Reason tracing method
A cause and cause group technology, applied in the field of computer artificial intelligence, can solve the problems of low efficiency, long traceability process, and high technical requirements for discrimination, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency and saving investigation time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
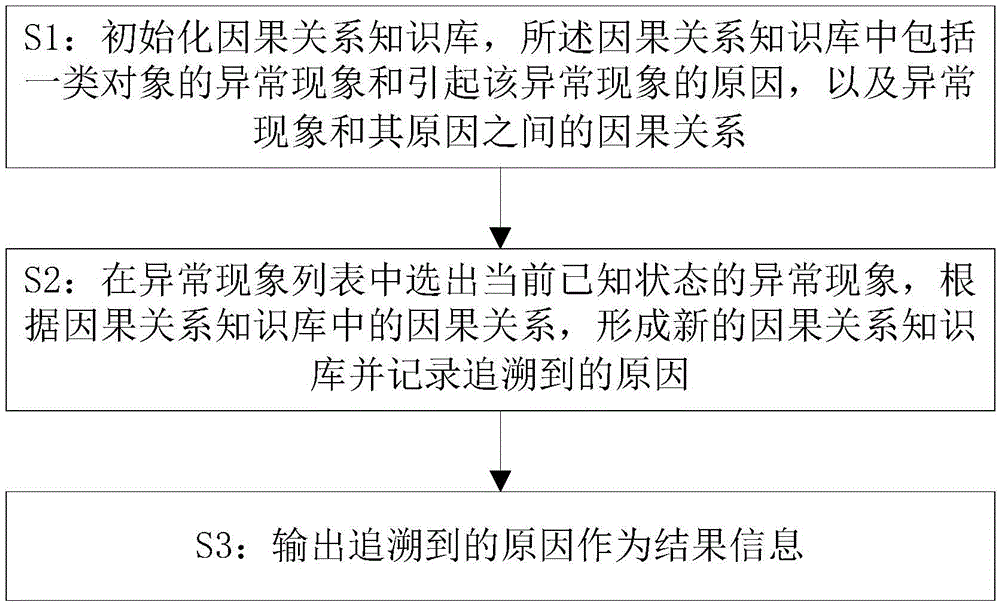
[0042] Such as figure 1 A kind of cause tracing method of the present invention shown, comprises the following steps:
[0043] S1: Initialize the causality knowledge base. The causality knowledge base includes the abnormal phenomenon of a class of objects and the cause of the abnormal phenomenon, as well as the causal relationship between the abnormal phenomenon and the cause of the abnormal phenomenon. The class of objects is Common objects that have been recognized are events that follow natural laws and have been recognized by humans in the real world and the virtual world. They can be events such as wind and rain, or events in the virtual environment. Events, such as program crashes or transmission failures, etc.;
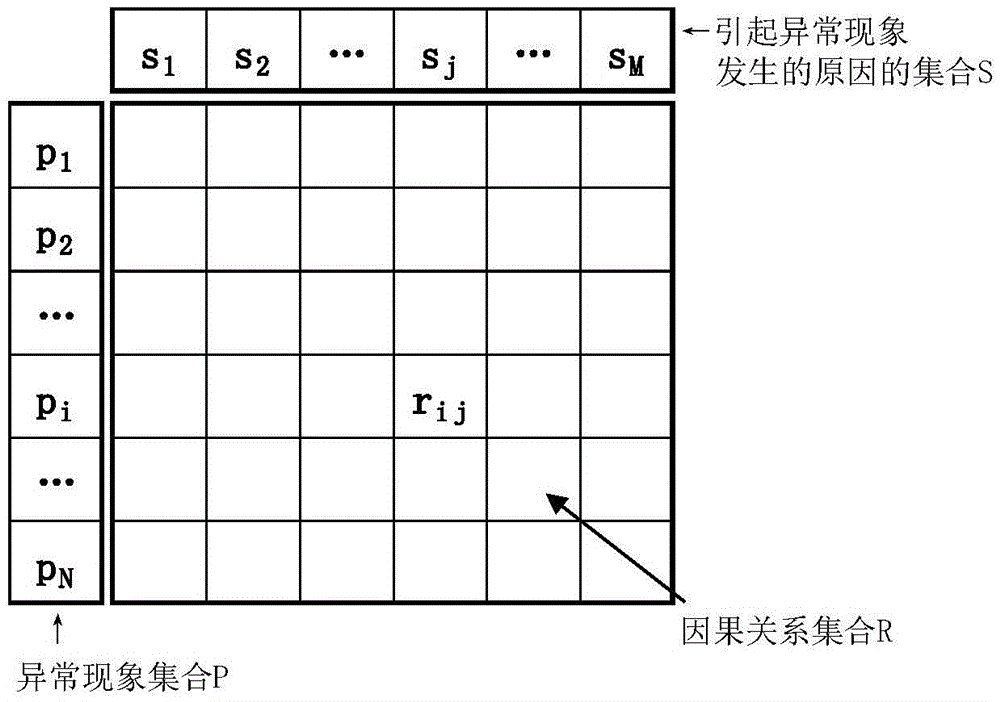
[0044] The causal relationship knowledge base is a data set that meets specific structural rules in artificial intelligence technology. The present invention only provides the constituent elements of the causal relationship knowledge base, the relationship bet...
Embodiment 2
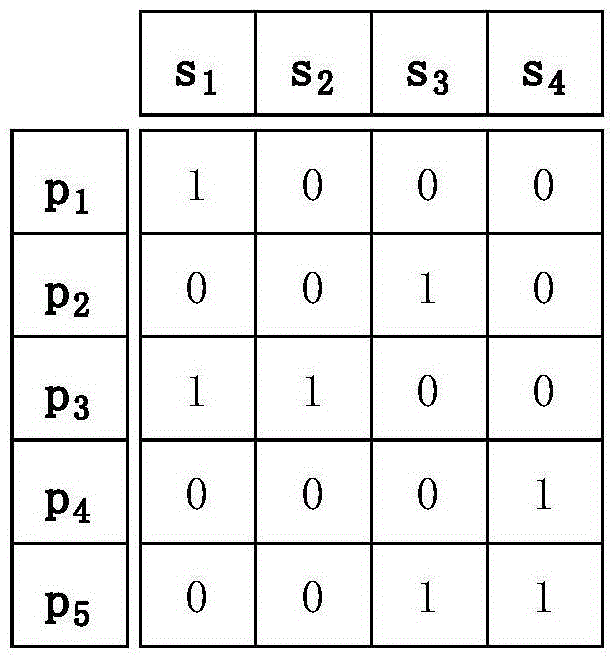
[0054] On the basis of the method for tracing the cause described in Embodiment 1, the step S2 is specifically: sequentially select the currently known abnormal phenomenon, establish a new cause group, record the traced reason, and establish a new phenomenon group to build a new causal relationship knowledge base.
[0055] The process of creating a new reason group and recording the traced reasons is as follows:
[0056] Group the abnormal phenomena in the current confirmation state: the first phenomenon group is the confirmed abnormal phenomenon, the second phenomenon group is the confirmed non-occurrence phenomenon, and the remaining unconfirmed phenomenon status is the third phenomenon group. In a preferred embodiment, when the current first phenomenon group is missing, that is, when there is no input confirmation phenomenon, the current third phenomenon group is used instead, and the first phenomenon group at this time is copied from the third phenomenon group. The three-...
Embodiment 3
[0065] On the basis of the cause tracing method described in the above embodiment, the "result information" also includes the corresponding causal relationship between the phenomenon group that has been confirmed and the cause that has been traced, but the result information does not Limited to this, it is also possible to output the causality knowledge base and the data generated in the traceability process according to the needs of the user, which can be changed according to actual usage conditions. Step S3 is responsible for outputting the traceability of the cause as the last step of the present invention. result. The reason being traced back is the necessary output content of step S3. At the same time, due to different usage requirements, the output content and functions of S3 can also be richer:
[0066] (1) While outputting the cause and result, output all abnormal phenomena confirmed during the traceability process, which can help users use other technical methods to v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com