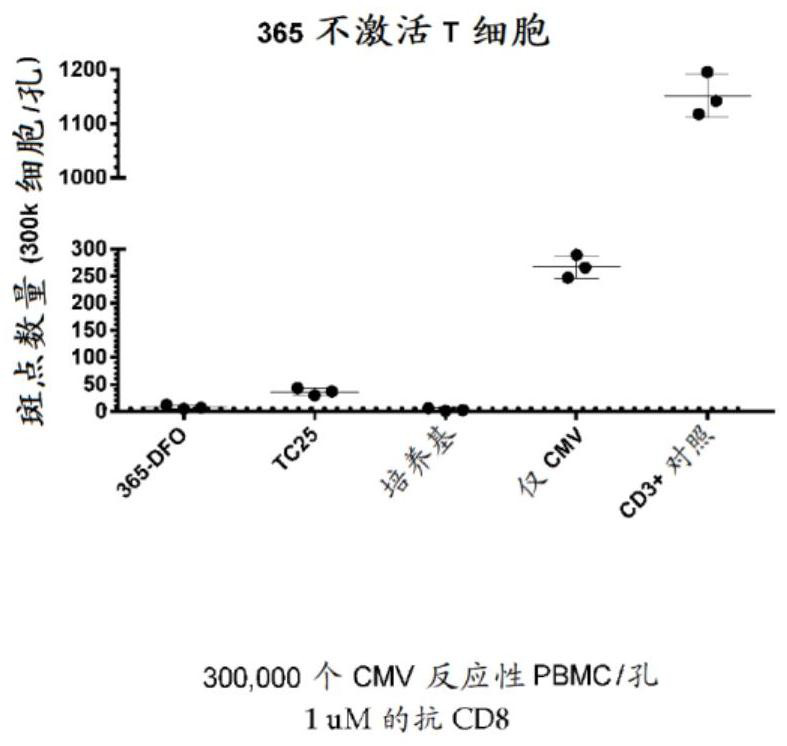
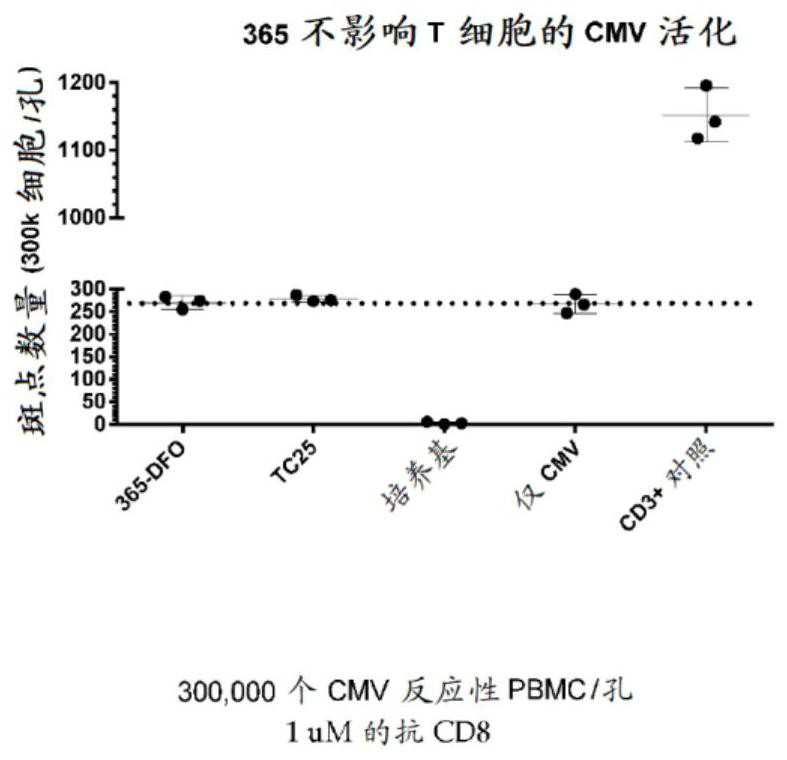
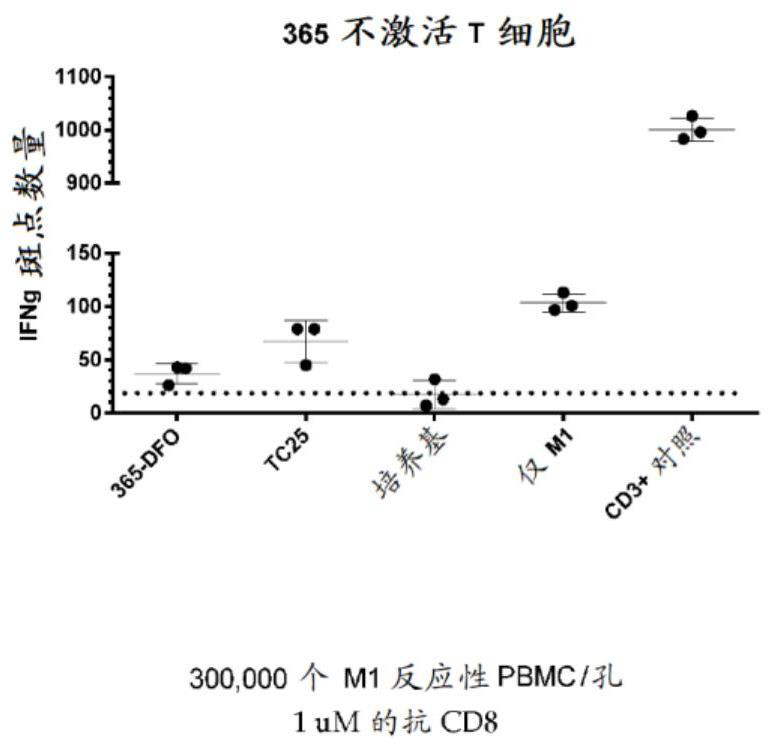
Fibronectin type III domain that binds CD8A
A protein and conjugation technology, applied in the field of fibronectin type III domain, can solve the problems of changes in the number and location of immune cells, and the inability to reflect dynamic and spatial information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0119] The invention also provides the following non-limiting embodiments.
[0120] 1) An isolated FN3 domain that specifically binds a human CD8A protein comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:35.
[0121] 2) The isolated FN3 domain of embodiment 1, wherein said FN3 domain cross-reacts with a cynomolgus monkey CD8A protein comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:271.
[0122] 3) The isolated FN3 domain of embodiment 2, wherein
[0123] a) the FN3 domain is based on the Tencon sequence of SEQ ID NO:1;
[0124] b) said FN3 domain is based on the Tencon27 sequence of SEQ ID NO:4; and / or
[0125] c) said FN3 domain is isolated from a library comprising the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2, 3, 5, 6, 7 or 8.
[0126] 4) The isolated FN3 domain of embodiment 3, wherein said FN3 domain is conjugated to a second molecule.
[0127] 5) The isolated FN3 domain of embodiment 4, wherein said second molecule is a detectable label.
[0128] 6) The isolated FN3 domain of embodim...
Embodiment 1
[0149] Example 1. Construction of a TENCON library with randomized loops
[0150] Tencon (SEQ ID NO:1) is an immunoglobulin-like scaffold, fibronectin type III (FN3) domain, designed from the consensus sequence of 15 FN3 domains from human tenascin-C (Jacobs et al. , Protein Engineering, Design, and Selection, 25:107-117, 2012; US Patent No. 8,278,419). The crystal structure of Tencon shows six surface-exposed loops connecting seven β-strands. Selected residues within these loops, or within each loop, can be randomized in order to construct libraries of fibronectin type III (FN3) domains that can be used to select novel molecules that bind to specific targets.
[0151] Tencon:
[0152] LPAPKNLVVSEVTEDSLRLSWTAPDAAFDSFLIQYQESEKVGEAINLTVPGSERSYDLTGLKPGTEYTVSIYGVKGGHRSNPLSAEFTT (SEQ ID NO 1):
[0153] Generate various libraries using tencon scaffolds and various design strategies. In general, libraries TCL1 and TCL2 produced good binders. Generation of TCL1 and TCL2 libraries...
Embodiment 2
[0206] Example 2: Generation of TENCON libraries with alternative binding surfaces
[0207] The choice of residues to be randomized in a particular library design determines the overall shape of the resulting interaction surface. X-ray crystallographic analysis of maltose-binding protein (MBP)-binding FN3 domain-containing scaffold proteins selected from a library in which the BC, DE, and FG loops were randomized revealed a largely curved interface suitable for the MBP active site (Koide et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:6632-6637, 2007). In contrast, ankyrin repeat scaffold proteins that selectively bind to MBP were found to have a flatter interaction surface and bind to the outer surface of MBP away from the active site (Binz et al., Nat Biotechnol 22:575-582, 2004 ). These results suggest that the shape of the binding surface of scaffold molecules (curved vs. flat) can determine which target proteins or specific epitopes on those target proteins can be efficiently bound ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com