Fast Convergence Method and Device for End System Address Distribution Information Protocol
An end system and address technology is applied in the field of fast convergence method and device of end system address distribution information protocol, which can solve the problem that ESADI protocol cannot converge in time, and achieve the effect of timely update of topology structure and rapid convergence.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
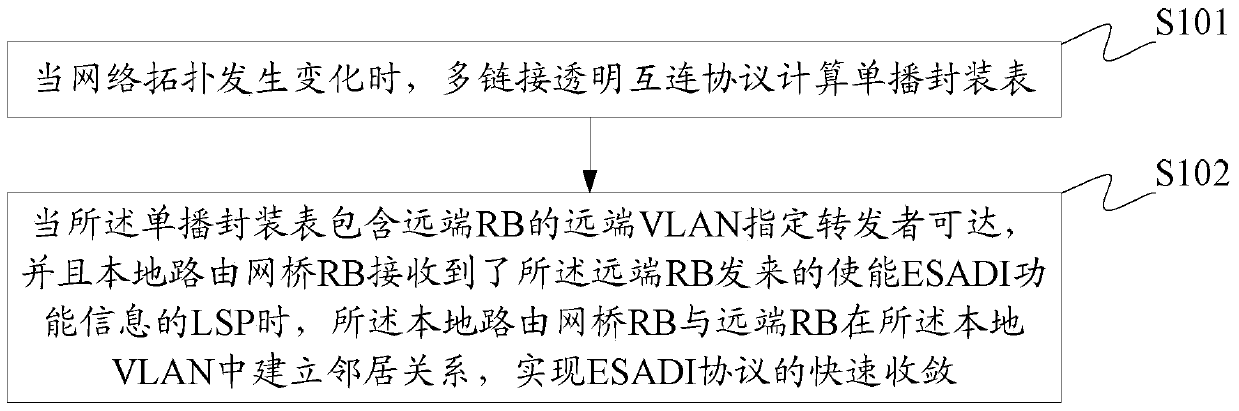
[0050] In order to solve the defect that the ESADI protocol cannot converge in time in the existing ESADI protocol, this embodiment provides a convergence method of the ESADI protocol, which is suitable for RBs whose neighbor relationship changes due to changes in the network topology, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0051] S101: When the network topology changes, the multi-link transparent interconnection protocol calculates the unicast encapsulation table;
[0052] When the network topology is broken, RBs are added or RBs are deleted, etc., the multi-link transparent interconnection protocol calculates the unicast encapsulation table to determine the unicast reachability of all current RB remote VLAN designated forwarders.
[0053] S102: When the unicast encapsulation table contains the remote VLAN designated forwarder of the remote RB and the local RB receives the LSP with ESADI function information enabled from the remote RB, the local RB and The remote ...
Embodiment 2
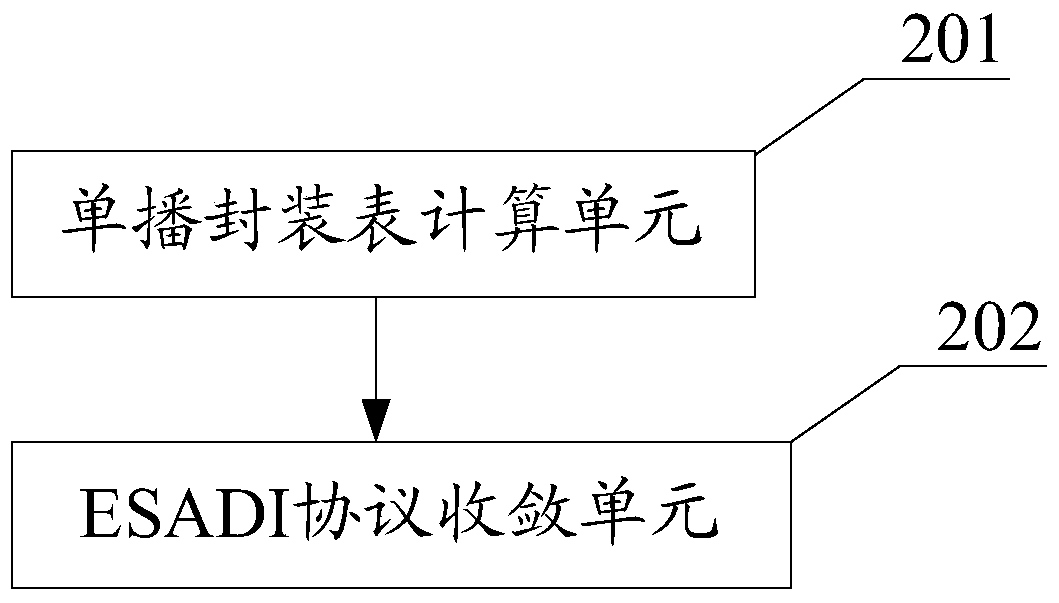
[0062] This embodiment and Embodiment 1 belong to the same inventive concept. This embodiment provides a convergence device for the ESADI protocol, such as figure 2 As shown, the device includes:
[0063] The unicast encapsulation table calculation unit 201 is configured to recalculate the unicast encapsulation table when the network topology changes, and the transparent interconnection of multiple links protocol (TRILL) converges;
[0064] The ESADI protocol convergence unit 202 is configured to be used when the unicast encapsulation table contains the remote VLAN designated forwarder of the remote RB and the local RB receives the LSP that enables the ESADI function information sent by the remote RB. , the local RB establishes a neighbor relationship with the remote RB in the local VLAN, so as to realize fast convergence of the ESADI protocol.
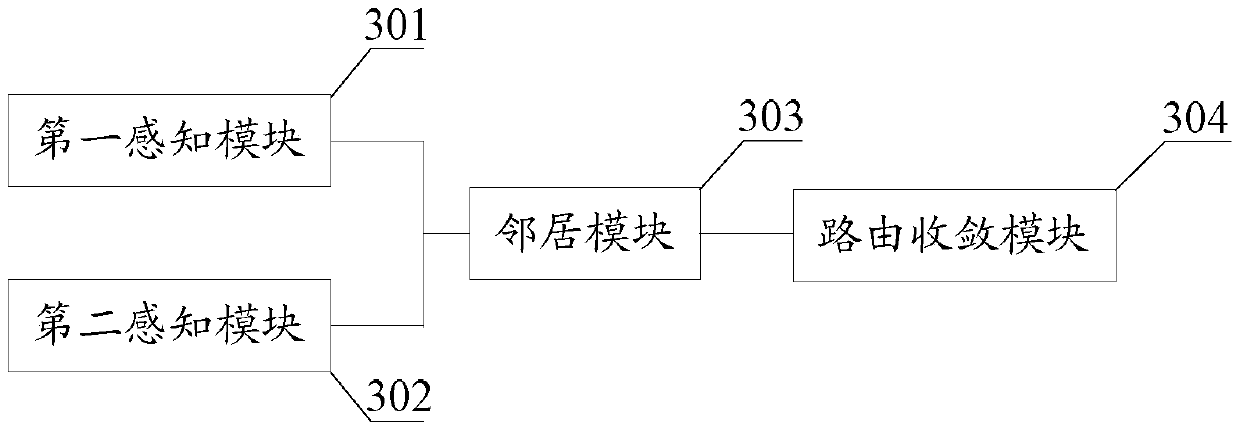
[0065] Specifically, such as image 3 As shown, the ESADI protocol convergence unit 202 includes:
[0066] The first sensing mo...
Embodiment 3
[0071] In this embodiment, the remote specified forwarder represented by the nickname (nickname) and the VLAN field in the Interested VLANs and Spanning TreeRoots sub-TLV carried by the LSP of the TRILL protocol performs unicast encapsulation table calculation, relying on the unicast encapsulation table calculation to form The dynamic reachability of unicast encapsulation information maintains neighbor relationships, achieves the purpose of quickly responding to the network topology to establish or delete ESADI neighbors, quickly discovers DRB failures, elects a unified new DRB, and speeds up the synchronization of ESADI LSPs, improving the convergence performance of the ESADI protocol.
[0072] The flow chart of this embodiment is as follows Figure 4 shown, including:
[0073] S401: Obtain and perceive whether the remote RB enables the ESADI function in the VLAN, from the VLAN enabling ESADI information represented by the nickname and VLAN fields in the Interested VLANs and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com