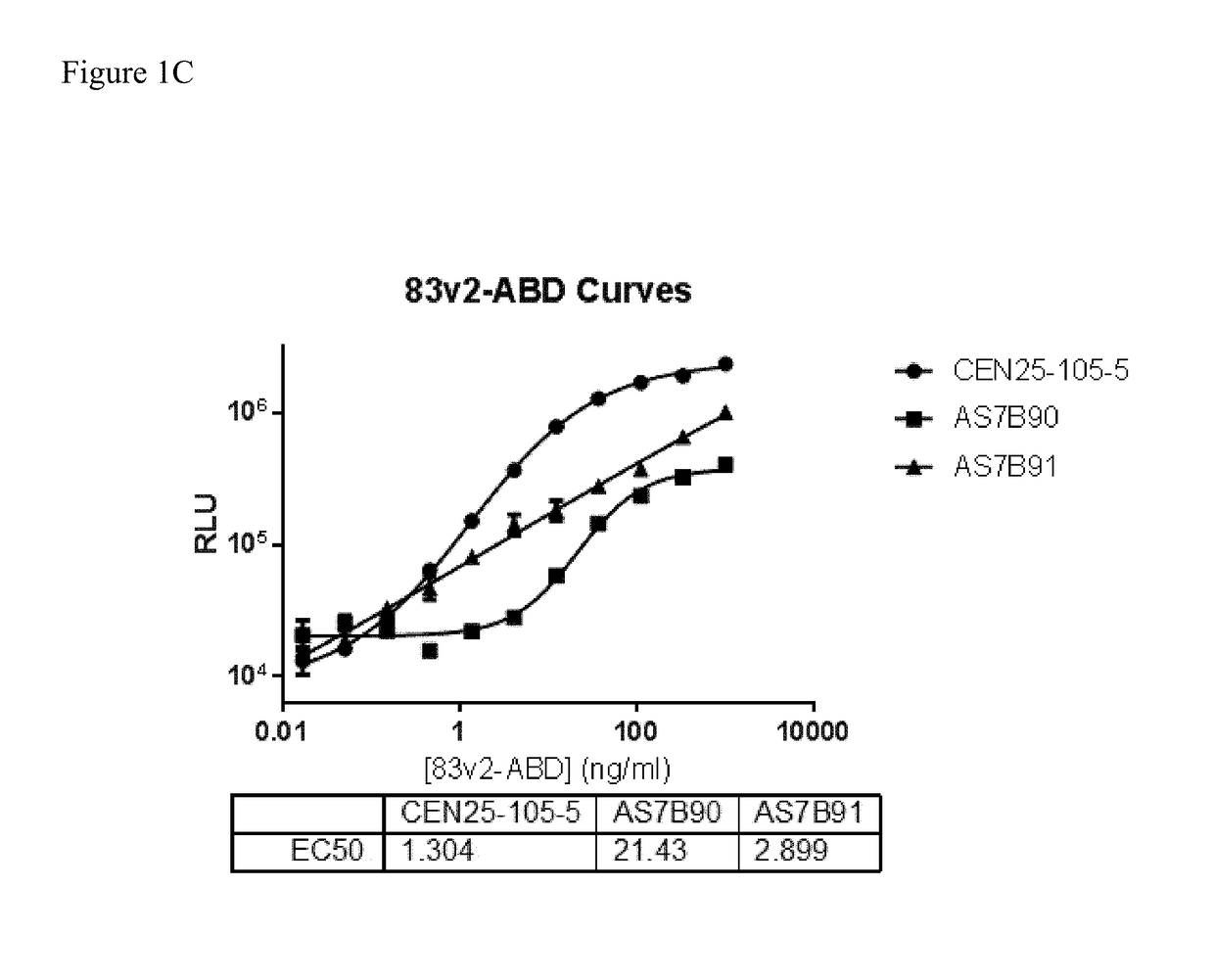
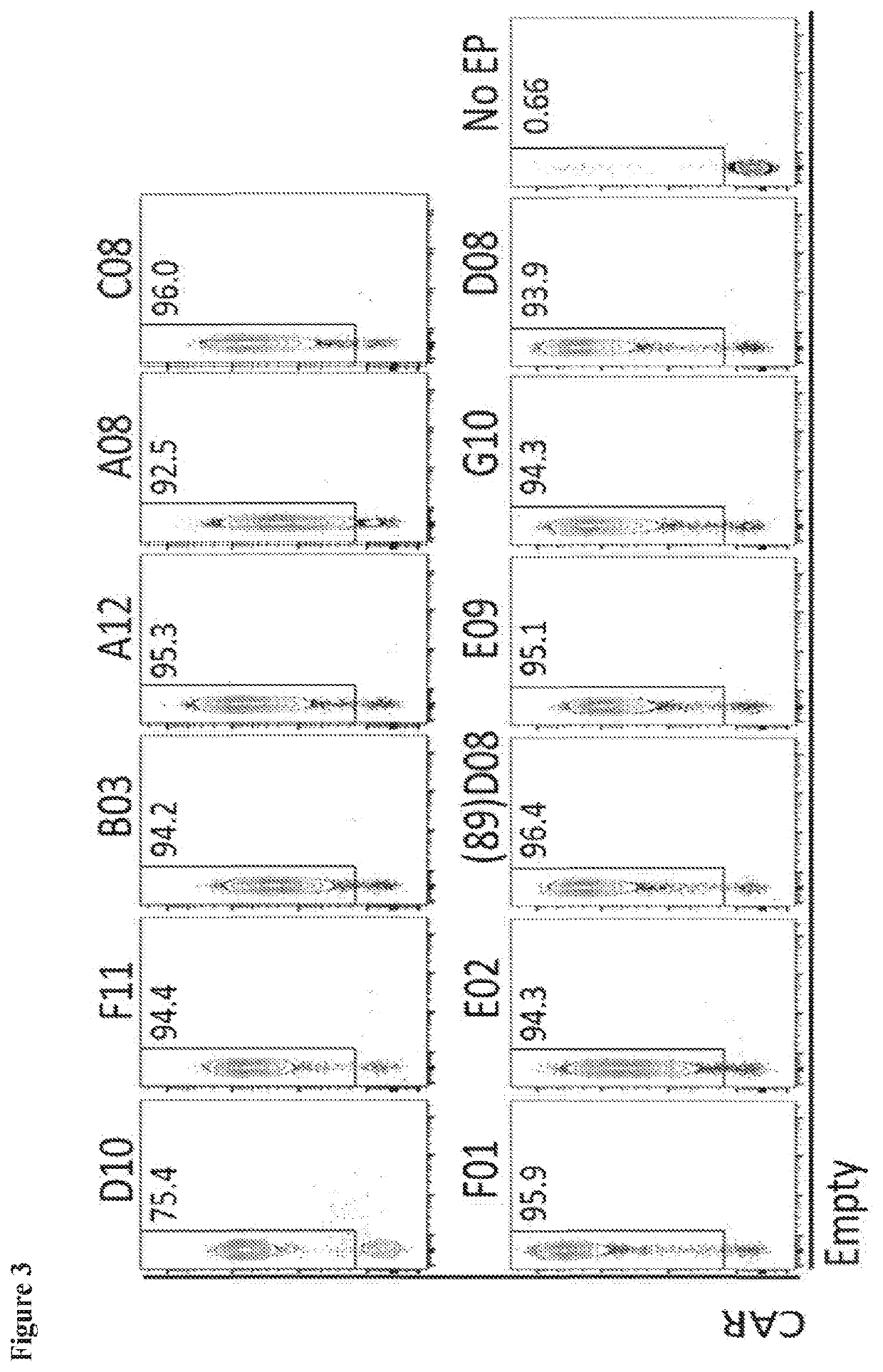
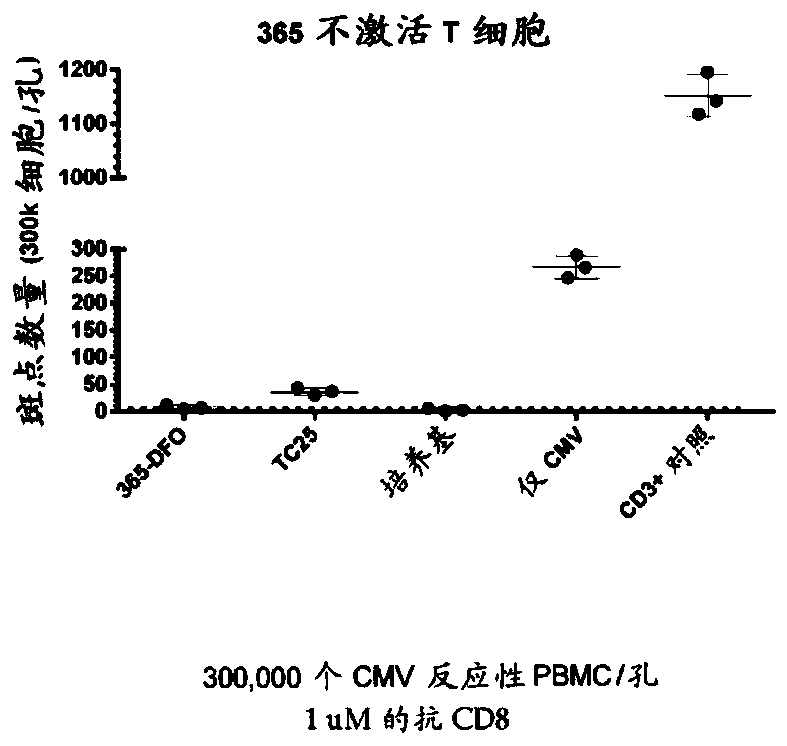
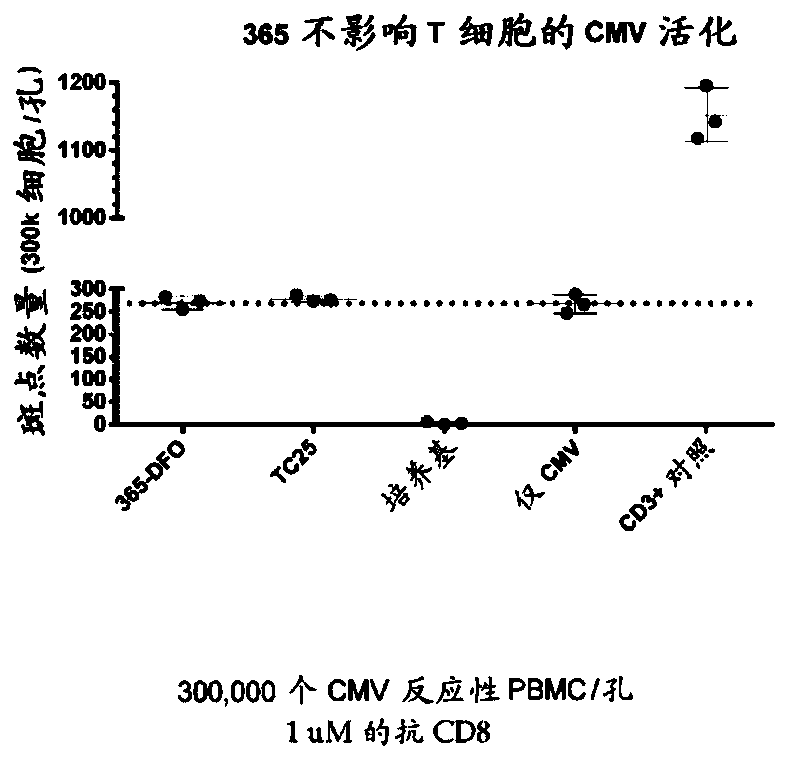
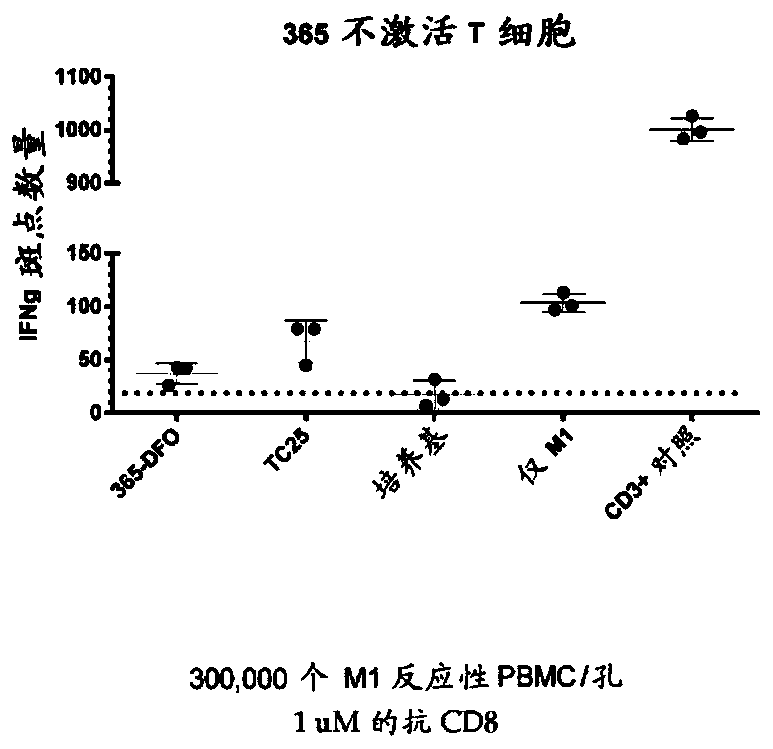
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Fibronectin type III domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
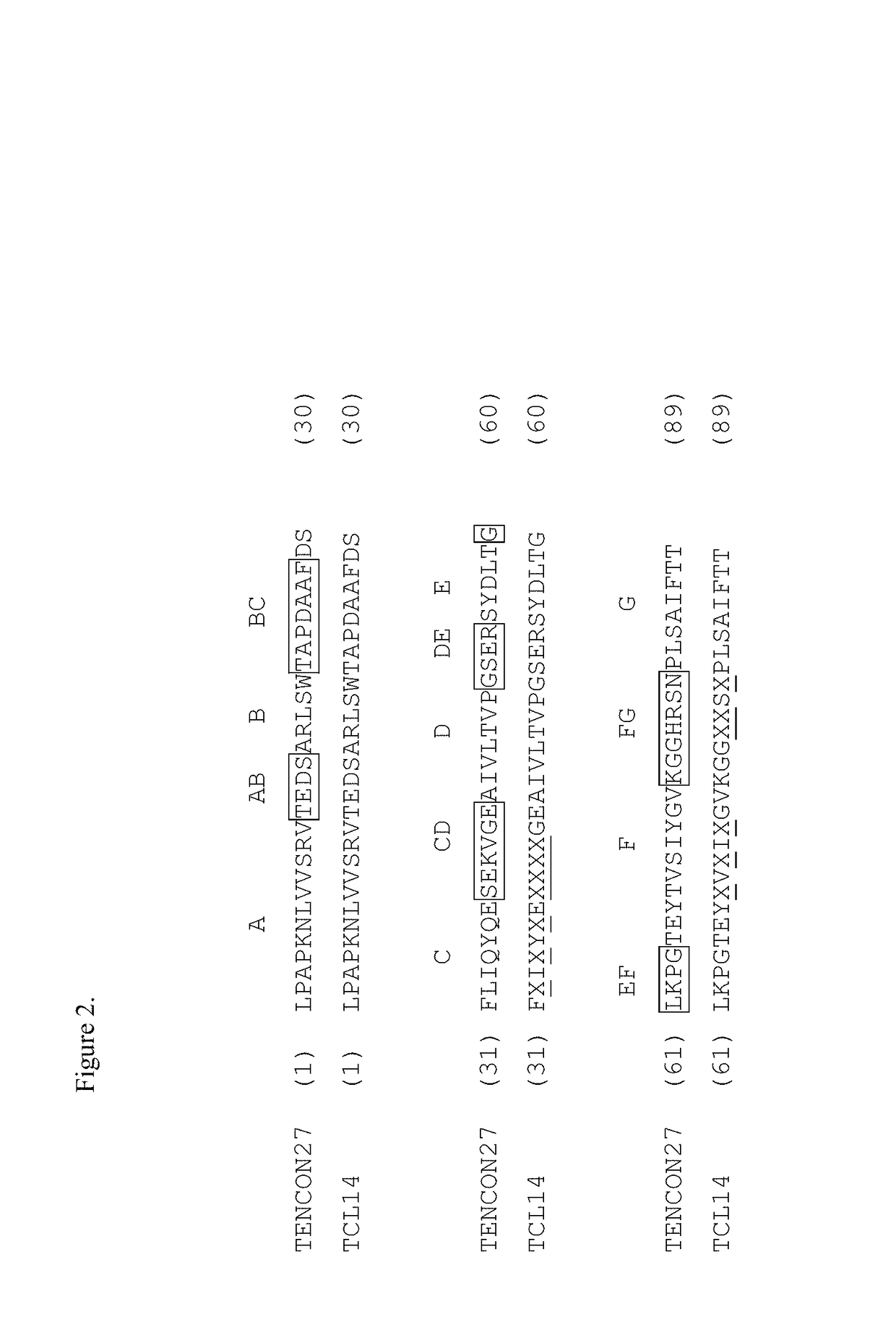
The Fibronectin type III domain is an evolutionary conserved protein domain that is widely found in animal proteins. The fibronectin protein in which this domain was first identified contains 16 copies of this domain. The domain is about 100 amino acids long and possesses a beta sandwich structure. Of the three fibronectin-type domains, type III is the only one without disulfide bonding present. Fibronectin domains are found in a wide variety of extracellular proteins. They are widely distributed in animal species, but also found sporadically in yeast, plant and bacterial proteins.
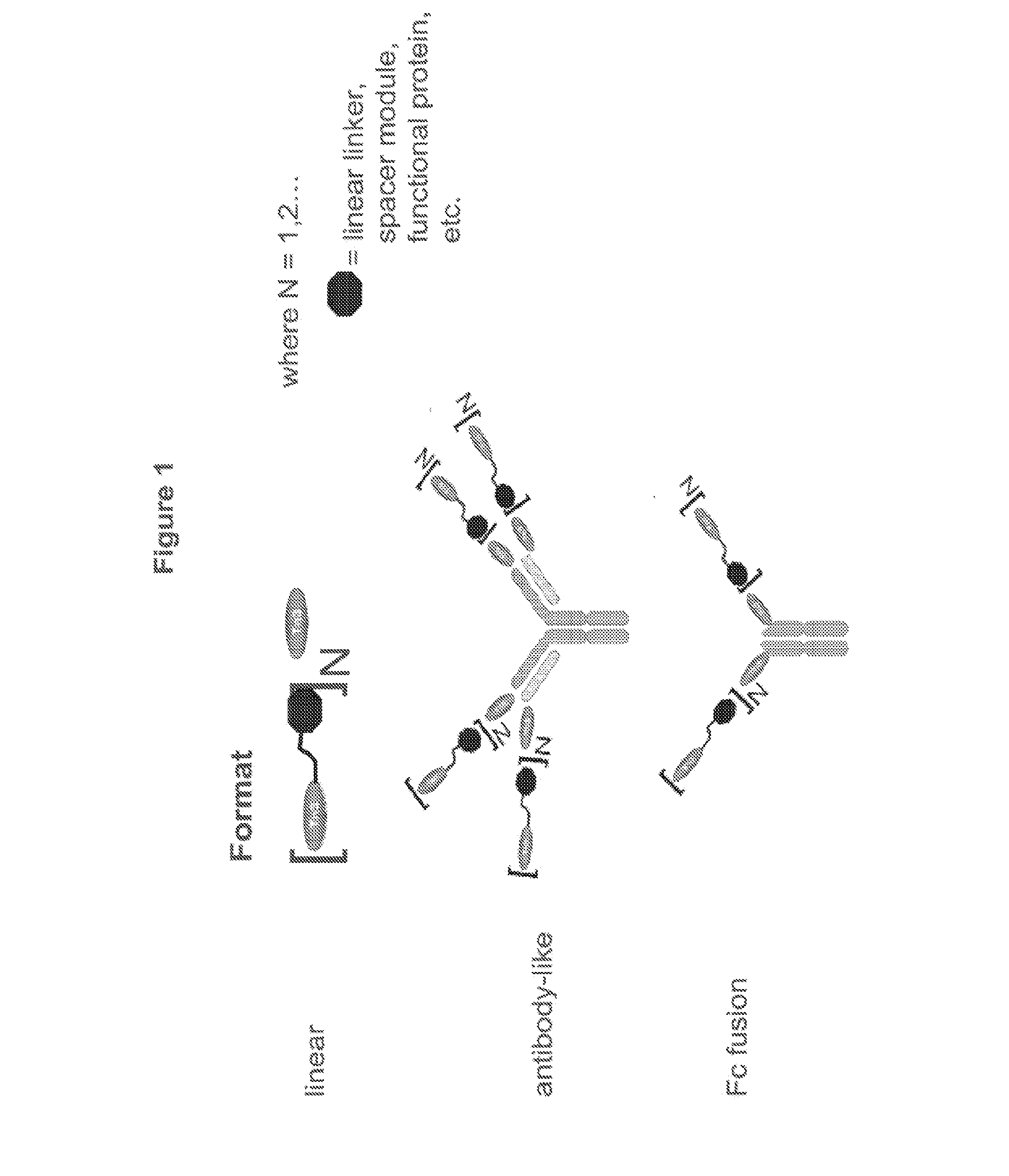
Protein scaffolds for antibody mimics and other binding proteins
InactiveUS20050255548A1Easy to foldImprove stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsWAS PROTEINAntibody
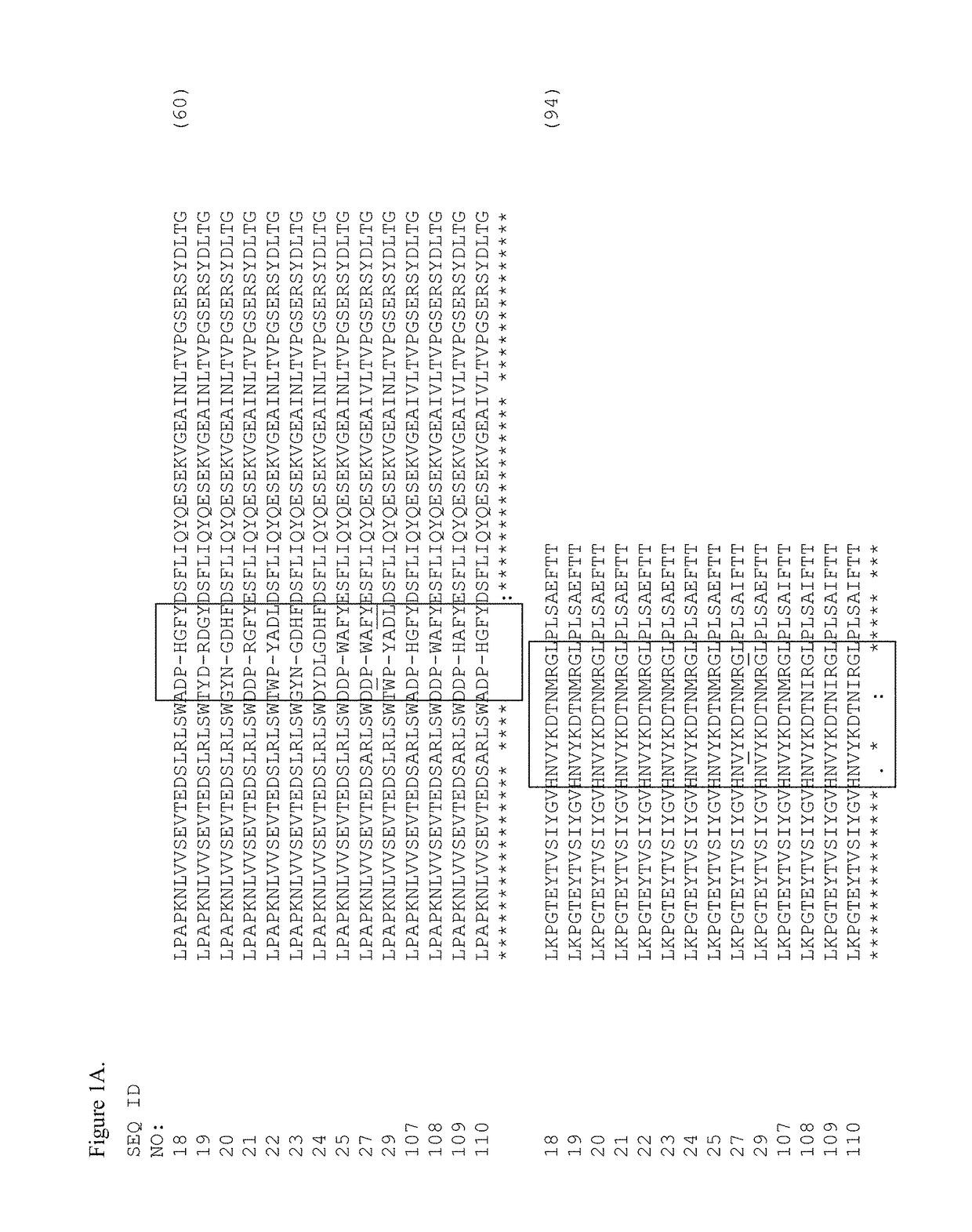
Disclosed herein are proteins that include a fibronectin type III domain having at least one randomized loop. Also disclosed herein are nucleic acids encoding such proteins and the use of such proteins in diagnostic methods and in methods for evolving novel compound-binding species and their ligands.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
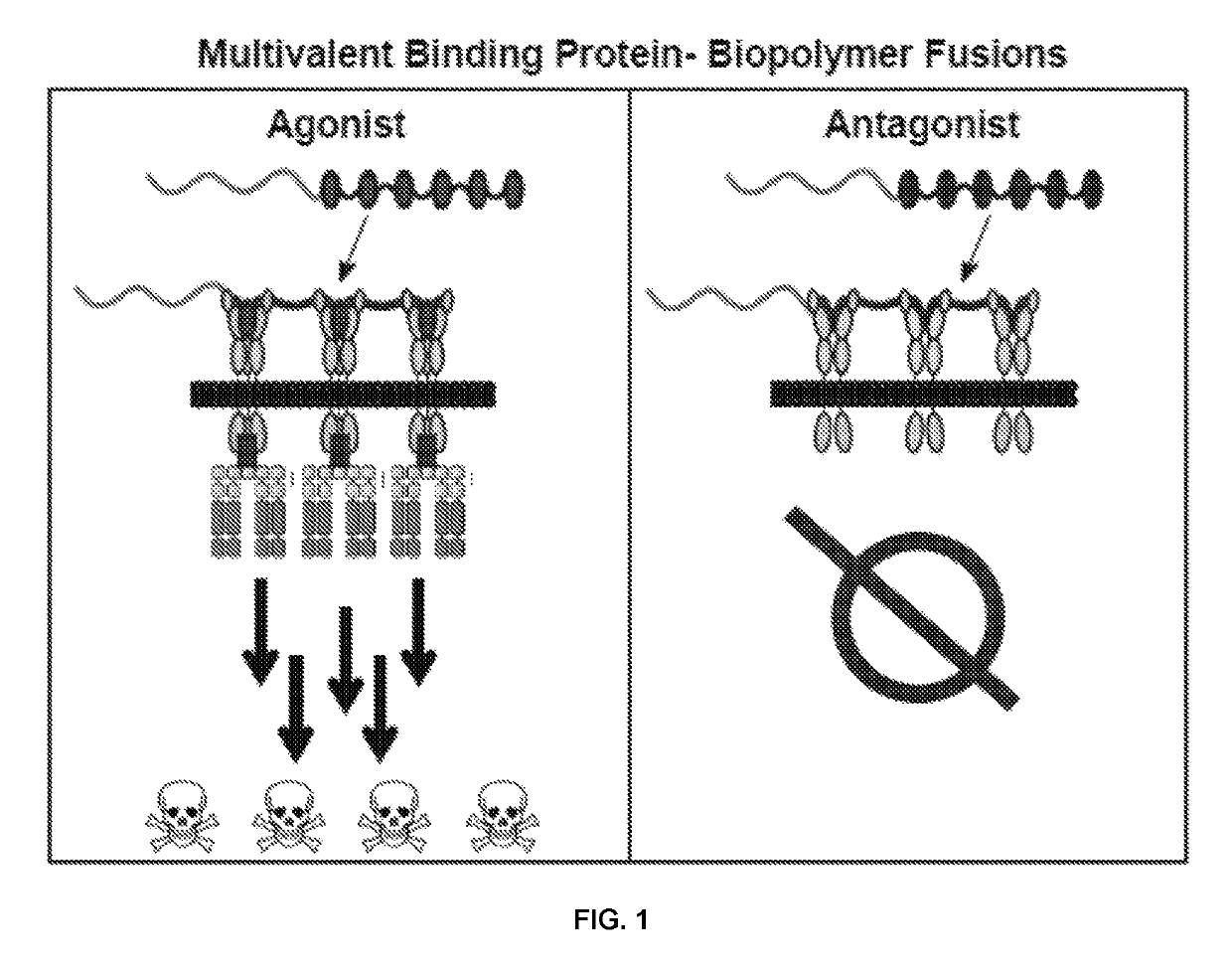
Fibronectin type iii domain-based multimeric scaffolds
InactiveUS20130079280A1High affinityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDiagnostic agentTarget antigen
The present invention provides fibronectin type III (Fn3)-based multimeric scaffolds that specifically bind to one or more specific target antigen. The invention further provides bispecific Fn3-derived binding molecules that bind to two or more target antigens simultaneously, fusions, conjugates, and methods to increase the stability of Fn3-based binding molecules. Furthermore, the present invention is related to a prophylactic, therapeutic or diagnostic agent, which contains Fn3-based multimeric scaffolds.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Serum albumin binding molecules
ActiveUS20110305663A1Improve solubilityReduce aggregationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igeSerum protein albumin
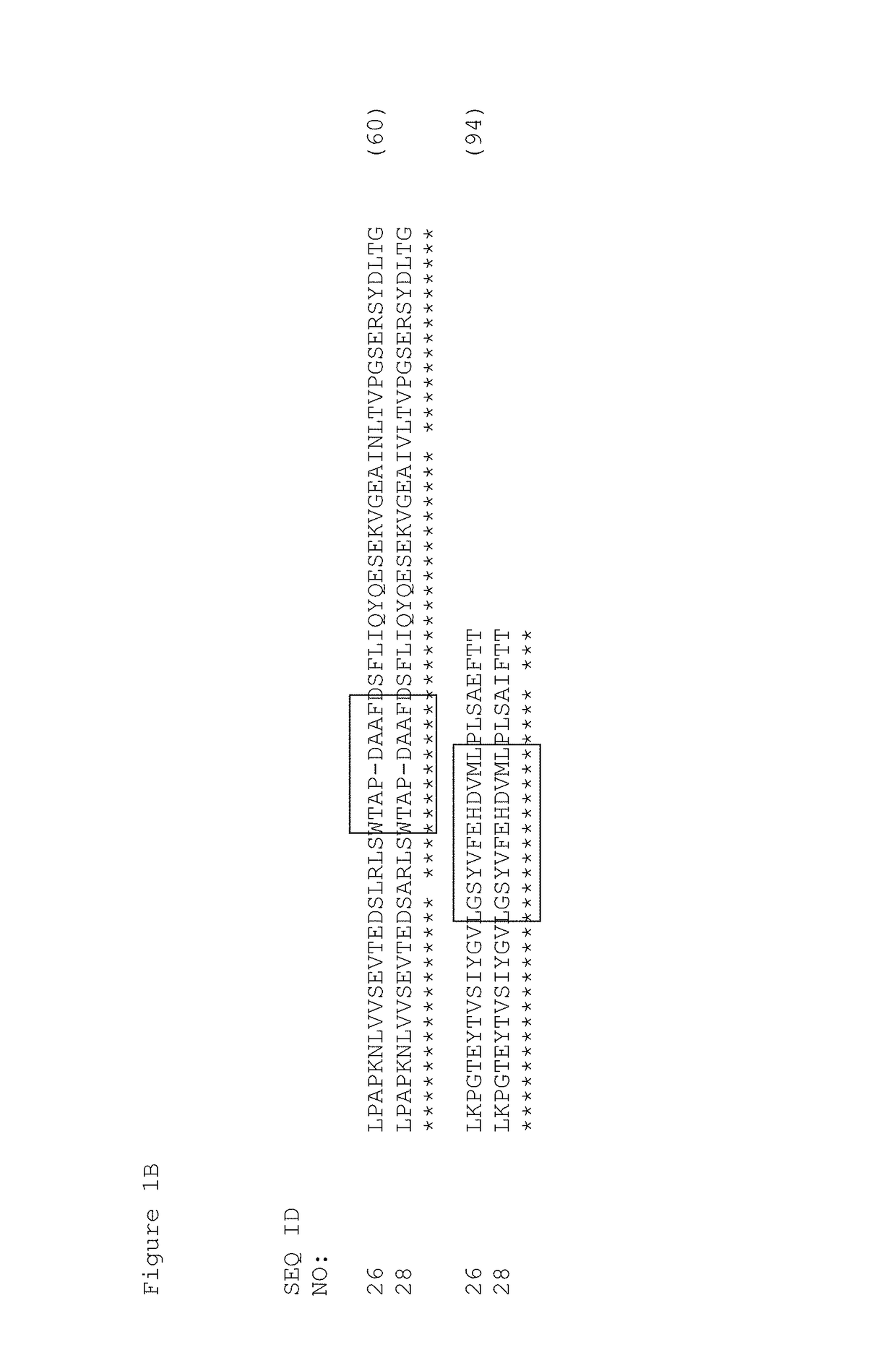
The present invention relates to an antibody-like protein based on the tenth fibronectin type III domain (10Fn3) that binds to serum albumin. The invention further relates to fusion molecules comprising a serum albumin-binding 10Fn3 joined to a heterologous protein for use in diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Serum albumin binding molecules
ActiveUS9540424B2Extended half-lifeReduced potencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSerum igeSerum albumin
The present invention relates to an antibody-like protein based on the tenth fibronectin type III domain (10Fn3) that binds to serum albumin. The invention further relates to fusion molecules comprising a serum albumin-binding 10Fn3 joined to a heterologous protein for use in diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
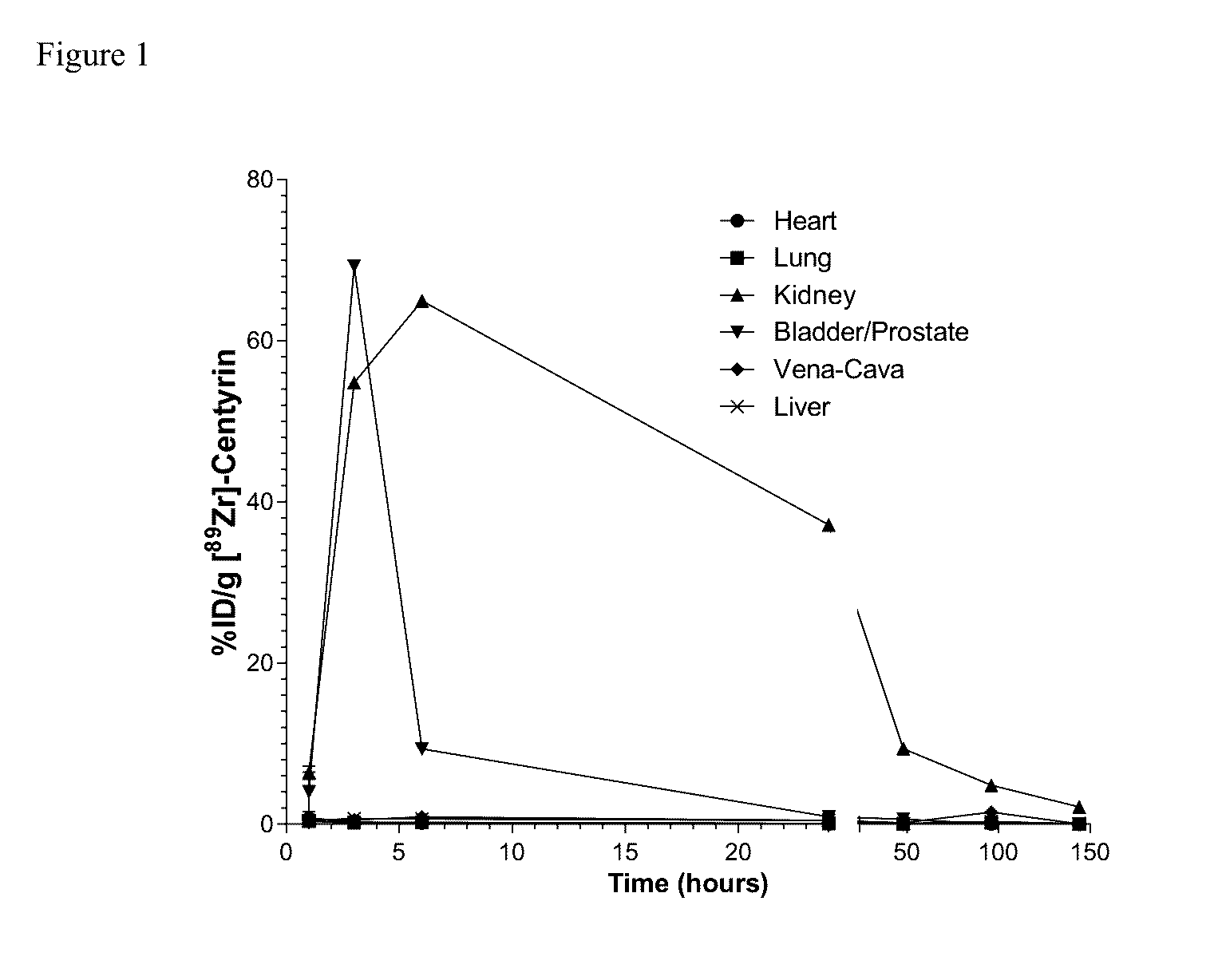
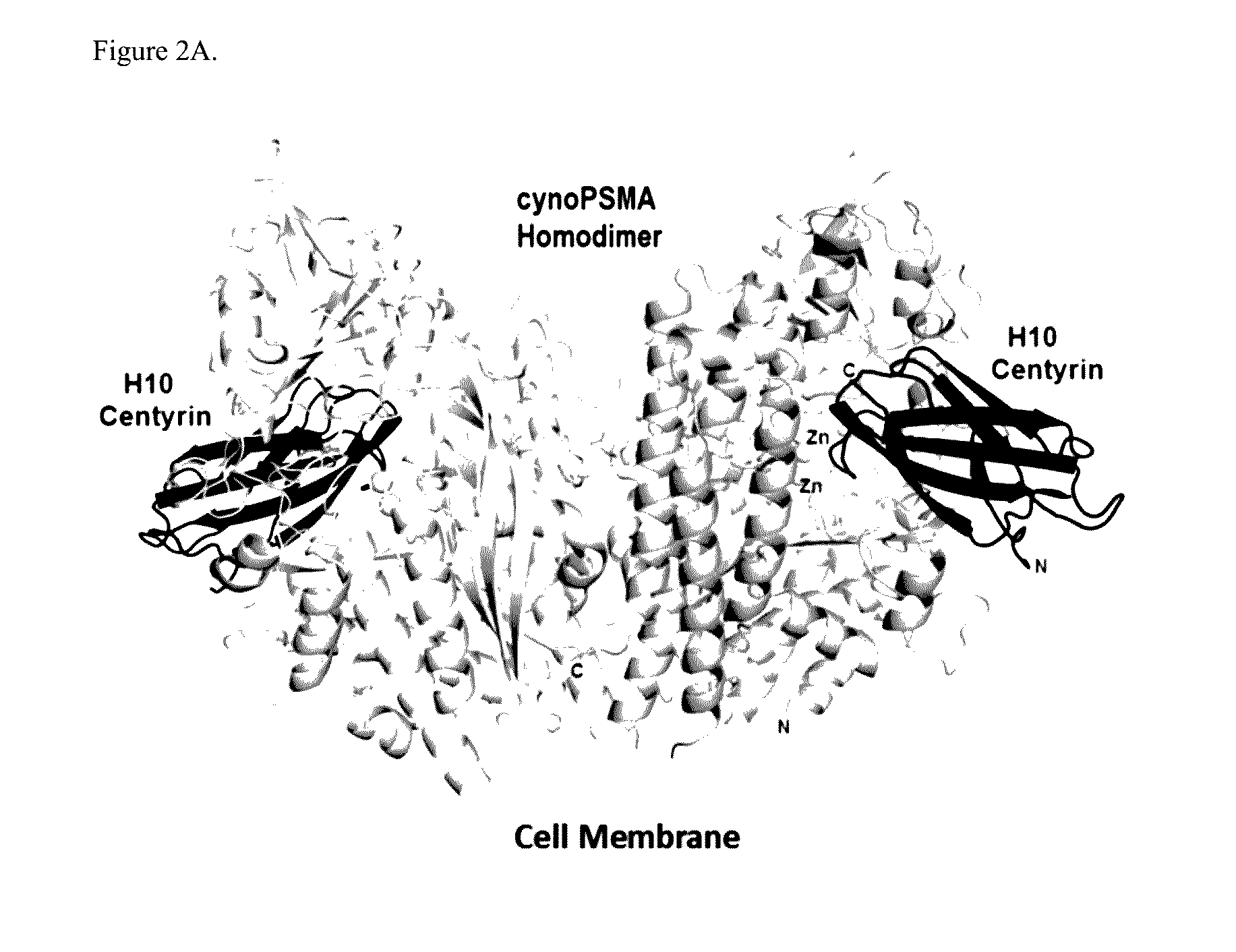
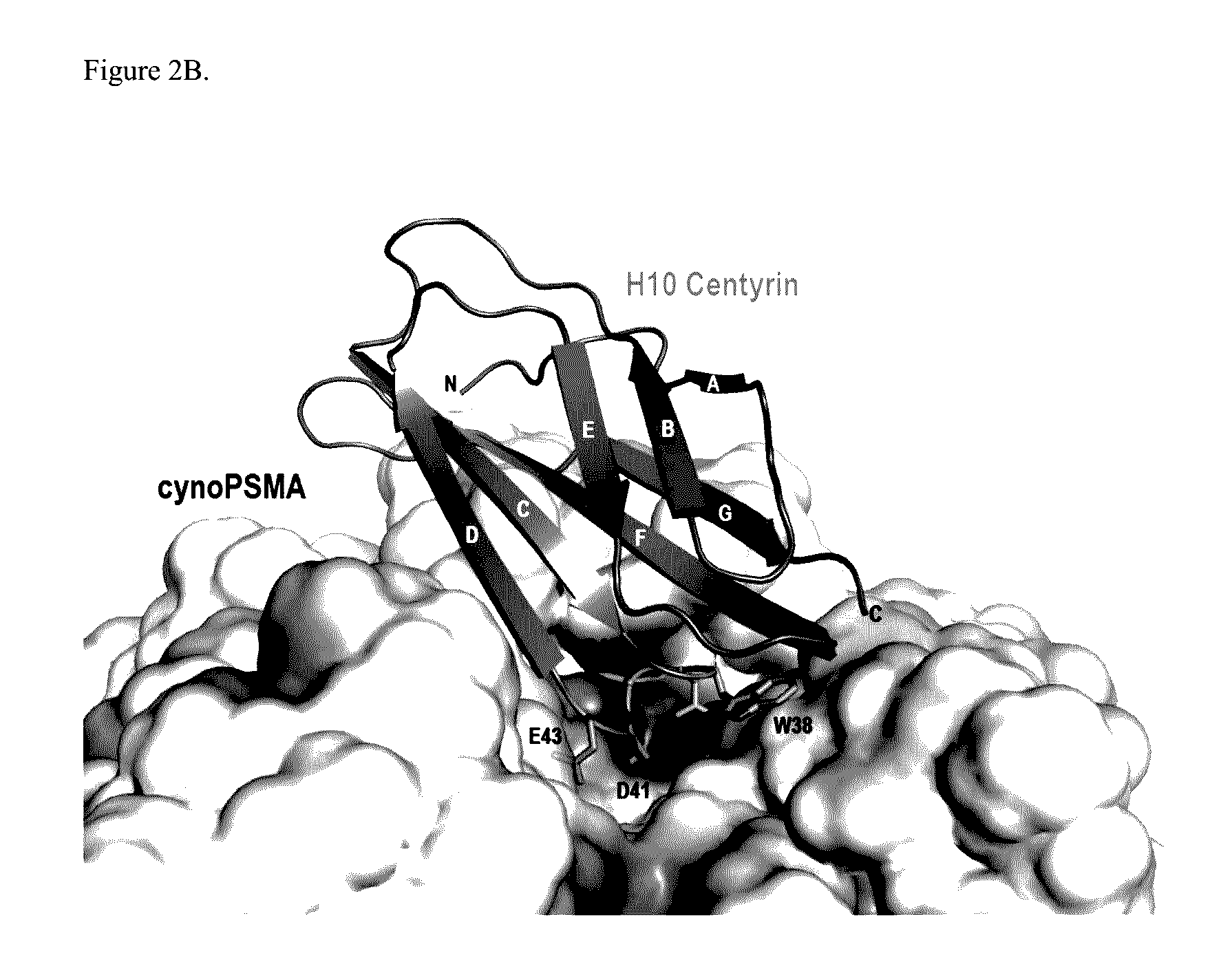
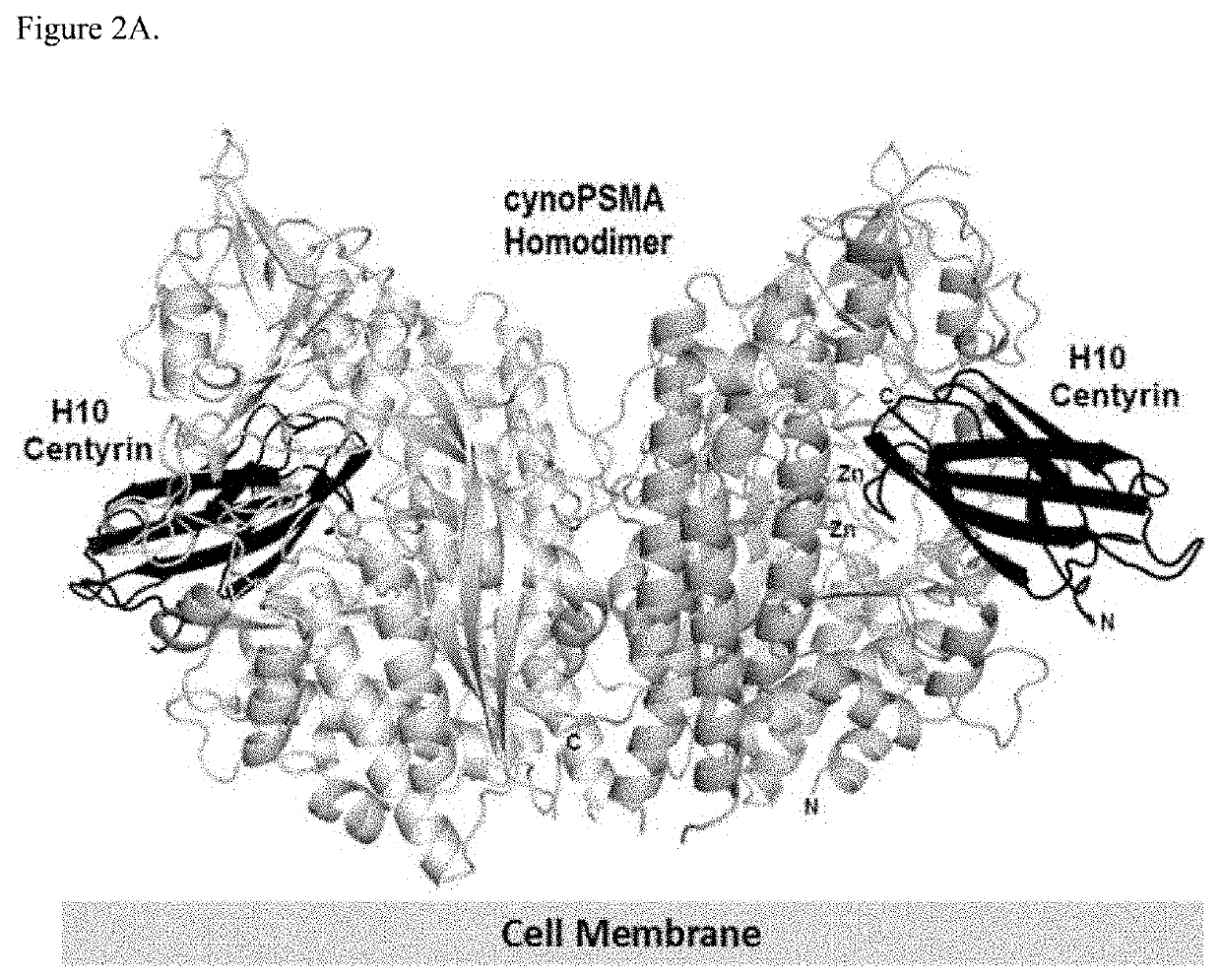
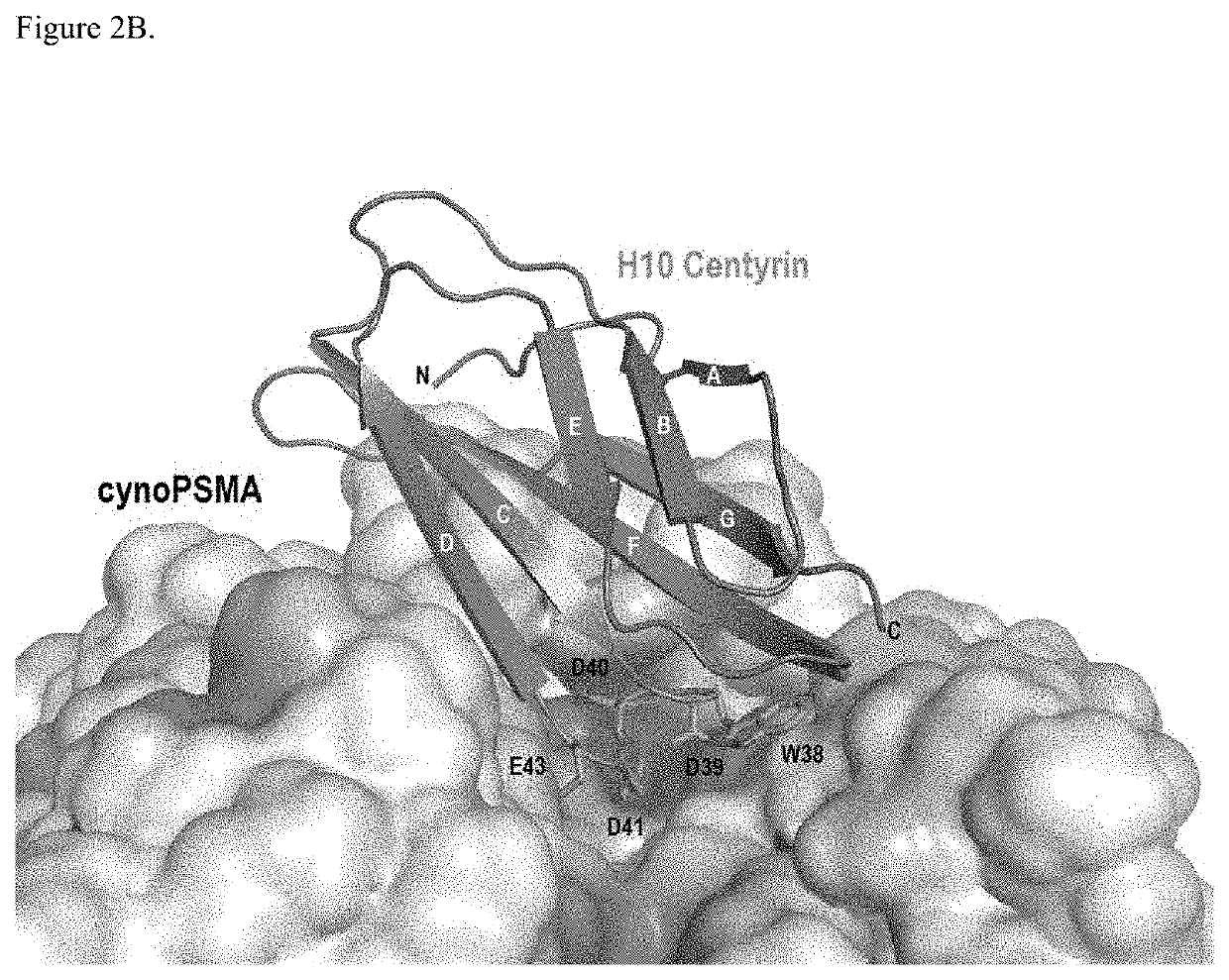
Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen Binding Fibronectin Type III Domains
ActiveUS20160326232A1Ensure adequate treatmentConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProstate specific membrane
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Fibronectin type III domain-based fusion proteins
ActiveUS10385115B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifConnective tissue peptidesDiseaseMedicine
Provided herein are fusion proteins including at least one binding polypeptide and at least one unstructured polypeptide. The fusion protein may further include at least one linker. Further provided are methods for determining the presence of a target in a sample, methods of treating a disease, methods of diagnosing a disease in a subject, and methods of determining the effectiveness of a treatment for a disease in a subject. The methods may include administering to the subject an effective amount of the fusion protein.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
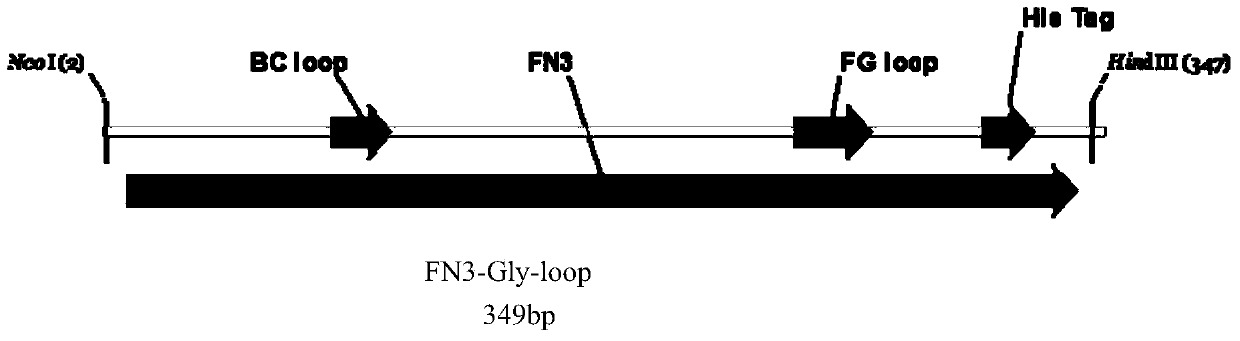
Method for building N-glycosylation efficiency detection receptor protein models in Escherichia coli by aid of skeleton proteins Fn3 (fibronectin type III domain)
ActiveCN105154461AImprove physical and chemical propertiesImprove solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliWestern blot
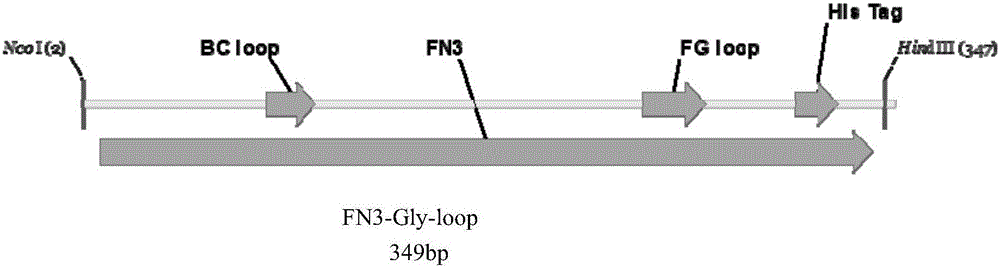
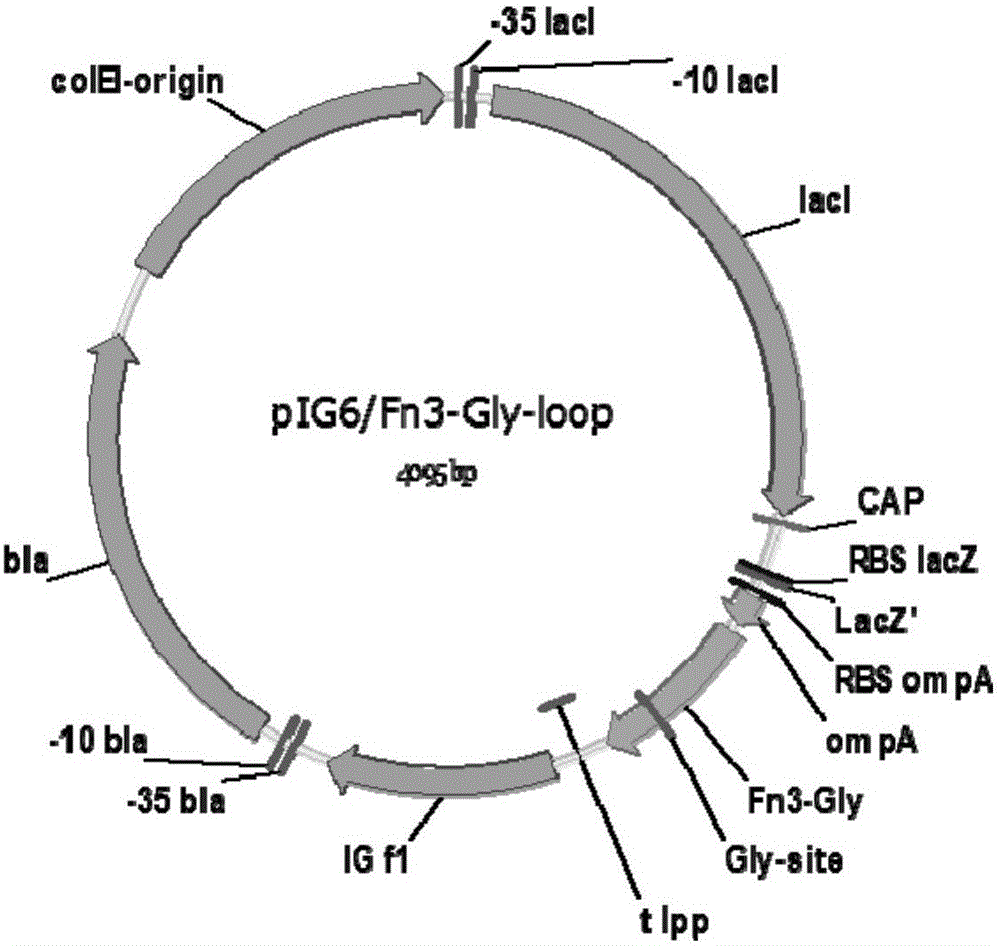
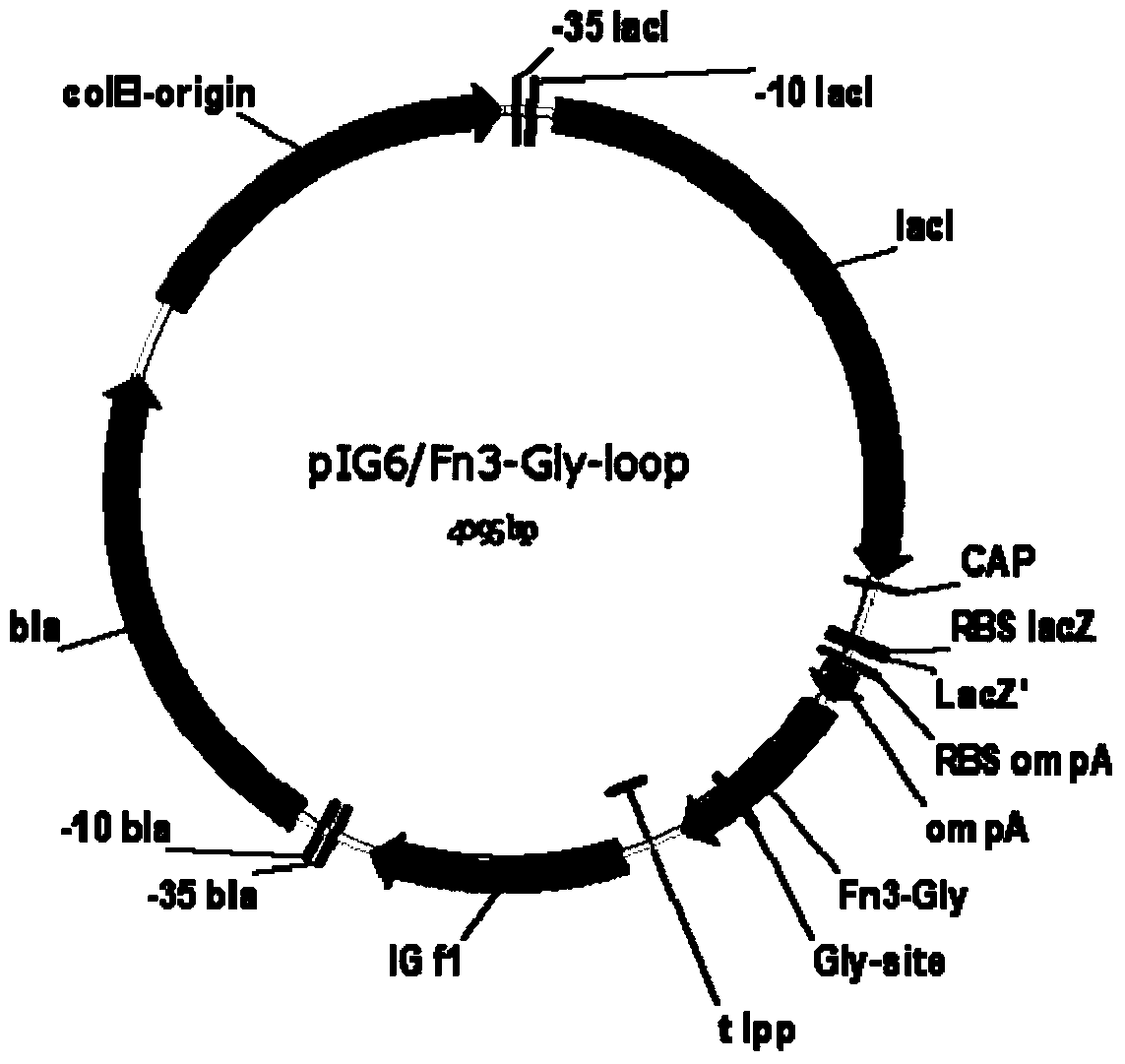
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnologies, and relates to a method for applying recombinant expression separated and purified human-derived protein Fn3 (fibronectin type III domain) mutants as N-glycosylation efficiency detection model proteins. The method includes steps of constructing Fn3-Gly-loop recombinant protein gene expression vectors of the Fn3 mutants; jointly transforming the constructed expression vectors into Escherichia coli engineering strains CLM37 by means of electric shock processes; screening the expression vectors by the aid of antibiotics to obtain positive clones. Recombinant proteins contain Fn3-Gly-loop proteins which are about to be modified by recombinant glycosyl, and the Fn3-Gly-loop fusion protein glycosylation efficiency can be detected by the aid of Western Blot processes. The method has the advantages that the skeleton proteins Fn3 in Escherichia coli are used as receptor proteins, accordingly, the model receptor proteins suitable for N-glycosylation modification efficiency research can be constructed, and the recombinant protein glycosylation efficiency can be easily, quickly and efficiently detected in the Escherichia coli.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Bispecific egfr/igfir binding molecules
The present invention relates to bispecific molecules comprising an EGFR binding domain and a distinct IGFIR binding domain for use in diagnostic, research and therapeutic applications. The invention further relates to cells comprising such proteins, polynucleotide encoding such proteins or fragments thereof, and vectors comprising the polynucleotides encoding the innovative proteins. Exemplary bispecific molecules include antibody-like protein dimers based on the tenth fibronectin type III domain.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method for preparing antigen substitute by using human fibronectin type III domain to display two antigenic epitopes
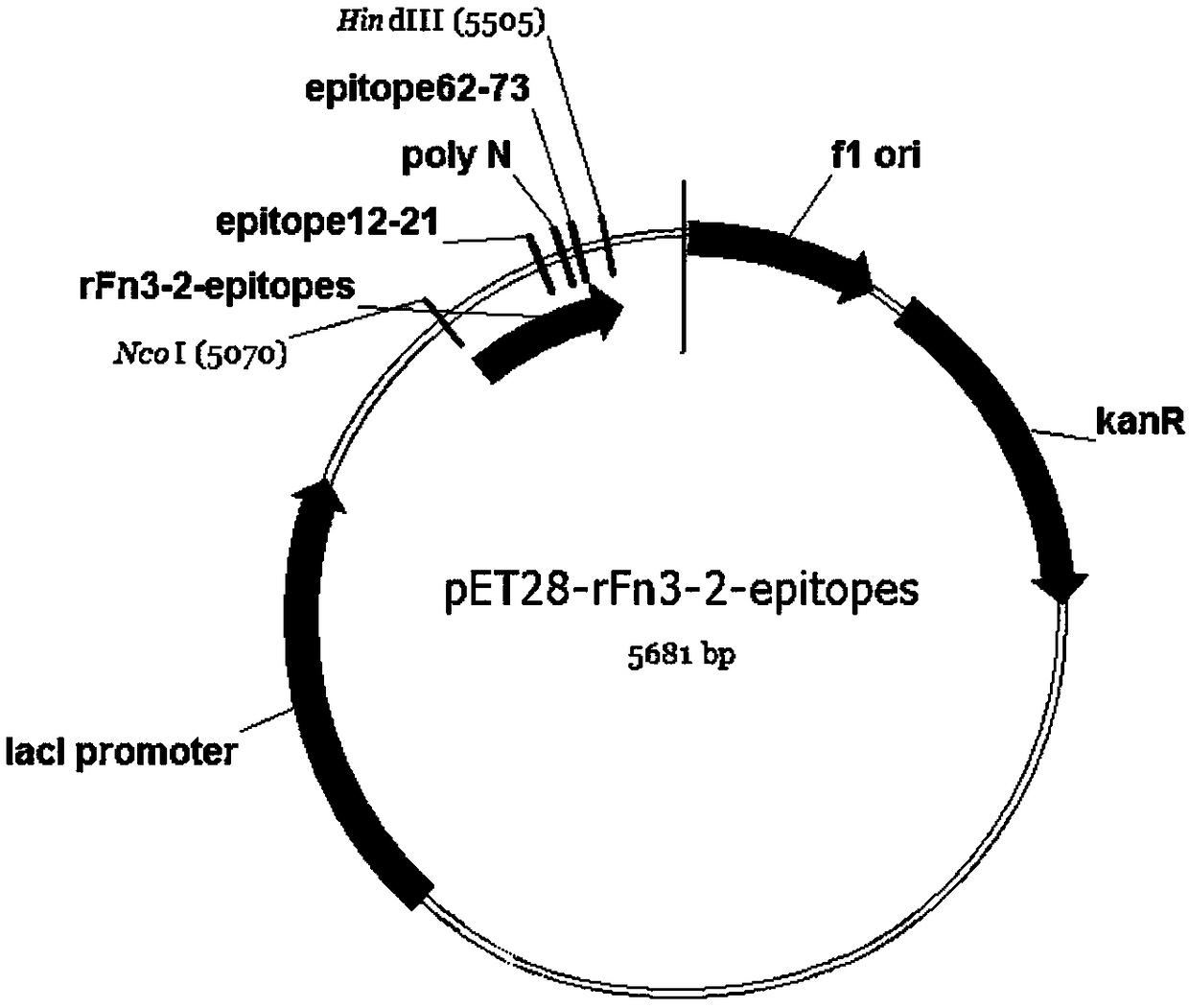
InactiveCN108179152AEasy to makeFast preparationConnective tissue peptidesBacteriaEscherichia coliEpitope
The present invention discloses a method for preparing an antigen substitute by using human fibronectin type III domain (Fn3) to display two antigenic epitopes. According to the method, through gene recombination, base sequences for encoding two antigenic epitopes are respectively recombined at the FG loop region and the 3' terminal of the sequence encoding Fn3 gene to from an Fn3 and double antigenic epitope fusion gene; and the fusion protein displaying the double antigenic epitope is efficiently and rapidly expressed and prepared with an Escherichia coli expression system. According to thepresent invention, the antigen substitute displaying the double antigenic epitopes can be simply, rapidly and efficiently prepared so as to establish the technical platform for the production of the corresponding immunological assay.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Cysteine engineered fibronectin type III domain binding molecules
The invention discloses cysteine engineered monospecific and bispecific EGFR and / or c-Met FN 3 domain containing molecules comprising one or more free cysteine amino acids. The molecules are prepared by mutagenizig a nucleic acid sequence of a parent molecule and replacing one or more amino acid residues by cysteine to encode the cysteine engineered FN3 domain containing monospecific or bispecific molecules; expressing the cysteine engineered FN3 domain containing molecules: and recovering the cysteine engineered FN3 domain containing molecule. Isolated cysteine engineered monospecific or bispecific FN3 domain containing molecules may be covalently attached to a detection label or a drug moiety and used therapeutically.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Chimeric Antigen Receptors Comprising BCMA-specific Fibronectin Type III Domains and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20190330361A1Stable and controllable CAR moleculesEasy to optimizeFibrinogenAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenAntigen receptors
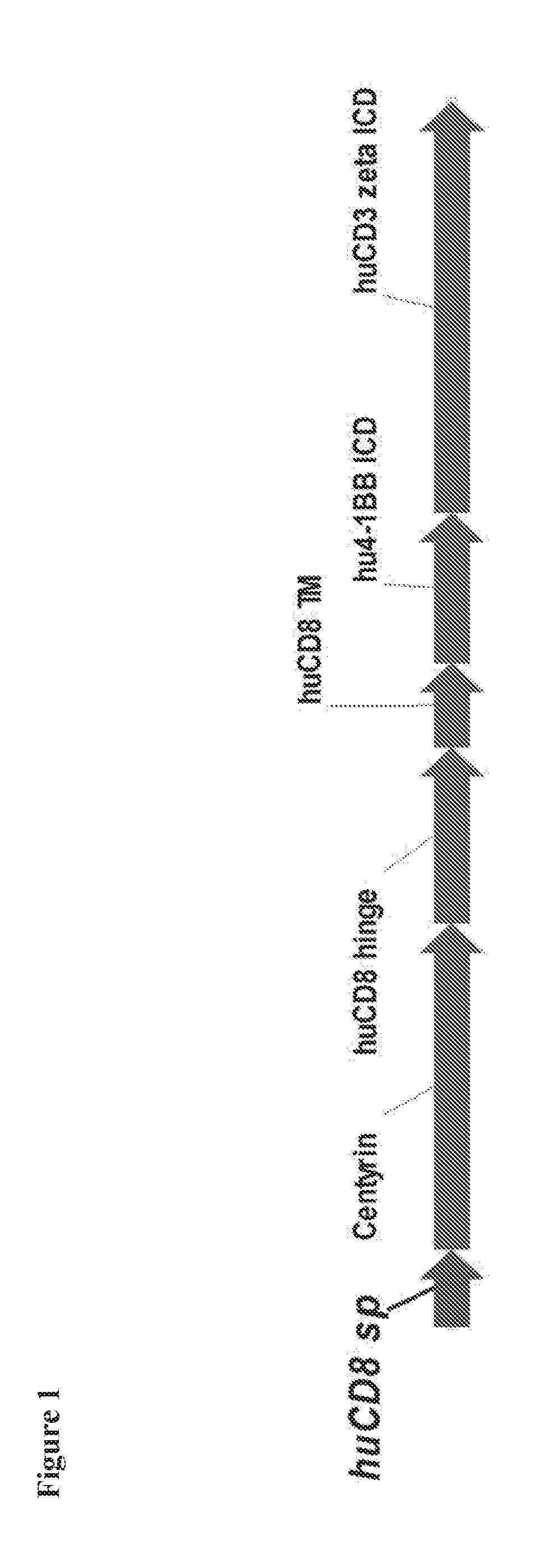
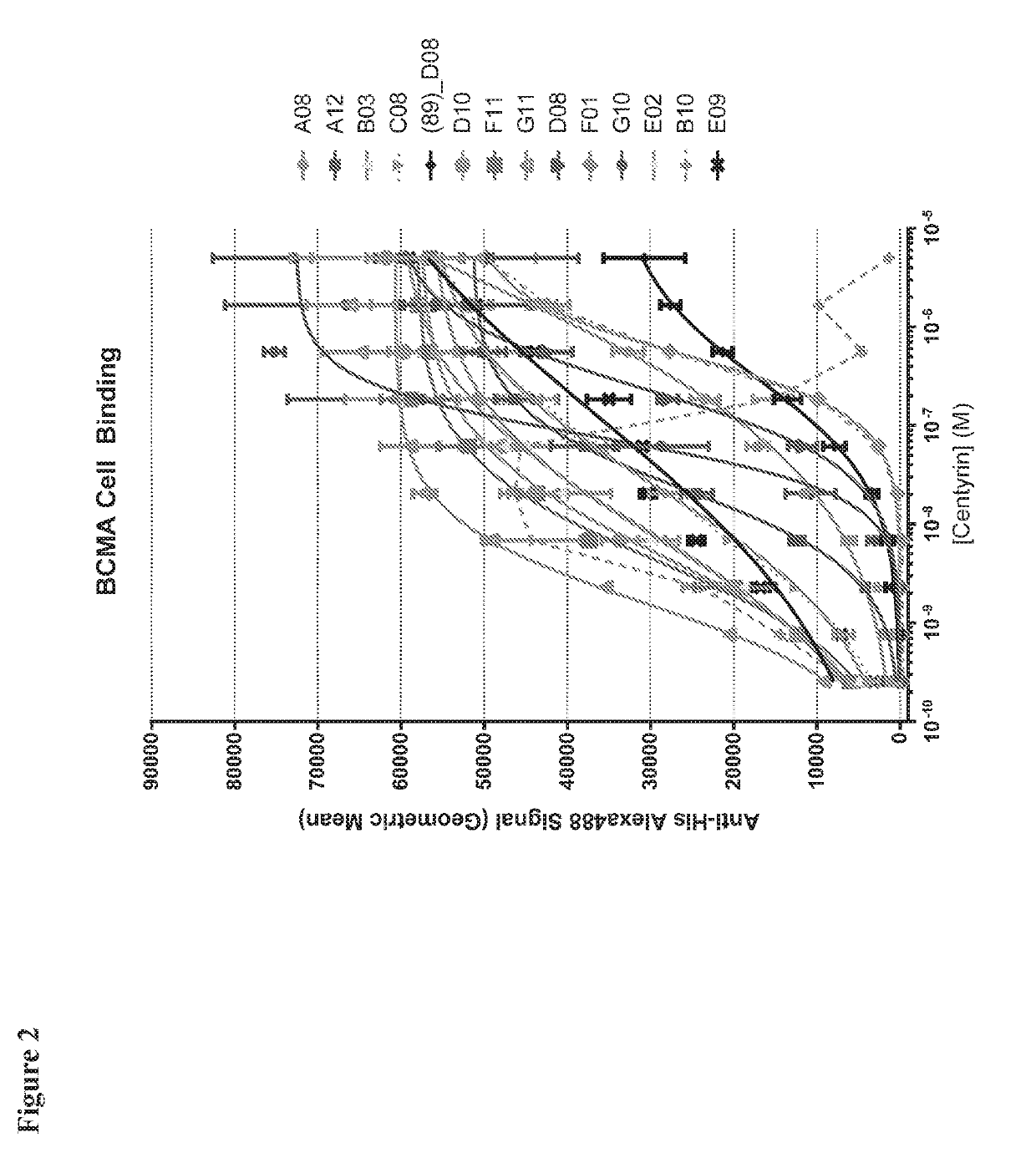
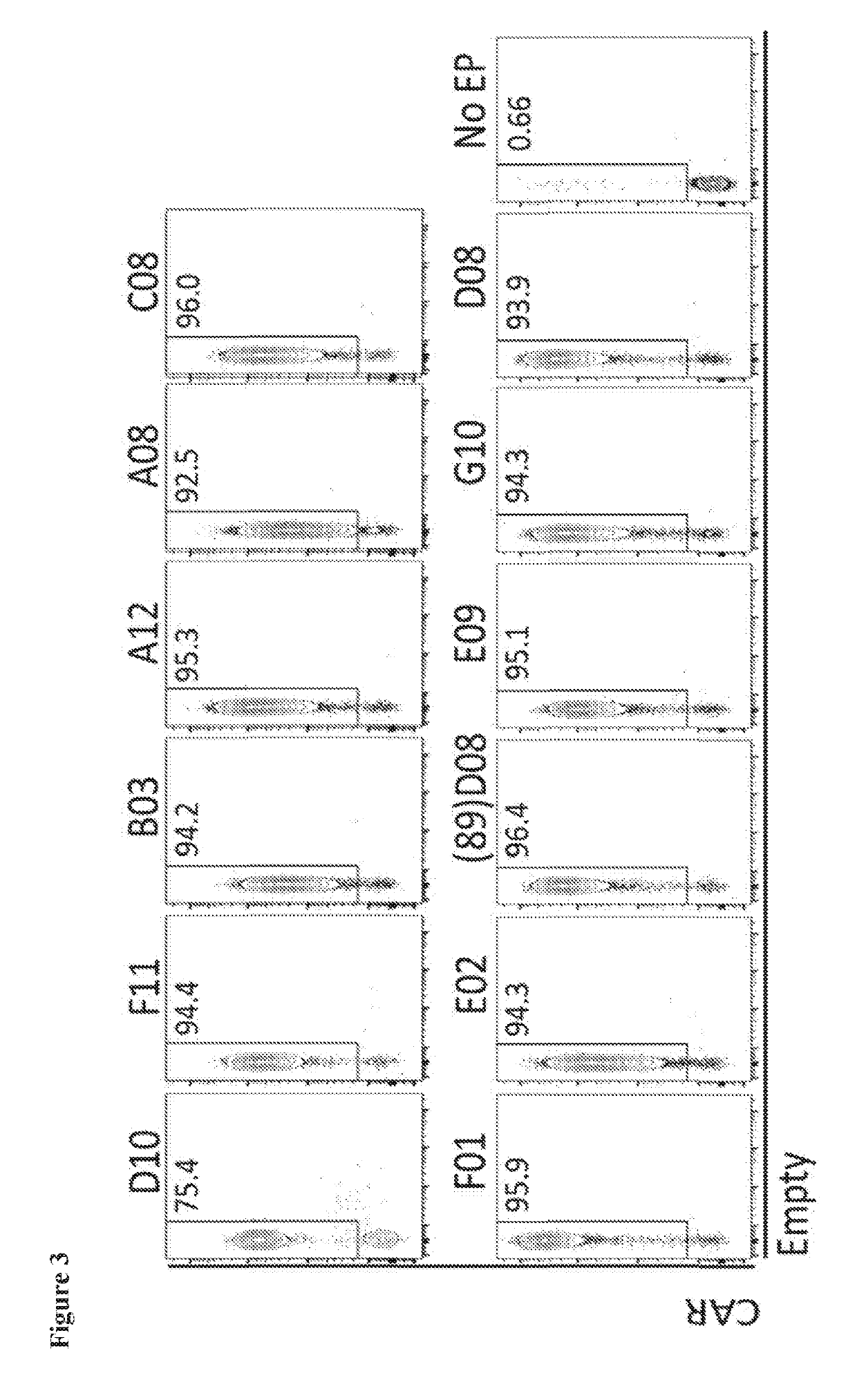
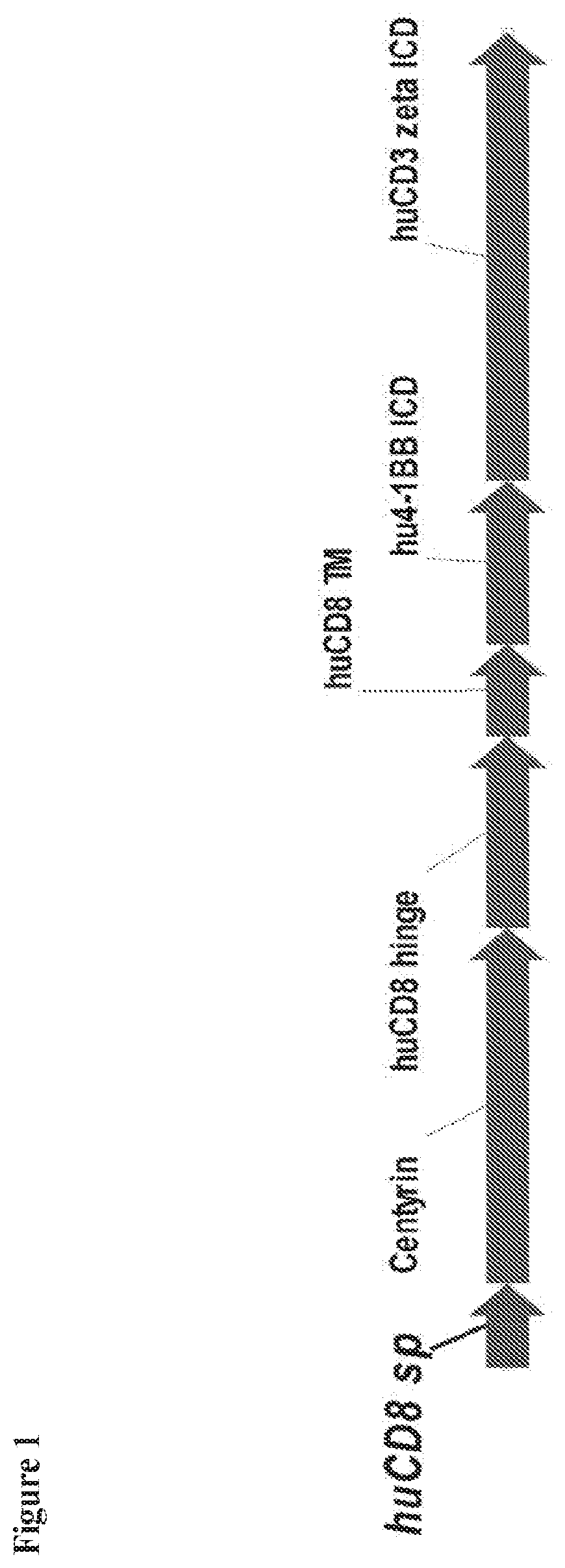
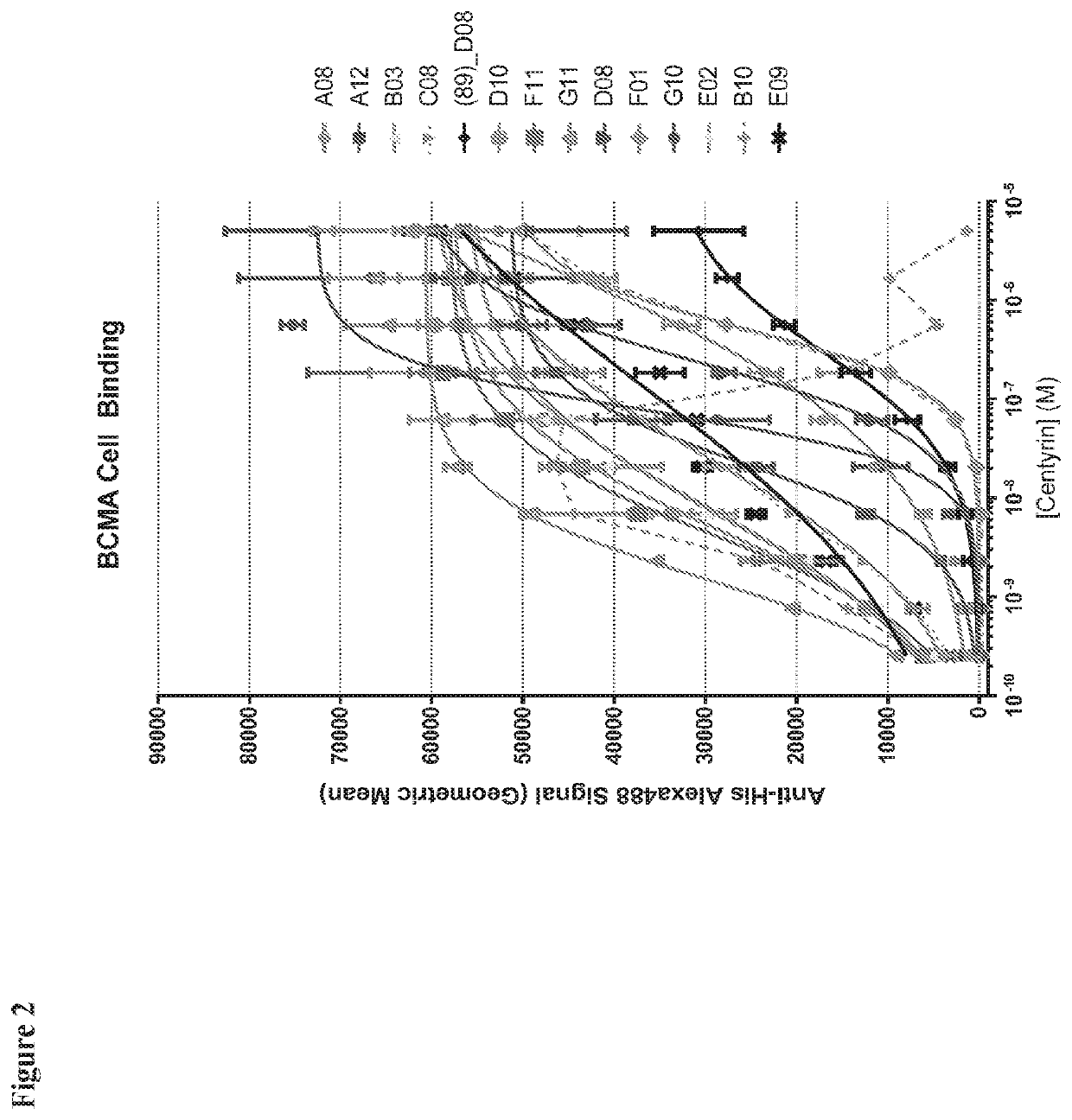
BCMA-specific fibronectin type III (FN3) domains, BCMA-targeting chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) comprising the FN3 domains, and engineered BCMA-targeting immune cells expressing the CARs are described. Also described are nucleic acids and expression vectors encoding the FN3 domains and the CARs, recombinant cells containing the vectors, and compositions comprising the engineered immune cells. Methods of making the FN3 domains, CARs, and engineered immune cells, and methods of using the engineered immune cells to treat diseases including cancer are also described.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
PD-L1 binding fibronectin type III domains
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
EGFR and C-Met fibronectin type III domain binding molecules
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Fast-off rate serum albumin binding fibronectin type III domains
ActiveUS10766946B2Extended half-lifeConnective tissue peptidesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousSerum protein albumin
Provided herein are polypeptides which include tenth fibronectin type III domains (10Fn3) that binds to serum albumin. Also provided are fusion molecules comprising a serum albumin binding 10Fn3 joined to a heterologous protein for use in diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
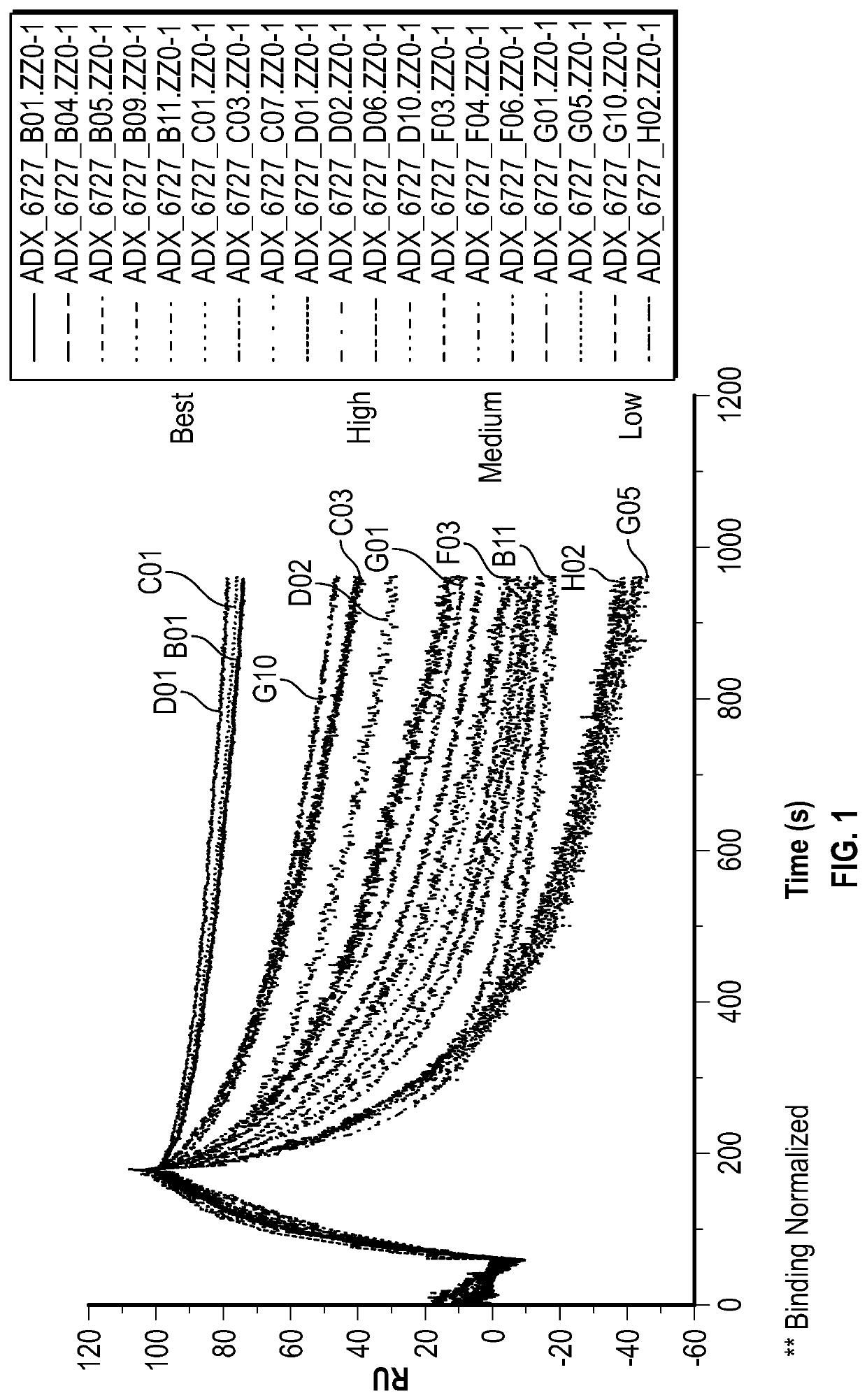
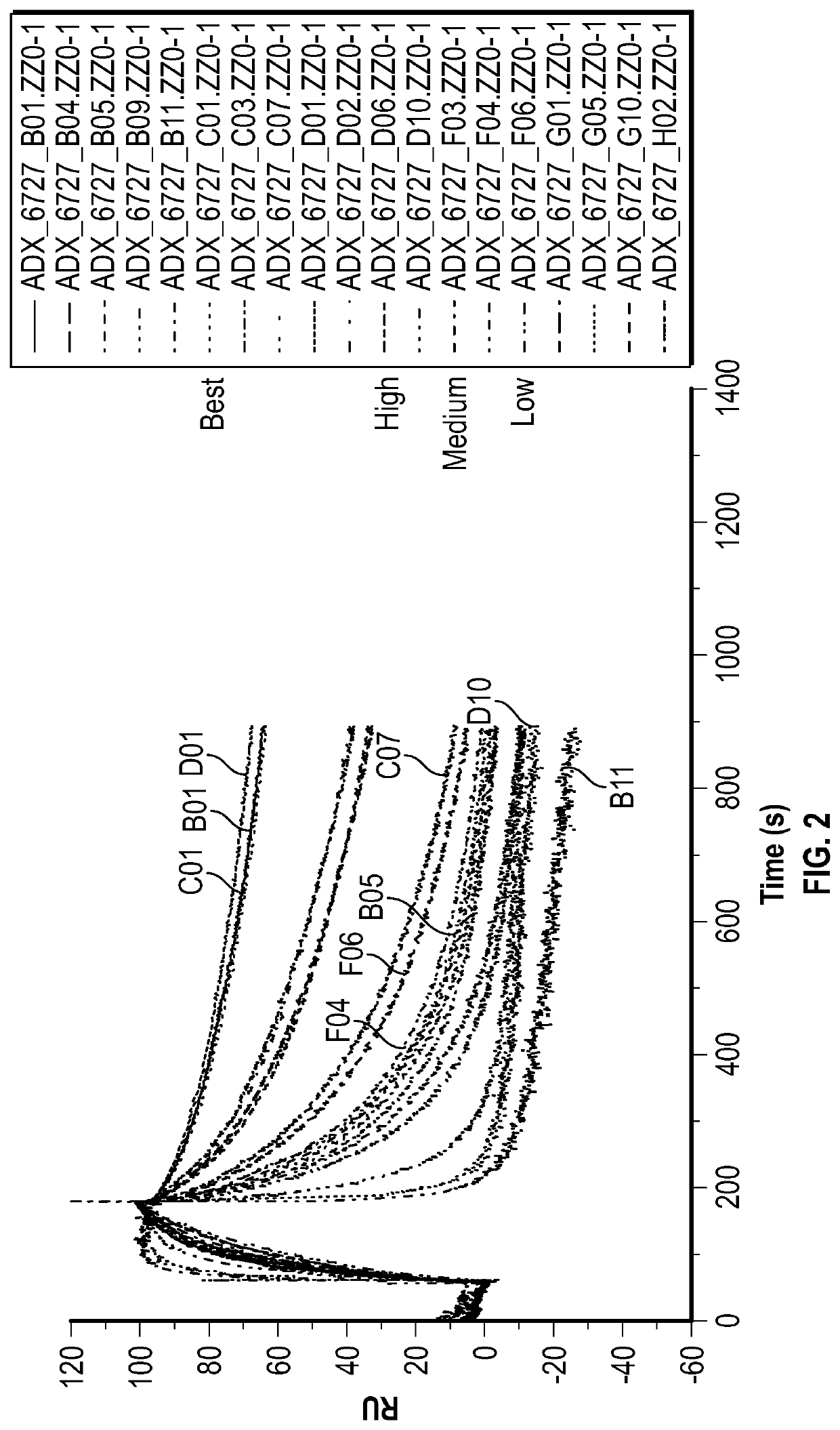
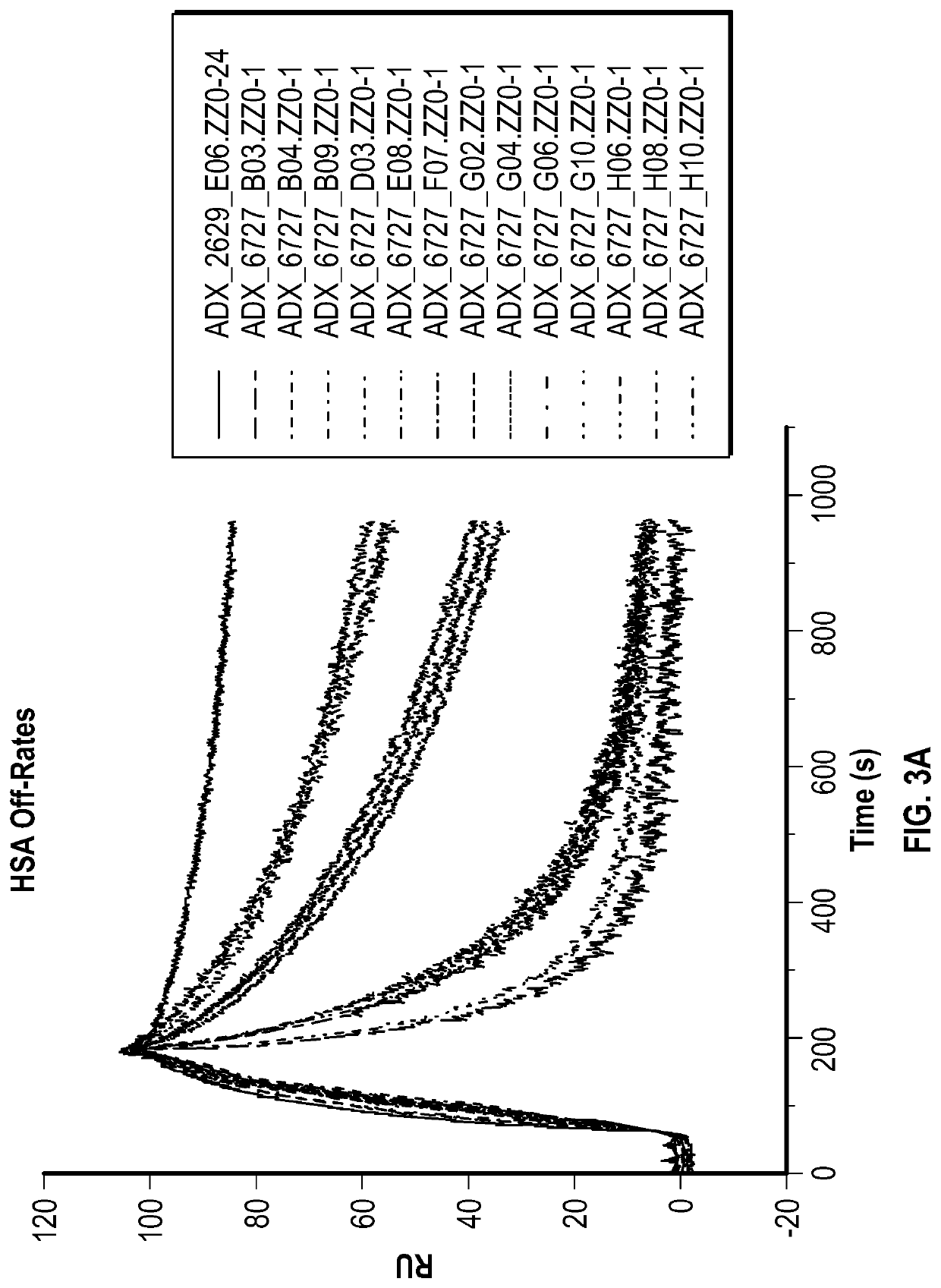
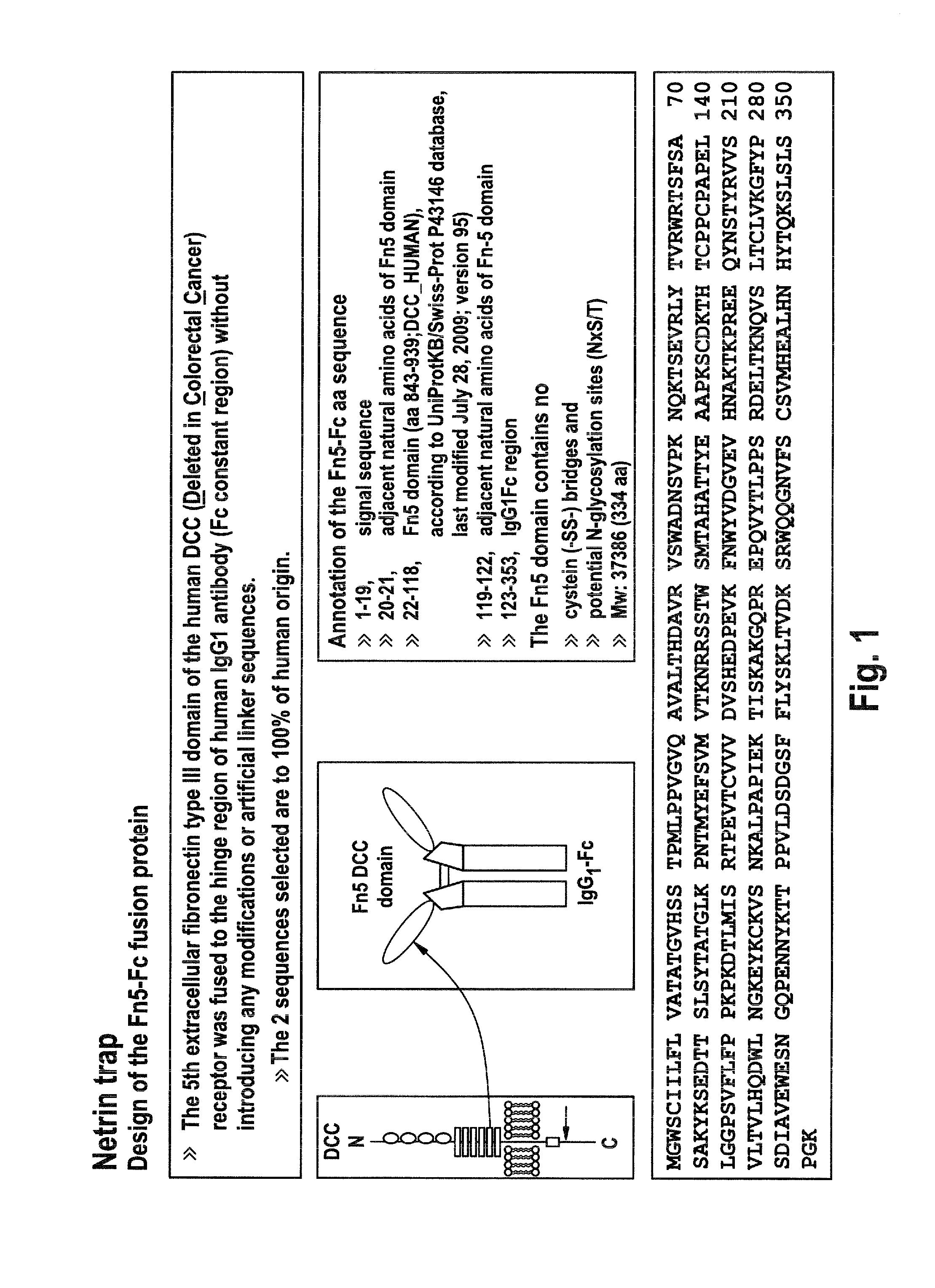
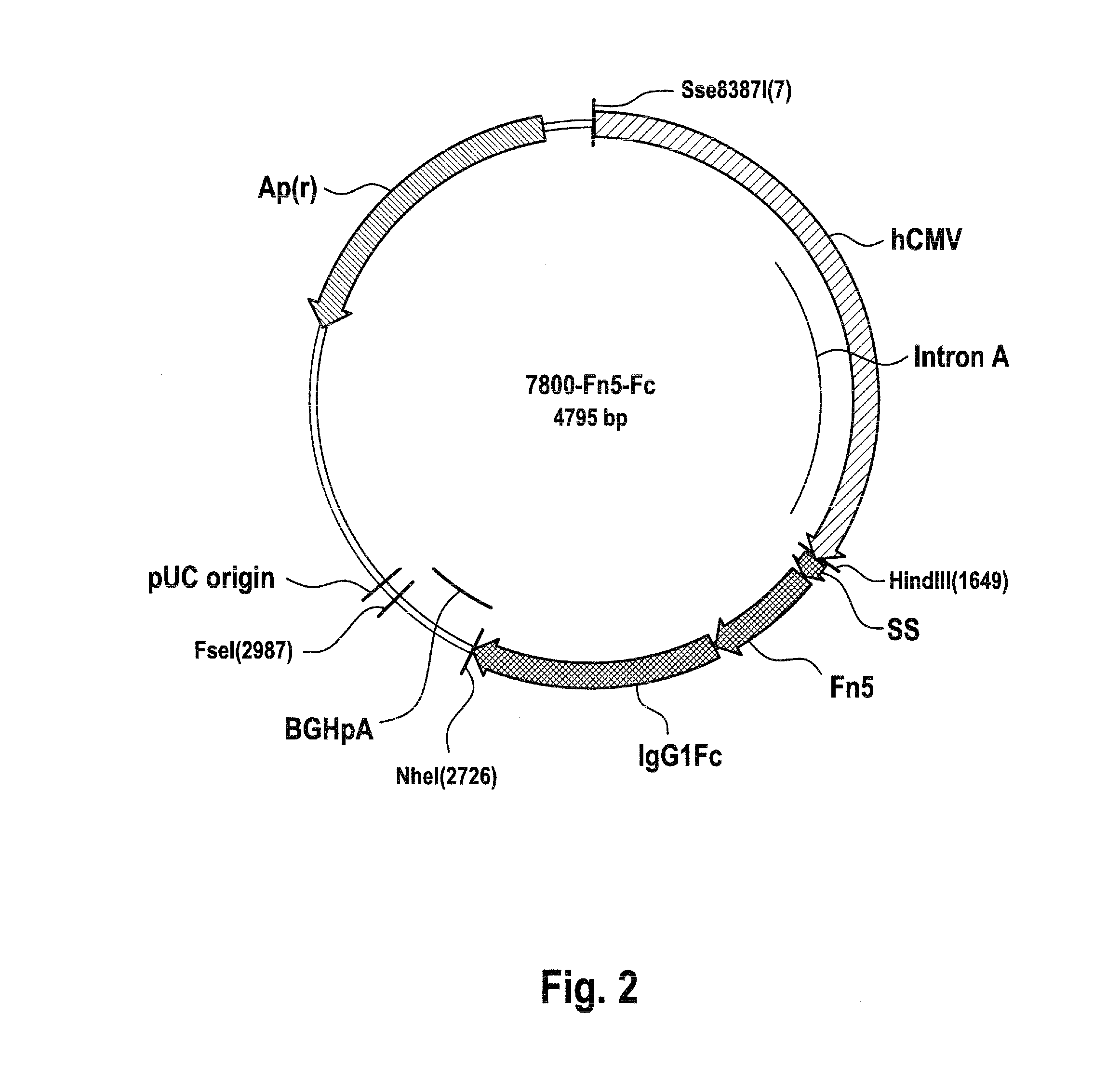
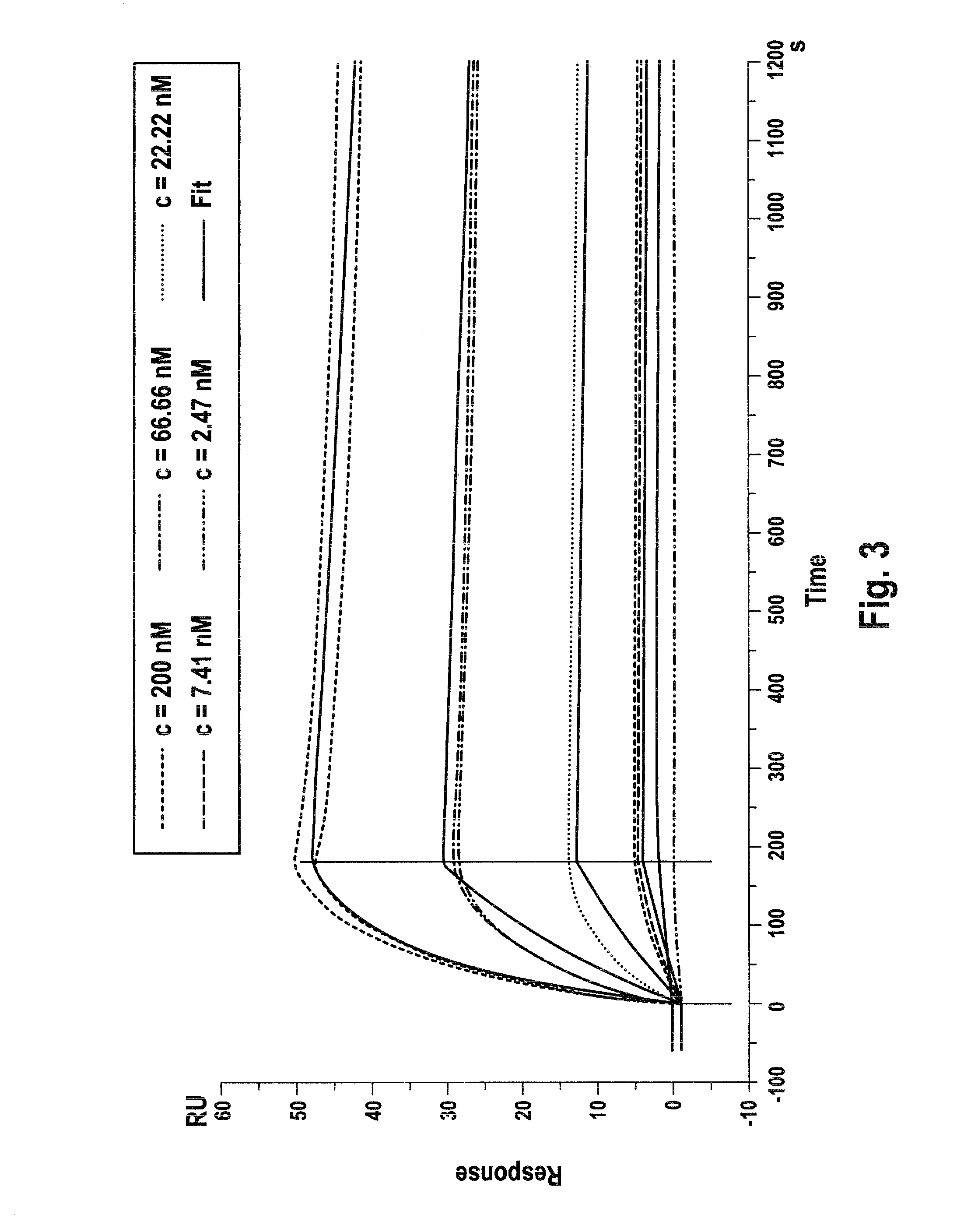
Recombinant fc-fusion protein of the fifth fibronectin type iii domain of dcc
InactiveUS20130336972A1Good pharmacological propertiesHigh affinityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesOncologyColorectal cancer
The present invention relates to DCC-fusion proteins, nucleic acid molecules encoding the DCC-fusion proteins, as well as methods for their production and their use in treatment of cancer such as colorectal cancer, NSCLC and metastatic breast cancer. The present invention also relates to methods of treating cancer such as colorectal cancer, NSCLC and metastatic breast cancer by administering DCC-fusion proteins.
Owner:KLEIN CHRISTIAN +5
PD-L1 Binding Fibronectin Type III Domains
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Fast-off rate serum albumin binding fibronectin type III domains
ActiveUS11434275B2Extended half-lifeConnective tissue peptidesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousSerum protein albumin
Provided herein are polypeptides which include tenth fibronectin type III domains (10Fn3) that binds to serum albumin. Also provided are fusion molecules comprising a serum albumin binding 10Fn3 joined to a heterologous protein for use in diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method for enhancing wound healing
InactiveUS20160256522A1High activityPromote wound healingPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismWound healingMedicine
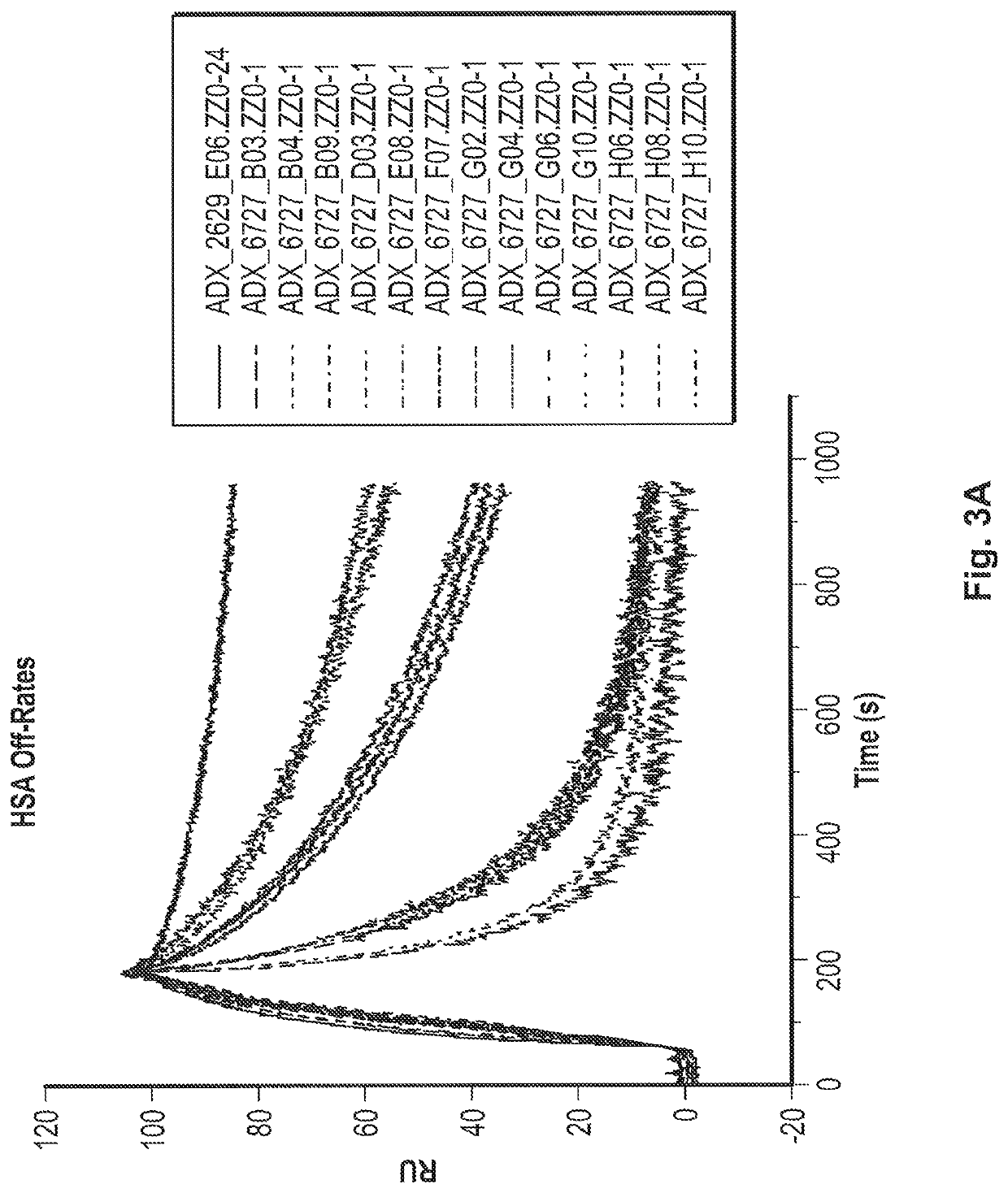
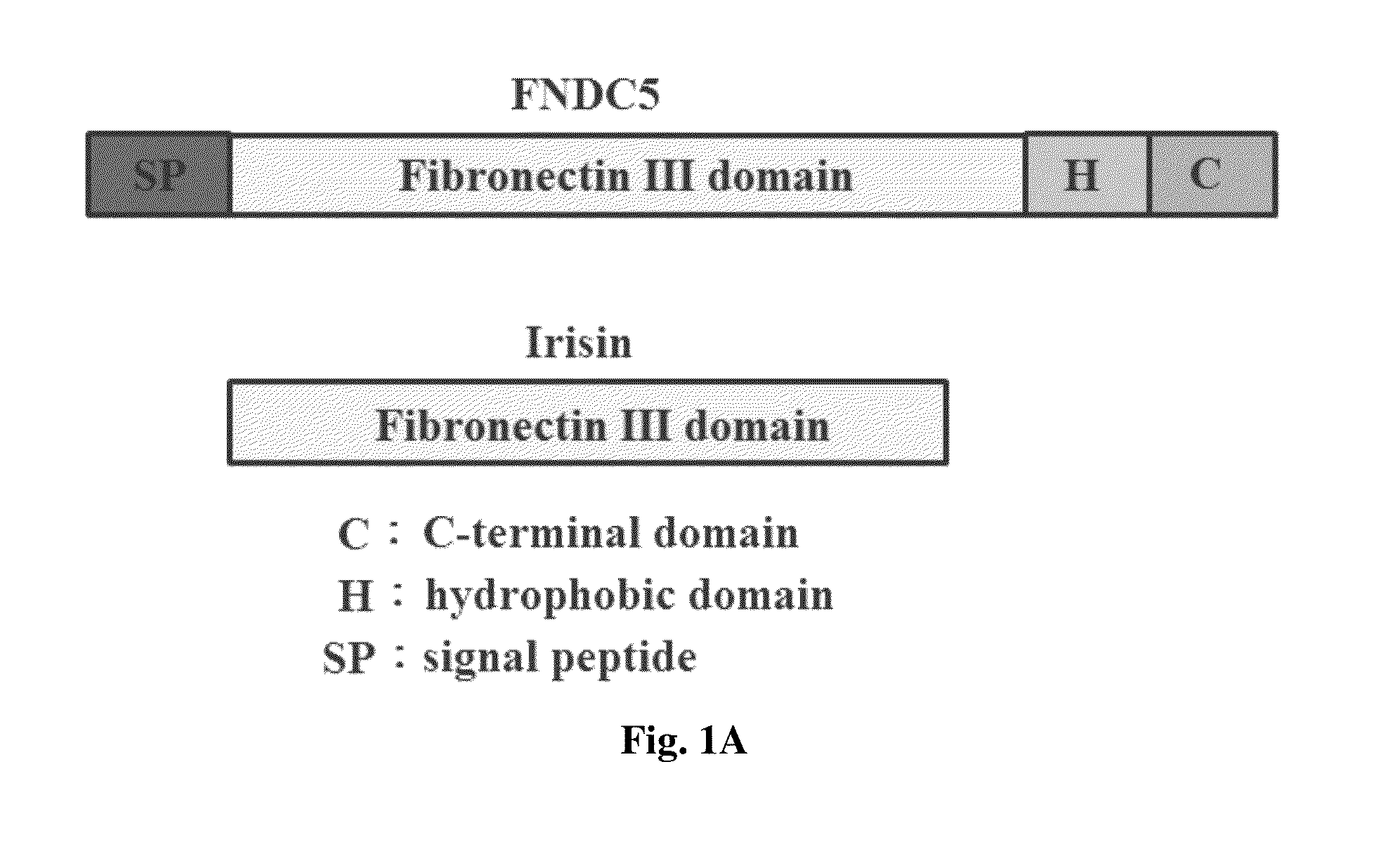
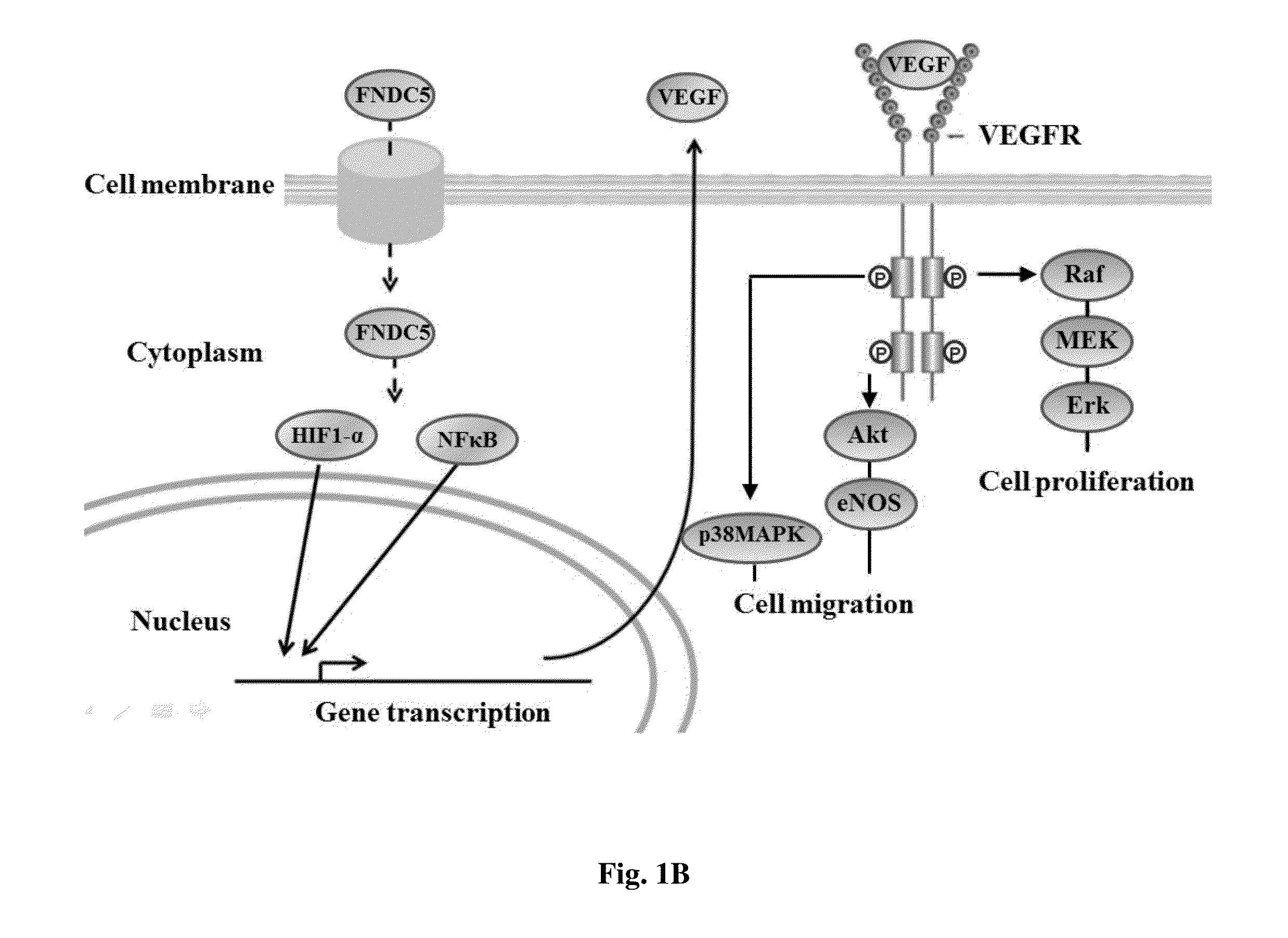
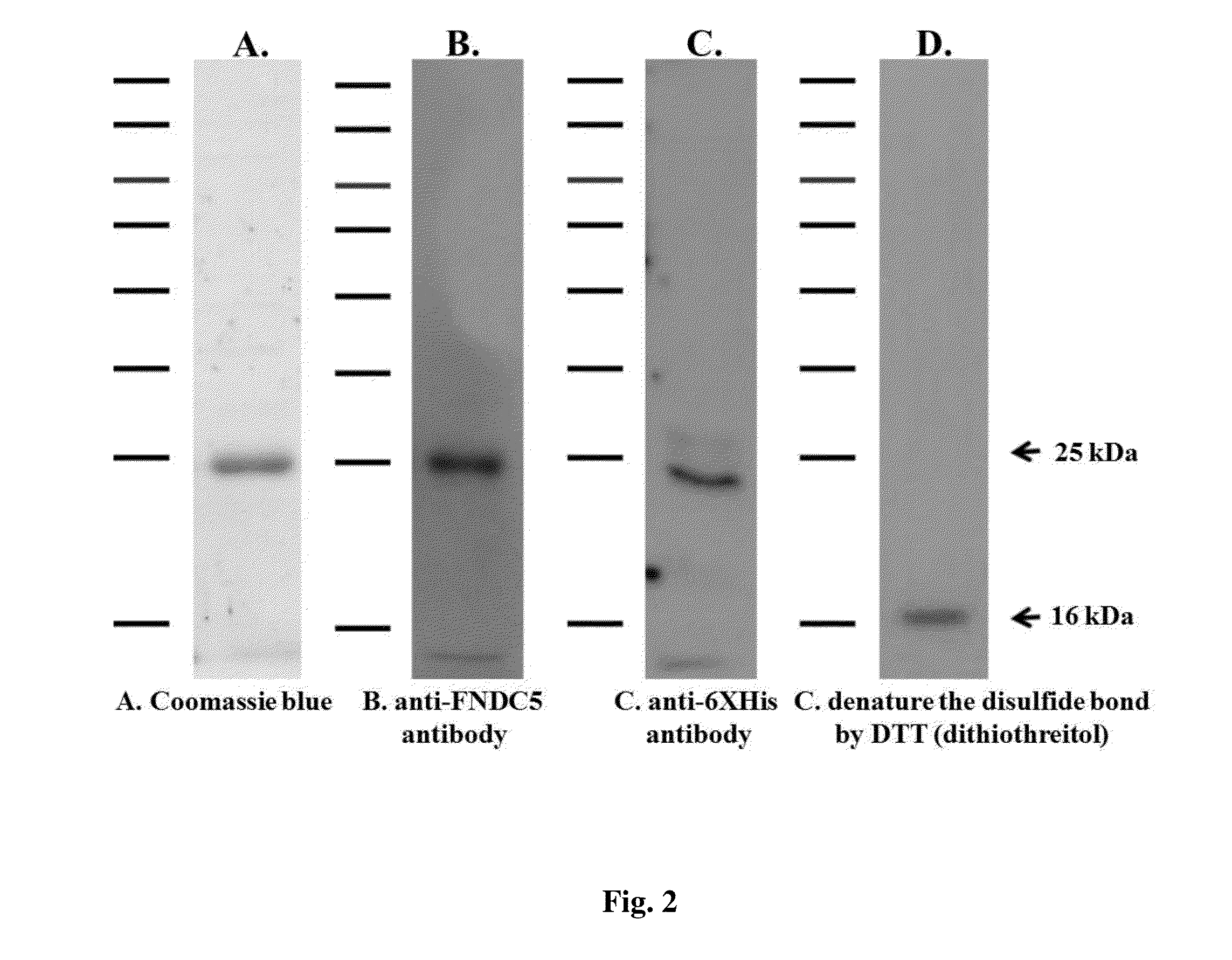
The invention relates to a method for enhancing wound healing in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering to the subject a composition comprising fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 (FNDC5) or its cleaved fragment irisin in an amount effective to enhance wound healing
Owner:NAT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
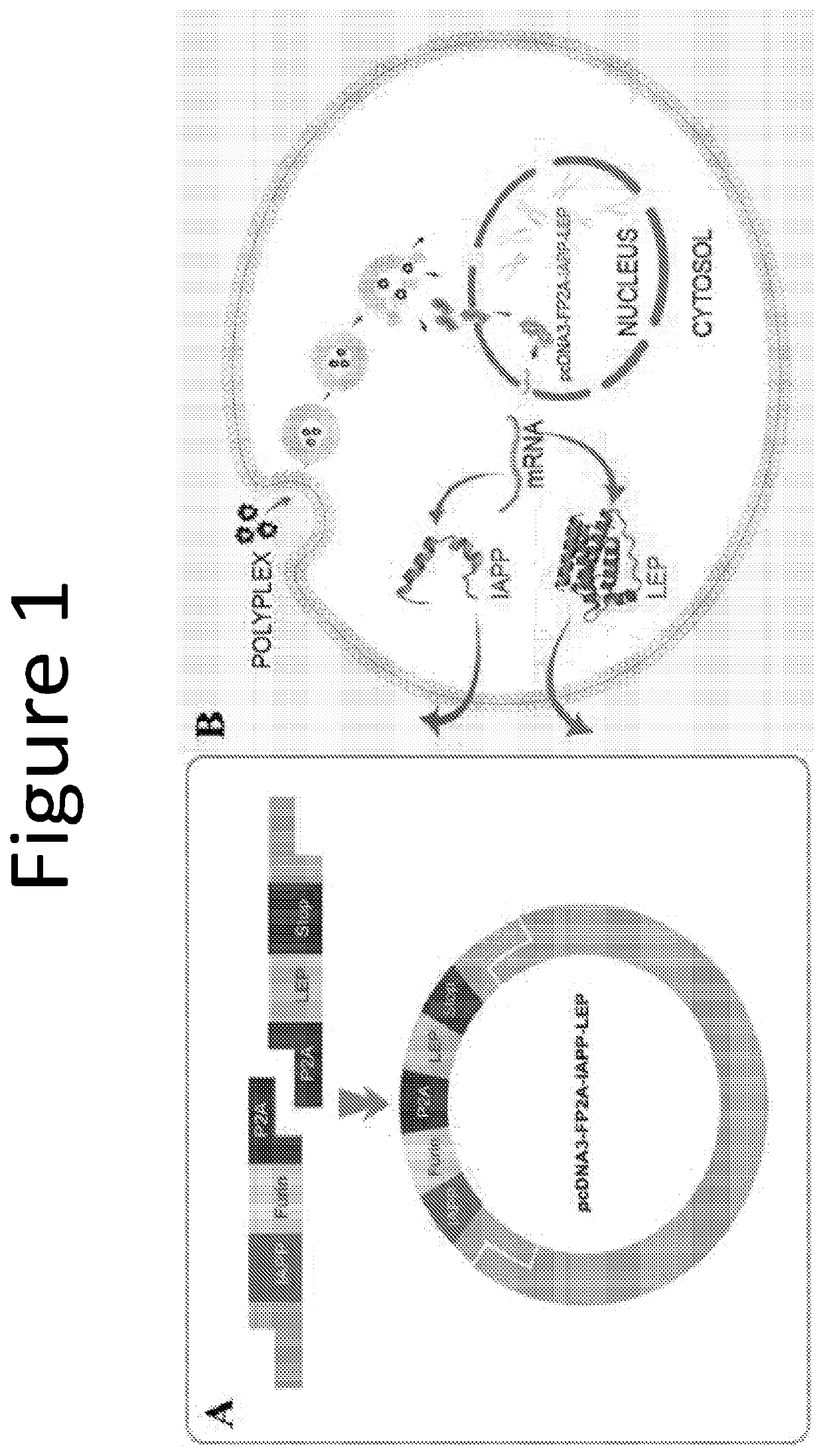
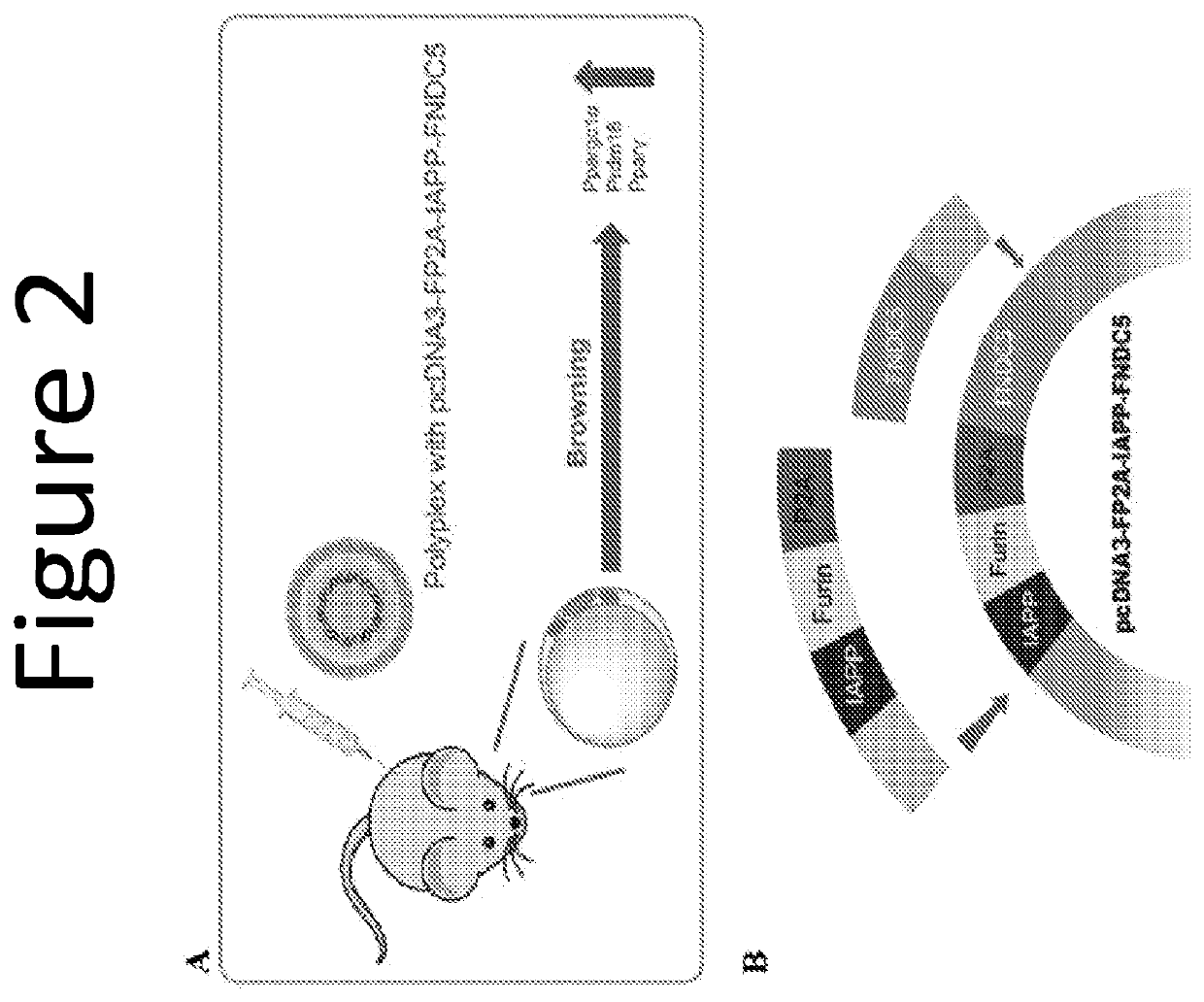
Combinatorial gene construct and non-viral delivery for anti-obesity
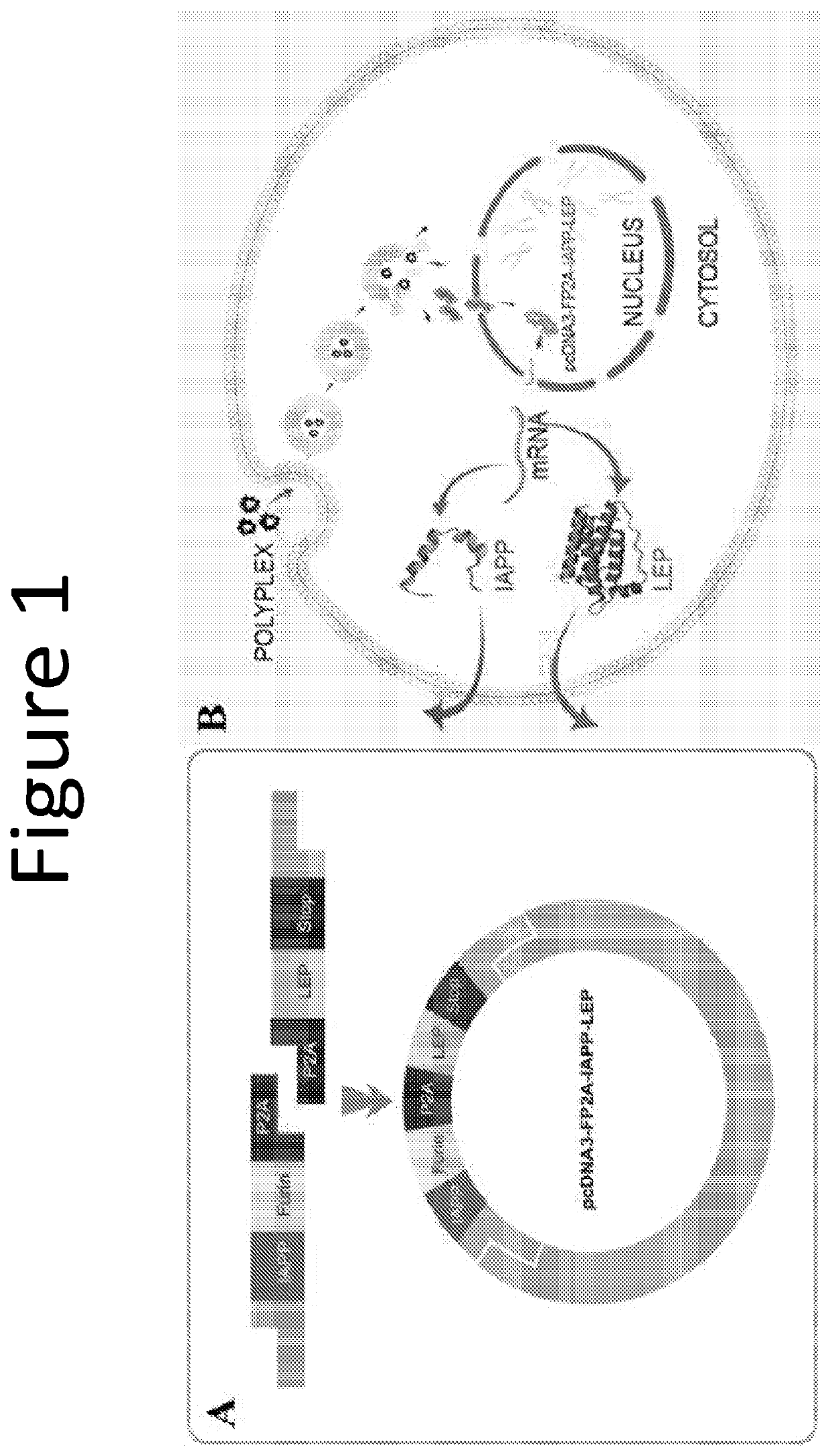
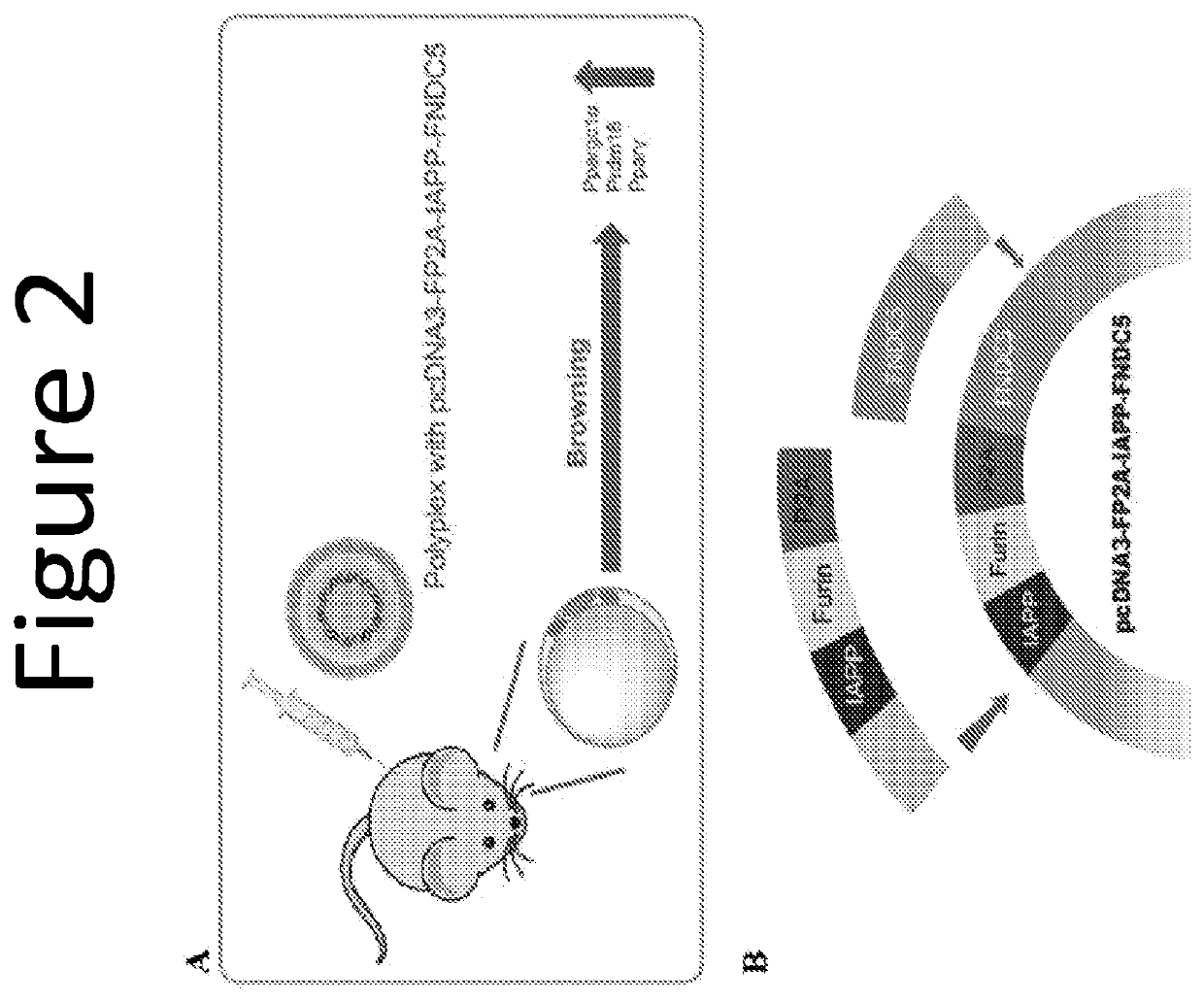
The invention provides a plasmid comprising two or more anti-obesity genes. Also provided by the invention are compositions and host cells comprising the plasmid and methods of increasing the metabolic activity in a mammal. The invention provides a plasmid comprising two or more of (a) a nucleic acid sequence encoding islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), (b) a nucleic acid sequence encoding leptin (LEP), and (c) a nucleic acid sequence encoding fibronectin type III domain containing 5 (FNDC5).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Bispecific EGFR/IGFIR binding molecules
The present invention relates to bispecific molecules comprising an EGFR binding domain and a distinct IGFIR binding domain for use in diagnostic, research and therapeutic applications. The invention further relates to cells comprising such proteins, polynucleotide encoding such proteins or fragments thereof, and vectors comprising the polynucleotides encoding the innovative proteins. Exemplary bispecific molecules include antibody-like protein dimers based on the tenth fibronectin type III domain.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Cysteine engineered fibronectin type iii domain binding molecules
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Combinatorial gene construct and non-viral delivery for Anti-obesity
ActiveUS20200247864A1Improve metabolic activityConnective tissue peptidesObesity gene productsAmyloidFNDC5
The invention provides a plasmid comprising two or more anti-obesity genes. Also provided by the invention are compositions and host cells comprising the plasmid and methods of increasing the metabolic activity in a mammal. The invention provides a plasmid comprising two or more of (a) a nucleic acid sequence encoding islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), (b) a nucleic acid sequence encoding leptin (LEP), and (c) a nucleic acid sequence encoding fibronectin type III domain containing 5 (FNDC5).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Prostate specific membrane antigen binding fibronectin type III domains
ActiveUS10844111B2Connective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProstate specific membrane
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
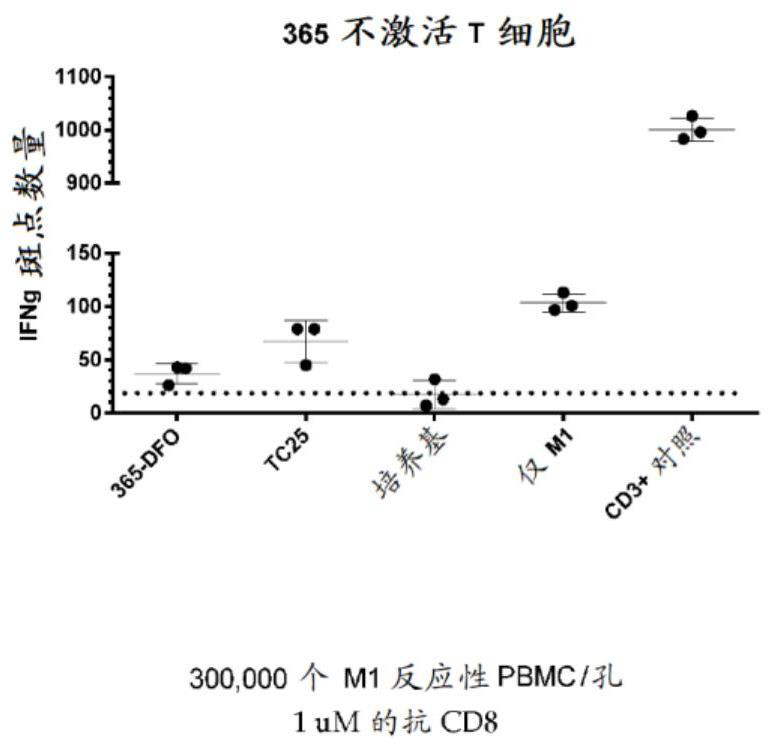
Fibronectin type III domain that binds CD8A
ActiveCN110225770BConnective tissue peptidesGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsPolynucleotideCD8A
Fibronectin type III domain (FN3) specifically binding to CD8A, related polynucleotides capable of encoding CD8A-specific FN3 domains, cells expressing FN3 domains, and related vectors, and detectably labeled FN3 domains Can be used in therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
A method for establishing an n-glycosylation receptor protein model in Escherichia coli using the skeleton protein fn3
ActiveCN105154462BImprove physical and chemical propertiesImprove physical and chemical properties such as solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliProkaryote organisms
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Antigen Binding Regions Against Fibronectin Type III Domains and Methods of Using The Same
ActiveUS20190016789A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseAntigen Binding Fragment
Fibronectin type III (FN3) domain antibodies, polynucleotides capable of encoding the FN3 domain antibodies or antigen-binding fragments, cells expressing FN3 domain antibodies or antigen-binding fragments, as well as associated vectors and detectably labeled FN3 domain antibodies or antigen-binding fragments may be used to engineer FN3 domain-targeting chimeric antigen receptors (CARs). Methods of making the FN3 domain antibodies, CARs, and engineered immune cells, and methods of using the engineered immune cells are applicable to treat diseases including cancer.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
A method for establishing a receptor protein model for n-glycosylation efficiency detection in Escherichia coli using the skeleton protein fn3
ActiveCN105154461BImprove physical and chemical propertiesImprove solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliReceptor
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnologies, and relates to a method for applying recombinant expression separated and purified human-derived protein Fn3 (fibronectin type III domain) mutants as N-glycosylation efficiency detection model proteins. The method includes steps of constructing Fn3-Gly-loop recombinant protein gene expression vectors of the Fn3 mutants; jointly transforming the constructed expression vectors into Escherichia coli engineering strains CLM37 by means of electric shock processes; screening the expression vectors by the aid of antibiotics to obtain positive clones. Recombinant proteins contain Fn3-Gly-loop proteins which are about to be modified by recombinant glycosyl, and the Fn3-Gly-loop fusion protein glycosylation efficiency can be detected by the aid of Western Blot processes. The method has the advantages that the skeleton proteins Fn3 in Escherichia coli are used as receptor proteins, accordingly, the model receptor proteins suitable for N-glycosylation modification efficiency research can be constructed, and the recombinant protein glycosylation efficiency can be easily, quickly and efficiently detected in the Escherichia coli.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Chimeric antigen receptors comprising bcma-specific fibronectin type iii domains and uses thereof
InactiveUS20220031822A1More stable and controllable CAR moleculesEasy to optimizeFibrinogenAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseAntigen receptor
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Cd8a-binding fibronectin type iii domains
ActiveCN110225770AConnective tissue peptidesGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsFibronectinsPolynucleotide
Fibronectin type III domains (FN3) that specifically bind to CD8A, related polynucleotides capable of encoding CD8A-specific FN3 domains, cells expressing the FN3 domains, as well as associated vectors, and detectably labeled FN3 domains are useful in therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Antigen Binding Regions Against Fibronectin Type III Domains and Methods of Using the Same
PendingUS20220127343A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseAntigen receptor
Fibronectin type III (FN3) domain antibodies, polynucleotides capable of encoding the FN3 domain antibodies or antigen-binding fragments, cells expressing FN3 domain antibodies or antigen-binding fragments, as well as associated vectors and detectably labeled FN3 domain antibodies or antigen-binding fragments may be used to engineer FN3 domain-targeting chimeric antigen receptors (CARs). Methods of making the FN3 domain antibodies, CARs, and engineered immune cells, and methods of using the engineered immune cells are applicable to treat diseases including cancer.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com