Tripod-type constant velocity joint
A constant velocity joint and three-ball pin technology, applied in the field of quick joints, can solve problems such as limitation and deviation, achieve effective wear characteristics, reduce operating noise, and achieve the effect of maintenance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
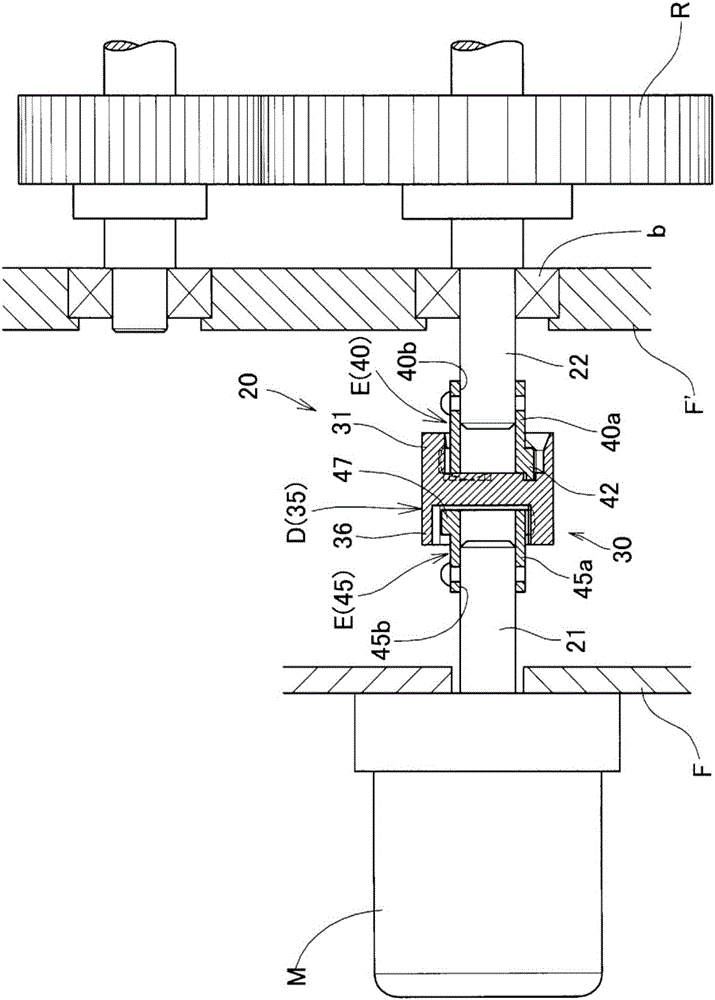
[0080] figure 1 Main parts of the rotation transmission mechanism using the tripod type constant velocity joint according to the first embodiment of the present invention are shown.
[0081] This rotation transmission mechanism includes: a rotating part R having a gear involved in the transmission of driving force, a driving source M constituted by a motor that rotates the rotating part R around an axis, and a mechanism for transmitting the driving force from the driving source M to the rotating part R. Drive transmission device 20 .
[0082] The drive transmission device 20 is provided with a tripod type constant velocity shaft connected by a drive shaft 21 extending from the drive source M and a driven shaft 22 extending from the rotation part R (hereinafter referred to as "rotation body shaft 22"). The connection unit 30 constituted by joints. The connecting unit 30 has the function of suppressing the state that the axis center of the rotating body shaft 22 and the axis c...
no. 2 approach
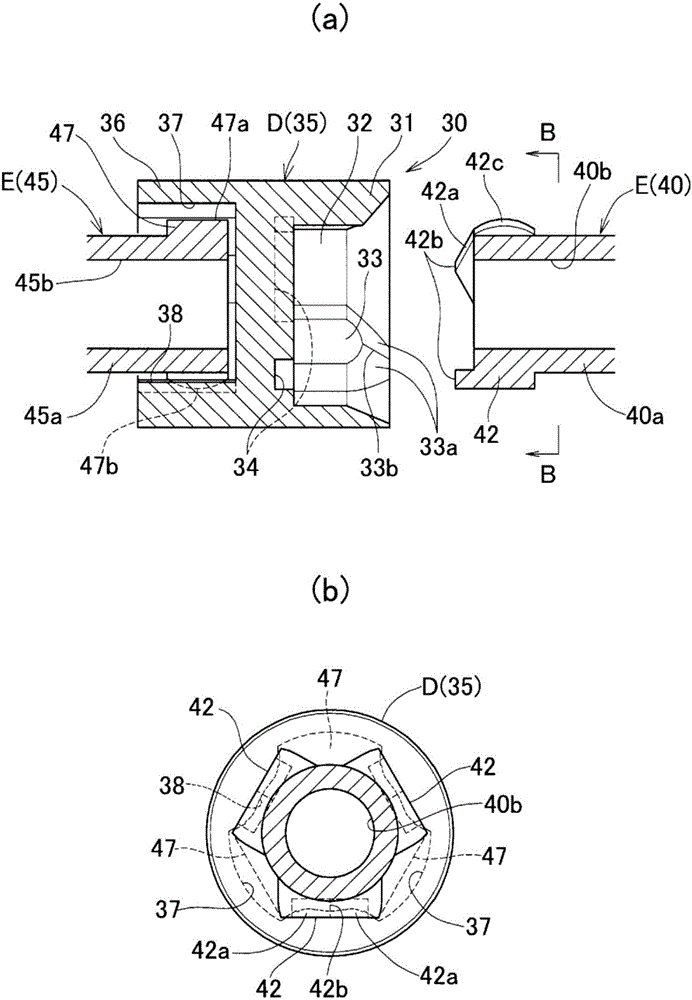
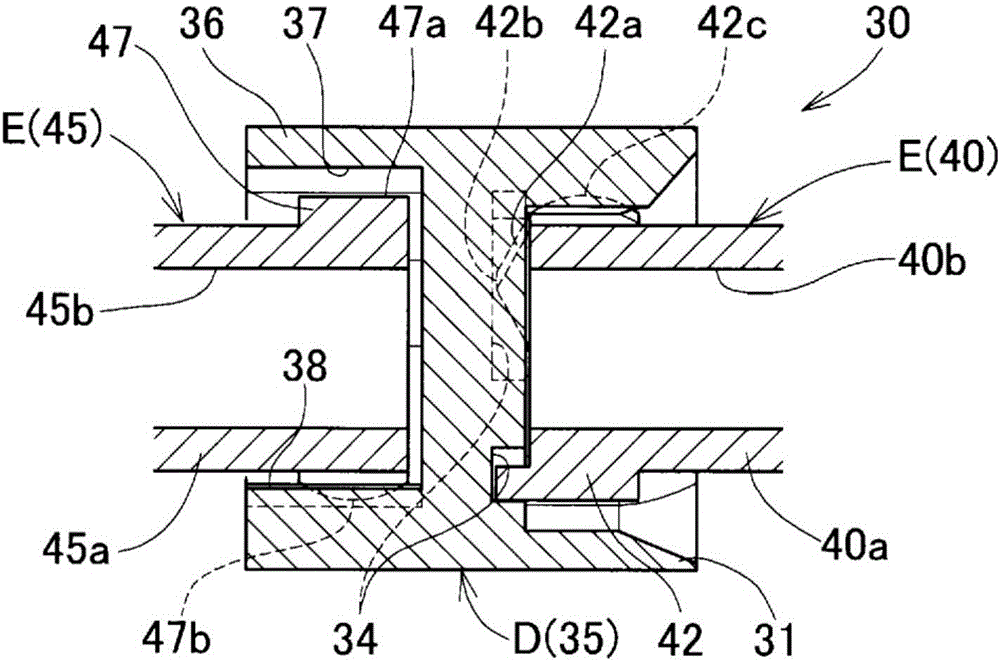
[0113] Figure 7 A second embodiment is shown. The coupling unit 30 of this embodiment is constituted by an intermediate member D and shaft end members E provided on the drive shaft 21 side end and the driven shaft 22 side end of the intermediate member D, respectively. Here, for the intermediate member D, the outer ring 31 is on either side in the axial direction, and the tripod member 45 is on the other side. For the shaft end member E, the side where the above-mentioned outer ring 31 is provided is the tripod member. In the pin member 40 , the side where the tripod member 45 is provided is the outer ring 36 .
[0114] The connection structure of the connection part on one axial side of the intermediate part D, that is, the outer ring 31 and the corresponding tripod part 40, and the connection part on the other side in the axial direction, that is, the outer ring 36 and the corresponding tripod part The connection structure of 45 is the same as that of the above-mentioned ...
no. 3 approach
[0119] Figure 8 Main parts of the rotation transmission mechanism of the tripod type constant velocity joint of the present invention using the third embodiment of the present invention are shown.
[0120] This rotation transmission mechanism includes: a rotating part R having a gear involved in the transmission of driving force, a driving source M constituted by a motor that rotates the rotating part R around an axis, and a mechanism for transmitting the driving force from the driving source M to the rotating part R. Drive transmission device 20 .
[0121] The drive transmission device 20 is provided with a tripod type constant velocity shaft connected by a drive shaft 21 extending from the drive source M and a driven shaft 22 extending from the rotation part R (hereinafter referred to as "rotation body shaft 22"). The connection unit 30 constituted by joints. The connection unit 30 has the function of suppressing the state that the axis center of the rotating body shaft 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com