Patents
Literature
48 results about "MEMS magnetic field sensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A MEMS magnetic field sensor is a small-scale microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) device for detecting and measuring magnetic fields (Magnetometer). Many of these operate by detecting effects of the Lorentz force: a change in voltage or resonant frequency may be measured electronically, or a mechanical displacement may be measured optically. Compensation for temperature effects is necessary. Its use as a miniaturized compass may be one such simple example application.
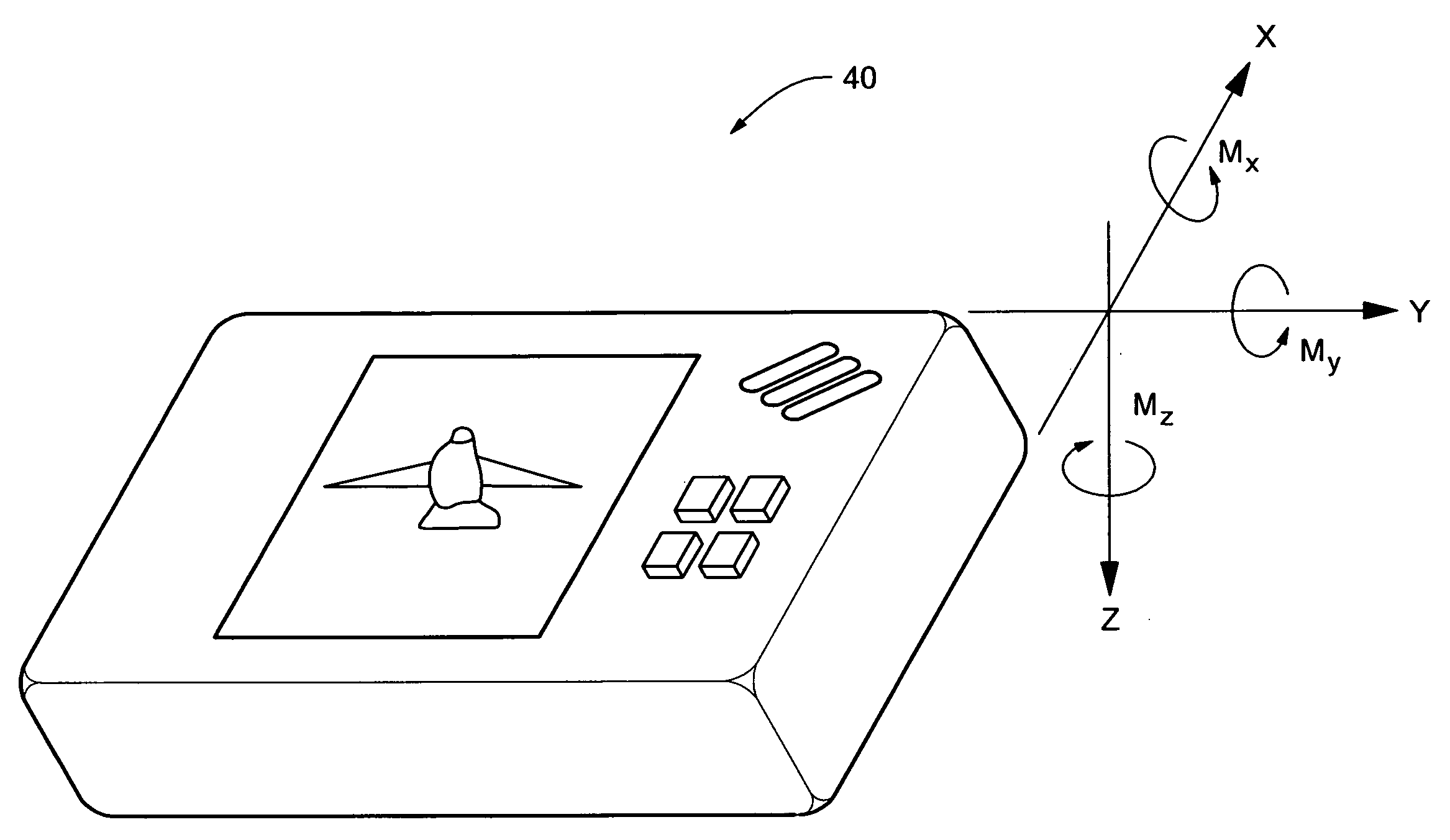
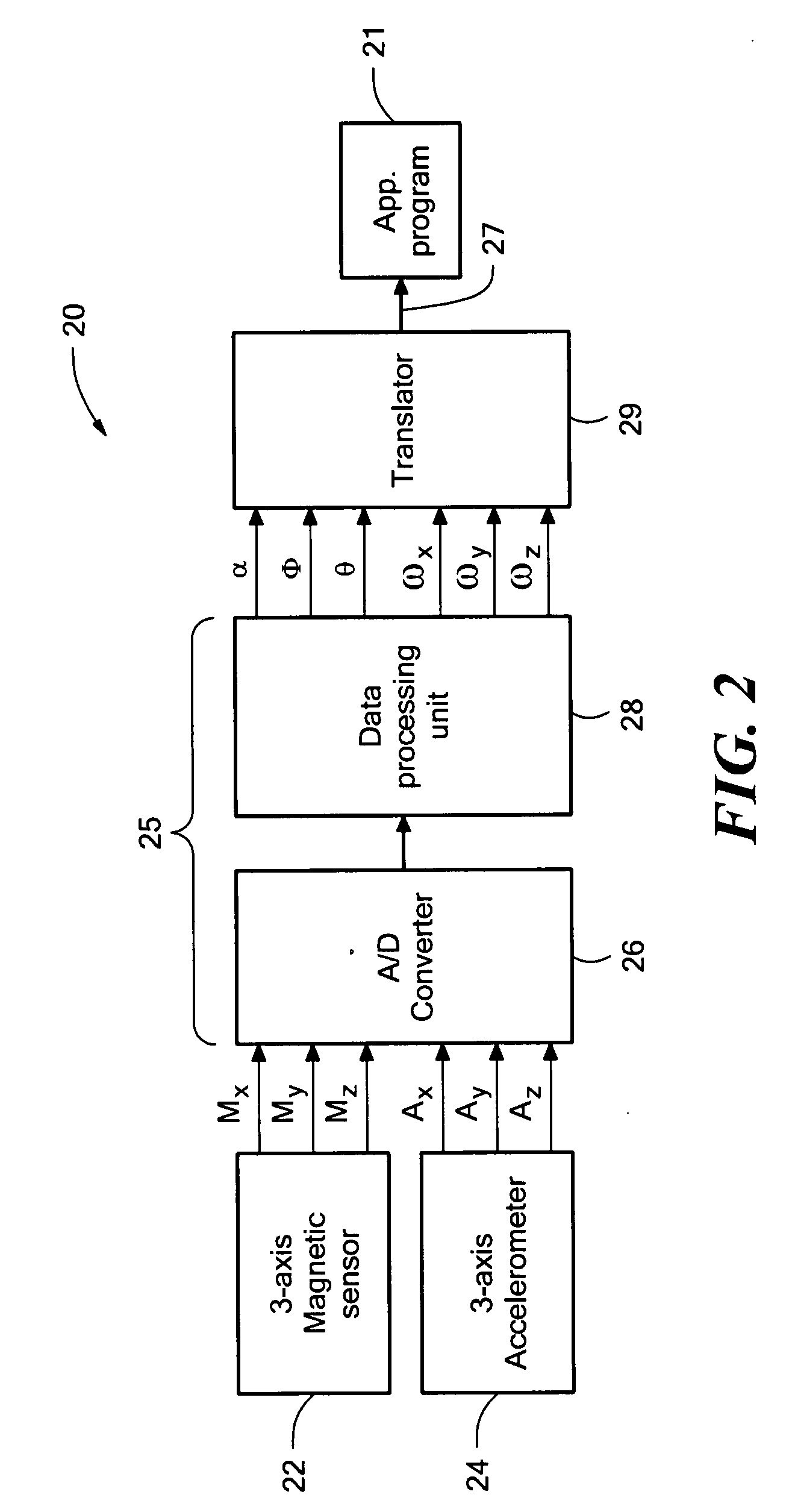
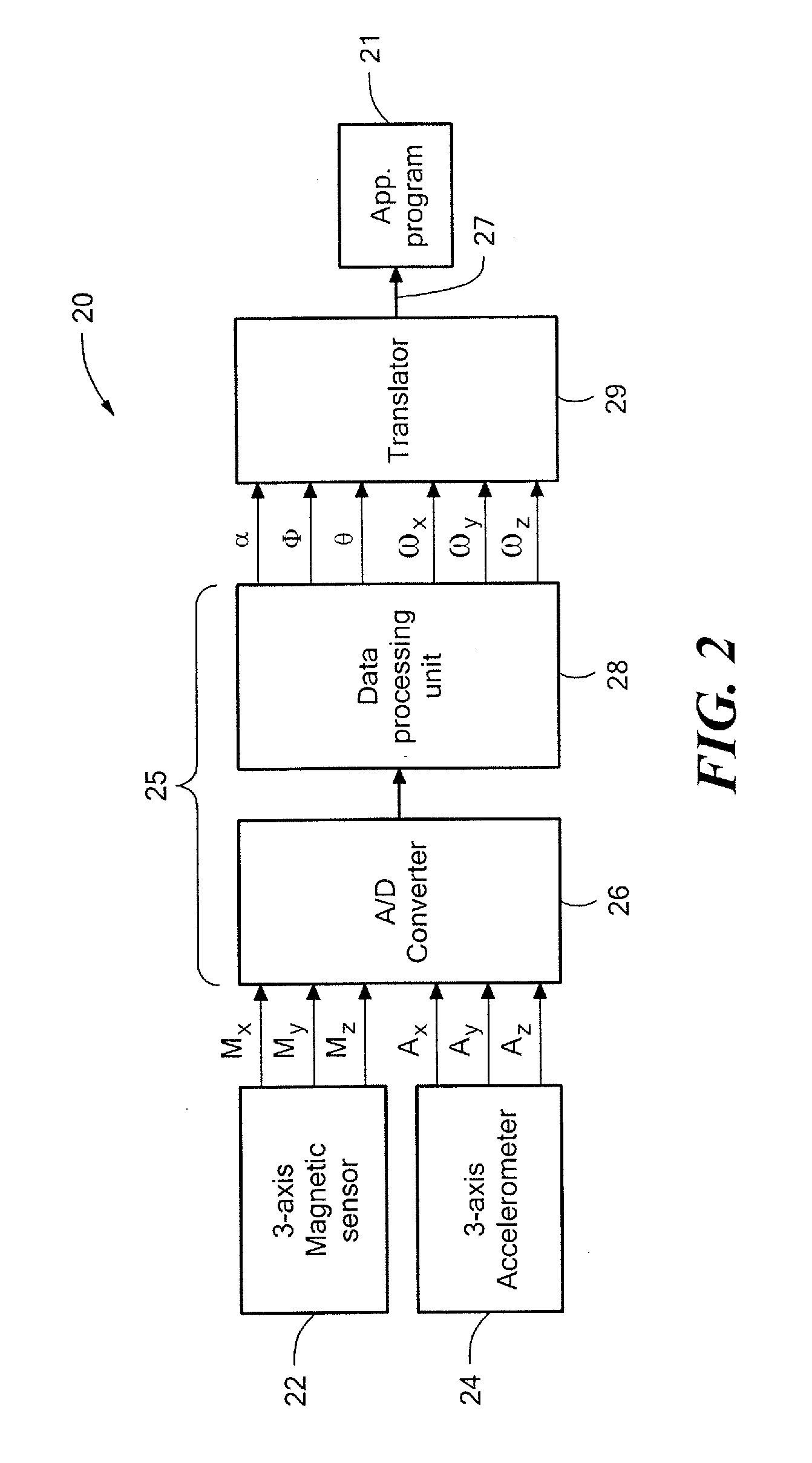
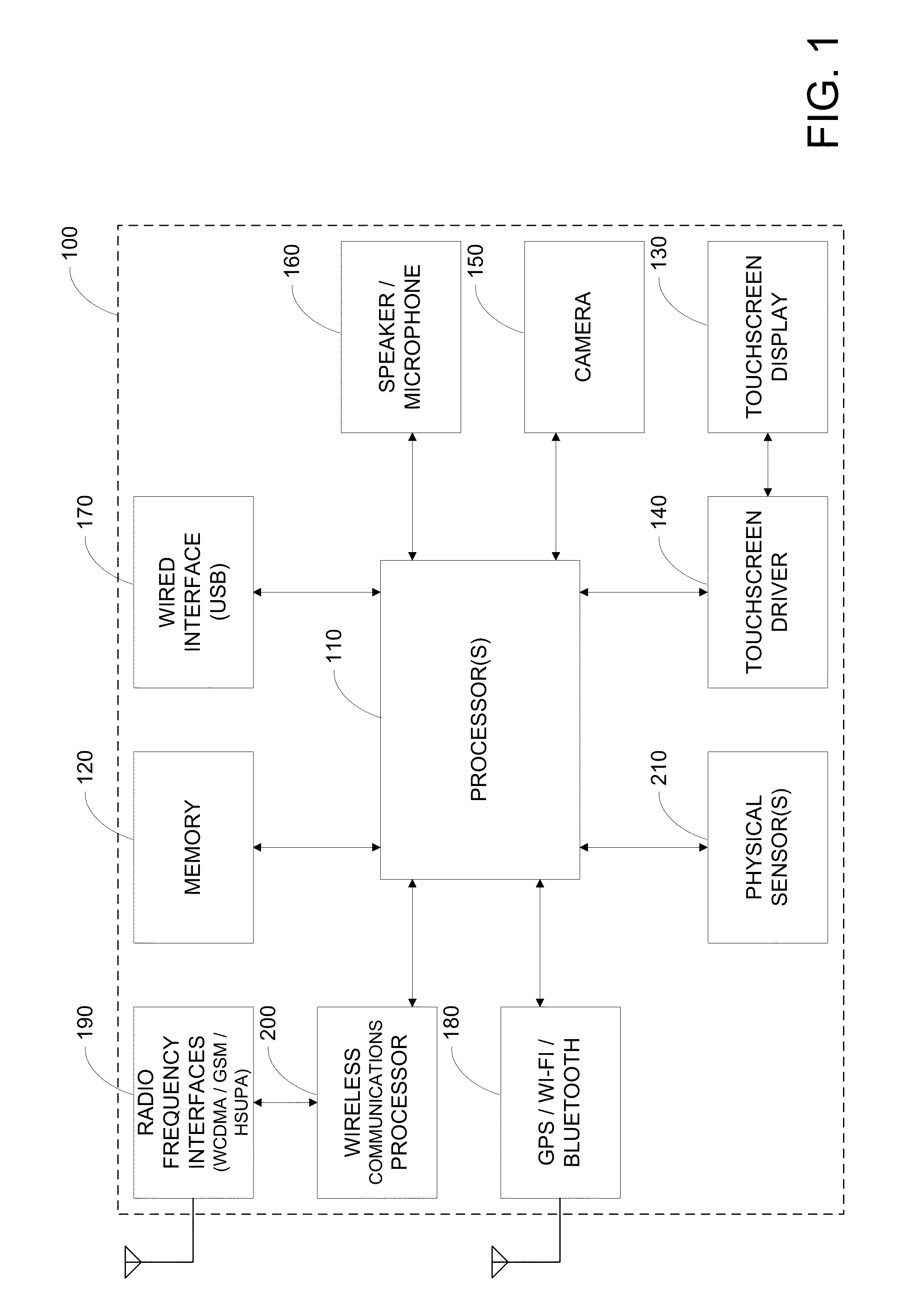
System for sensing yaw rate using a magnetic field sensor and portable electronic devices using the same
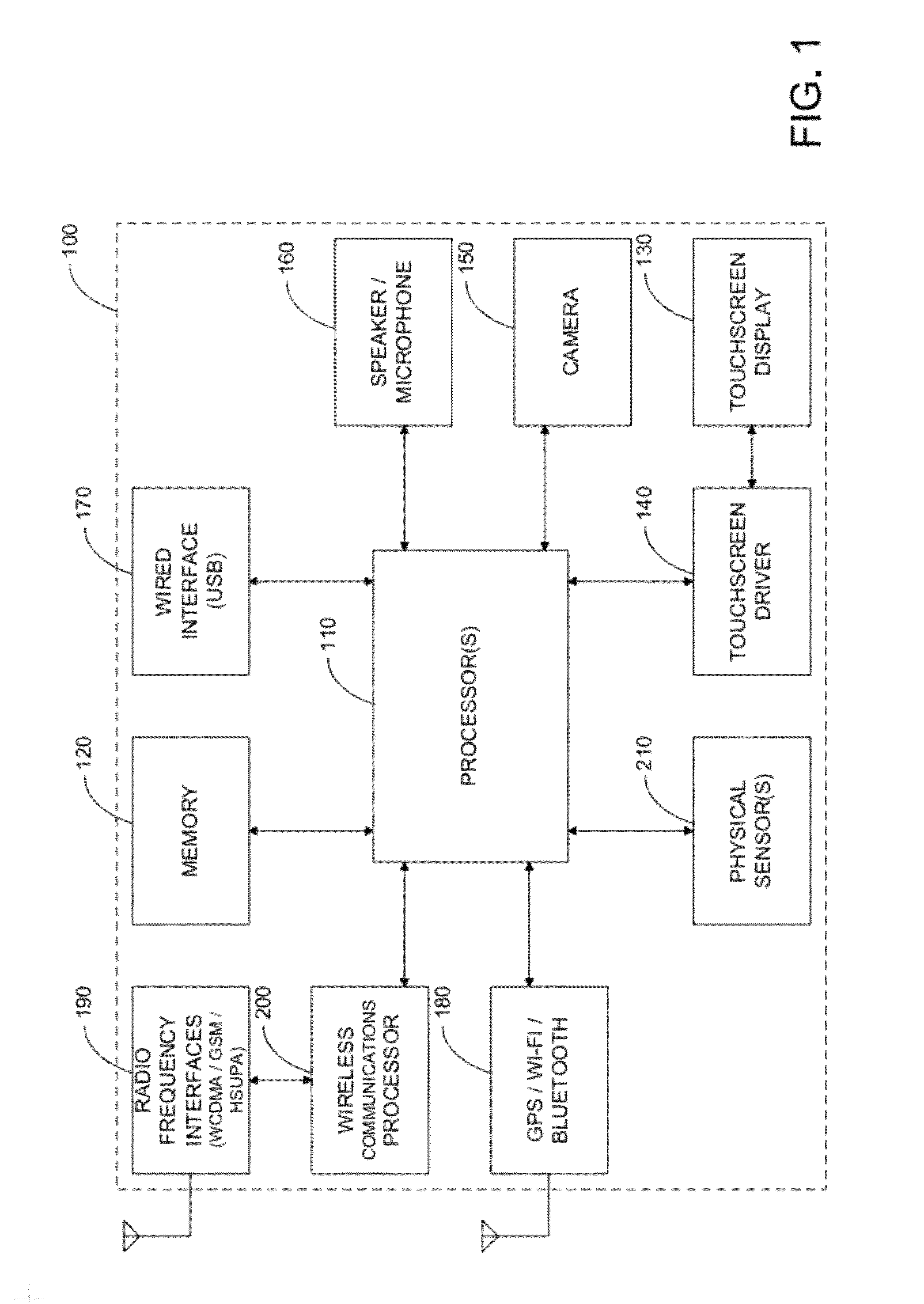
InactiveUS20080042973A1Digital data processing detailsAcceleration measurementTriaxial accelerometerMEMS magnetic field sensor
An attitude- and motion-sensing system for an electronic device, such as a cellular telephone, a game device, and the like, is disclosed. The system, which can be integrated into the portable electronic device, includes a two- or three-axis accelerometer and a three-axis magnetic compass. Data about the attitude of the electronic device from the accelerometer and magnetic compass are first processed by a signal processing unit that calculates attitude angles (pitch, roll, and yaw) and rotational angular velocities. These data are then translated into input signals for a specific application program associated with the electronic device.
Owner:MEMSIC
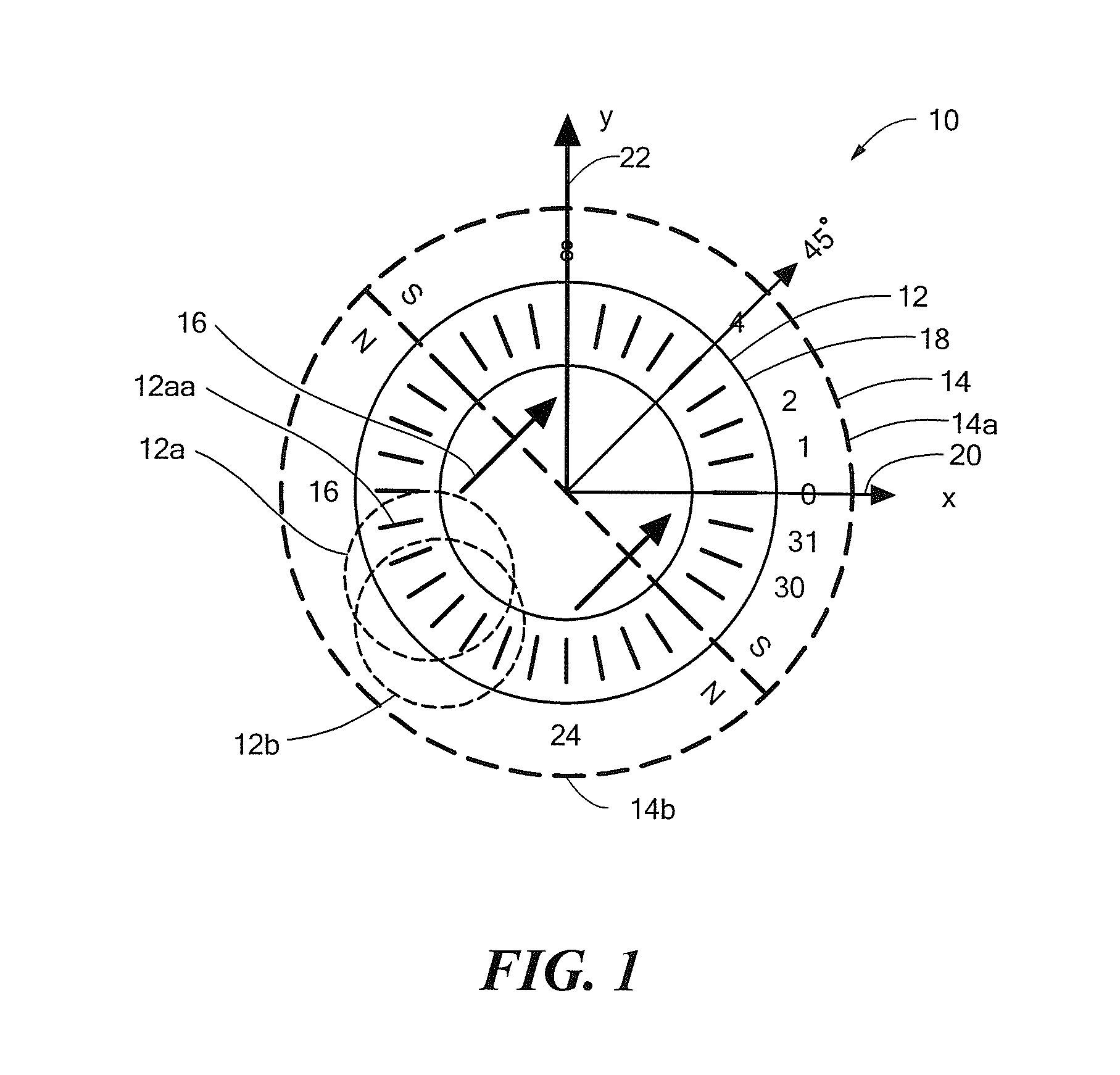
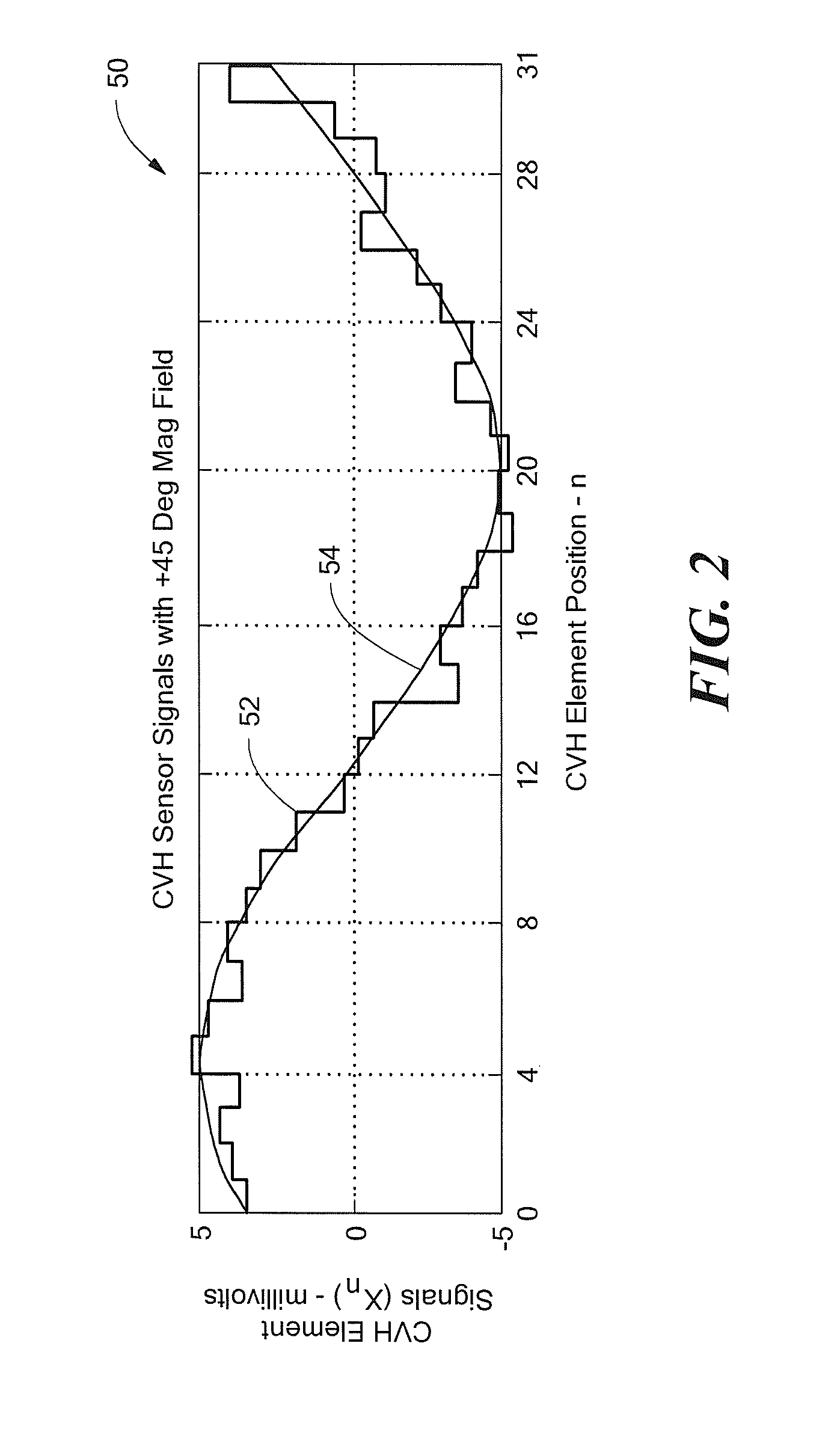
Arrangements for self-testing a circular vertical hall (CVH) sensing element and/or for self-testing a magnetic field sensor that uses a circular vertical hall (CVH) sensing element
ActiveUS20120313635A1Magnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesElectrical measurementsMEMS magnetic field sensorNormal mode
A switching arrangement around a circular vertical Hall (CVH) sensing element can provide a normal mode configuration responsive to magnetic fields at some times, and at least one of a first and a second self-test mode configuration not responsive to a magnetic field but simulating a magnetic field at other times. A corresponding method is also described.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
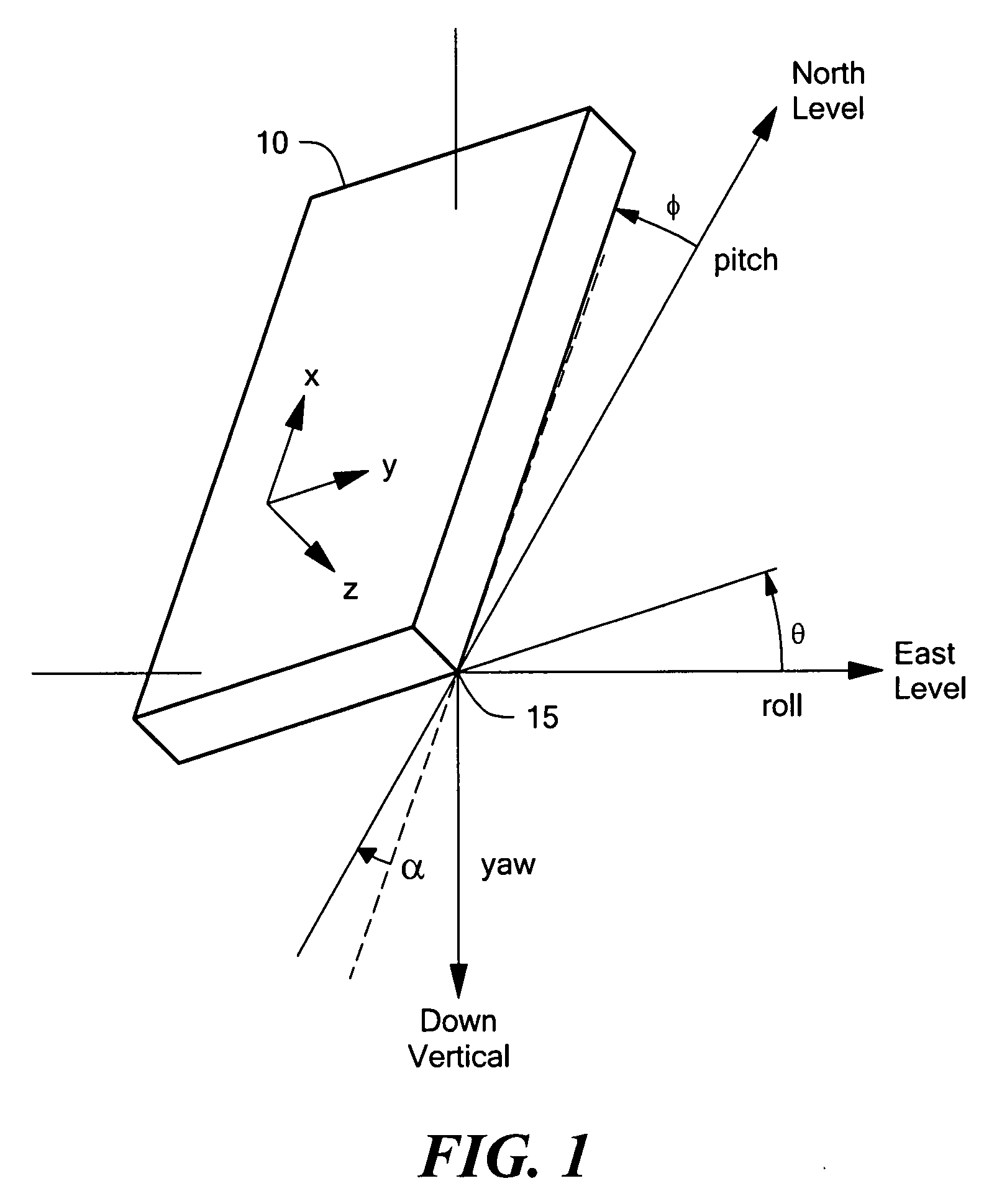
System and method of sensing attitude and angular rate using a magnetic field sensor and accelerometer for portable electronic devices
InactiveUS20110307213A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesDigital data processing detailsAccelerometerMEMS magnetic field sensor
A system for determining motion information including attitude and angular rate of a dynamic object. The system includes a magnetic-field sensing device to measure in the body coordinate frame of reference an intensity and / or direction of a magnetic field in three substantially orthogonal directions; an acceleration-sensing device adapted to measure total acceleration of the object in the body coordinate frame of reference; and a processor adapted to calculate attitude and angular rate by combining total acceleration measurement data and magnetic field measurement data with the kinematic model in a filter.
Owner:MEMSIC
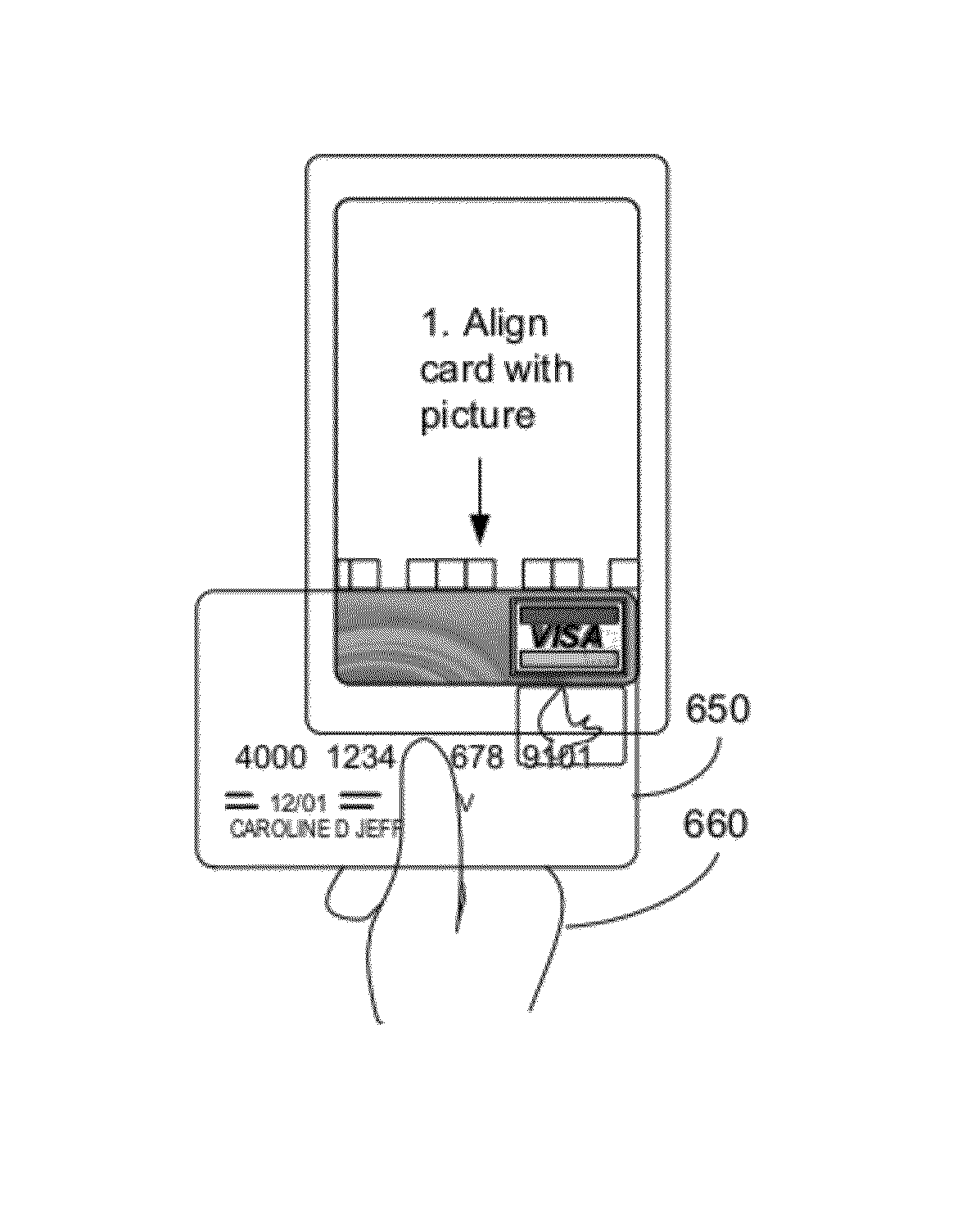
Methods and apparatus for facilitating capture of magnetic credit card data on a hand held device
ActiveUS8181874B1Digital data processing detailsDevices with sensorCredit cardMEMS magnetic field sensor
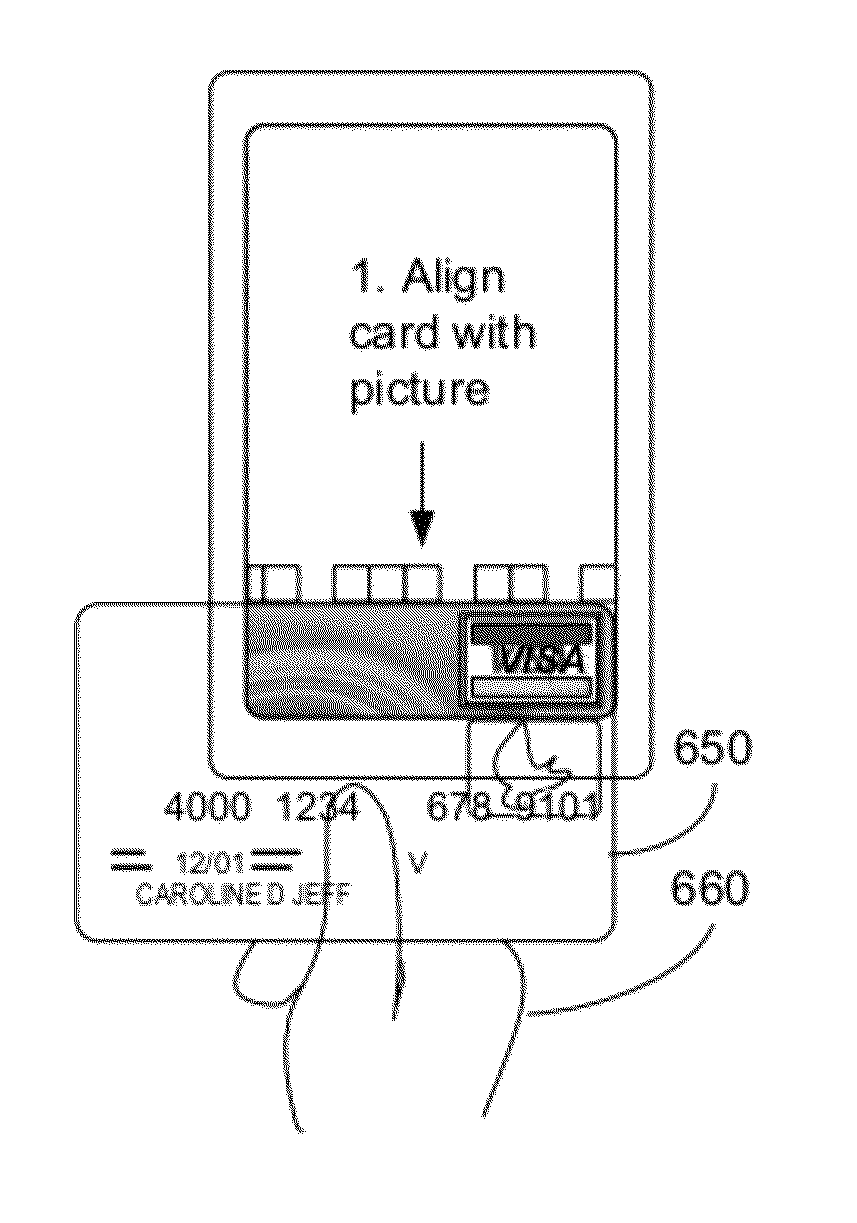
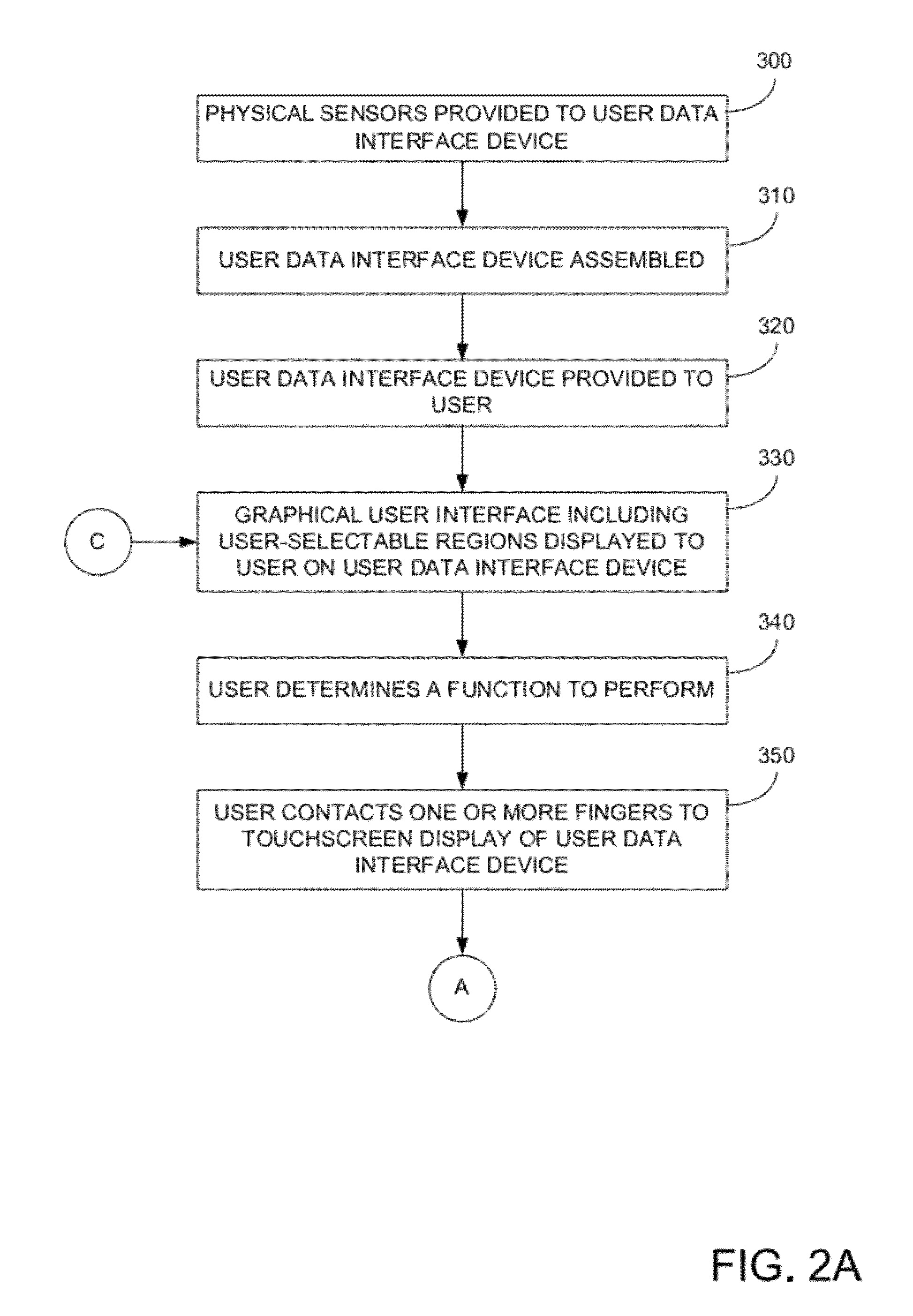
A computer implemented method for processing data stored on a magnetic stripe of a user medium performed by a hand-held computer system includes displaying an alignment GUI on a display of the computer system, wherein the GUI includes a visual alignment mark on the display at a first offset relative to a MEMS magnetic field sensor in the computer system, wherein when a user aligns the user medium to the alignment mark GUI, a portion of a first track of the magnetic stripe is disposed above the MEMS magnetic field sensor, sensing, by the MEMS magnetic field sensor, magnetic data stored on the first track when the user aligns the user medium to the visual alignment mark, and moves the user medium along the visual alignment mark, and determining user data stored on the first track from the magnetic data stored on the first track.
Owner:MOVELLA INC
Methods and apparatus for capturing magnetic credit card data on a hand held device
A handheld device for capturing magnetic credit card data includes a MEMS magnetic field sensor disposed within the housing, wherein the MEMS magnetic field sensor is configured to determine a plurality of magnetic data stored on a magnetic stripe of a user provided media when the user disposes a user provided media proximate to the housing, and a processor disposed within the housing and coupled to the MEMS magnetic field sensor, wherein the processor is programmed to receive the plurality of user data stored on the user provided media, wherein the processor is configured to execute an application program, and wherein the processor is programmed to provide at least a subset of the plurality of user data to the application program.
Owner:MOVELLA INC
Micro electro-mechanical system magnetic field sensor and measuring method
InactiveCN101320081ASimple structureReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMEMS magnetic field sensorResonance
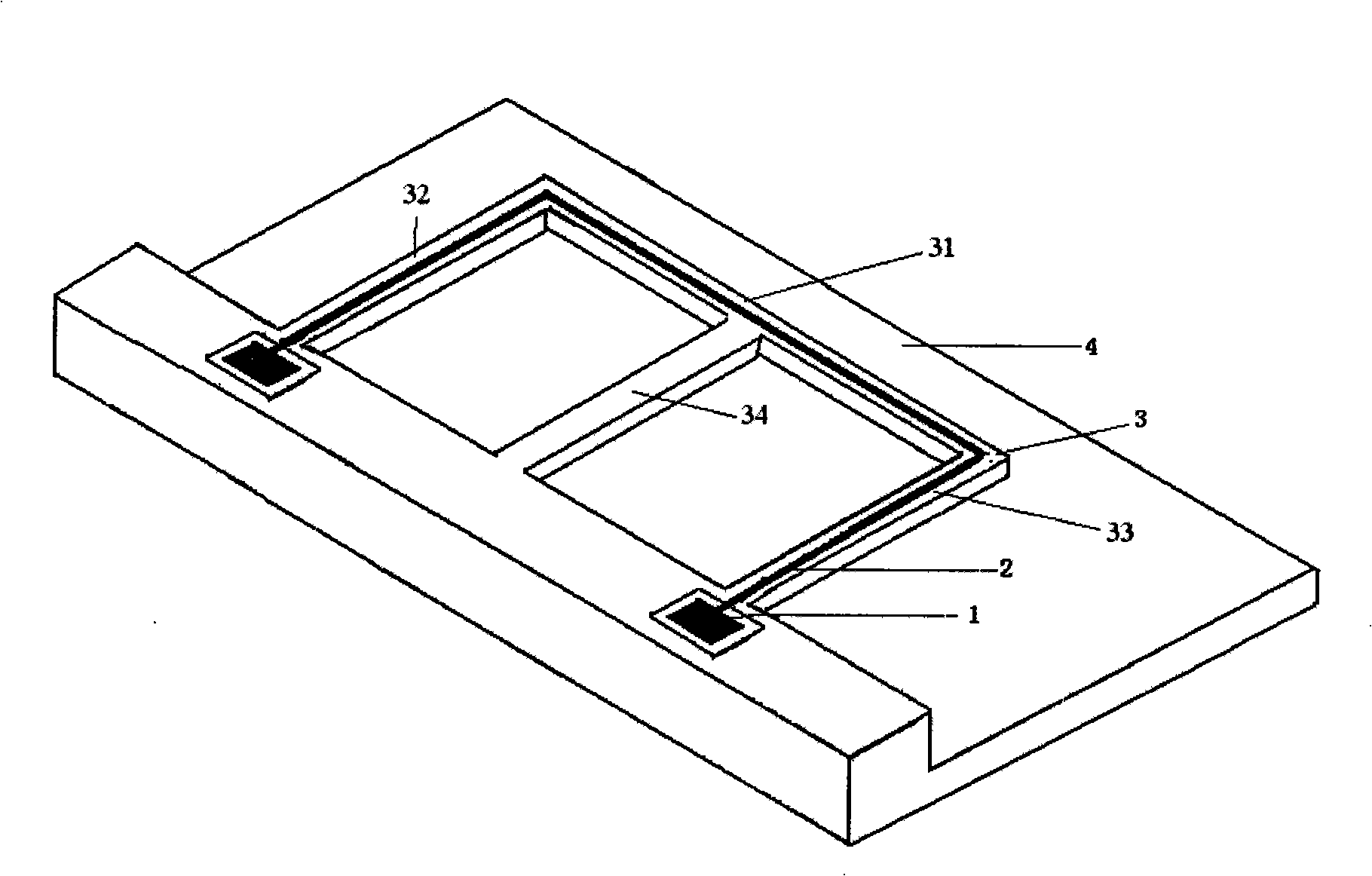
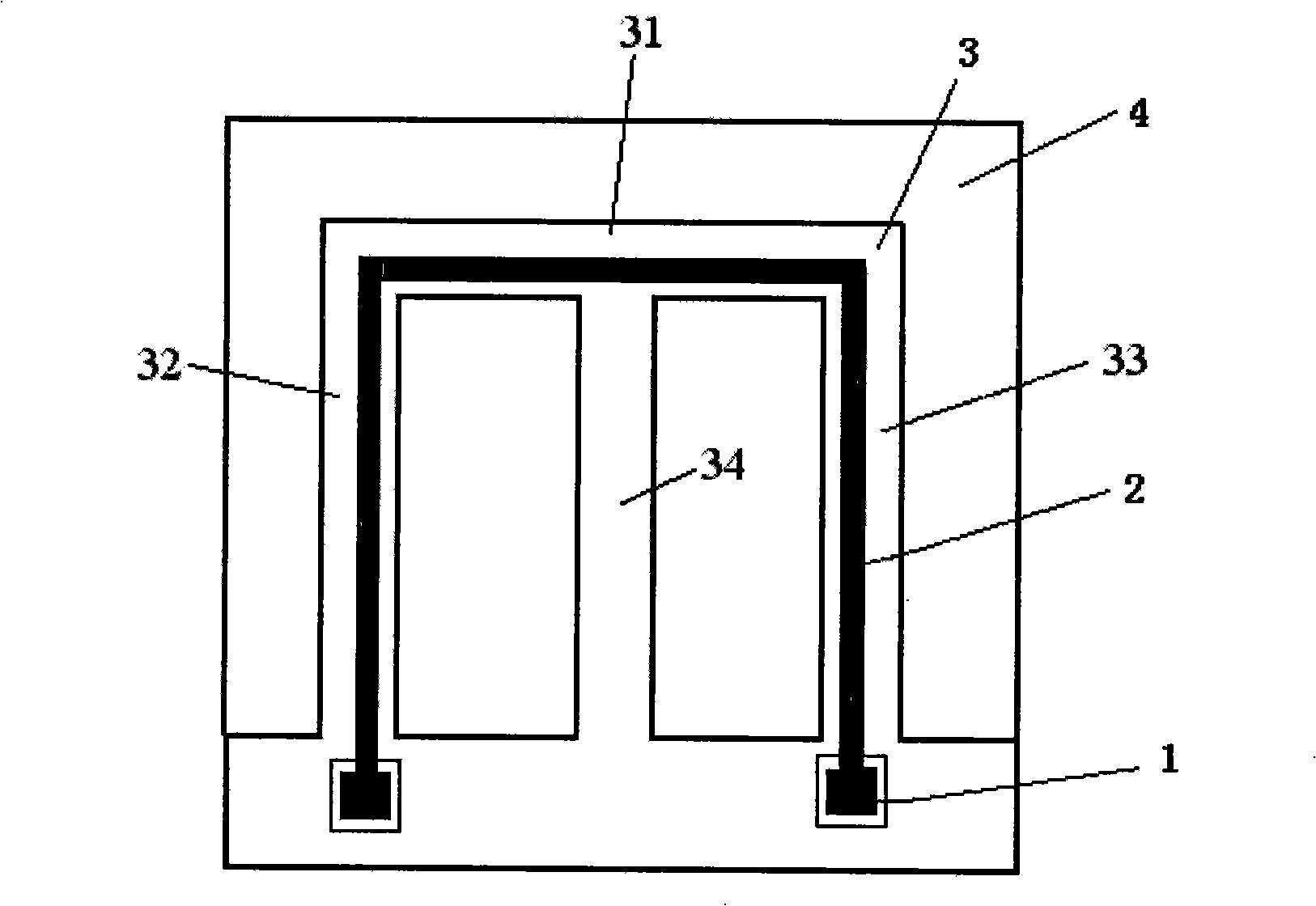
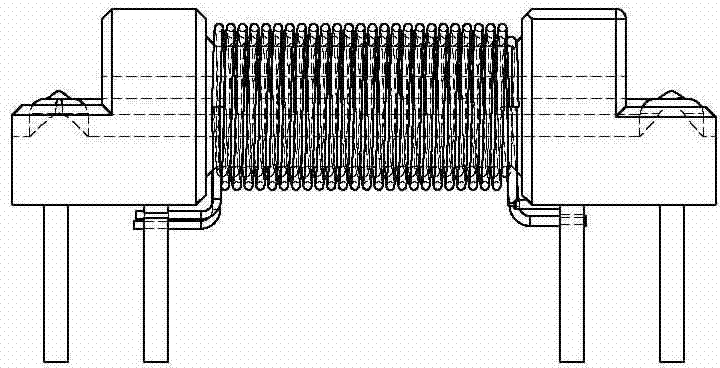
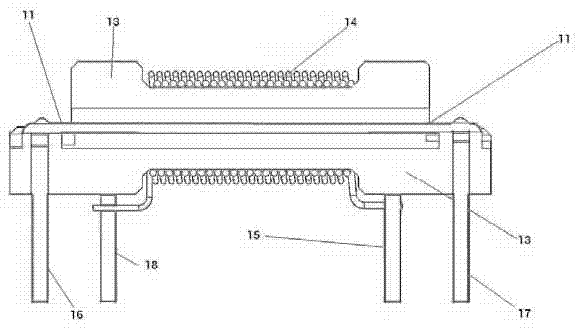
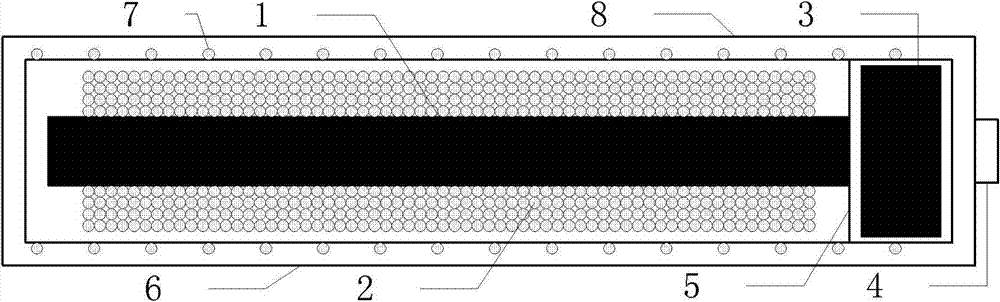
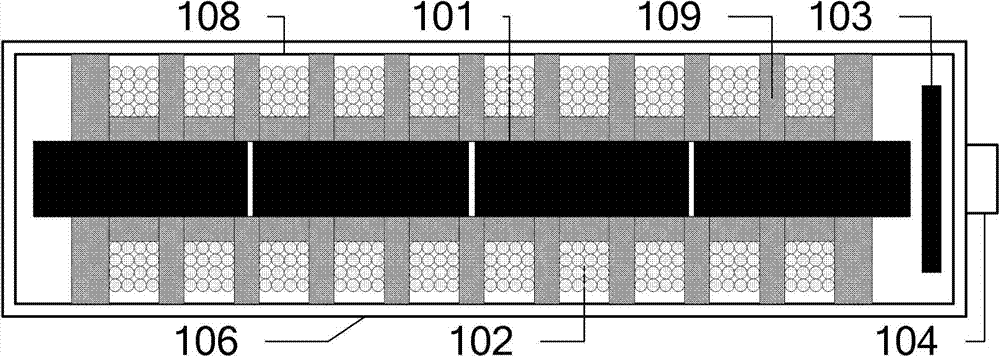
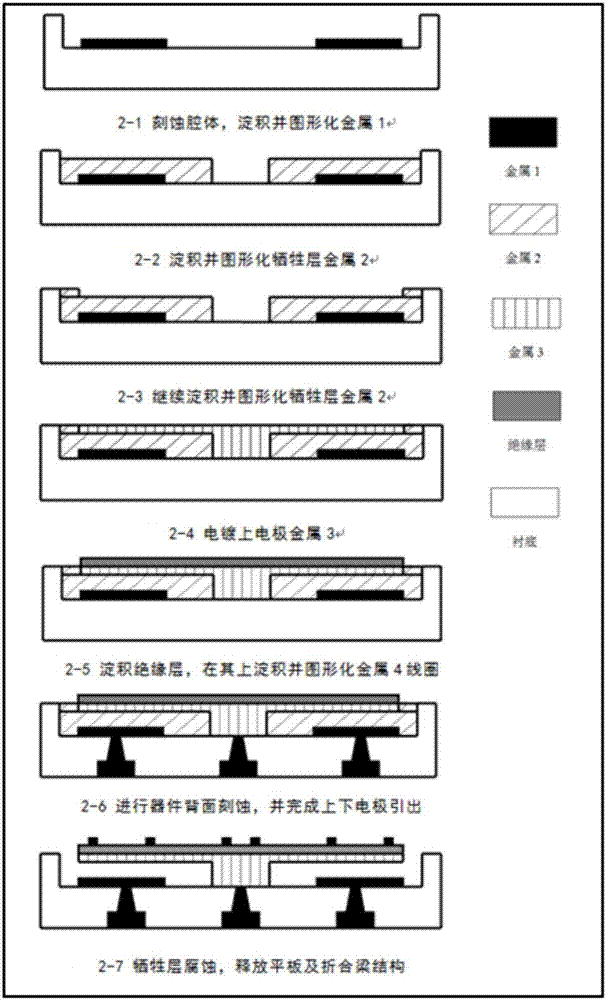
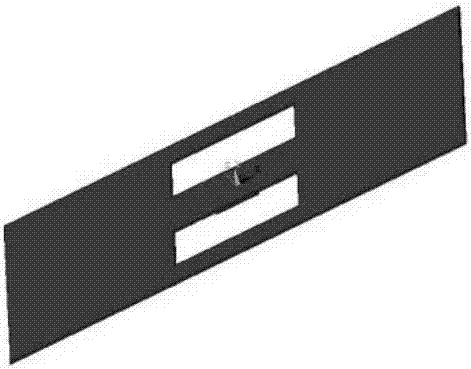
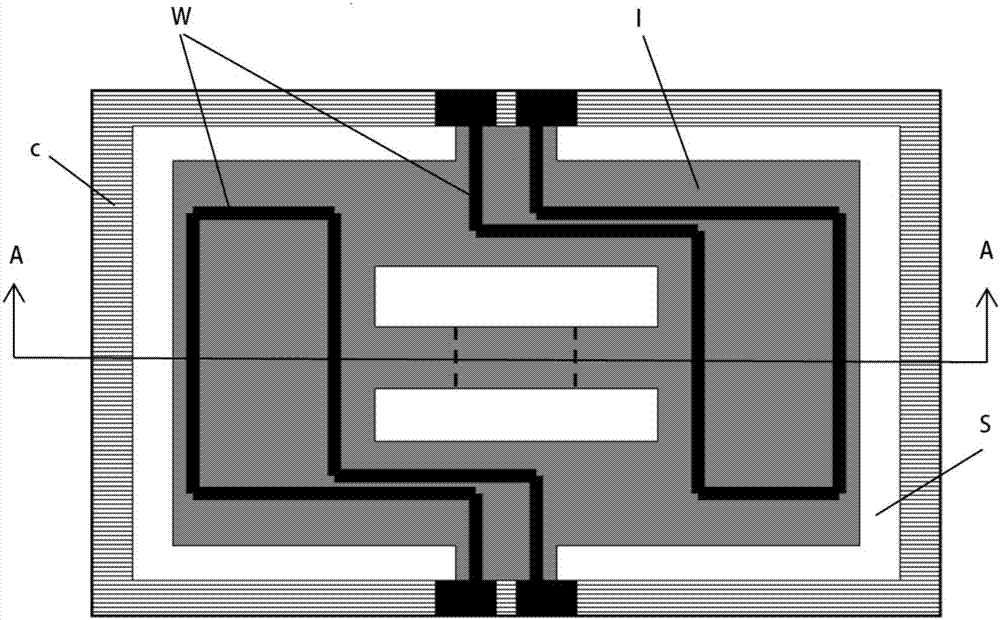
A micro-electro-mechanical system magnetic field sensor and a measuring method relates to a magnetic field sensor and a measuring method, which have low energy consumption, simple structure, quick response and high reliability. The sensor is composed of an anchor area (1), induced metal wires (2), an E-type cantilever beam (3) and a substrate (4); wherein, the E-type cantilever beam is actuated by the static or driven by the Lorentz force, and is forced to generate the vibration; the cantilever beam generates the resonance under the action of a certain frequency; the induced metal wires (2) which are plated on the E-type cantilever beam (3) can move along with the vibration of the E-type cantilever beam (3). The induced metal wires (2) make the movement of cutting the magnetic lines of force in the magnetic field; thus induced voltage can be induced in the metal wires; the induced voltage in the induced metal wires (3) are measured to achieve the purpose of measuring the magnetic field.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
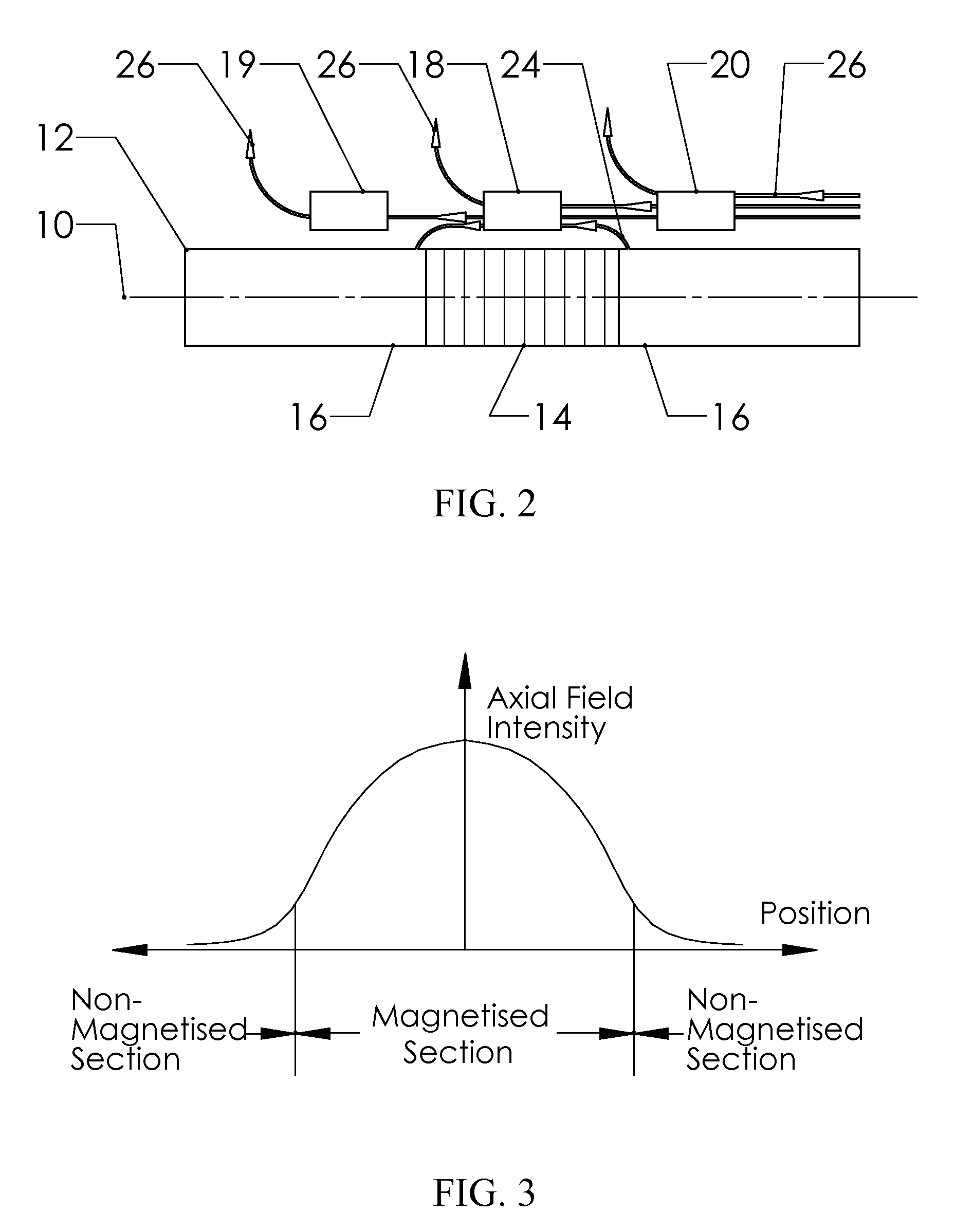
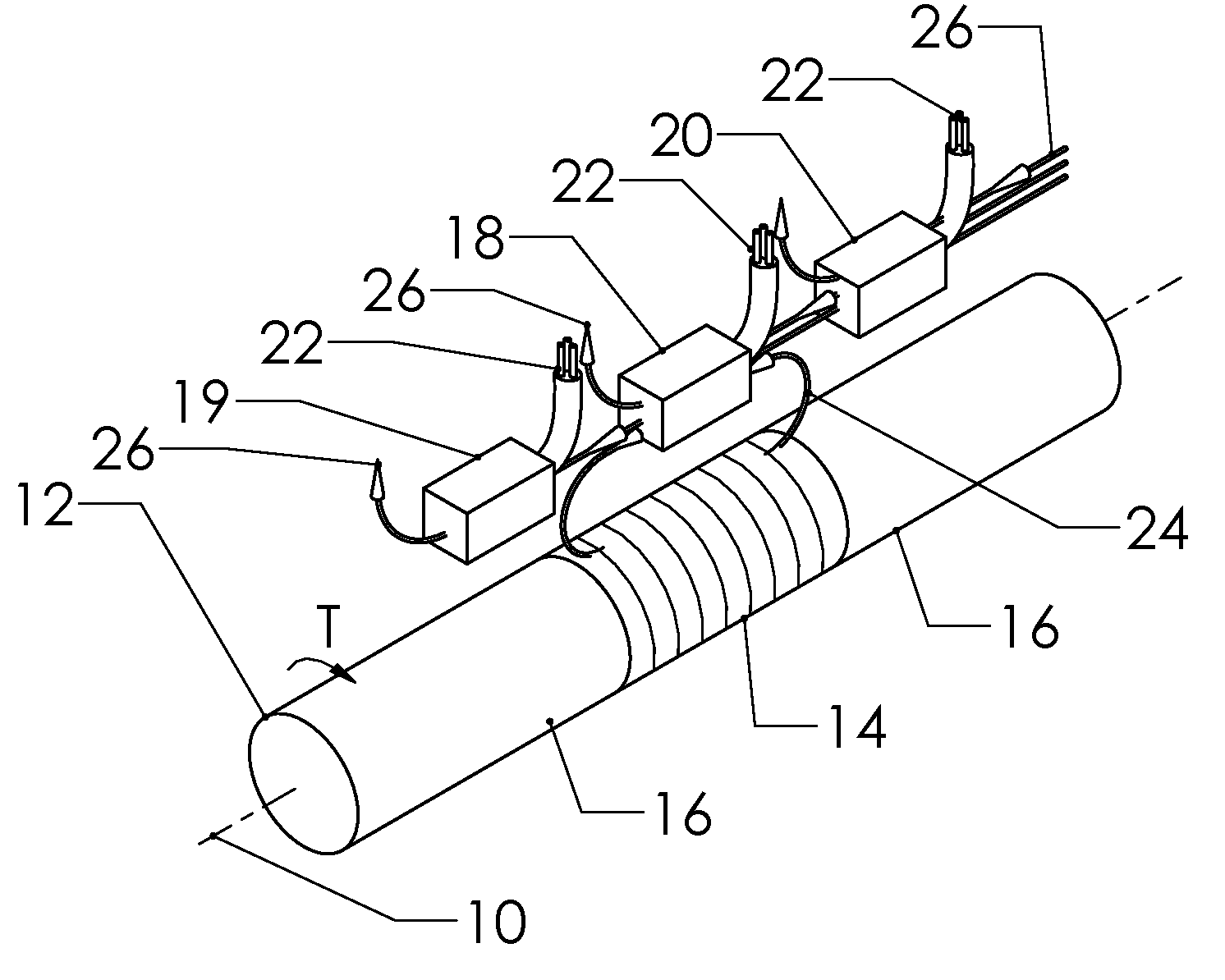
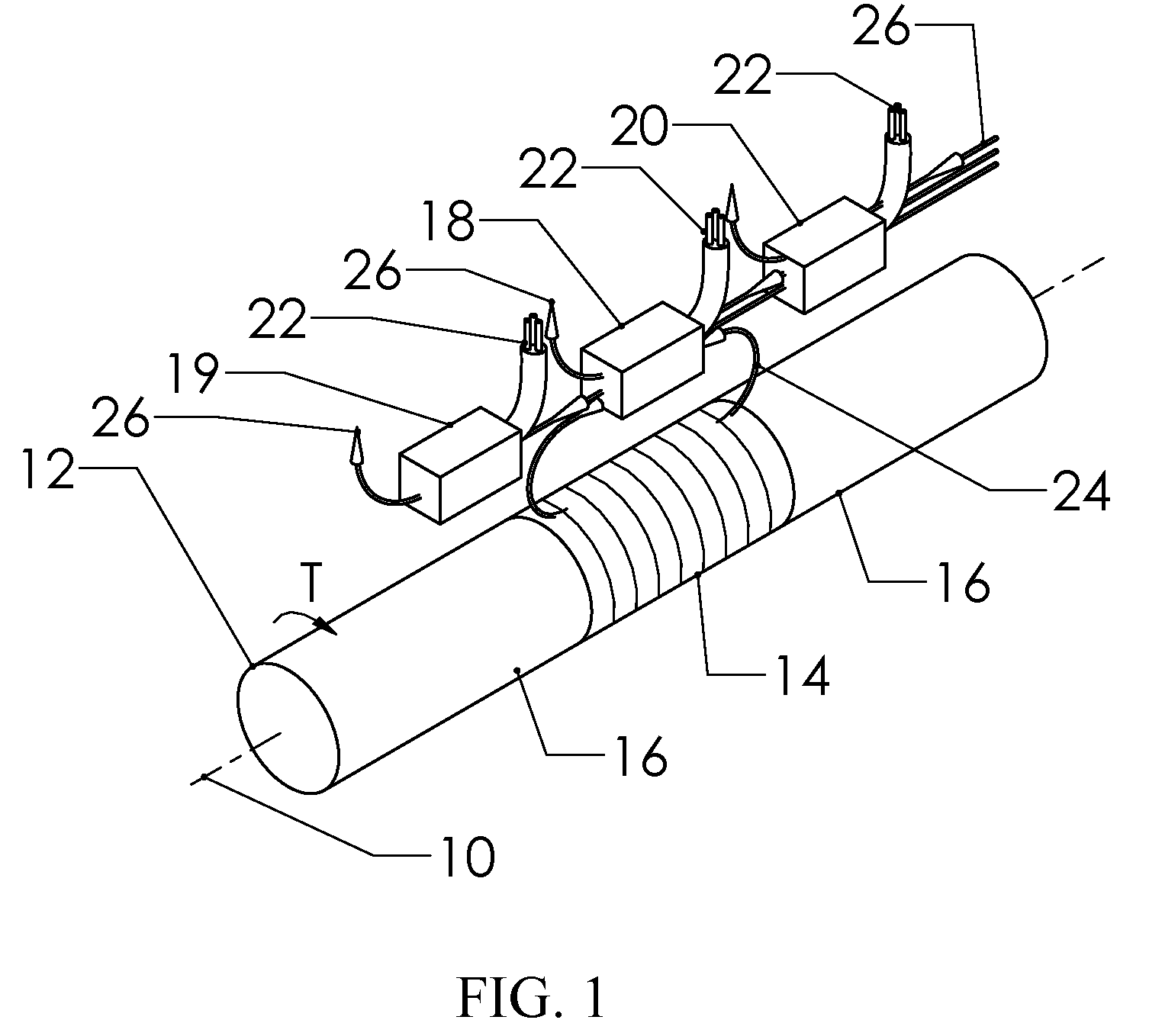
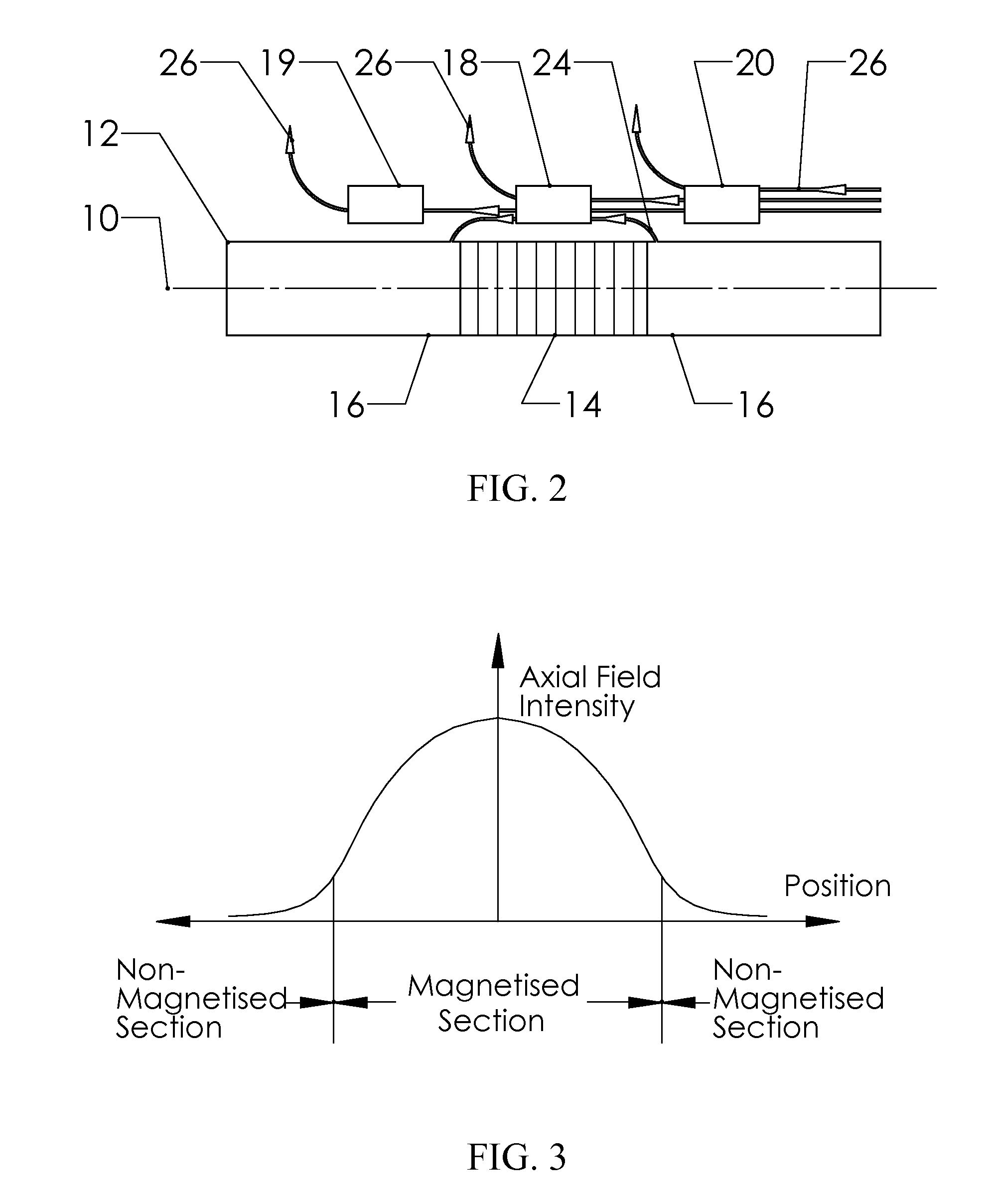
Self-compensating magnetoelastic torque sensor system
InactiveUS8001849B2Improve reliabilityWork measurementMagnetostrictive property measurementsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic source
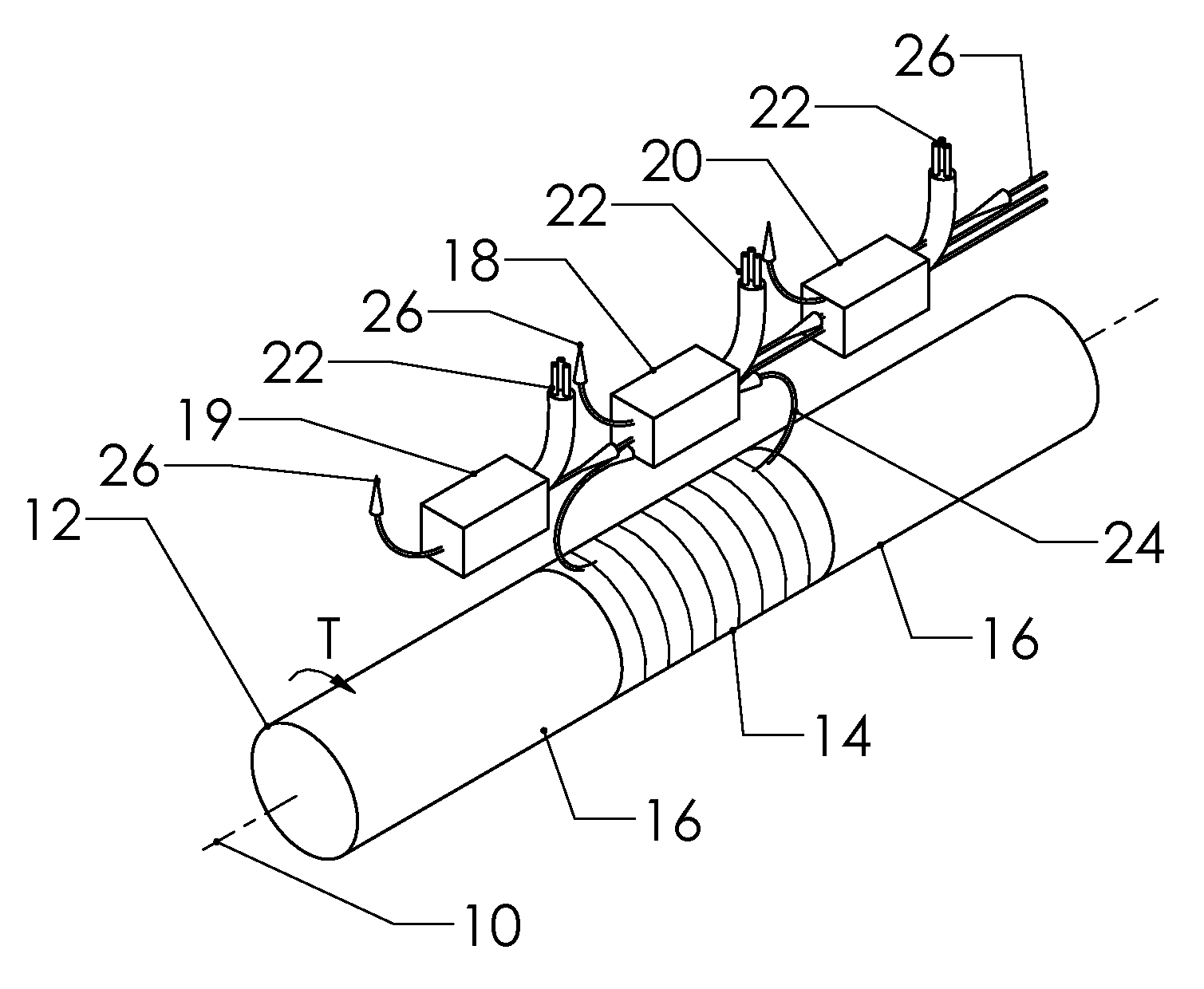
A magnetic torque transducer arrangement for self-compensating effects of external magnetic sources and temperature offset includes a shaft with at least one magnetized zone, at least one active magnetic field sensor and at least one passive magnetic field sensor disposed in such a way that the active field sensor is always in a position with higher magnetic field strength arising from applied torque than that of the passive sensor. Passive field sensors may also be placed on both sides of the active field sensor, or on only one side of the active field sensor. The transducer output is obtained by subtracting the output of the passive field sensors from that of the active field sensor, thus canceling out the effect of the interfering magnetic field flux and temperature offset on the torque transducer, and partially filtering out the temperature sensitivity drift and rotational dependant signal.
Owner:WENG WENSHENG
Self-compensating magnetoelastic torque sensor system
InactiveUS20100242626A1Improve reliabilityWork measurementMagnetostrictive property measurementsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic source
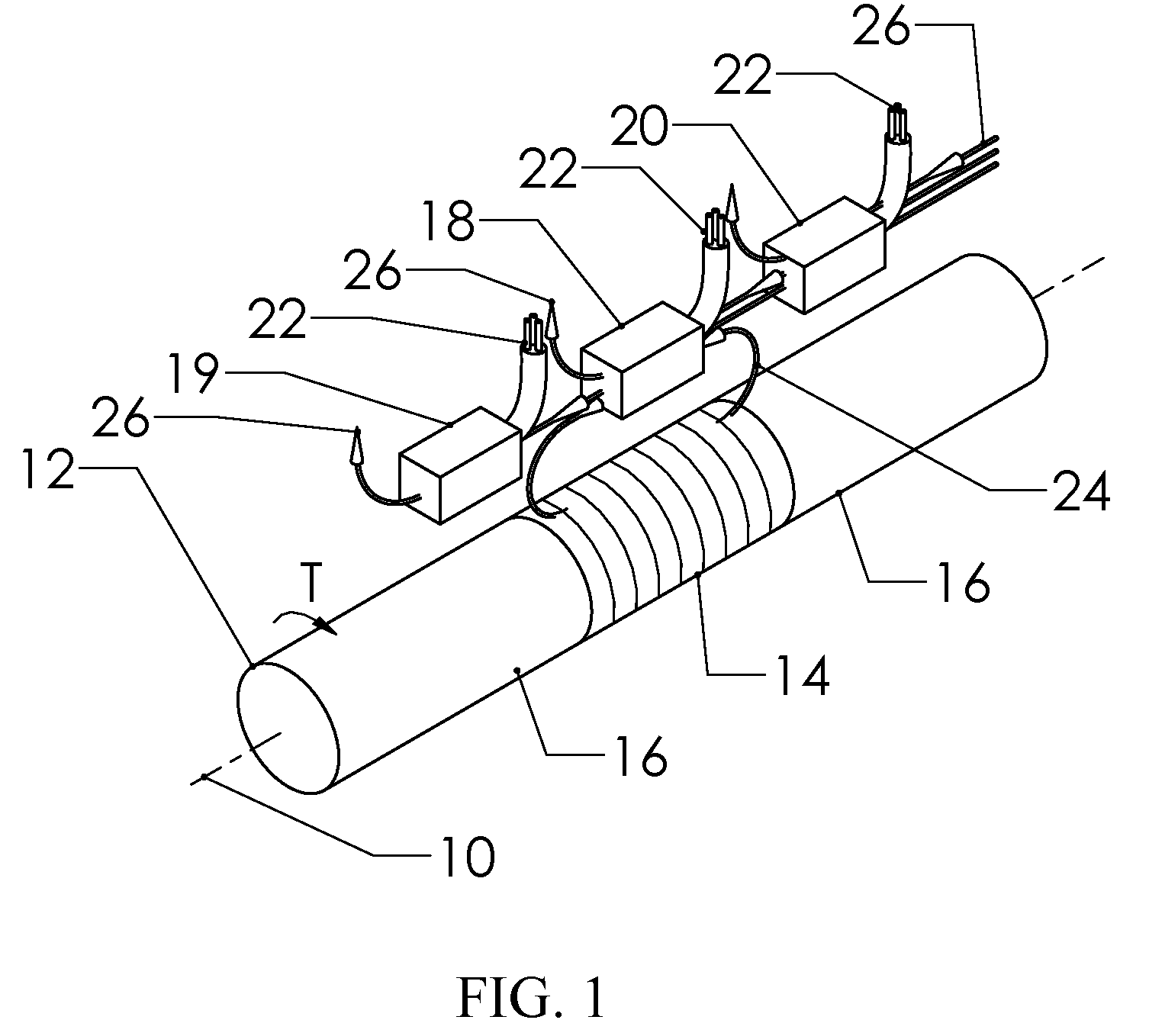
An improved magnetic torque transducer arrangement for self-compensating effects of external magnetic sources and temperature offset comprises a shaft with at least one magnetized zone, at least one active magnetic field sensor and at least one passive magnetic field sensor disposed in such a way that active field sensor always in a position with higher magnetic field strength arise from applied torque than that of passive sensor. Passive field sensors may also be placed in both sides of the active field sensor, or on one side of active field sensor only. The transducer output is obtained by subtract the output of passive field sensors from that of active field sensor thus cancel out the effect of interfering magnetic field flux and temperature offset on the torque transducer, and partially filter out temperature sensitivity drift and rotational dependant signal. The sensitivity of active and passive field sensors can also be electrically matched by calibrating them in a uniform magnetic field, thus a completely common mode rejection can be achieved. The sensor arrangements may also be utilized in other type of sensors that extract changes in magnetic fields to indirectly detect direction, speed, presence, force, linear position, or angle to cancel out interfering magnetic field and temperature offset effect.
Owner:WENG WENSHENG
Micro-mechanical magnetic field sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102680917AHigh strengthReduce power consumptionDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesMEMS magnetic field sensorElectromotive force
The invention provides a micro-mechanical magnetic field sensor and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of micro-electro-mechanical systems. The method comprises the following steps of: manufacturing metal coils and a pad on a device structure layer; manufacturing a device structure by dry etching; and releasing the device structure to form a harmonic oscillator. The harmonic oscillator of the micro-mechanical magnetic field sensor provided by the invention operates in an extension mode, so induced electromotive force which is generated by each section of metal cutting magnetic induction line on each metal coil can be superposed, and the intensity of an output signal is improved. Moreover, the micro-mechanical magnetic field sensor has the advantages of low power consumption, simple driving / detection circuit, simple process, high industrial value and the like and is slightly influenced by temperature.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
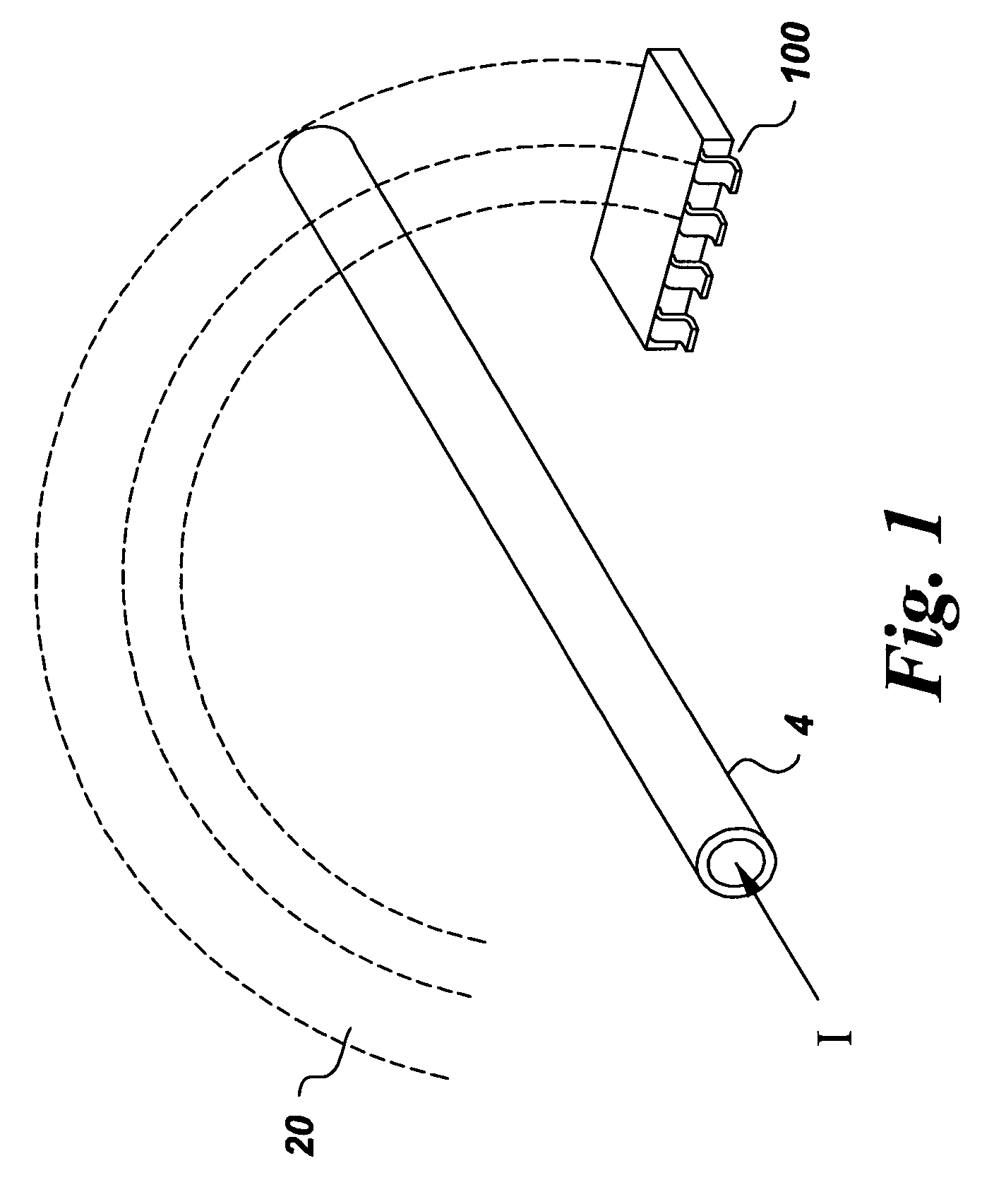
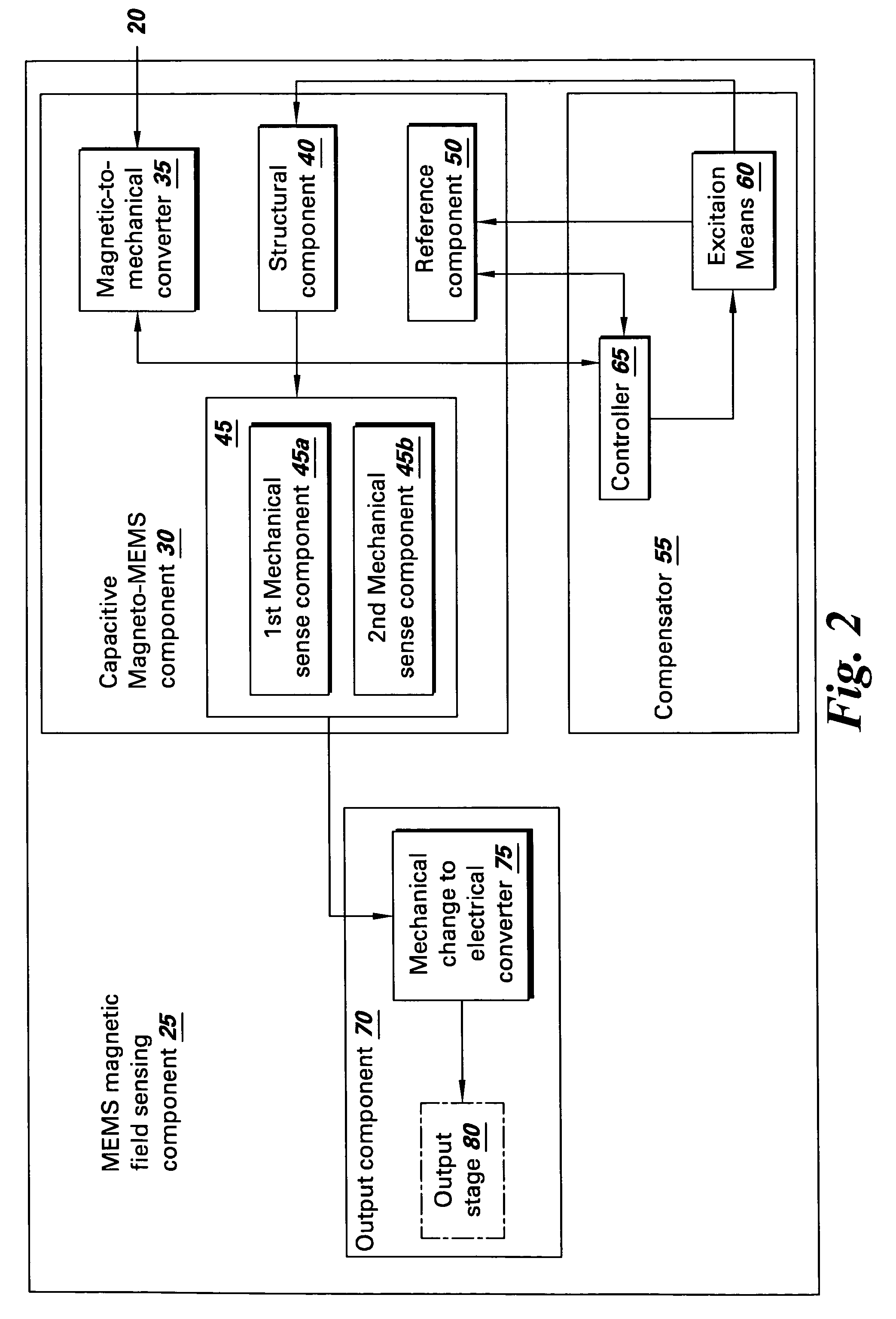
Micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) based current and magnetic field sensor having capacitive sense components
ActiveUS7315161B2Measurement using dc-ac conversionBase element modificationsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) based current & magnetic field sensor includes a MEMS-based magnetic field sensing component having a capacitive magneto-MEMS component, a compensator and an output component for sensing magnetic fields and for providing, in response thereto, an indication of the current present in a respective conductor to be measured. In one embodiment, first and second mechanical sense components are electrically conductive and operate to sense a change in a capacitance between the mechanical sense components in response to a mechanical indicator from a magnetic-to-mechanical converter.
Owner:ABB SPA
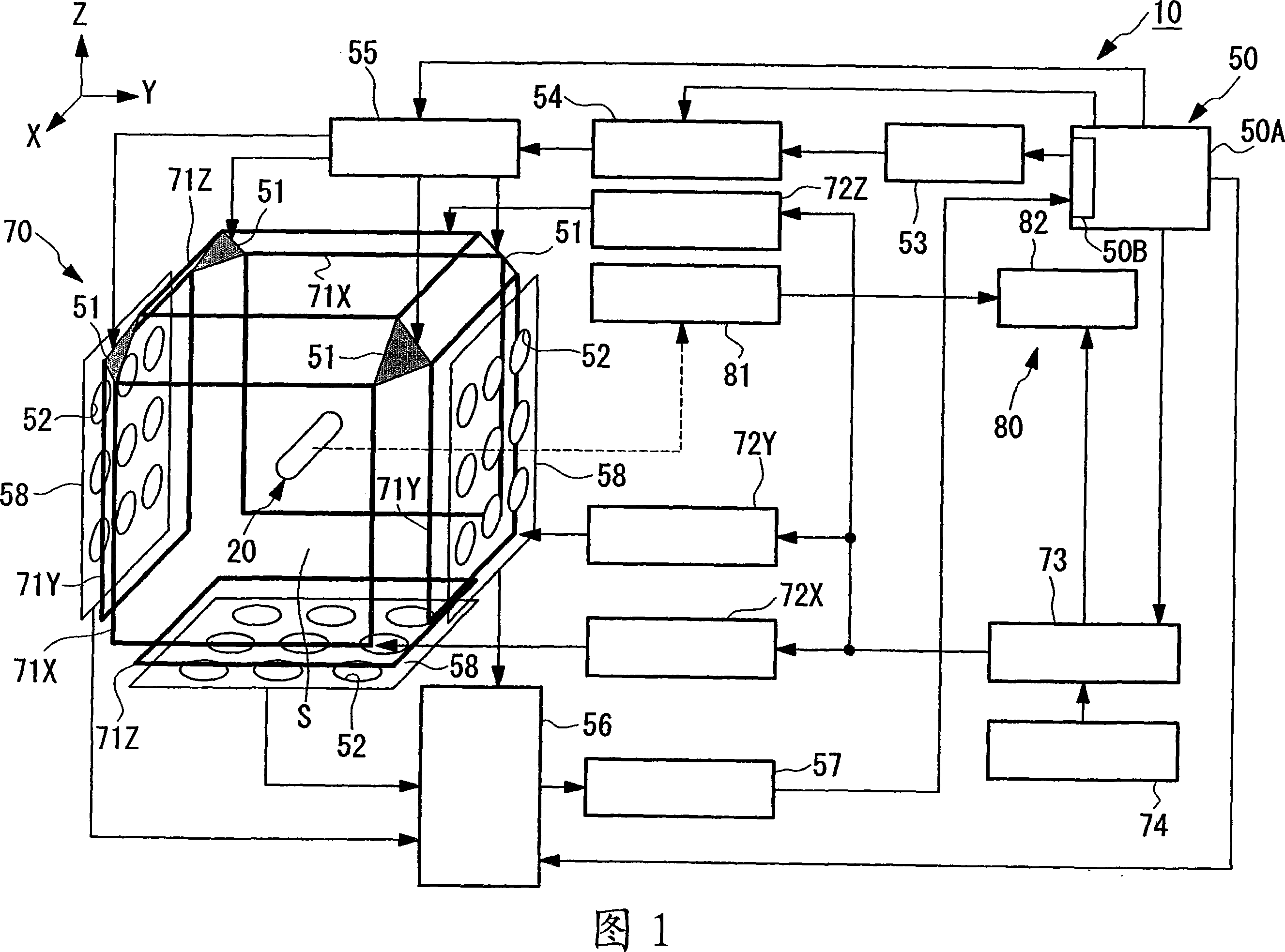
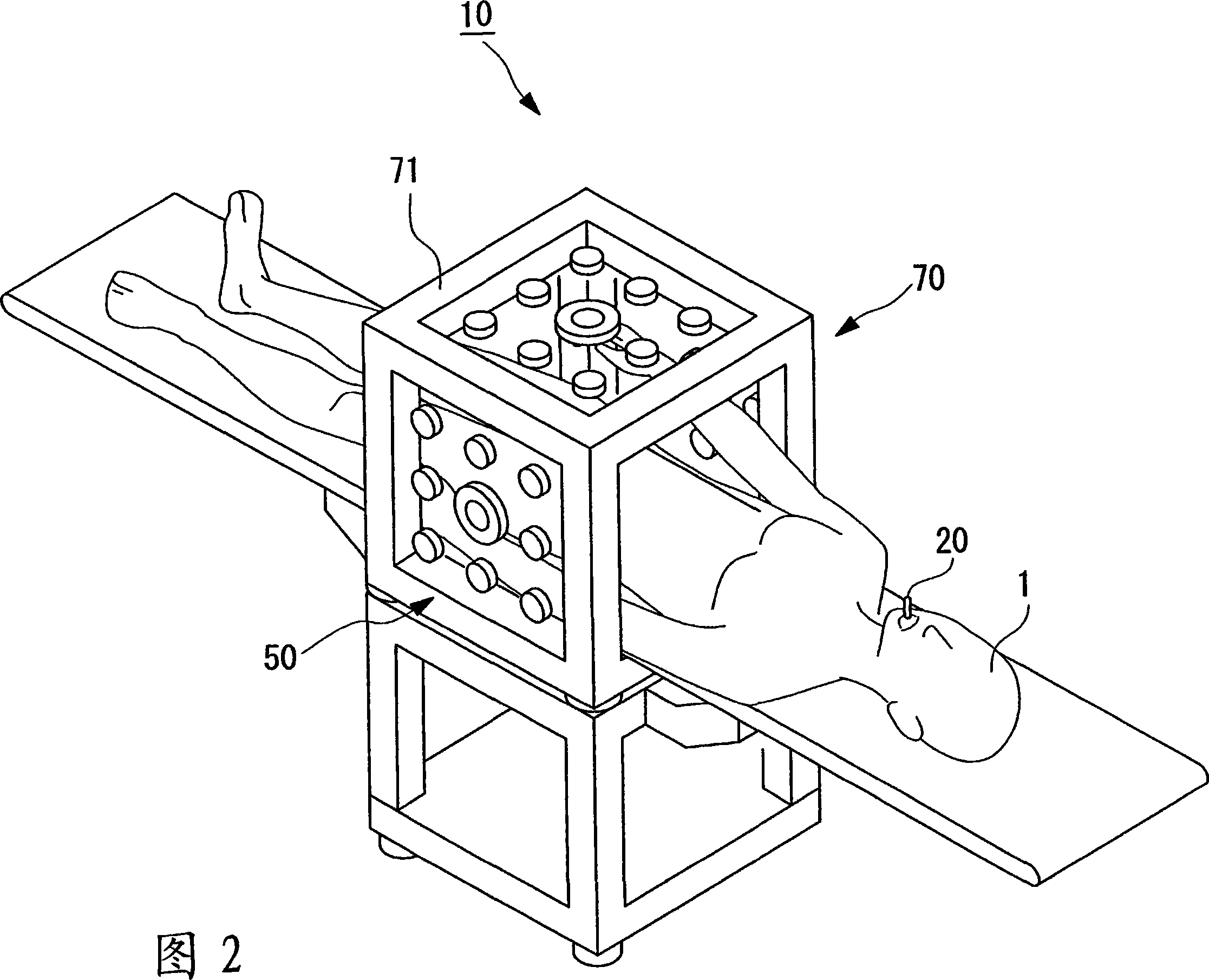
Position detection system, guidance system, position detection method, medical device, and medical magnetic-induction and position-detection system
InactiveCN101080198AImprove performanceGuaranteed to workEndoscopesDiagnostic recording/measuringGuidance systemResonance
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Arrangements for self-testing a circular vertical hall (CVH) sensing element and/or for self-testing a magnetic field sensor that uses a circular vertical hall (CVH) sensing element
ActiveUS8890518B2Solid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMEMS magnetic field sensorNormal mode
A switching arrangement around a circular vertical Hall (CVH) sensing element can provide a normal mode configuration responsive to magnetic fields at some times, and at least one of a first and a second self-test mode configuration not responsive to a magnetic field but simulating a magnetic field at other times. A corresponding method is also described.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
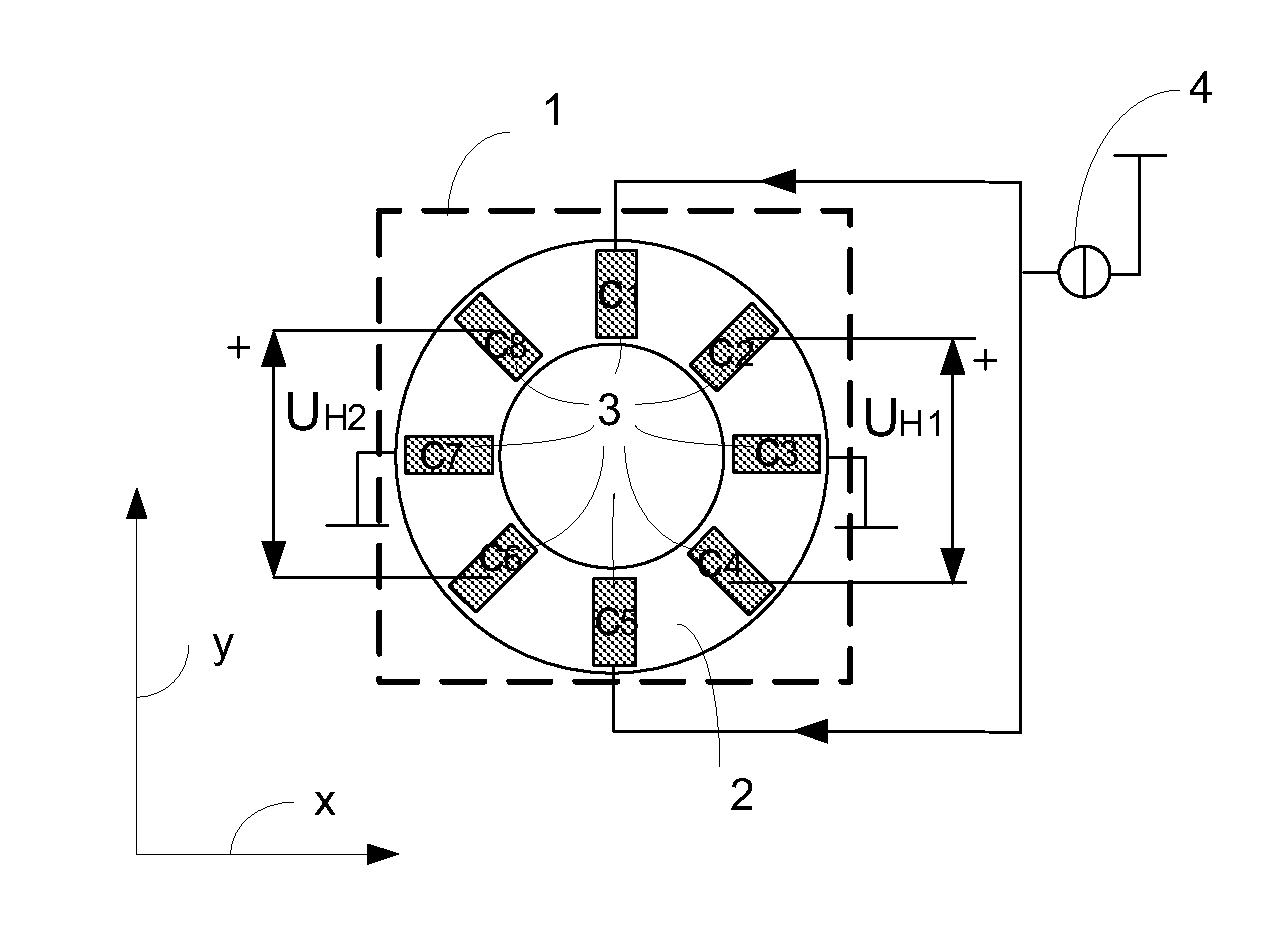
Magnetic field sensor measuring a direction of a magnetic field in a plane and current sensor
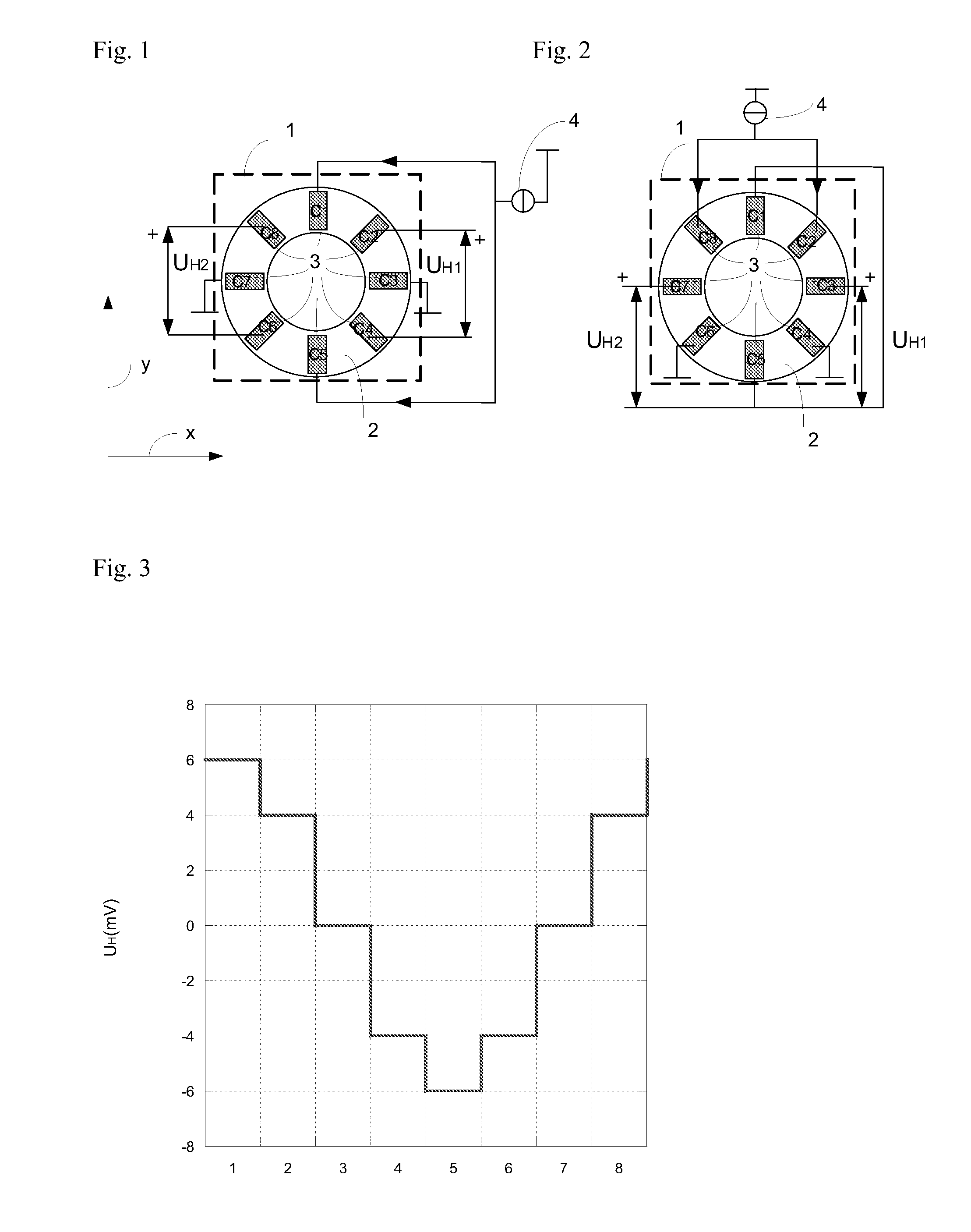
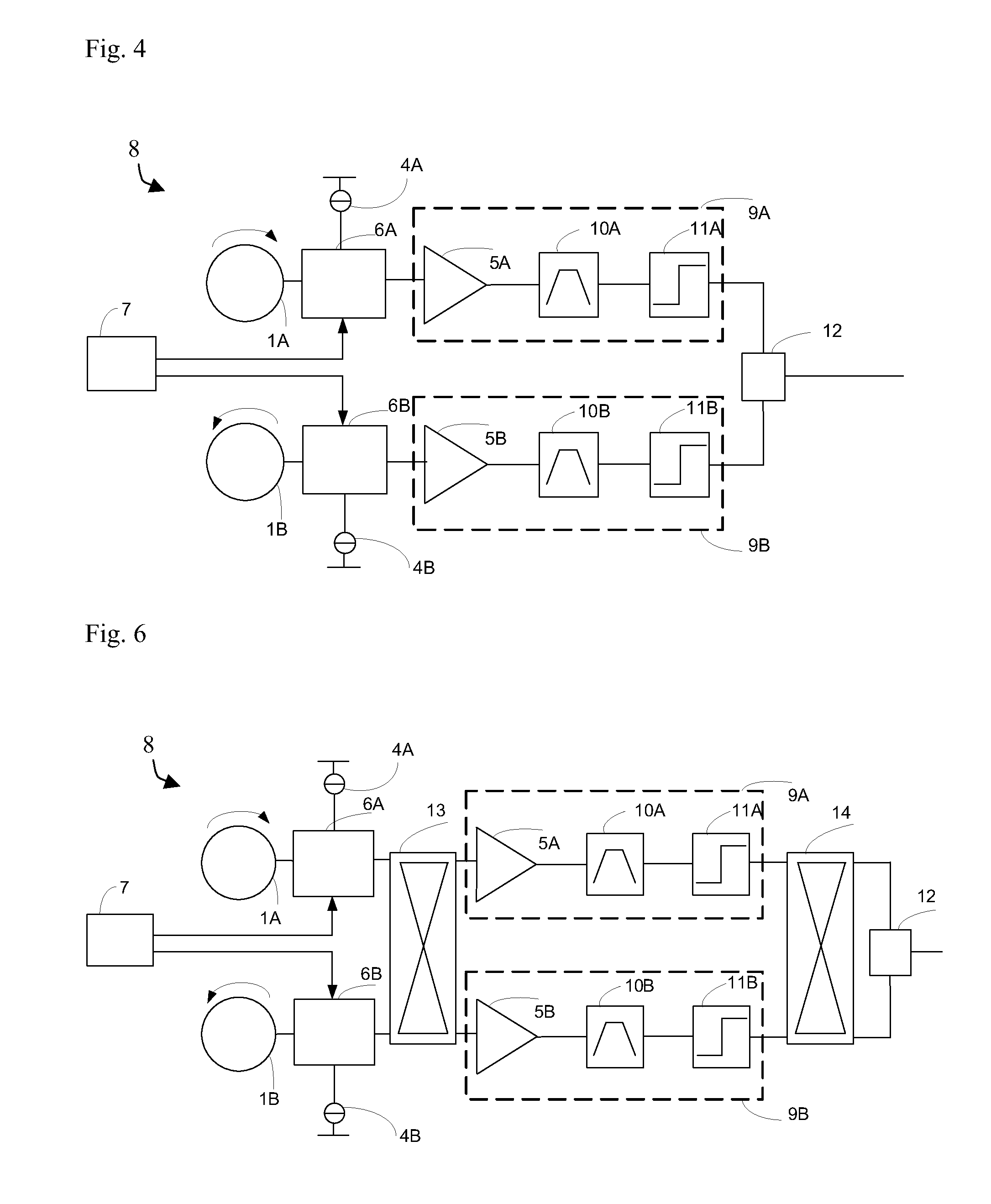
InactiveUS20110101975A1Improve accuracyMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesVoltage/current isolationElectrical conductorMEMS magnetic field sensor
A magnetic field sensor for measuring a direction of a magnetic field in a plane comprises two sensing structures (1A; 1B) that can be operated as a rotating Hall element. The two Hall elements are rotated in discrete steps in opposite directions. Such a magnetic field sensor can be used as current sensor for measuring a primary current flowing through a conductor (15).
Owner:SENIS
Methods and apparatus for object tracking on a hand-held device
ActiveUS8928602B1Transmission systemsMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMEMS magnetic field sensorDisplay device
A handheld device includes a housing, a display, a MEMS magnetic field sensor disposed within the housing, wherein the MEMS magnetic field sensor is configured to sense a plurality of perturbations in magnetic fields in response to a perturbation source when the user displaces the perturbation source proximate to the handheld device, and a processor disposed within the housing and coupled to the MEMS magnetic field sensor and to the display, wherein the processor is programmed to receive the plurality of perturbations in magnetic fields, wherein the processor is programmed to determine a plurality of spatial locations in at least two-dimensions in response to the plurality of perturbations, and wherein the processor is programmed output an indication of the plurality of spatial locations on the display.
Owner:MOVELLA INC
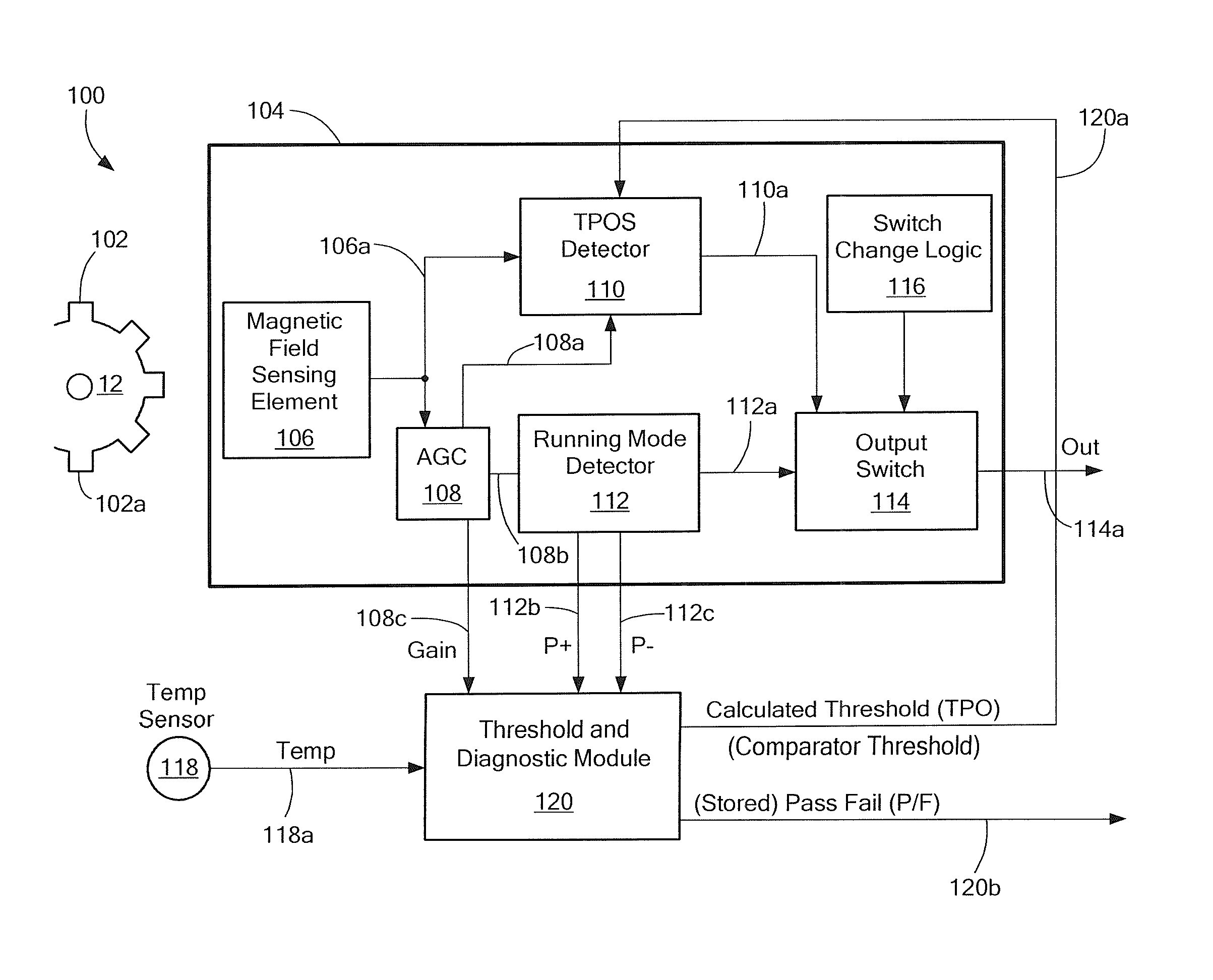
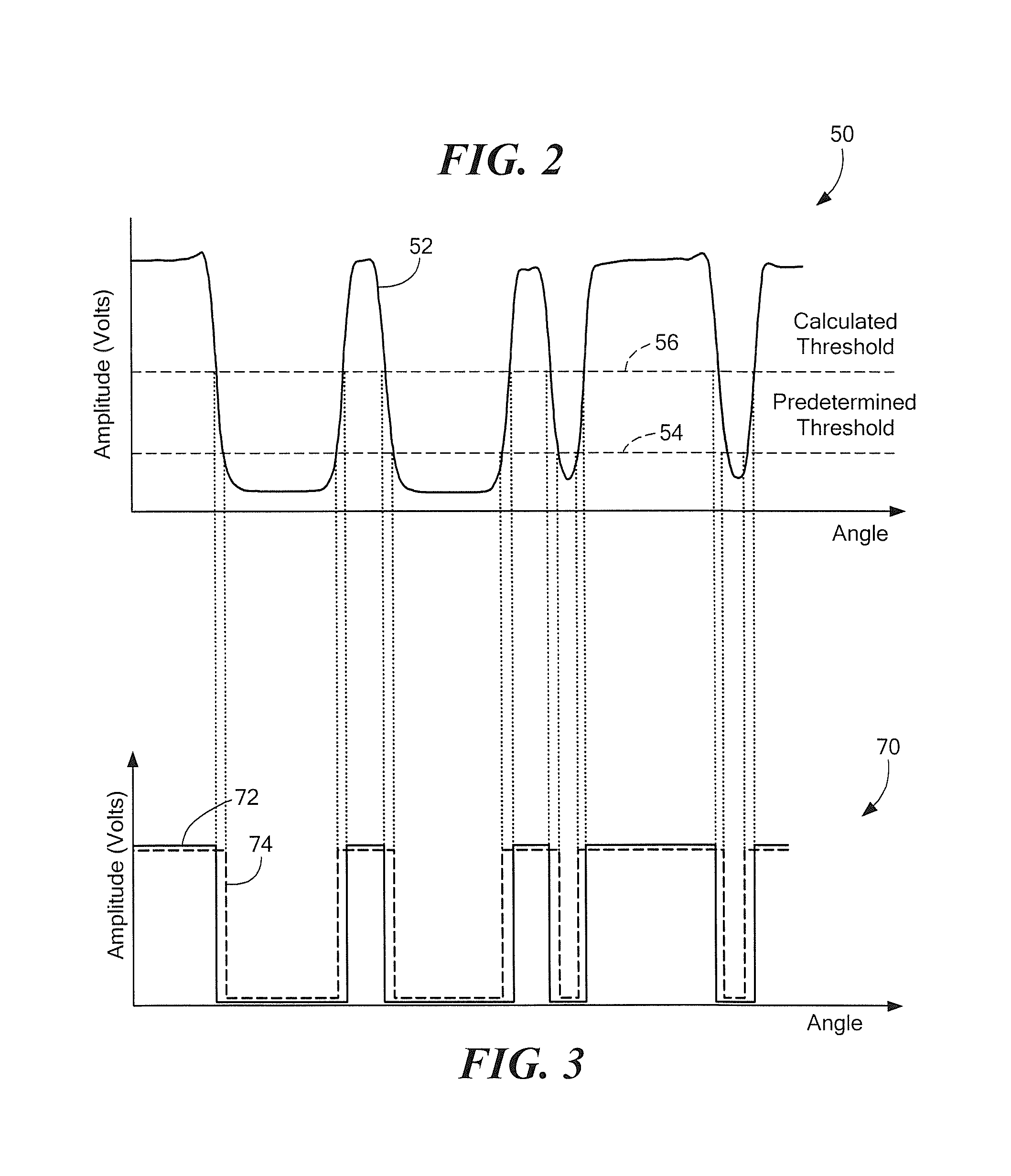
Magnetic field sensor and associated method that can establish a measured threshold value and that can store the measured threshold value in a memory device
ActiveUS8736260B2Thermometer detailsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMEMS magnetic field sensorPhysics
A magnetic field sensor includes a true power on state (TPOS) detector for which a measured threshold value is stored prior to power down and recalled upon power up. A corresponding method is associated with the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Current transducer for measuring a current
InactiveCN103529267ACurrent/voltage measurementMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleCurrent transducerMagnetic transducers
The invention concerns a current transducer for measuring a current flowing through a cable, comprising at least one magnetic field sensor and an electronic circuit. The current transducer comprises a head (40) with at least two ferromagnetic cores (46) optimized to reduce the effects of external magnetic fields. The current transducer optionally comprises a magnetic transducer comprising a magnetic field sensor and an electronic circuit. The electronic circuit comprises at least one current source (2), a transformer (3), a fully differential preamplifier (4) coupled to the transformer (3), a phase sensitive detector (6) coupled to the preamplifier (4) and a logic block (5, 5a) configured to operate the magnetic field sensor(s) to provide an AC output voltage. The magnetic field sensor(s) is preferably either a Hall element (1) or an AMR sensor (19) or a flux-gate sensor.
Owner:SENIS
Resonance micro electromechanical system magnetic field sensor and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN101515026ASimple structureReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsSemi-permeable membranesResonanceMEMS magnetic field sensor
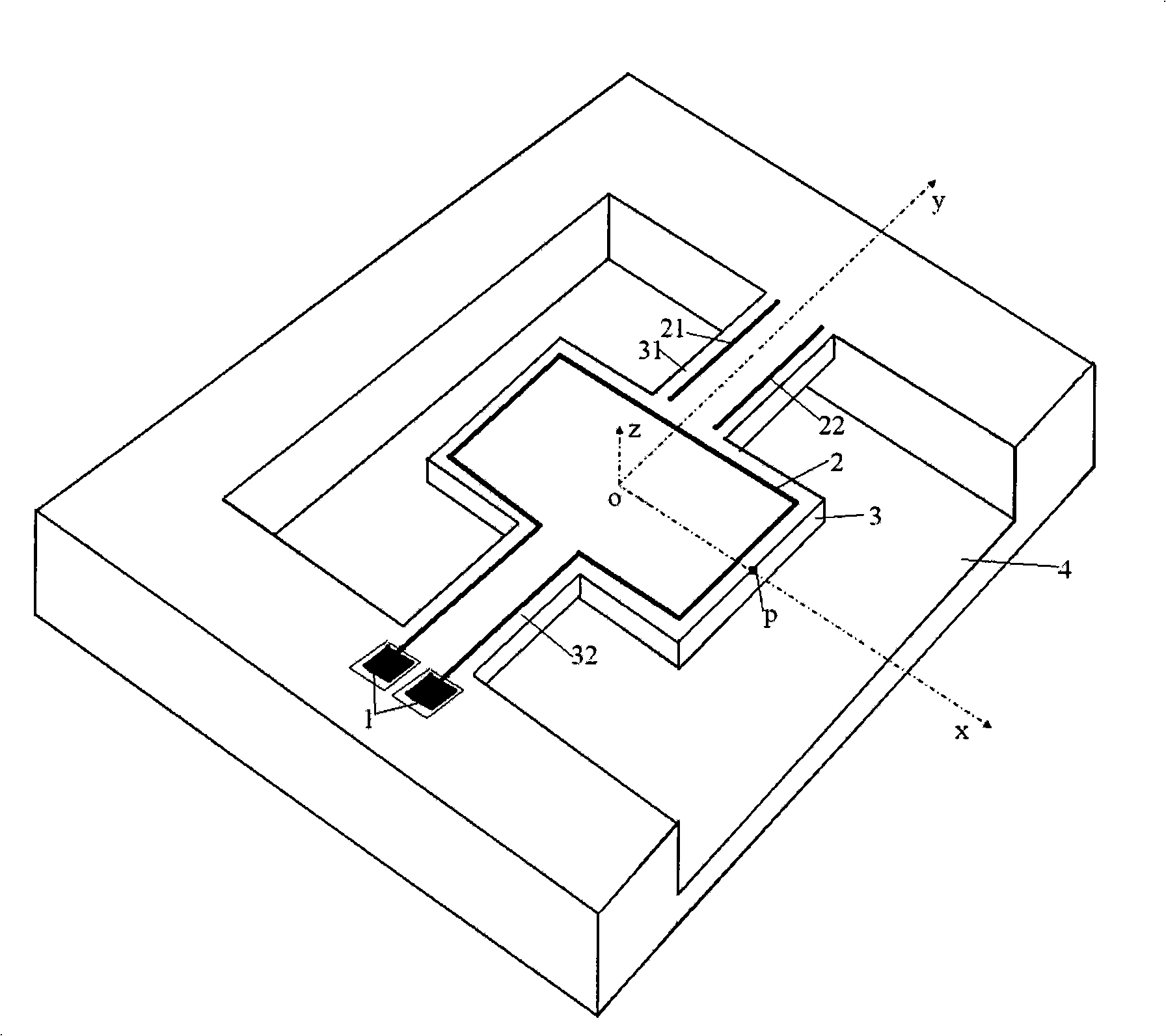
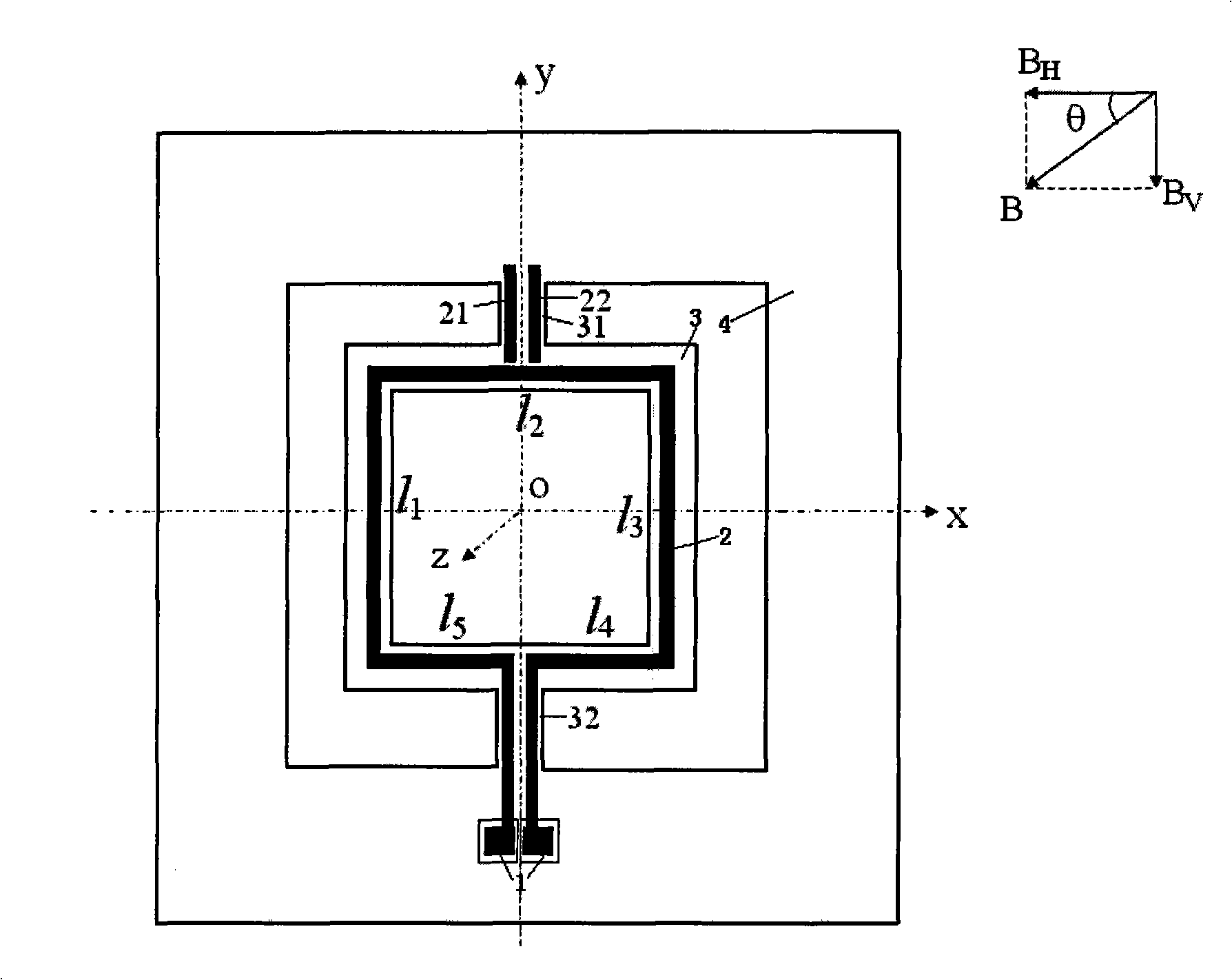
The invention relates to a resonance micro electromechanical system magnetic field sensor and a measuring method thereof, having the advantages of low power consumption, simple structure, rapid respondency and good reliability. The magnetic field sensor comprises an anchorage (1), a metal wire (2), a contilever plate (3) and a substrate (4). The metal wire (2) plated on the contilever plate (3) drives the contilever plate (3) under the action of lorentz force to generate vibration; excitation is respectively used for producing resonance having the same excitation frequency as first order and second order of the contilever plate; when the first order and the second order are in resonance, the structure has the directions with the difference of 90 degrees; the different displacements of a p point are measured by measuring the displacement of the p point on the contilever plate after the magnetic field directions of the first order and the second order are changed, thus the measurement of the magnetic field directions can be realized. The invention aims at providing a micro electromechanical system magnetic field sensor which has low power consumption, high sensitivity and precision and simple structure, and is seldom influenced by temperature.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Magnetic field sensor measuring a direction of a magnetic field in a plane and current sensor
InactiveUS8624587B2Improve accuracyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesPower flowElectrical conductor
A magnetic field sensor for measuring a direction of a magnetic field in a plane having two sensing structures (1A; 1B) that can be operated as a rotating Hall element. The two Hall elements are rotated in discrete steps in opposite directions. Such a magnetic field sensor can be used as current sensor for measuring a primary current flowing through a conductor (15).
Owner:SENIS
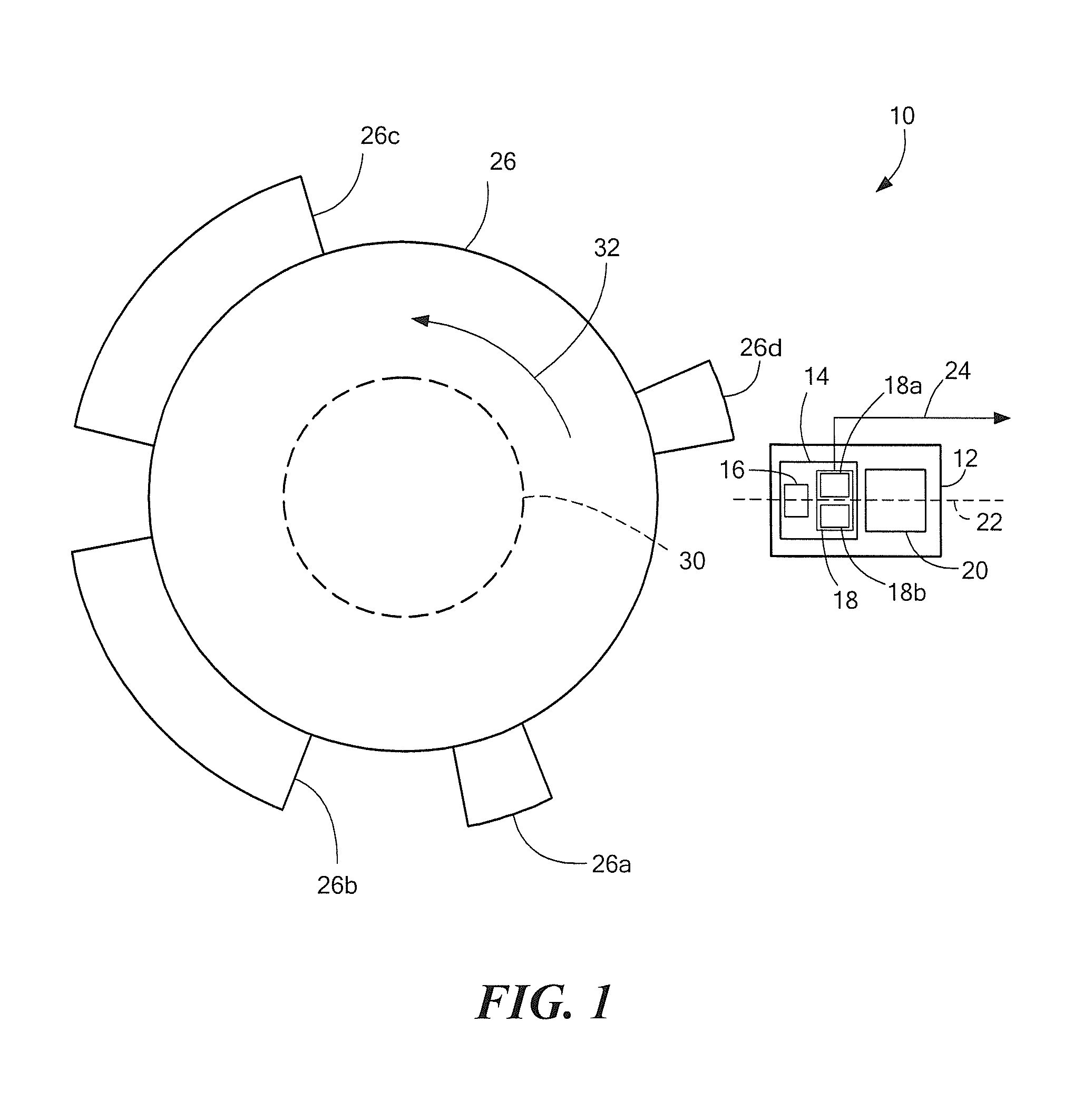
Magnetic field sensor
InactiveUS7391203B2Easy to adaptEasy to anchorSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMEMS magnetic field sensorMagnet
A magnetic field sensor for measuring the rotational speed of a rotating gear component is disclosed. The sensor includes a Hall probe, at least one permanent magnet and housing. The Hall probe is arranged in the influence area of the magnetic field of the permanent magnet. The intent is to produce the magnetic field sensor in a less complex manner. This is achieved by virtue of the fact that the permanent magnet is secured to the housing. One particular advantage of the device is that it is extraordinarily robust and is only slightly sensitive to vibrations.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
An integrated low-power consumption tri-axial magnetic field sensor with high Z-direction resolving force
ActiveCN107894576AImprove resolutionImprove three-axis orthogonalityMagnetic measurementsHysteresisMEMS magnetic field sensor
The invention provides an integrated low-power consumption tri-axial magnetic field sensor with high Z-direction resolving force. The integrated low-power consumption tri-axial magnetic field sensor comprises an insulation substrate, an orbit transfer soft magnetic block and four magnetic measuring units. The four magnetic measuring units are arranged on the surface of the insulation substrate incentral symmetry; the orbit transfer soft magnetic block is placed on the four magnetic measuring units in central symmetry with respect to the center points of the four magnetic measuring units; onepart of each magnetic measuring unit is located right under the orbit transfer soft magnetic block. In order to solve the problem of insufficient Z-direction resolving force and low compensation efficiency in the prior art, the orbit transfer soft magnetic block and the four centrally-symmetrical magnetic measuring units achieve high-efficiency orbit transfer of Z-direction magnetic fields, gathering, amplification and planar measurement of tri-axial magnetic fields can be achieved, the tri-axial orthogonality and the Z-direction magnetic field resolving force are effectively improved, and high-resolving force measuring for weak tri-axial magnetic field signals and high efficiency compensation for hysteresis can be achieved. The integrated low-power consumption tri-axial magnetic field sensor has the advantages of low energy consumption and low cost.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Magnetic probe and magnetic field sensor having same
InactiveCN104849679AGood linear relationshipSolve the problem of micromagnetic detection at room temperatureMagnetic measurementsSignal conditioning circuitsMEMS magnetic field sensor
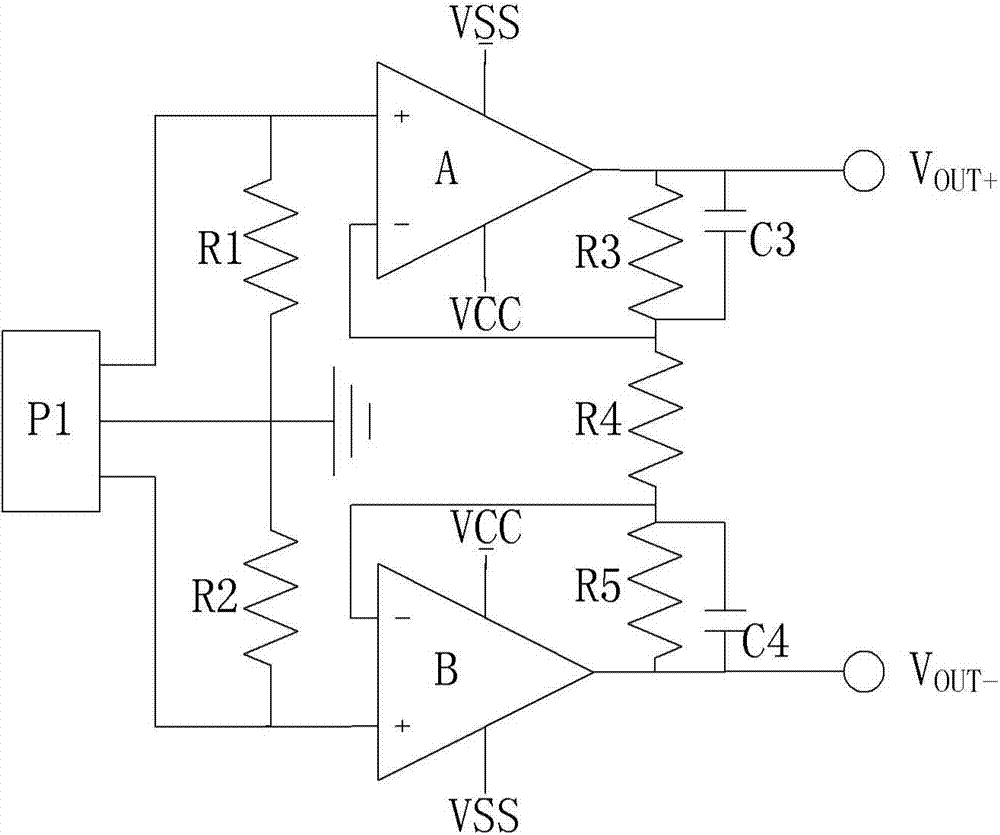
The invention provides a magnetic probe comprising the following elements: a frame having a cavity; a magnetic part penetrating the frame through the cavity and allowing pulse current to pass; a detection coil winding on an outer surface of the frame. The invention also provides a magnetic field sensor comprising the following structures: an oscillating source circuit used for generating an oscillating source signal; a magnetic detection circuit used for detecting outer magnetic field and comprising the magnetic probe, wherein the oscillating source signal injects into the magnetic part of the magnetic probe, and the magnetic detection circuit outputs a superpose superheterodyne signal; a signal conditioning circuit comparing the oscillating source signal with the superpose superheterodyne signal so as to obtain an outer magnetic field signal. The magnetic field sensor can detect high speed field change weak magnetic field in normal temperature, can detect space weak PT-level magnetic field, and can detect a space weak gradient magnetic field.
Owner:BEIJING CEGT SCI & TECH
Computer pointing device employing a magnetic field source and magnetic field sensors
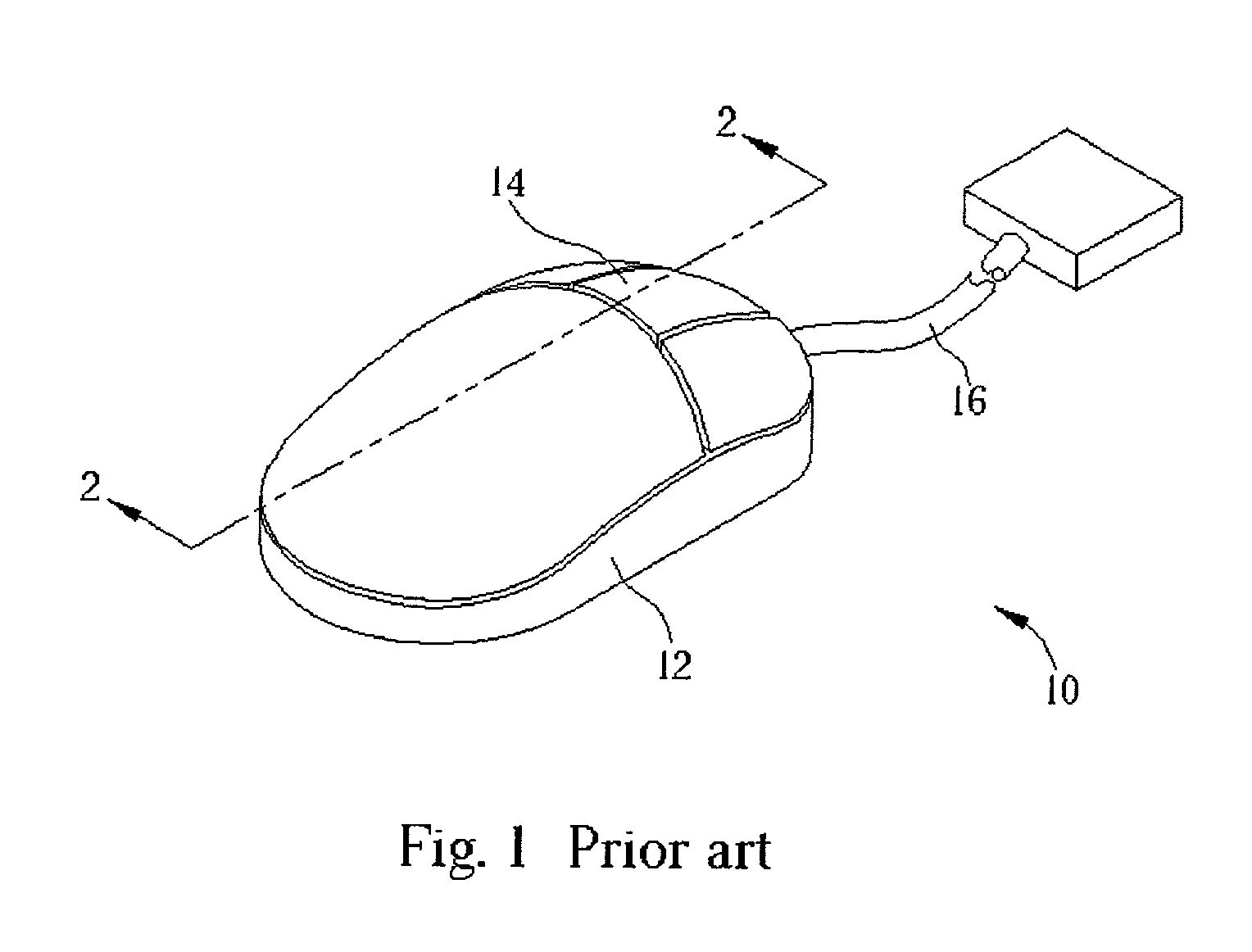
InactiveUS7034804B2Protection from damageCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingMEMS magnetic field sensorPointing device
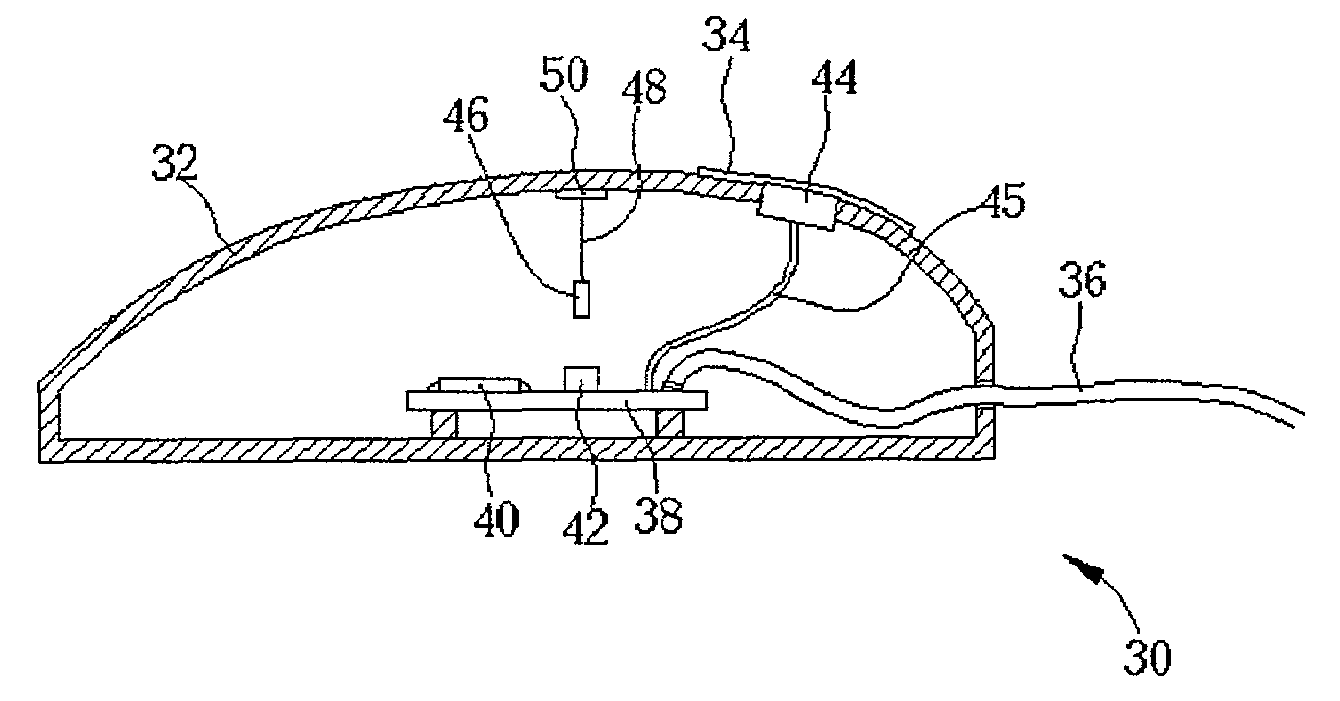
A pointing device for a computer includes a magnetic field source, a magnetic field sensor, and a flexible member that connects the magnetic field source and the magnetic field sensor. When a user accelerates the pointing device the position of magnetic field source with respect to the magnetic field sensor changes and this positional change is measured by the magnetic field sensor, which outputs corresponding electrical signals. The pointing device further includes a processor that receives the electrical signals output by the magnetic field sensor, generates a corresponding standard location signal of the pointing device, and outputs the location signal to a computer via a transmission system.
Owner:INVENTEC APPLIANCES CORP
MEMs Amplitude Modulator and MEMs Magnetic Field Sensor Including Same
ActiveUS20160211803A1Amount of variation in variableImproving sensing functionMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesAmplitude modulation with mechanical/acoustic driven partsCapacitanceMEMS magnetic field sensor
The present invention provides an amplitude modulator, which is disposed in an area through which a magnetic field flows so as to modulate amplitudes, comprising: a substrate; a first driving electrode which receives a first frequency signal and a second frequency signal supplied from the substrate and carries out resonant motion by the magnetic field; and a second driving electrode for receiving the second frequency signal and carries out resonant motion by the first driving electrode and the magnetic field, wherein a modulated signal is generated by modulating the amplitudes of the first and second frequency signals through the resonant motions of the first and second driving electrodes. Therefore, since the signal generated by modulating a carrier signal through mechanical resonance according to the magnetic field is outputted, amplitude modulation can be carried out without a complicated circuit configuration. In addition, since an MEMS device is a single structure that does not include an insulating layer, a single signal is applied to one structure, thereby simplifying driving, and all the driving electrodes of both ends thereof are driven so as to double a change in variable capacitance, thereby improving sensing ability.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Magnetic field sensor
ActiveCN103969690AReduce eddy currentReduce distributed capacitanceElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationMEMS magnetic field sensorCondensed matter physics
The invention discloses a magnetic field sensor which comprises a shell which is in a cylindrical structure, a hollow skeleton which is a hollow columnar body, a segmented magnetic core, multiple sections of coils and an amplifying circuit, wherein the outer surface of the hollow skeleton is provided with a plurality of same annular grooves at equal spacings; the segmented magnetic core is arranged in a hollow part of the hollow skeleton and is formed by connecting multiple sections of magnetic core materials equal in length; the multiple coils respectively winds in the annular grooves of the hollow skeleton and are serially connected to the amplifying circuit; the amplifying circuit is arranged at one end in the shell and used for amplifying and outputting induction signals of the multiple coils. According to the magnetic field sensor disclosed by the invention, a working band is completely expanded and the influence of the sensor on magnetic field measurement is effectively reduced; moreover, the electric field interface of an environment surrounding is shielded and the accuracy of measuring magnetic field signals is guaranteed. The magnetic field sensor disclosed by the invention is small in volume, light in weight, and effectively applicable to engineering application of a ground transverse electric and magnetic field (TEM).
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Driving circuit of magnetic field sensor based on amorphous filler metal and application method of driving circuit
ActiveCN104459571AEliminate hysteresisImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsField-effect transistorConductor Coil
The invention discloses a driving circuit of a magnetic field sensor based on amorphous filler metal and an application method of the driving circuit. The driving circuit comprises a magnetic core motivation portion, a magnetic core replacement portion, a signal sampling and amplifying portion and a power source portion. A symmetric difference sampling circuit structure is adopted, and the charge injection effect brought by an analogue switch or a field effect transistor is eliminated. A current is exerted in metal receiving coils to replace magnetic cores, and therefore the magnetic-lag of the magnetic cores is removed; the even number of series-connection magnetic cores and a metal receiving coil structure in a symmetric winding manner are adopted, and therefore the inductive coupling effect between the magnetic cores and the receiving coils is eliminated, and the capacitive coupling effect of motivation current on the metal receiving coils is reduced, so that the signal-to-noise ratio and the linearity of output signals of the sensor are improved; each magnetic core is segmented into a plurality of isometric small segments, and the magnetic field detection range and the magnetic field sensitivity of the sensor can be conveniently controlled.
Owner:HEBERSON TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
MEMS magnetic field sensor of folded beam structure and preparation method
ActiveCN107271930ALarge displacement degrees of freedomNot prone to fatigue fractureMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsCapacitancePower flow
The invention relates to an MEMS magnetic field sensor of a folded beam structure and a preparation method. The sensor includes a metal T-shaped folded beam processed on a substrate and fixed in the center. An electrode formed by the folded beam and an electrode on the substrate form a variable capacitor. The principle of the MEMS magnetic field sensor of the folded beam structure is that a metal coil processed on the T-shaped folded beam structure is subjected to lorentz force after current is introduced, thus the beam bends and deforms, thereby changing an interval of the two electrodes, and realizing change of a capacitance value. The magnitude of a magnetic field can be measured through detection of capacitance variation. The folded beam structure can realize effective support for a movable polar plate, and provide a smaller equivalent elastic coefficient compared with a traditional structure, and compared with a traditional torsion beam structure, various residual stress in a sensor processing process can be reduced, sensitivity of the sensor can be improved, and power consumption can be reduced. Since the T-shaped folded beam structure of the sensor can achieve a function of releasing stress, the service life of the sensor is prolonged.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic measurement system
InactiveCN106166064AMedical imagingDiagnostic signal processingMagnetic measurementsMEMS magnetic field sensor
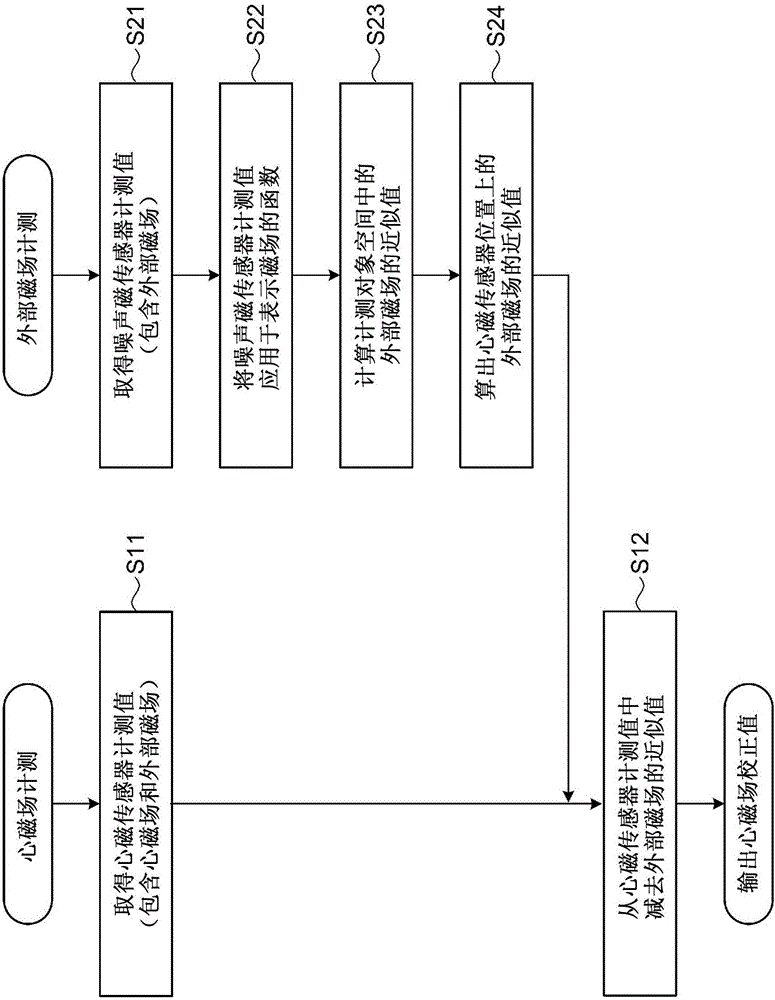
The invention provides a magnetic measurement system capable of measuring the magnetic field of the measured target with high accuracy even in a case where an external magnetic field stronger than a weak magnetic field of a measured target is present. A magnetic measurement system (1) includes a heart magnetic field sensor (10) that measures a first magnetic field and a second magnetic field, a noise magnetic sensor (30) that measures the second magnetic field, and a magnetic measurement apparatus (2) that computes an approximate value of the second magnetic field in the heart magnetic field sensor (10) by using a measurement value in the noise magnetic sensor (30) and a multi-variable polynomial. The magnetic measurement apparatus (2) subtracts the approximate value of the second magnetic field from a measurement value in the heart magnetic field sensor (10).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
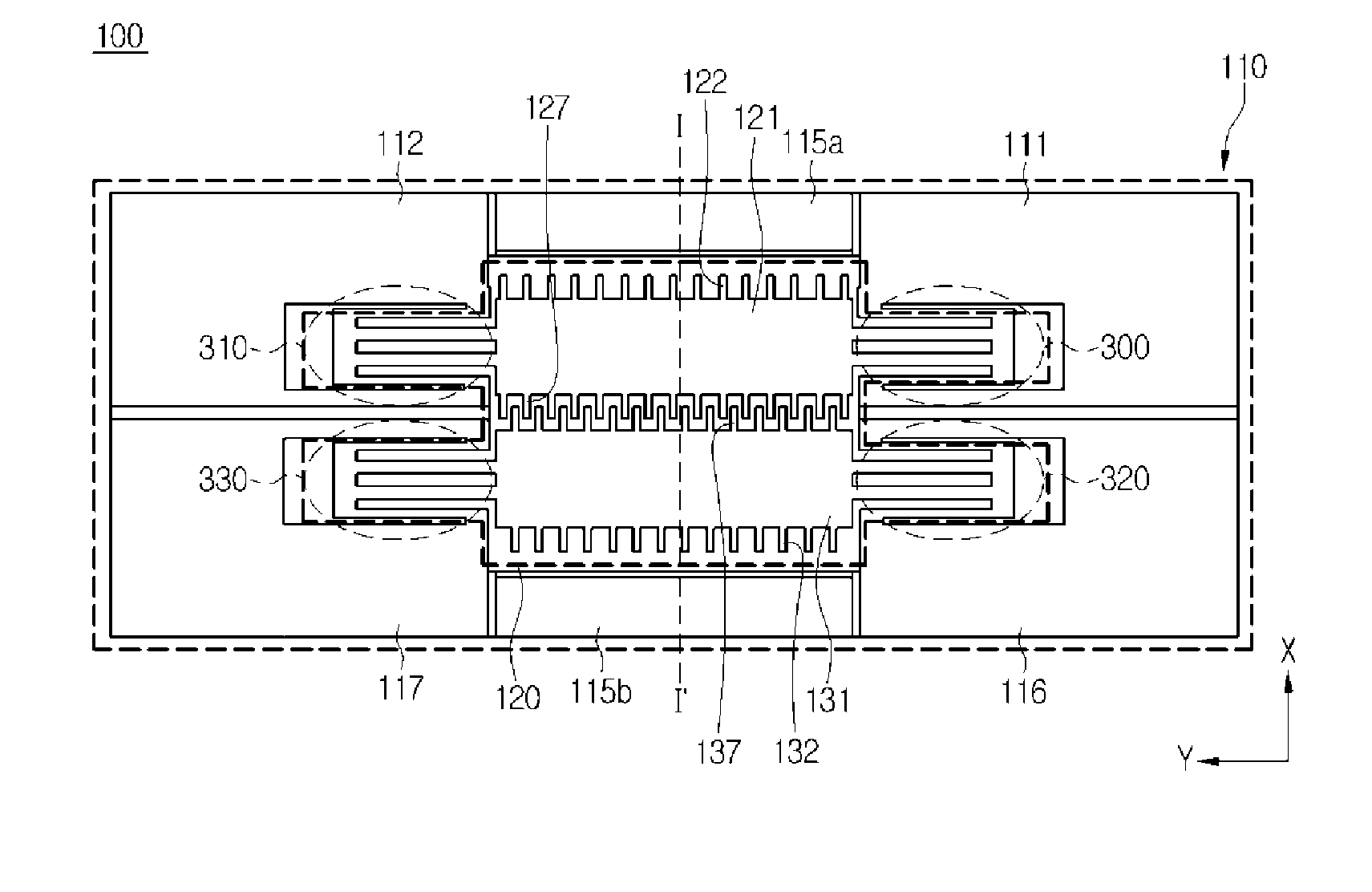
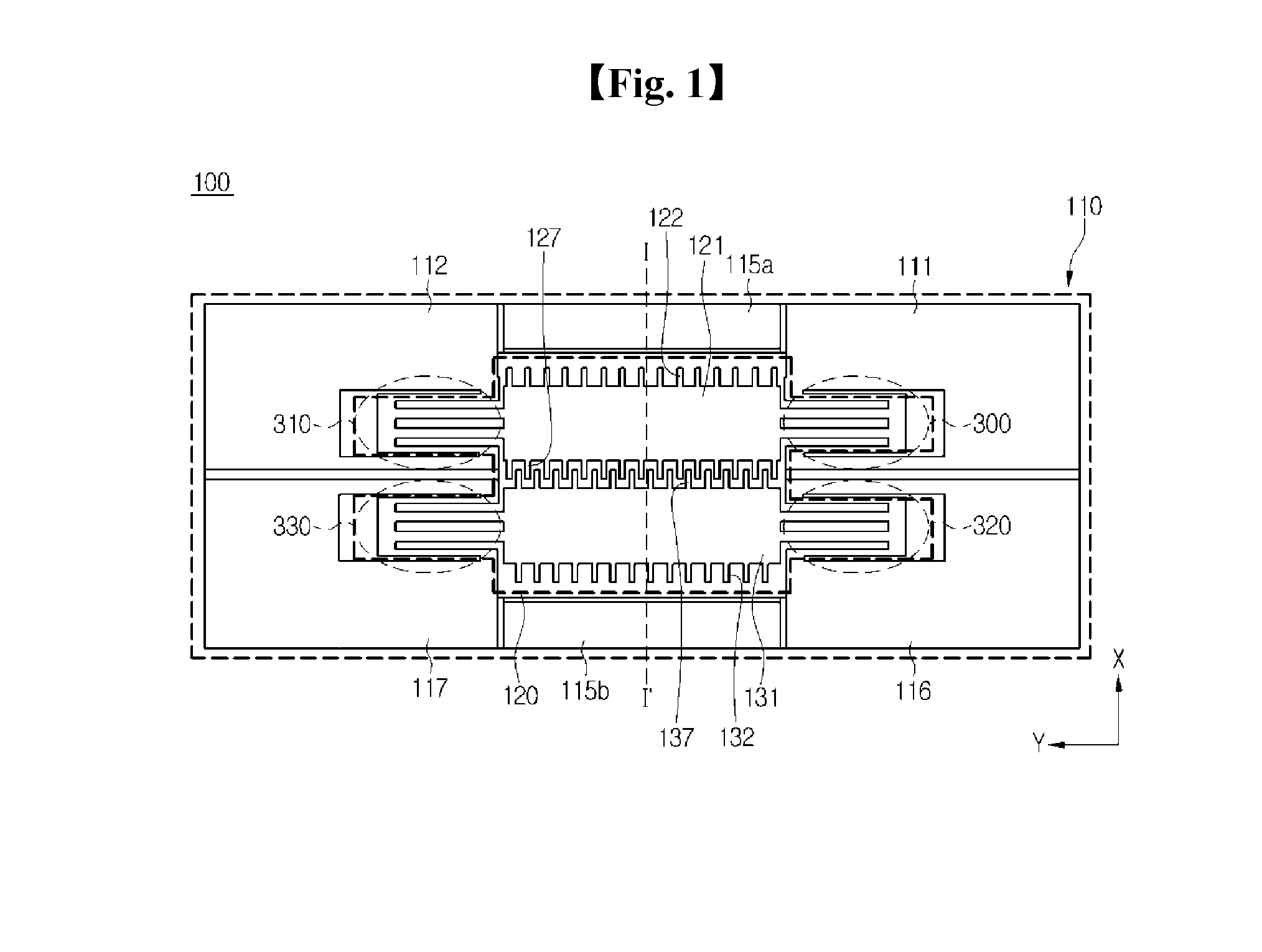
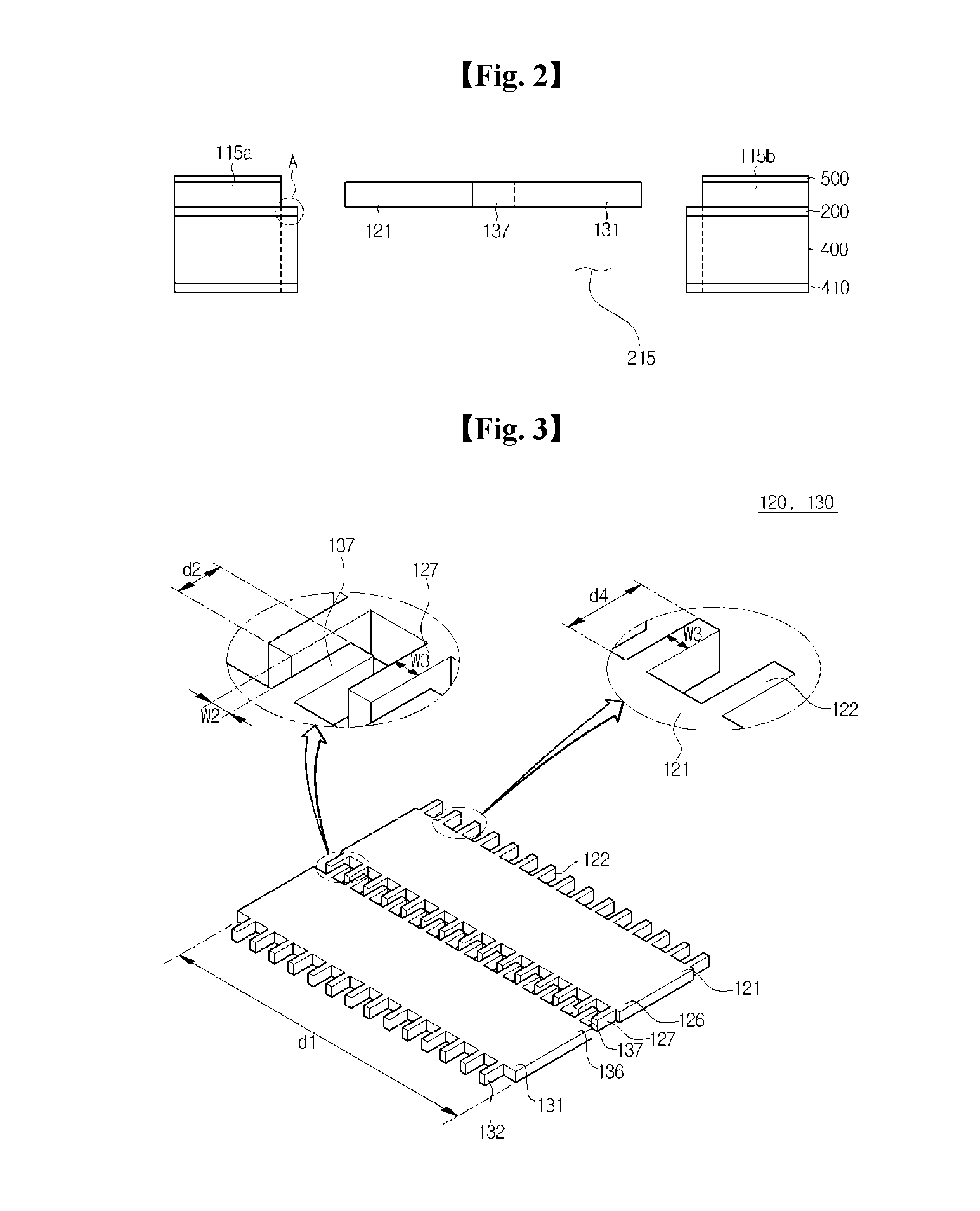
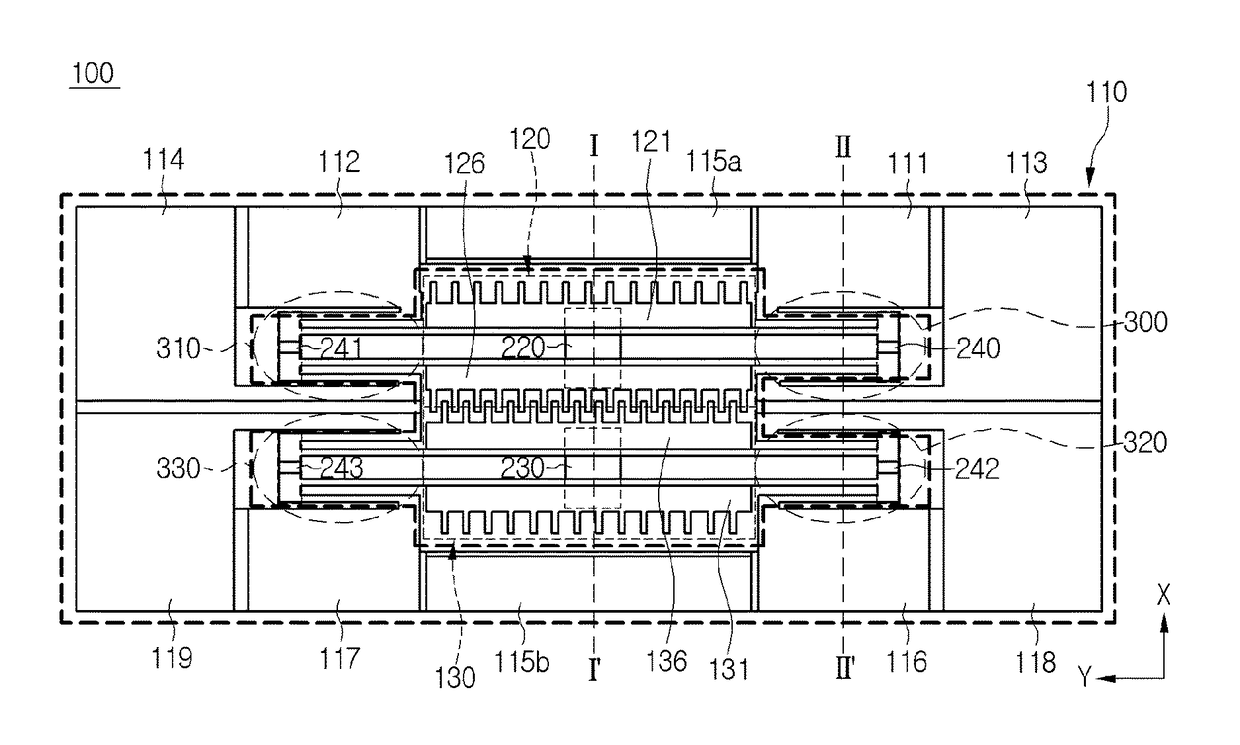
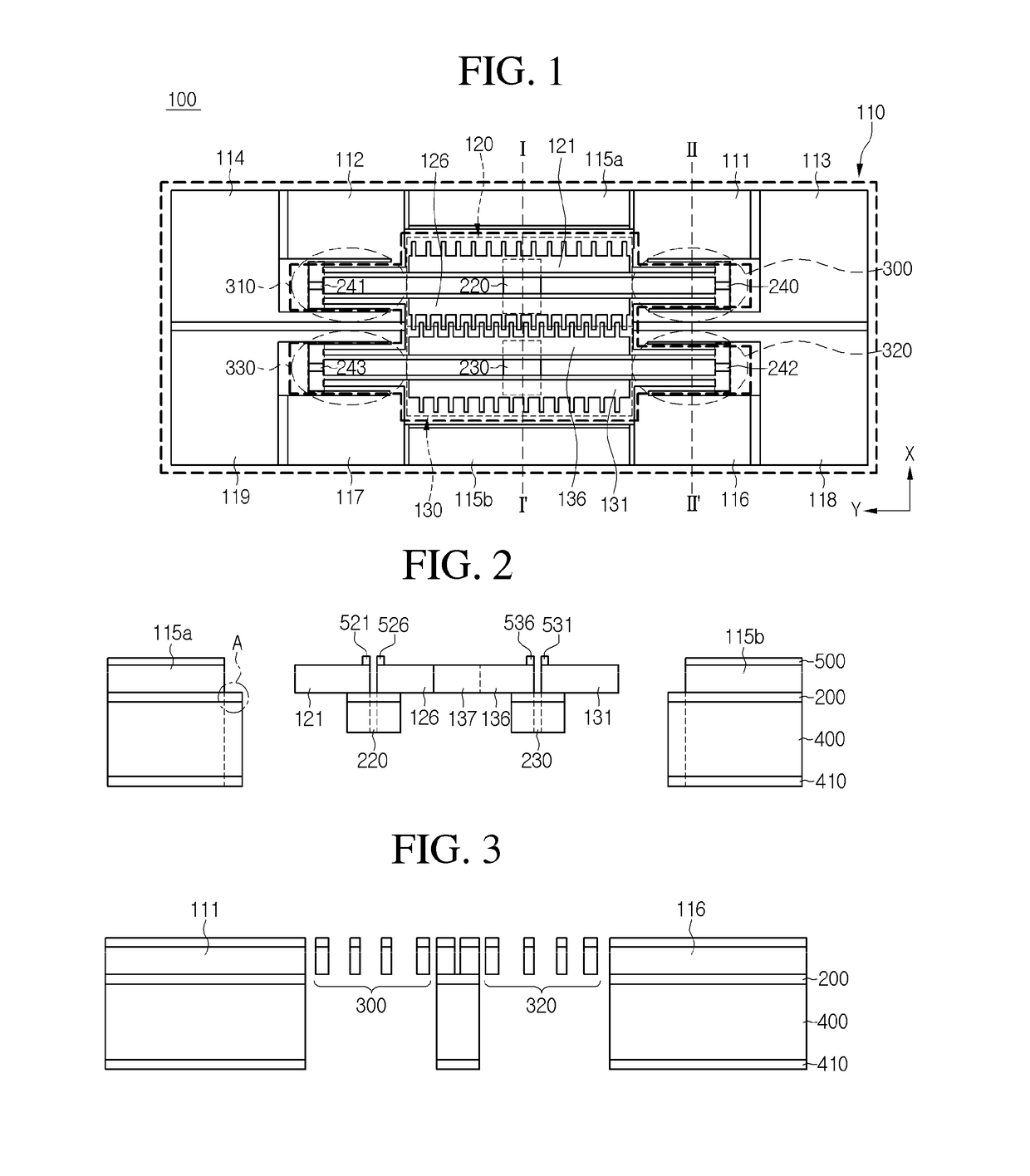
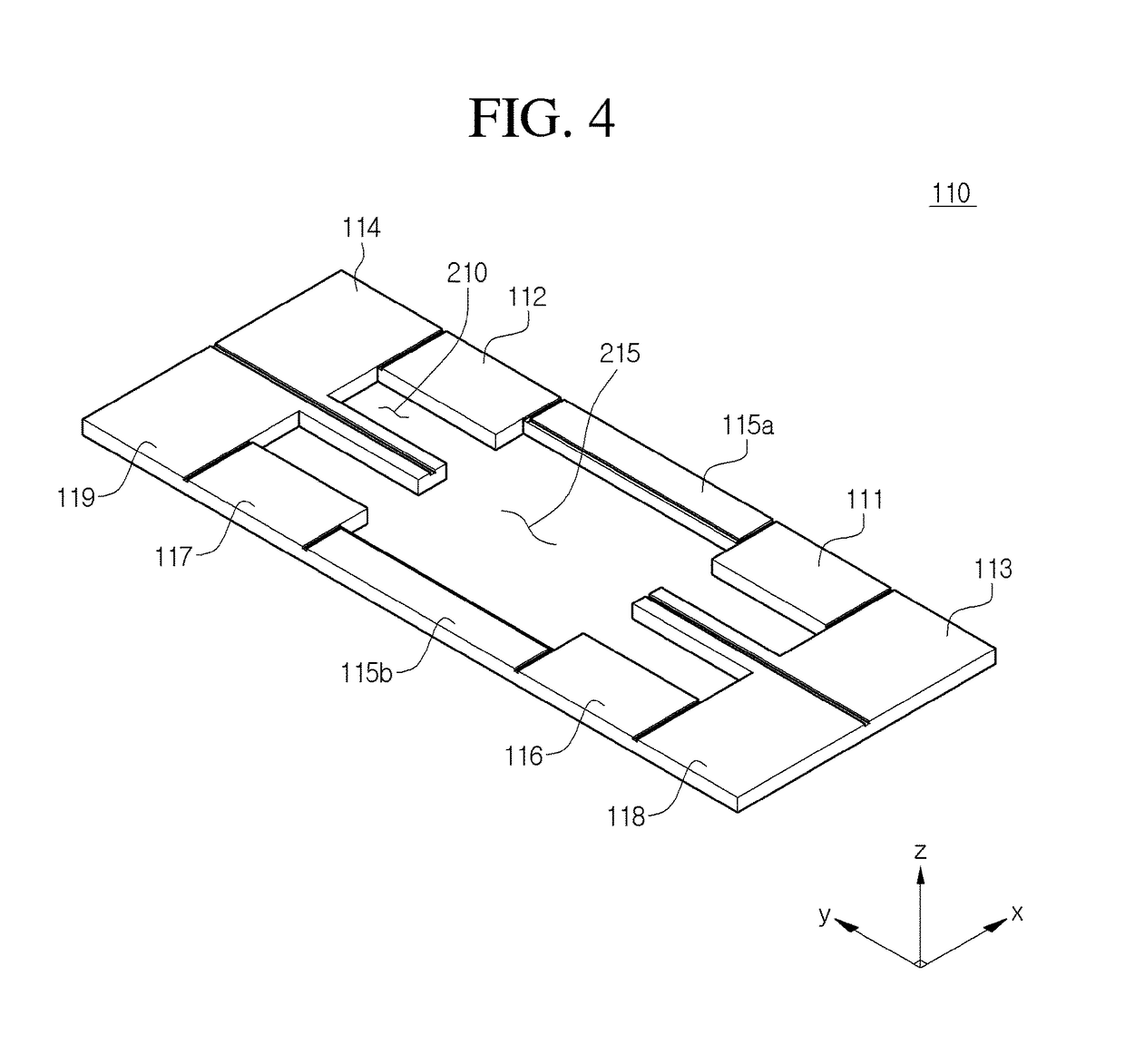
MEMS magnetic field sensor
ActiveUS9804233B2Mechanical displacement can be maximizedImprove Sensing PerformanceResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrodynamic magnetometersCapacitanceMEMS magnetic field sensor
The disclosure provides a magnetic field sensor for sensing the magnetic field caused by a current to be measured, which includes: substrate; a first drive electrode with a path for flowing a reference current supplied from the substrate arranged so as to be moveable by the magnetic field of the current to be measured; and a second drive electrode with a path for flowing a reference current supplied from the substrate arranged so as to be moveable by the magnetic field of the current to be measured, thus measuring the variation of a capacitance caused by the movement of the first drive electrode and the second drive electrode. Hence, the sensing is achieved by the two drive electrodes with no reference electrode, thus maximizing the mechanical displacement to improve the sensing capability.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
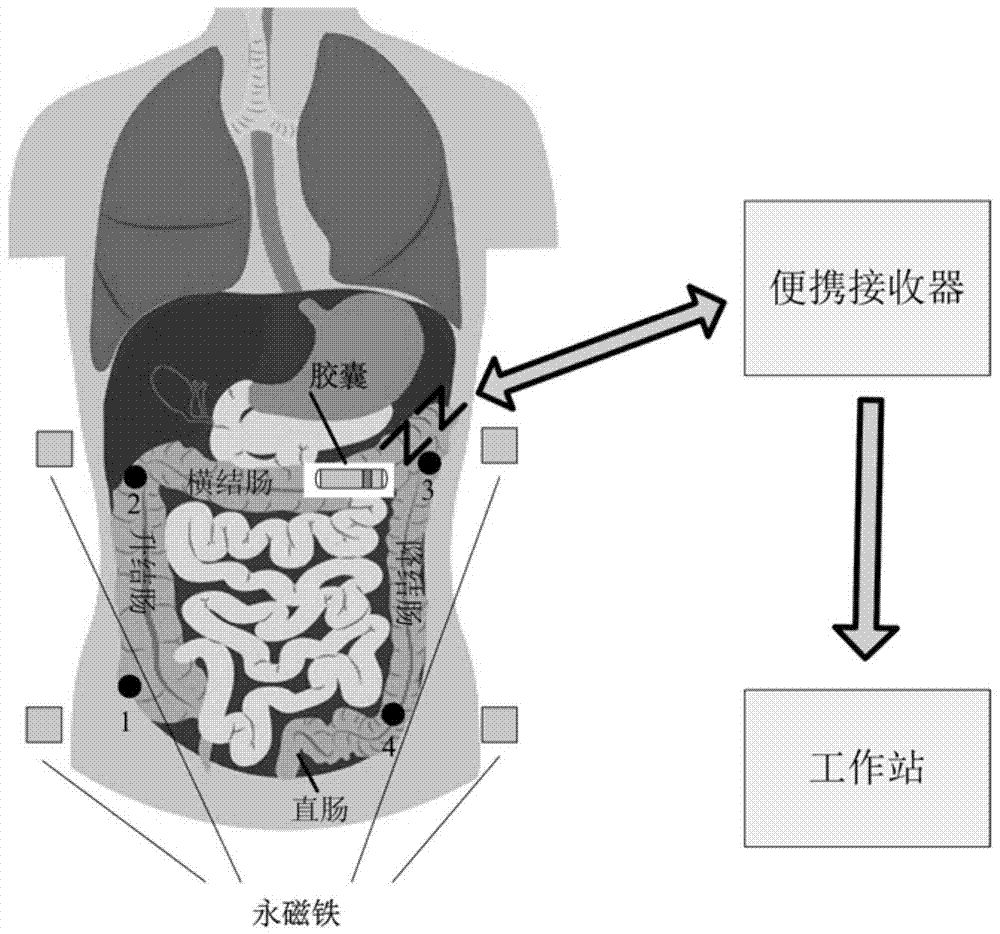
Colon cavity inner capsule system positioning device
InactiveCN104720807AReduce volumePrecise positioningSurgeryEndoradiosondesMEMS magnetic field sensorPeak value
A colon cavity inner capsule system positioning device is composed of an in-vivo capsule with an MEMS magnetic field sensor, and an in-vivo system wirelessly connected with the in-vivo capsule and transmitting magnetic field intensity information. An in-vitro system comprises four permanent magnets and a data processing mechanism. The collected magnetic field intensity information is processed, and an in-vivo capsule is positioned; that is, the magnetic field intensity is determined by the distances between the capsule and the four permanent magnets, and the closer the device gets to any permanent magnet, the higher the detected magnetic field intensity is. The change situation of the magnetic field intensity can be monitored in real time, and the position of the capsule can be accurately positioned and the moment when the capsule passes by a colon cavity can be determined through a denoising preprocessing and peak value detecting algorithm.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
A mems magnetic field sensor with a folded beam structure and its preparation method
ActiveCN107271930BLarge displacement degrees of freedomNot prone to fatigue fractureMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsCapacitanceMEMS magnetic field sensor
The invention relates to a MEMS magnetic field sensor with a folded beam structure and a preparation method thereof. The sensor includes a centrally fixed metal T-shaped folded beam processed on a substrate. The electrodes formed by the folded beams and the electrodes on the substrate form a variable capacitance. The principle of the invention is that the metal coil processed on the T-shaped folded beam structure is subjected to the Lorentz force after the current is applied to cause the beam to bend and deform, thereby changing the distance between the two electrodes and realizing the change of the capacitance value. The magnitude of the magnetic field can be measured by detecting the change in capacitance. The folded beam structure can effectively support the movable plate and provide a smaller equivalent elastic coefficient than the traditional structure. Compared with the traditional torsion beam structure, it can reduce various residual stresses in the sensor processing process and improve the sensor's performance. sensitivity, reducing its power consumption. Because the T-shaped folded beam structure of the sensor can release the stress, thereby increasing its service life.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com