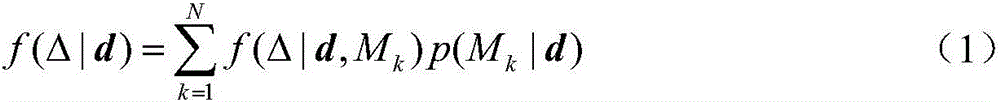Method for quantitatively analyzing underground water numerical simulation uncertainty based on information entropy
An uncertainty and numerical simulation technology, applied in complex mathematical operations, data processing applications, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve unreliable, variance concepts that cannot reasonably describe uncertainty in probability distributions, and concepts that cannot describe similar structures Problems such as model overlap and uncertainty, to achieve the effect of expanding the scope of application and reasonably describing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0032] Embodiment: In information theory, for discrete variable x, information entropy H is defined as:
[0033] H ( x ) = - Σ i p ( x i ) l o g p ( x i ) - - - ( 6 )
[0034] where p(x i ) for x i The probability. For a continuous variable x, the information entropy H is defined as:
[0035] H(x)=-∫f(x)logf(x)dx (7)
[0036] where f(x) is the probability density function of x.
[0037] The Kullback-Leibler (K-L) divergence (or relative entropy D) is used to represent the relative distance between two probability distributions:
[0038] D ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com