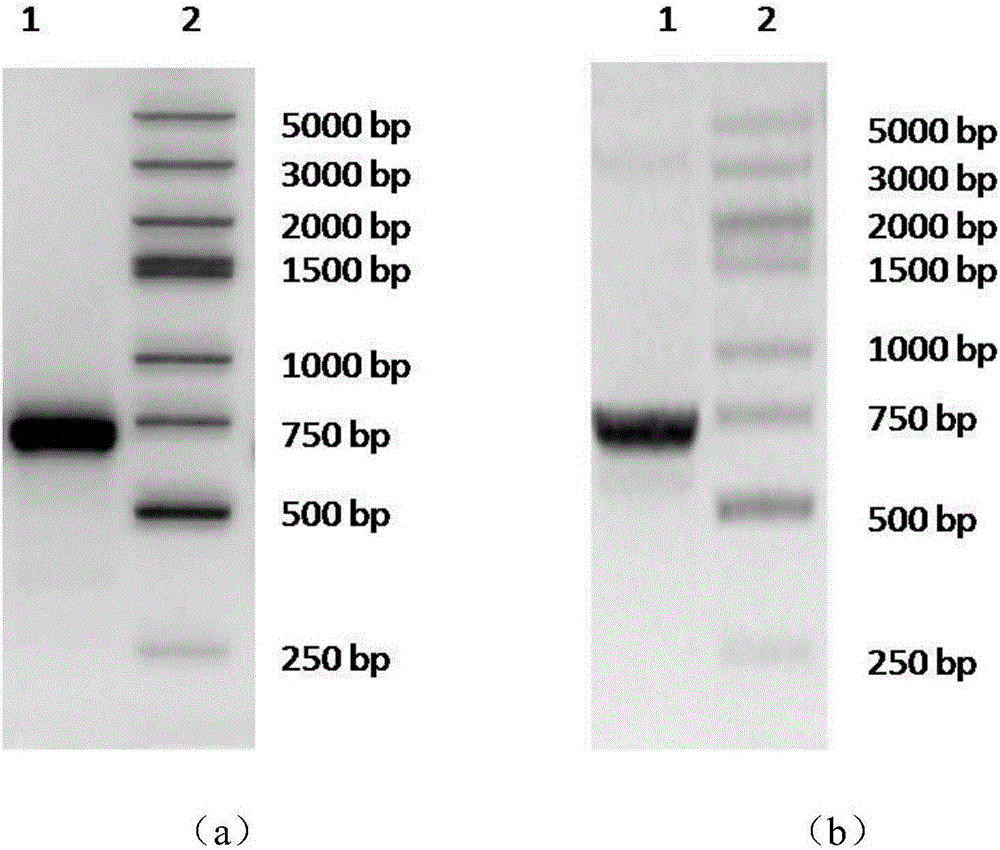
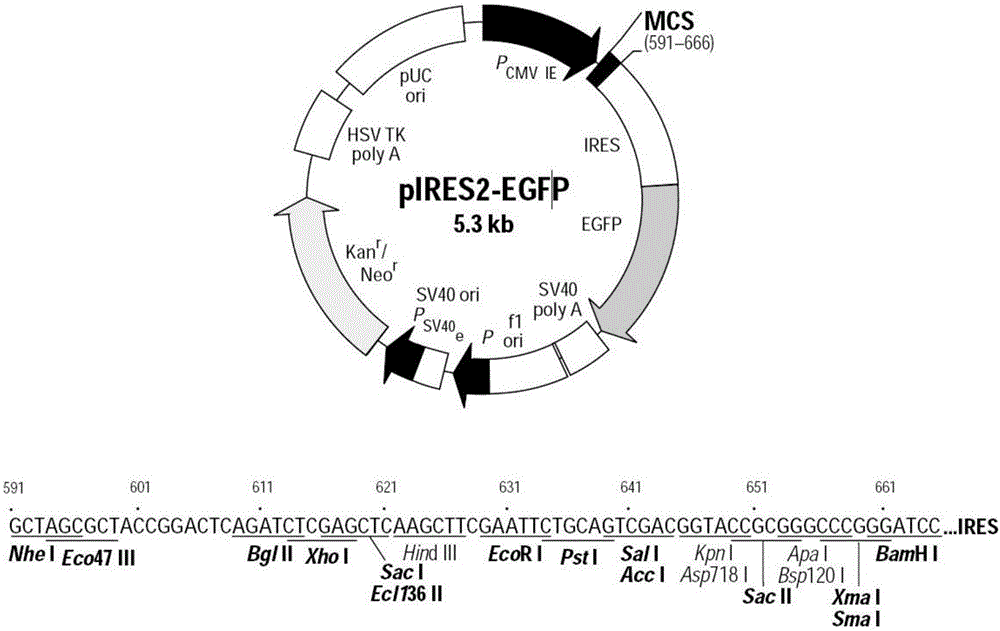
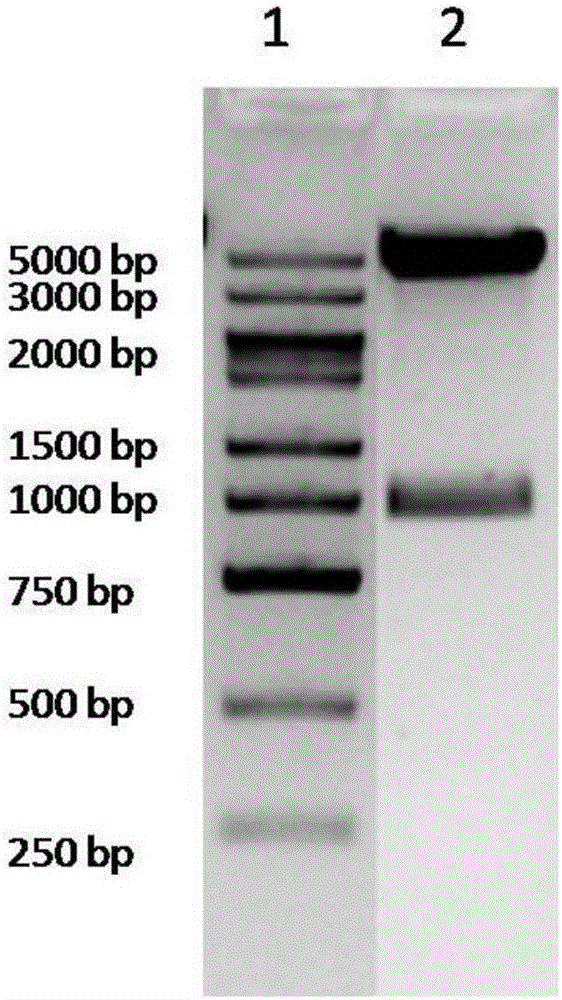
Application of PDL1-IgGFc fusion protein in inhibition of severe malaria morbidity
A fusion protein, PD-1 technology, applied in the direction of fusion polypeptides, peptide/protein components, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., can solve problems such as incomplete elucidation, and achieve the effect of prolonging survival time and relieving cerebral malaria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments, which are explanations of the present invention rather than limitations.
[0034] The pre-experimental results of the present invention in the mouse model of PD-1 gene knockout cerebral malaria have proved that the regulation of the PD-1 / PD-L pathway has a significant impact on the outcome of cerebral malaria, which makes it possible to properly up-regulate PD- The 1 / PD-L pathway makes possible an immunotherapy strategy to alleviate the symptoms of severe malaria such as cerebral malaria.
[0035] Based on the above research results, the present invention puts forward the following hypothesis: if vascular endothelial cells can specifically overexpress PD-L ligands in the mouse cerebral malaria model, then CD8+ CTL cells will receive more PD from endothelial cells. -L signal, more PD-1 receptors on the surface will be activated, thereby transducing more inhibitory si...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com