Planet safe landing guidance method employing landing point on-line selection
A safe landing and landing point technology, applied in the field of deep space exploration, can solve problems such as lack of analysis and discussion, limited accuracy of planetary surface information, and inability to accurately reach the scheduled landing point, and achieve the effect of overcoming errors and external interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] In order to better illustrate the purpose and advantages of the present invention, the content of the invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples.
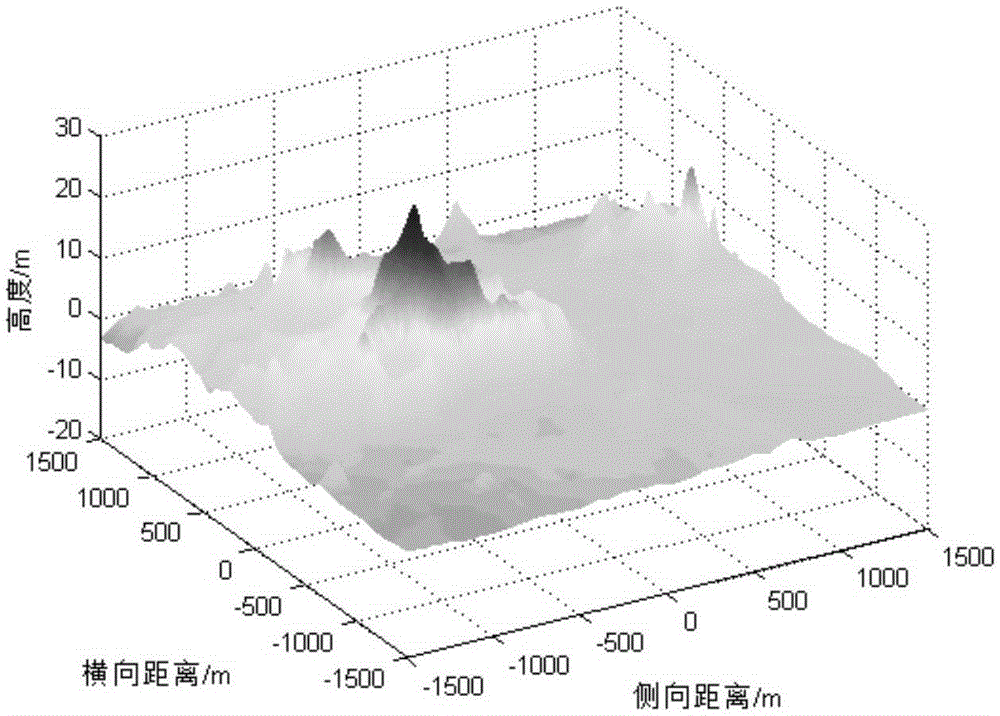
[0062] In this example, the specific impulse I of the thrust engine sp is 225s, the mass m of the detector is 1905kg, the maximum velocity increment ΔV is 190m / s, the landing time Δt is 35s, and the initial position r of the dynamic descent section of the detector is 0 is [-300,-200,1700]m, initial velocity v 0 It is [18,20,-80]m / s, and the negative sign indicates that the direction is vertically downward. The terrain used in the simulation is shown in Figure 3.
[0063] A planetary safe landing guidance method for online selection of a landing point disclosed in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0064] Step 1: Determine the safe landing point selection range. After the maneuverability boundary is obtained, the area covered by the maneuverability is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com