Geostatistical method for variation function simulation of surface spatial data of seas and mountains
A technology of geostatistics and surface space, applied in the field of geostatistics, can solve the problems that traditional methods cannot be effective, KRIGING estimation cannot be performed, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
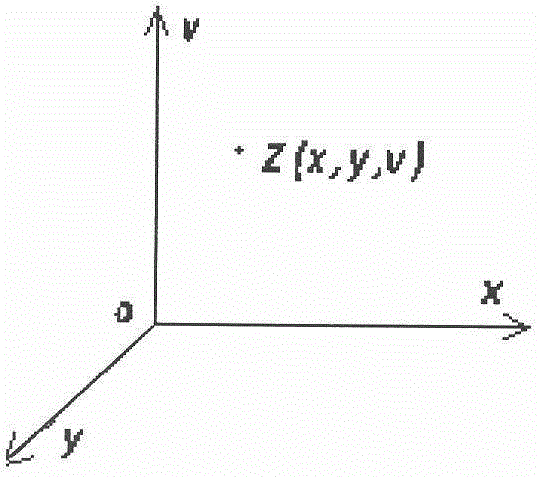
[0063] Such as figure 1 As shown, use Z to represent a random variable, which is a function of coordinates, and expressed by Z(x, y, v), which is a vector function in a typical three-dimensional coordinate system; for example, this random variable can represent a certain three-dimensional sea area salinity within , in the domain of There is a definite salinity value at any point in ; the domain or random field of this typical three-dimensional random variable has both length, width and thickness, that is, values can be taken continuously in the three coordinate directions of z.
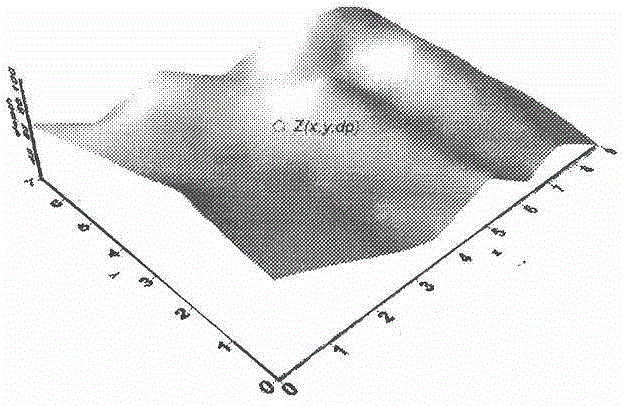
[0064] Such as figure 2 As shown, the cobalt-rich crust parameters on the surface of the seamount slope are regarded as random variables, which belong to the 3D surface random variable (3DSurfaceRandomVariable), and are expressed by Z(x, y, dp). For the experimental data, Z(x, y, dp) represents the thickness data of cobalt-rich crusts on a slope at a water depth of dp at a geographic location ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com