Shifting register unit, grid driving circuit and display device
A shift register and gate technology, which is applied in the field of gate drive circuits, display devices, and shift register units, can solve the complex structure of shift register units, the different cascade relationships of shift register units, and the difficulty in application of display devices. big problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
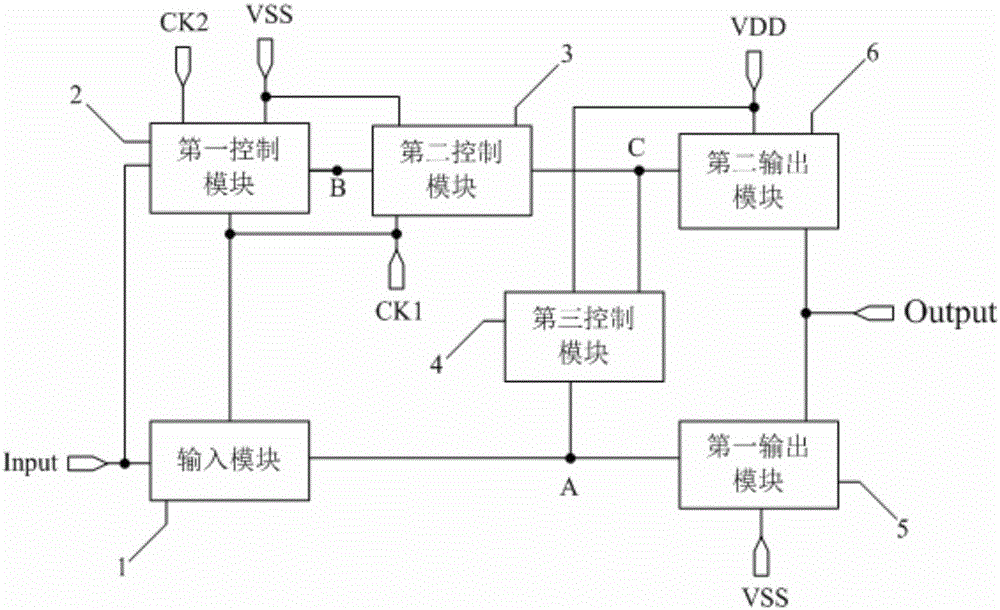
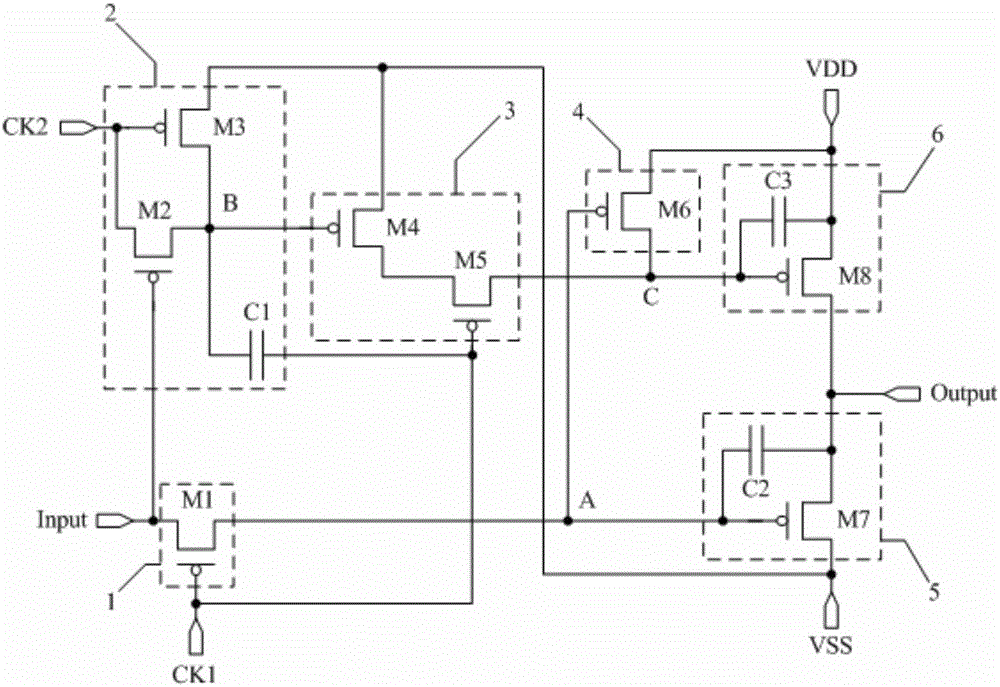
[0101] by Figure 2a The structure of the shift register unit shown is taken as an example to describe its working process, wherein, in Figure 2a In the shift register unit shown, the potential of the first reference signal terminal VSS is low potential, and the potential of the second reference signal terminal VDD is high potential; the corresponding input and output timing diagram is as follows Figure 3a Shown, specifically, select as Figure 3a There are five stages T1, T2, T3, T4, and T5 in the shown input and output timing diagram, and the T2 stage is further divided into two stages, T21 and T22.
[0102] In the T1 stage, Input=0, CK1=0, CK2=1.
[0103] Since CK2=1, the third switch transistor M3 is turned off; because Input=0, the second switch transistor M2 is turned on; because the second switch transistor M2 is turned on and provides the high potential signal of the second clock signal terminal CK2 to The second node B, so the potential of the second node B is a ...
Embodiment 2
[0128] by Figure 2a The structure of the shift register unit shown is taken as an example to describe its working process, wherein, in Figure 2a In the shift register unit shown, the potential of the first reference signal terminal VSS is low potential, and the potential of the second reference signal terminal VDD is high potential; the corresponding input and output timing diagram is as follows Figure 3b Shown, specifically, select as Figure 3b There are five stages T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 in the shown input and output timing diagram, and the T2 stage is further divided into four stages T21, T22, T23 and T24.
[0129] In the T1 stage, Input=0, CK1=0, CK2=1. The specific working process is the same as the working process of the T1 stage in the first embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
[0130] In the T2 stage, wherein, in the former time period of the T21 stage, Input=1, CK1=1, CK2=1; in the middle time period, Input=1, CK1=1, CK2=0; in the later time period, Input...
Embodiment 3
[0145] by Figure 2a The structure of the shift register unit shown is taken as an example to describe its working process, wherein, in Figure 2a In the shift register unit shown, the potential of the first reference signal terminal VSS is low potential, and the potential of the second reference signal terminal VDD is high potential; the corresponding input and output timing diagram is as follows Figure 3c Shown, specifically, select as Figure 3c There are five stages T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5 in the input and output timing diagram shown, and the T2 stage is further divided into six stages T21, T22, T23, T24, T25 and T26.
[0146] In the T1 stage, Input=0, CK1=0, CK2=1. The specific working process is the same as the working process of the T1 stage in the first embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
[0147] In the T2 stage, wherein, in the former time period of the T21 stage, Input=1, CK1=1, CK2=1; in the middle time period, Input=1, CK1=1, CK2=0; in the later time peri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com