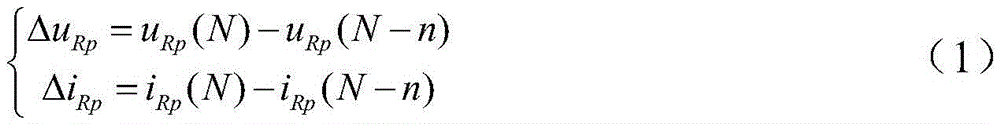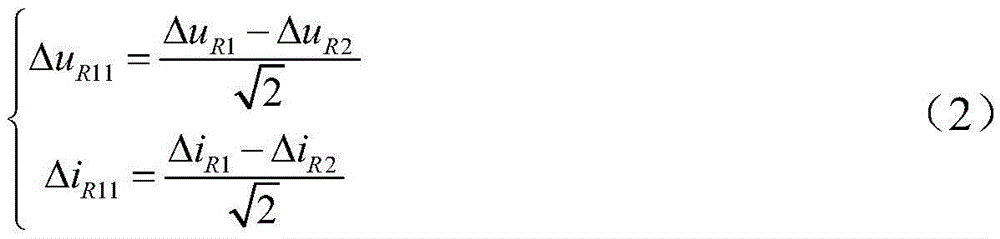High-voltage direct current transmission line internal fault and external fault identification method based on backward traveling waves
A high-voltage direct current and fault identification technology, which is applied in the field of power systems, can solve problems such as slow operation speed, high requirements for communication equipment, and lack of line backup protection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0046] A method for identifying internal and external faults of high-voltage direct current transmission lines based on reverse traveling waves according to the present invention comprises the following steps:
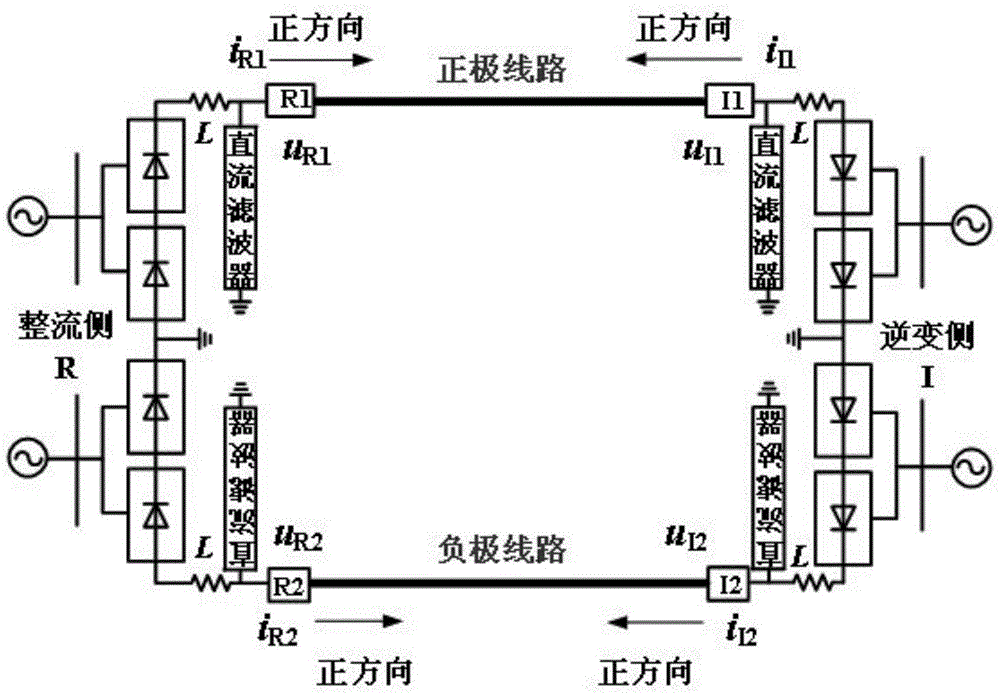
[0047] (a) The voltage and current transformers installed on the line side of the rectifier station and inverter station of the DC transmission system respectively collect the voltage and current at both ends of the positive and negative lines; Two wires of different polarities (ie, positive and negative) are used for power transmission, and these two wires are referred to as the positive line and the negative line for short. Among them, the outlet terminal of the converter station is called the positive pole if it is positive to the ground potential, and the negative pole is called the negative pole, such as figure 1 shown.
[0048] (b) Utilize the collected voltage and current at both ends of the line to calculate the voltage mutation and current mutation at both en...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com