Timber density determination method based on iteration weight least square estimate method
A least squares, iterative weighting technique, applied in the estimation field of wood density determination, can solve the problem of large batch wood error, and achieve the effect of accurate estimation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
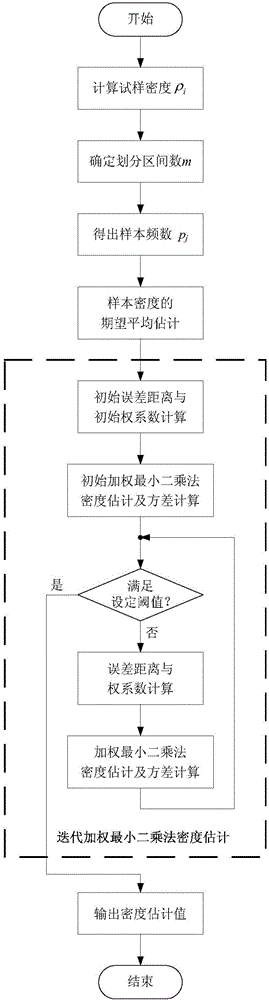
[0042] A wood density determination method based on iterative weighted least squares estimation method, comprising the following steps:
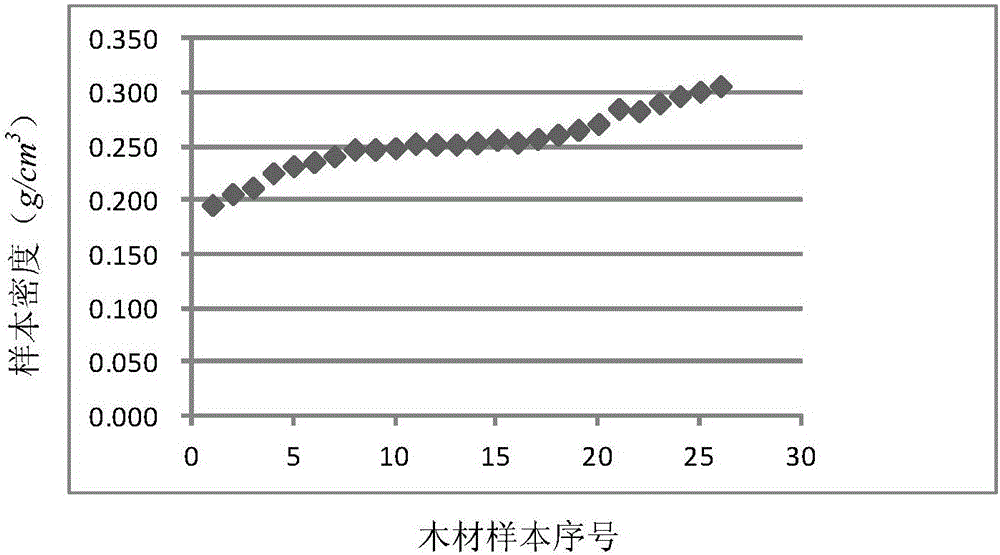
[0043] Step 1. Randomly select samples for a batch of wood, and calculate the density ρ of each sample i ;
[0044] Step 2. Expected average estimate of sample density:
[0045] Step 2.1, frequency statistics of sample density:
[0046] from ρ i The maximum value ρ was determined in max and the minimum value ρ min ;
[0047] Take a=[ρ min *10 l-1 -0.5] / 10 l-1 , b=[ρ max *10 l-1 +0.5] / 10 l-1 ; l is ρ i , ρ max or ρ min The effective number of digits after the decimal point, the [ ] operation means to take an integer;
[0048] Divide the interval [a,b] into m small intervals, and calculate the number of sample densities p falling into each small interval j , this p j is the frequency, the total number of samples
[0049] Step 2.2, expected average estimate:
[0050] The expected average estimate of the sample density can b...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0080] The specific process of step 1 of this embodiment is as follows:
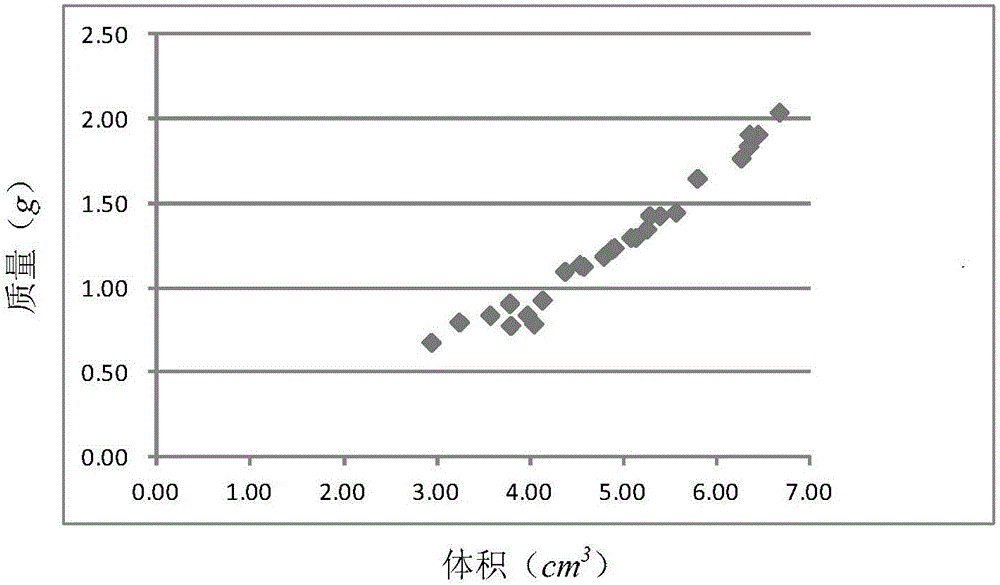
[0081] Randomly select samples from a batch of wood (need to be representative, the number of samples should account for more than a quarter of the total samples, and not less than 20), and measure according to "GB / T 1933-2009 Wood Density Determination Method" Get the volume v of each sample i , mass g i , i is the serial number of the sample, i=1,2...n;
[0082] Calculate the density of each sample by formula (1)
[0083] ρ i = g i v i - - - ( 1 ) .
[0084] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0085] The method for determining m described in step 2.1 of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0086] From the empirical formula m≈[Δ·(n-1) 0.4 ] Determine the interval m to be divided; Δ takes a value of 1.80 to 1.90;
[0087] In the formula, the [·] operation means to take an integer.
[0088] Other steps and parameters are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com