Viscous debris flow river-blocking calculation method and application thereof
A calculation method and mud-rock flow technology, applied in calculation, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of adverse mud-rock flow prevention and control effects, calculation errors, and the accuracy of mud-rock flow blocking rivers, etc., to simplify the judgment of factors and judgments of river blocking The effect of accurate model and concise judgment result
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] A method for calculating river blocking by viscous debris flow, comprising the following steps:
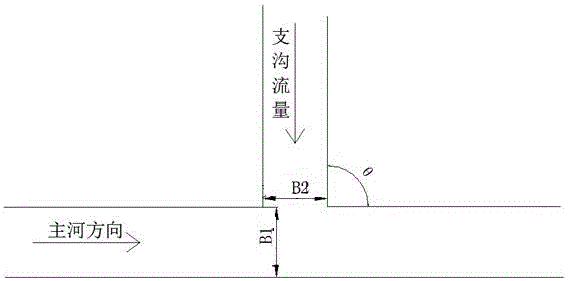
[0050] a. The confluence angle between the tributary ditch and the main river measured on the spot or on the topographic map , 85° 95°;
[0051] b. Measure the average width of the main river at the intersection of the main river and the tributaries B. 1 , unit m, main river flow Qm, unit m 3 / s, according to formula 1 to determine the single-width discharge Q of the main river 1 , unit m 2 / s;
[0052] (Formula 1);
[0053] c. Measure the average width of the tributary at the intersection of the main river and the tributary on the spot B 2 , unit m, debris flow flow , unit m 3 / s, according to the formula 2 to determine the flow rate of the single width of the tributary ditch 2 , unit m 2 / s;
[0054] (Formula 2);
[0055] d. The single-width flow Q of the main river 1 and tributary single width flow 2 Substitute into Equation 3 to determine...
Embodiment 2
[0066] A method for calculating river blockage by viscous debris flow is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0067] a. The confluence angle between the tributary ditch and the main river measured on the spot or on the topographic map , 85° 95°;
[0068] b. Measure the average width of the main river at the intersection of the main river and the tributaries B. 1 , unit m, main river flow Qm, unit m 3 / s, according to formula 1 to determine the single-width discharge Q of the main river 1 , unit m 2 / s;
[0069] (Formula 1);
[0070] c. Measure the average width of the tributary at the intersection of the main river and the tributary on the spot B 2 , unit m, debris flow flow , unit m 3 / s, according to the formula 2 to determine the flow rate of the single width of the tributary ditch 2 , unit m 2 / s;
[0071] (Formula 2);
[0072] d. The single-width flow Q of the main river 1 and tributary single width flow 2 Substitute in...
Embodiment 3
[0084] A method for calculating river blockage by viscous debris flow is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0085] a. The confluence angle between the tributary ditch and the main river measured on the spot or on the topographic map , 85° 95°;
[0086] b. Measure the average width of the main river at the intersection of the main river and the tributaries B. 1 , unit m, main river flow Qm, unit m 3 / s, according to formula 1 to determine the single-width discharge Q of the main river 1 , unit m 2 / s;
[0087] (Formula 1);
[0088] c. Measure the average width of the tributary at the intersection of the main river and the tributary on the spot B 2 , unit m, debris flow flow , unit m 3 / s, according to the formula 2 to determine the flow rate of the single width of the tributary ditch 2 , unit m 2 / s;
[0089] (Formula 2);
[0090] d. The single-width flow Q of the main river 1 and tributary single width flow 2 Substitute into...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com