Sensing of a magnetic target
A technology for magnetic targets and targets, which is applied in the field of magnetic target sensing and can solve problems such as positioning errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
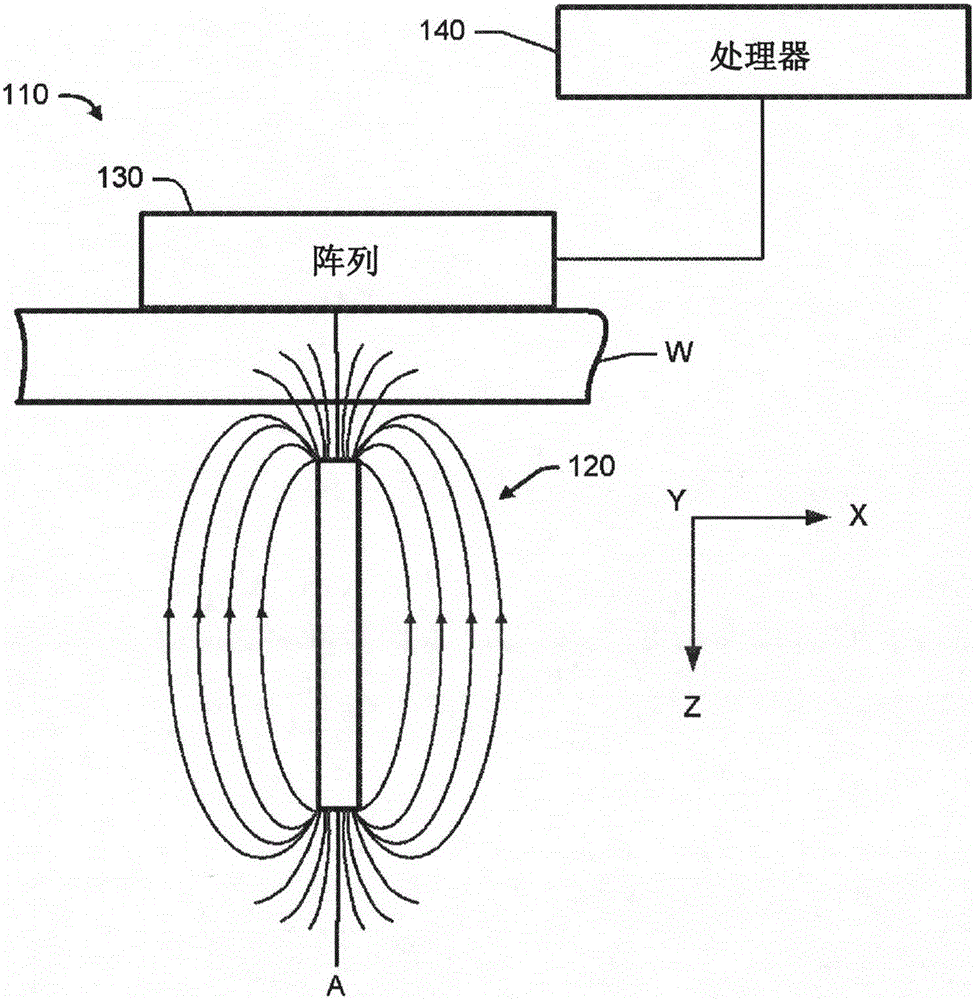
[0018] refer to figure 1 , which illustrates an apparatus 110 comprising a magnetic target 120 for generating a magnetic field that is fairly uniform and concentric about its central axis (A). Flux lines radiate outward from the magnetic target 120 .
[0019] The magnetic target 120 defines a global X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis that form a global coordinate system. The Z axis coincides with the central axis (A) of the magnetic target 120, and a global X-Y plane is formed by the X and Y axes. The global X-Y plane is perpendicular to the central axis (A). The flux lines are assumed to be straight considering that the magnetic field is fairly uniform and concentric when viewed in the global X-Y plane.
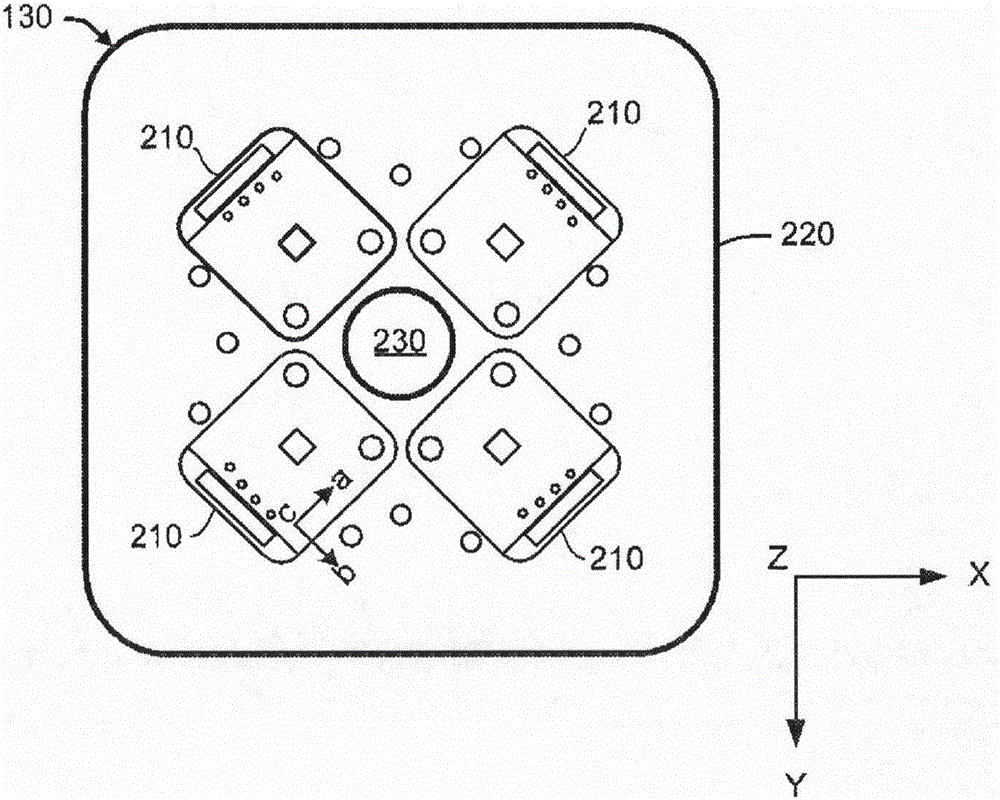
[0020] The device 110 further includes an array 130 of three-axis digital magnetic compasses for sensing magnetic fields. Each digital magnetic compass senses the magnetic field along its local a, b, and c axes, which form a local coordinate system. For example, each digital ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com