Liquid crystal lens and stereoscopic display device
A liquid crystal lens and stereoscopic display technology, applied in optics, instruments, nonlinear optics, etc., can solve problems such as crosstalk of liquid crystal lens units, achieve the effects of optimizing electric field intensity distribution, eliminating crosstalk, and reducing crosstalk phenomena
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
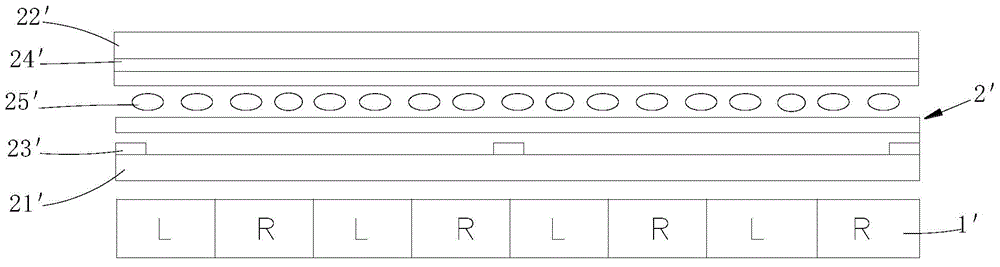
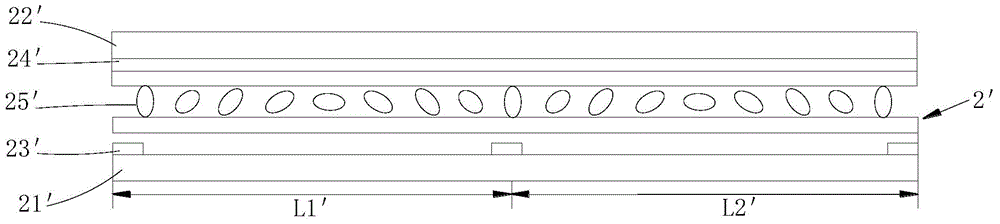
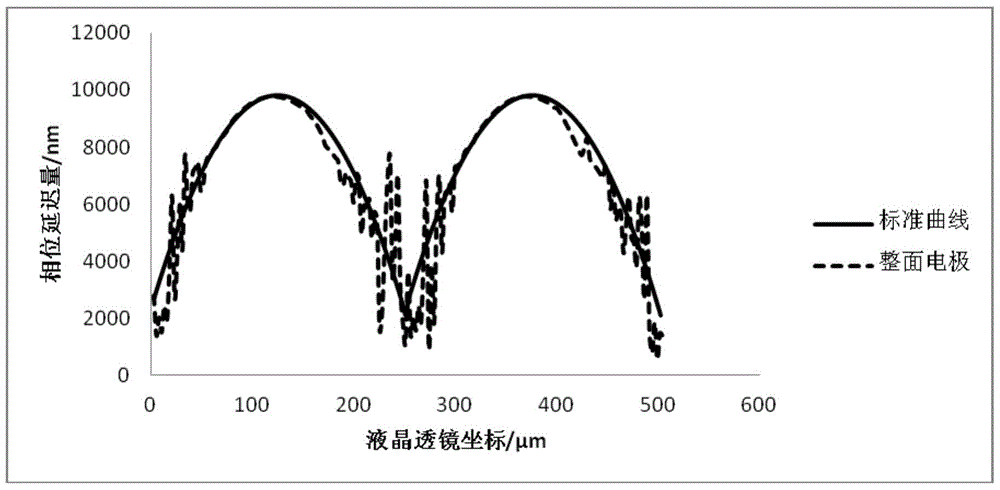
[0039] Such as Figure 5 and Figure 6 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a liquid crystal lens 2, including a first substrate 21 and a second substrate 22 oppositely arranged, and liquid crystal molecules 23 are arranged between the first substrate 21 and the second substrate 22, and on the first substrate 21 A plurality of first electrodes 24 are provided, and each first electrode 24 is arranged at intervals from each other, and a plurality of second electrodes 25 are provided on a side of the second substrate 22 facing the first substrate 21 . When the liquid crystal lens 2 is used for stereoscopic display, the first voltage is applied to the first electrode 24, and the second voltage is applied to the second electrode 25. The potential difference between the first voltage and the second voltage is between the first substrate 21 and the second substrate. 22, a first electric field with different electric field strengths is formed, the first electric...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Such as Figure 9 As shown, the structure of the liquid crystal lens 3 provided in this embodiment is substantially the same as that of the liquid crystal lens 2 provided in Embodiment 1, the difference is that each liquid crystal lens unit L1 corresponds to m first electrodes 34, m is a natural number, and m≥3 . In this embodiment, each liquid crystal lens unit L1 corresponds to six first electrodes 34 . For the liquid crystal lens 3 of this structure, a symmetrical fourth driving voltage is applied to each first electrode 34, specifically, in the liquid crystal lens unit L1, each strip electrode such as S11, S12, S13, S14, S15, S16 A symmetrical voltage is applied, specifically (V(S11)=V(S16))>(V(S12)=V(S15))>(V(S13)=V(S14)). Similarly, in the liquid crystal lens unit L2, a symmetrical voltage is applied to each strip electrode such as S16, S17, S18, S19, S3, S21, specifically (V(S16)=V(S21))>(V(S17 )=V(S3))>(V(S18)=V(S19)), the fifth driving voltage is applied to ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Such as Figure 11As shown, the structure of the liquid crystal lens 4 provided by the embodiment of the present invention is substantially the same as that of the liquid crystal lens 3 provided by the second embodiment. The liquid crystal lens 4 includes a first substrate 41 and a second substrate 42 oppositely arranged, and the second substrate 42 is arranged on the first substrate 42. Above the substrate 41, liquid crystal molecules 43 and spacers 40 are arranged between the first substrate 41 and the second substrate 42, the second electrode 45 is arranged on the second substrate 42, and the first electrode 44 is arranged on the first substrate 41. An opening 46 is formed between two adjacent second electrodes 45 . The difference is that a third electrode 47 is provided between the first substrate 41 and the first electrode 44, an insulating layer 48 is provided between the third electrode 47 and the first electrode 44, and each first electrode 44 is provided on the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com