A Tone Mapping Method for High Dynamic Range Images Based on Regularized Layering
A technology of high dynamic range and mapping method, which is applied in image enhancement, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to guarantee significant edges, image blurring in the base layer, and image halo phenomenon, so as to avoid halo or tone The effect of the reversal phenomenon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
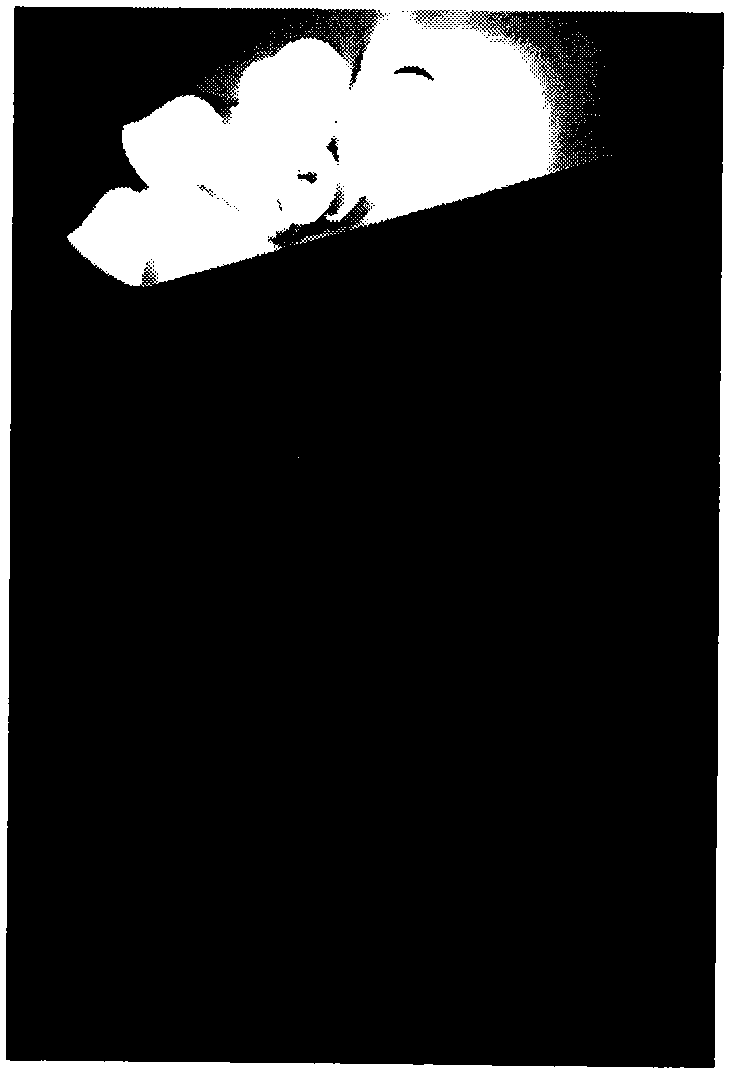
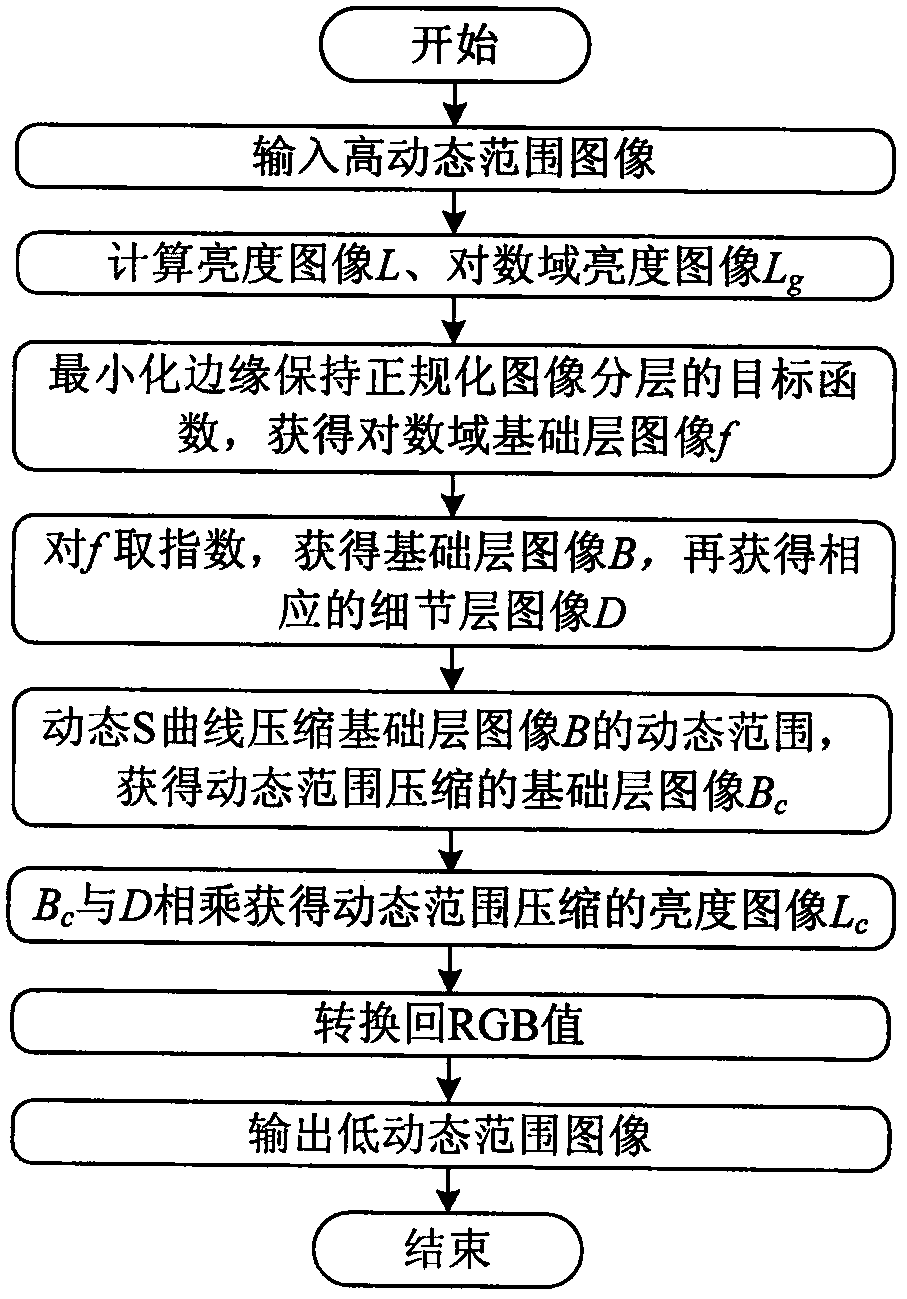
[0036] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. In an embodiment, an HDR image rend04_o80A (61027:1 dynamic range) is processed with the method of the present invention.
[0037] see figure 1 , the embodiment is processed in the following steps:
[0038] Step 1, read the pixel value (RGB) of the HDR image, R, G, and B are the color values of the red, green, and blue channels of the HDR image respectively, and obtain its brightness image L through the conversion of RGB to Lab color space;
[0039] Step 2, take the logarithm of the brightness image L, and obtain the brightness image L in the logarithmic domain g , calculated as follows:
[0040] L g =log(max(L, 10 -6 )),
[0041] Among them, the function max( ) means to take the maximum value;
[0042] Step 3, establish an objective function based on edge-preserving regularized image layering, and decompose the logarithmic domain brig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com