Myoelectricity-controlled exoskeleton assistant robot
A walking-assisting robot and myoelectric control technology, which are applied in the direction of devices that help people walk, medical science, diagnosis, etc., can solve the problems of ignoring the wearer's actual needs, wearer's discomfort, lack, etc., so as to avoid the wearer's discomfort and improve Wearing comfort and the effect of improving exercise performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
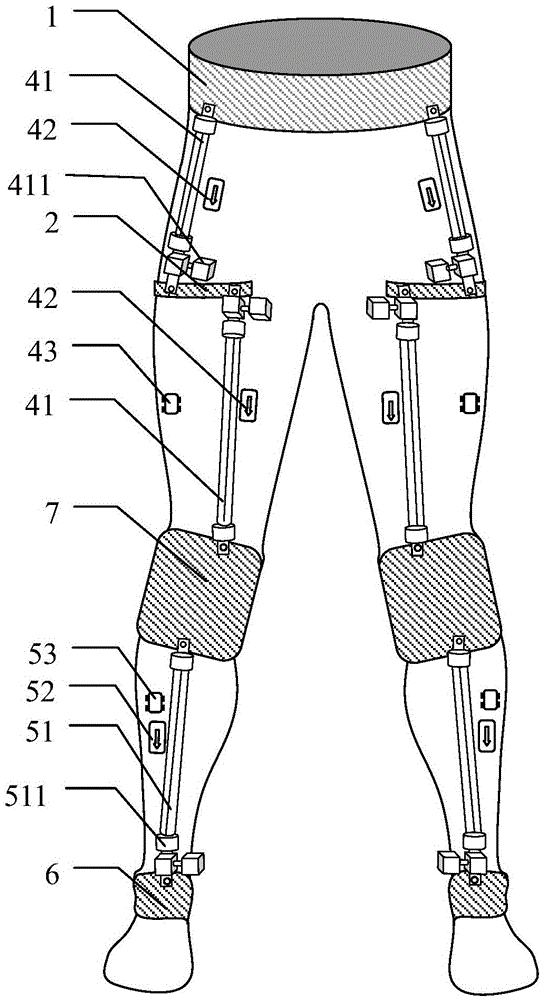
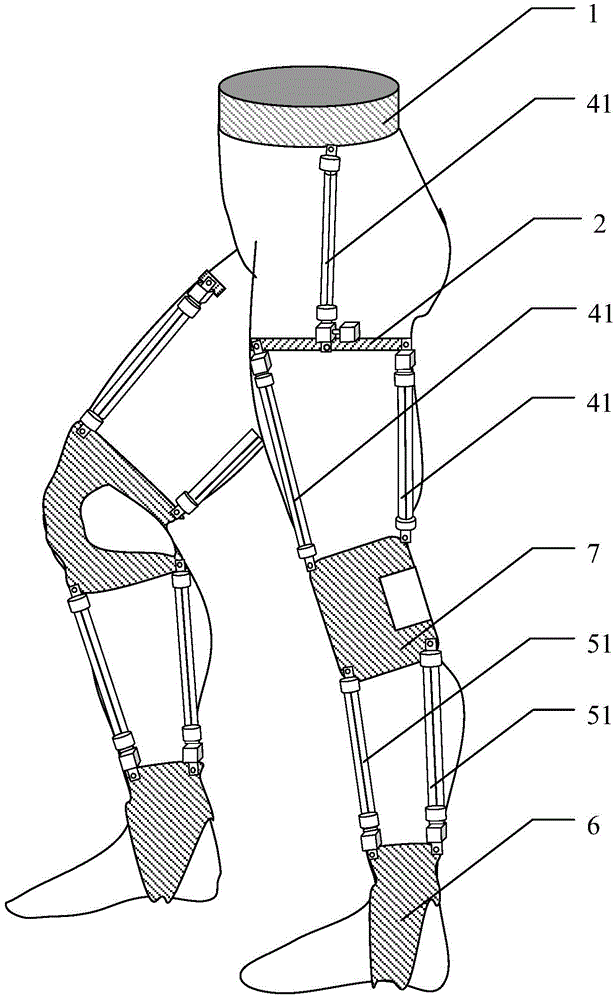
[0034] In this example (see Figure 1-3 ) thigh pneumatic execution module 41 is provided with thigh No. 1 pneumatic muscle, thigh No. 2 pneumatic muscle and thigh No. 3 pneumatic muscle; described thigh No. 1 pneumatic muscle is located on the tensor fascia lata of thigh, and thigh No. 2 pneumatic muscle is located in the thigh On the rectus femoris muscle, the No. 3 pneumatic muscle of the thigh is located on the biceps femoris of the thigh; the thigh EMG signal sensor module 42 includes the No. 1 thigh EMG signal sensor, the No. 2 thigh EMG signal sensor and the No. 3 thigh EMG signal The sensors are respectively fixed on the surfaces of the tensor fascia lata, rectus femoris and biceps femoris in the embodiment, so as to monitor the surface electromyographic signal changes of the thigh muscles in real time.
[0035] In an embodiment, the calf pneumatic execution module 51 is provided with a calf 1 pneumatic muscle and a calf 2 pneumatic muscle, the calf 1 pneumatic muscle ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] In this example (see Figure 2-4 ), described thigh pneumatic execution module 41 is provided with thigh No. 1 pneumatic muscle, thigh No. 2 pneumatic muscle, thigh No. 3 pneumatic muscle and thigh No. 4 pneumatic muscle, and described thigh No. 1 pneumatic muscle is positioned at the tensor fascia lata of thigh Above, the No. 2 pneumatic muscle of the thigh is located above the rectus femoris muscle of the thigh, the No. 3 pneumatic muscle of the thigh is located above the biceps femoris of the thigh, and the No. 4 pneumatic muscle of the thigh is located above the vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh; the thigh EMG signal sensor module 42 includes The No. 1 thigh EMG signal sensor, the No. 2 thigh EMG signal sensor, the No. 3 thigh EMG signal sensor, and the No. 4 thigh EMG signal sensor are respectively fixed on the tensor fascia lata, rectus femoris, and femoral femoris in the embodiment. The surface of the head muscle and vastus lateralis muscle is used to monitor ...
Embodiment 1 and 2
[0039] The working principle and workflow of Examples 1 and 2 are:
[0040] (1) The wearer puts on the exoskeleton walking aid robot and starts the device;
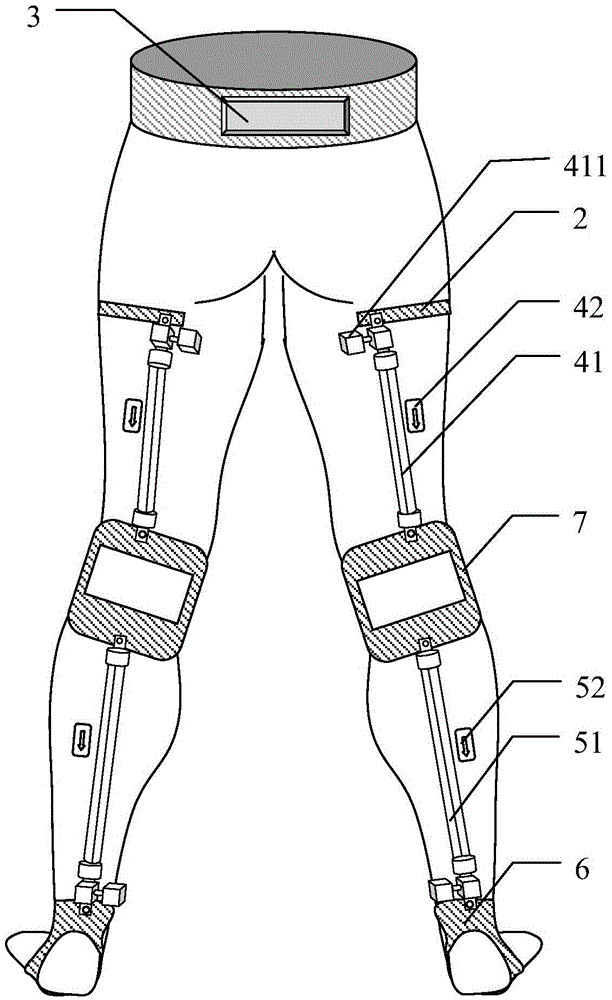
[0041] (2) the thigh EMG signal sensor module 42 and the calf EMG signal sensor module 52 work, collect the surface EMG signals of the main muscles of the lower limbs in real time, and then transmit them to the control device 3;
[0042] (3) The control device 3 analyzes the received surface EMG signal data, and decides whether to activate the thigh pneumatic execution module 41 and the calf pneumatic execution module 51;
[0043] (4) If it does not start, then repeat steps (2) and (3);
[0044] (5) If it needs to be started, the control device 3 sends an instruction to the thigh pneumatic execution module 41, the calf pneumatic execution module 51 and the air source, and starts to inflate the pneumatic muscles;
[0045] (6) Calculate the required torque according to the surface EMG signal, read the information of the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com