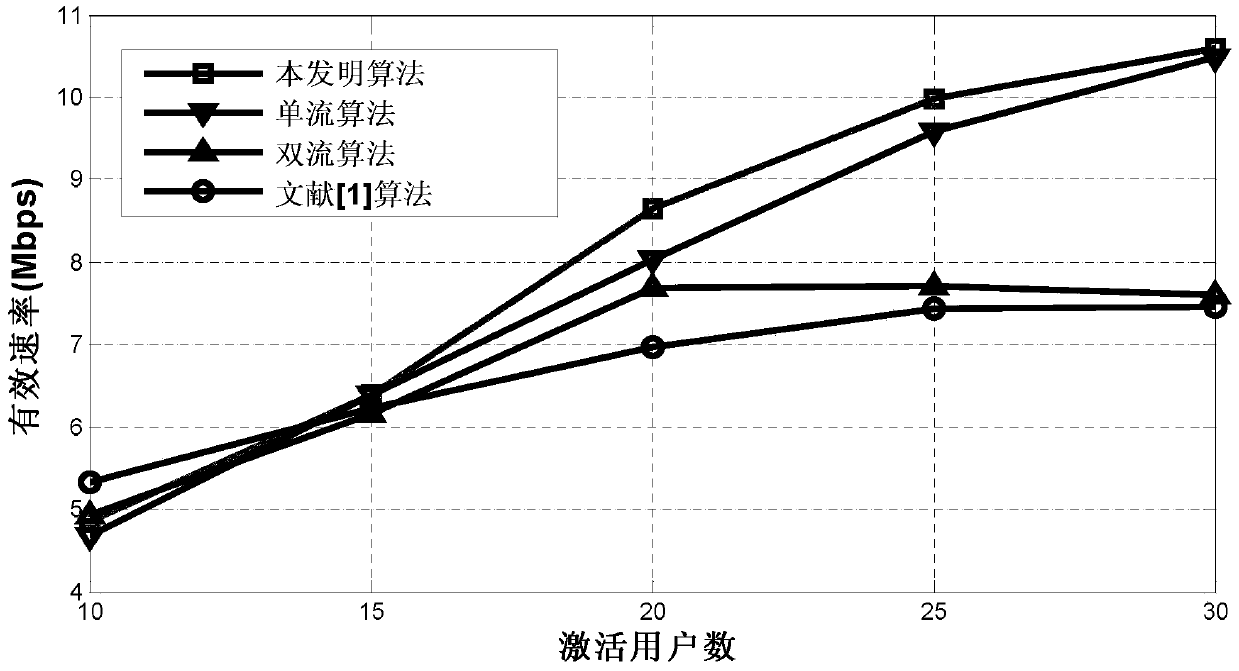
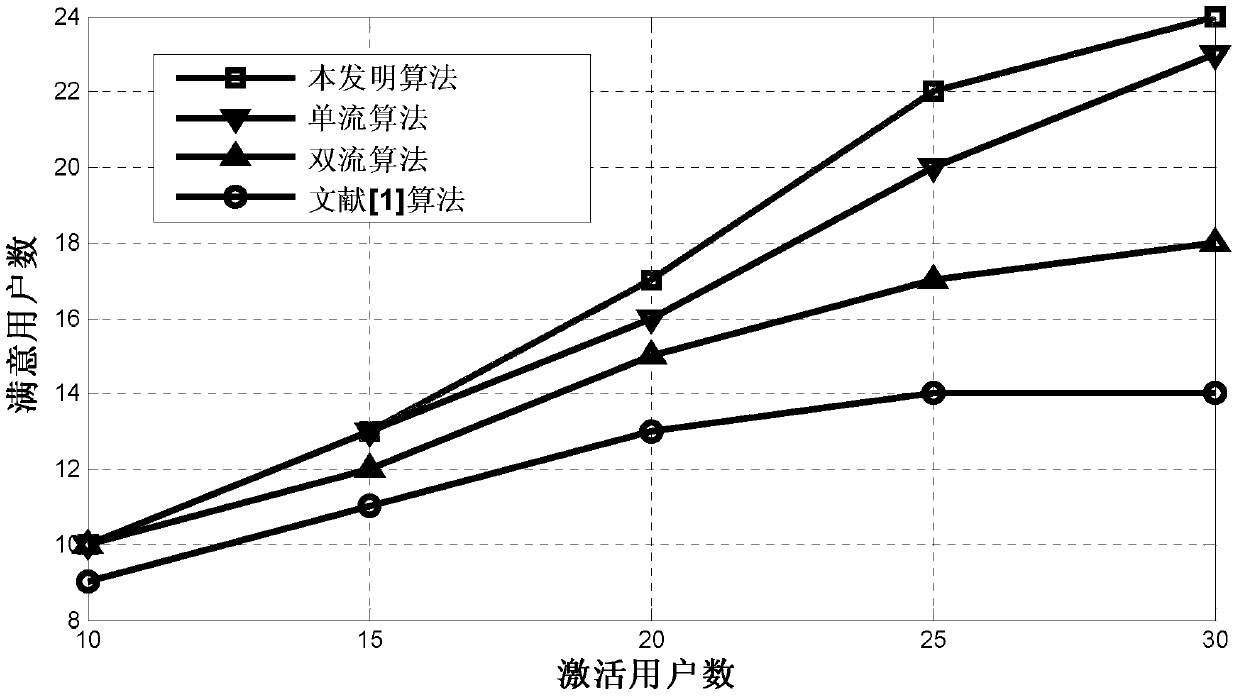
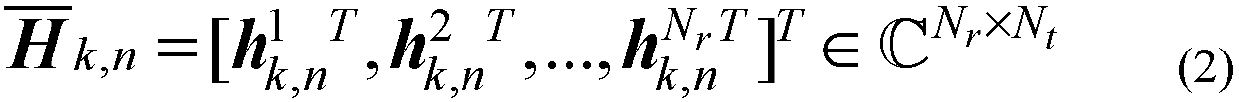A single-dual-stream switching method based on effective rate in beamforming
A beamforming, single-dual stream technology, applied in the field of single-dual stream switching based on effective rate, can solve the problems of low data rate, inability to ensure the target rate of user transmission rate, and inability to ensure user fairness, etc., to achieve the purpose of expanding capacity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0022] Specific implementation mode 1: A single-dual-stream switching method based on effective rate in beamforming in this implementation mode is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0023] For the single-stream and multi-stream hybrid transmission scenario under multi-user beamforming, select the appropriate number of transmission streams for each user in this scenario according to the user's channel quality and rate requirements, and complete the process according to the stream number and channel conditions of different users The allocation of multiple users on the RB realizes switching between single and dual streams based on the effective rate;
[0024] Step 1, utilize the system channel feedback to obtain the user's channel information; Assume that there are K users in the single cell of the LTE mobile cellular communication system, and each user is equipped with N r root receiving antennas, the cell base station is equipped with N t The calculation...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: in step two, use Calculate channel norm Compare channel norms and threshold H 0 OK in all N r Select the number of receiving antennas actually used by user k in the nth resource block in the root receiving antenna according to The specific process of determining the actual receiving antenna used is:
[0034] 1) In addition to the user's channel information, the rate requirement is also an important criterion for determining the number of streams; use r_remain k,n (t) to characterize the user's rate requirements:
[0035]
[0036] Among them, R k (t-1) is the average rate obtained by user k in the first t-1 subframes, r k,b (t) is the rate obtained by user k on RBb in t subframes, updated in real time; λ k is the target transmission rate of user k; RBb represents the bth RB; ρ k,b is the corresponding relationship between user k and...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0052] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that in step three, the corresponding relationship ρ between the user k and RBn of the actually used receiving antenna is established k,n Specific process:
[0053] Step 2 has completed the determination of the number of user streams and the determination of the antenna space, but the determination of the number of streams only indicates the transmission mode to be adopted when user k is allocated to RBn, and whether user k will actually be allocated It is uncertain to RBn. In the process of user k selection, the problem of user combination on different RBs must be solved, so as to complete a relatively complete scheduling process by combining the results of flow number determination in step 2; in order to select Small user combination, we will continue to use the concept of spatial correlation coefficient in user selection, the difference is that here is used to ev...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com