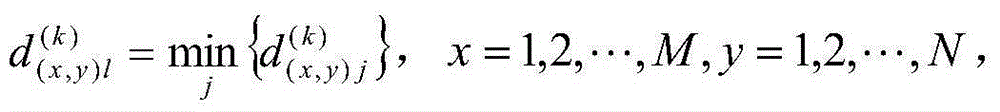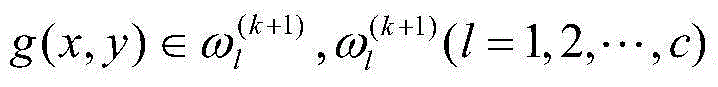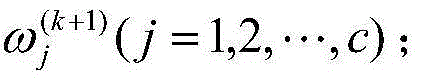Image C-mean clustering algorithm
A mean clustering and image technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as increasing the complexity of solving problems, and achieve the effect of good segmentation and clear edges.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] All features disclosed in this specification, or steps in all methods or processes disclosed, may be combined in any manner, except for mutually exclusive features and / or steps.
[0025] The information in an image includes three parts: target object, background and noise. Image binarization is an image processing method to obtain the target object in the image. After binarization, all pixels in the image will be will change to white or black. When the image contains only two parts of information, the foreground and the background, the pixel value of the foreground can be set to 1, and the pixel value of the background can be set to 0, so that the image is binarized. There are many methods of binarization, generally divided into global threshold method and local threshold method
[0026] The global threshold method refers to a method that uses only one global threshold T in the binarization process. It compares the gray value of each pixel of the image with T, if it i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com