Management method and device of congestion information
A management method and management module technology, applied in connection management, network traffic/resource management, telephone communication, etc., can solve problems such as out-of-sequence and message competition, and achieve the effect of reducing misjudgment operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
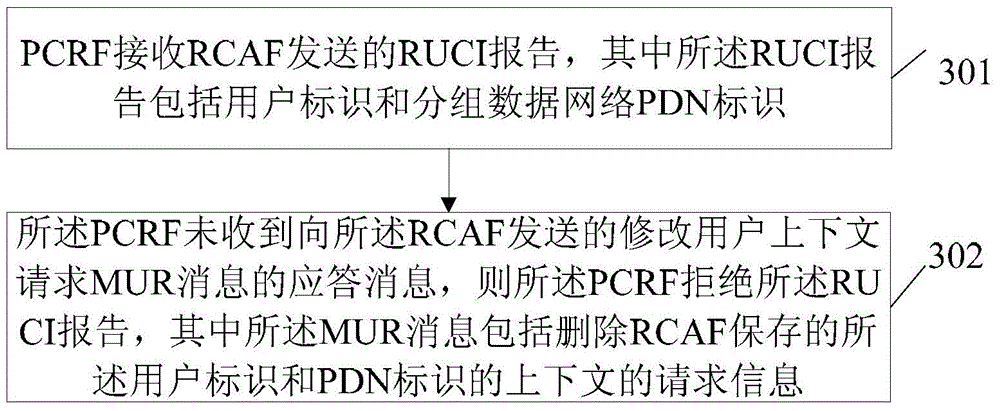
[0063] Figure 5 It is an interactive schematic diagram of the congestion information management method provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Figure 5 In the shown method, UE1 is initially in a congested area managed by RCAF1, and the context saved by PCRF also indicates that UE1 is in the congested area managed by RCAF1, and then UE1 moves to a congested area managed by RCAF2.
[0064] Step 501. RCAF1 obtains congestion-related OAM information and congested area from RAN OAM. For UTRAN access, RCAF1 also obtains user IDs under the congested area. For E-UTRAN access, RACF1 obtains the user ID in the congested area and the corresponding activated APN (ie, PDN ID) from the MME. For UTRAN access, RCAF1 obtains the APN (ie, PDN identifier) corresponding to the user identifier in the congested area from the SGSN. Assume that UE1 (user ID 1) is located in a congested area, and the activated APN is (PDN ID 1). Here, the congestion area where UE1 is located has chan...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Image 6 It is an interactive schematic diagram of the congestion information management method provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Image 6 In the method shown, UE1 is initially in a congested area managed by RCAF1, and the context saved by PCRF also indicates that UE1 is in the congested area managed by RCAF1, and then UE1 moves to a congested area managed by RCAF2, and then UE1 moves again Back to the congested area managed by RCAF1.
[0078] Step 601. RCAF1 obtains congestion-related OAM information and congested area from RAN OAM. For UTRAN access, RCAF1 also obtains user IDs under the congested area. For E-UTRAN access, RACF1 obtains the user ID in the congested area and the corresponding activated APN (ie, PDN ID) from the MME. For UTRAN access, RCAF1 obtains the APN (ie, PDN identifier) corresponding to the user identifier in the congested area from the SGSN. Assume that UE1 (user ID 1) is located in a congested area, and the activated APN is...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Figure 7 It is a schematic diagram of interaction of the congestion information management method provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Figure 7 In the shown method, UE1 is initially in a congested area managed by RCAF1, and the context saved by PCRF also indicates that UE1 is in the congested area managed by RCAF1, and then UE1 moves to a congested area managed by RCAF2.
[0100] Step 701. RCAF1 obtains congestion-related OAM information and congested area from RAN OAM. For UTRAN access, RCAF1 also obtains user IDs under the congested area. For E-UTRAN access, RACF1 obtains the user ID in the congested area and the corresponding activated APN (ie, PDN ID) from the MME. For UTRAN access, RCAF1 obtains the APN (ie, PDN identifier) corresponding to the user identifier in the congested area from the SGSN. Assume that UE1 (user ID 1) is located in a congested area, and the activated APN is (PDN ID 1). Here UE1 is located in the congestion area from conge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com