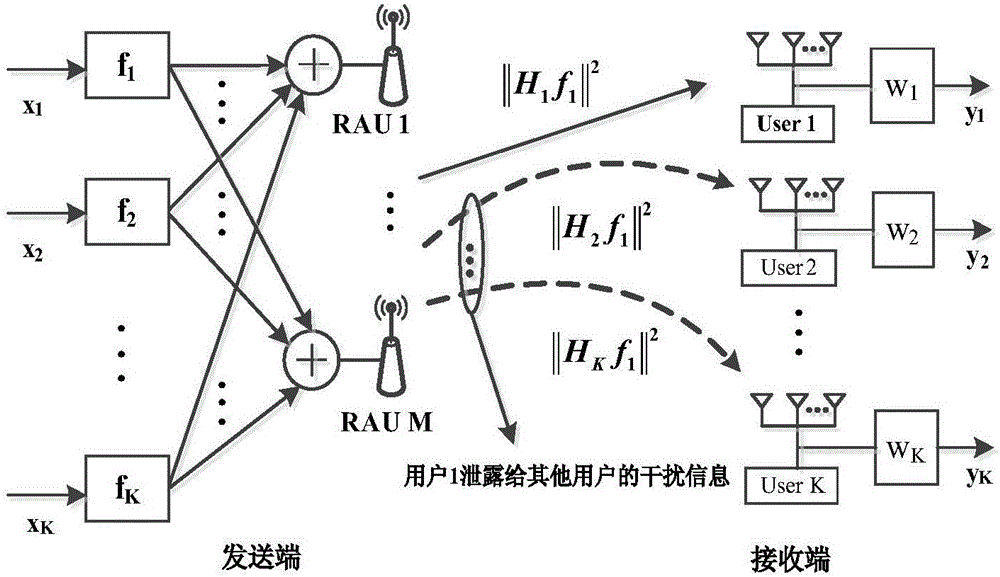
Downlink precoding method for multi-user distributed MIMO multi-antenna system
A multi-antenna system and downlink technology, applied in the field of multi-user distributed MIMO multi-antenna system downlink precoding, can solve the problems of joint processing of unreceived signals, mutual interference of received signals, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] Embodiment 1 A Distributed MIMO Multi-antenna System Scenario
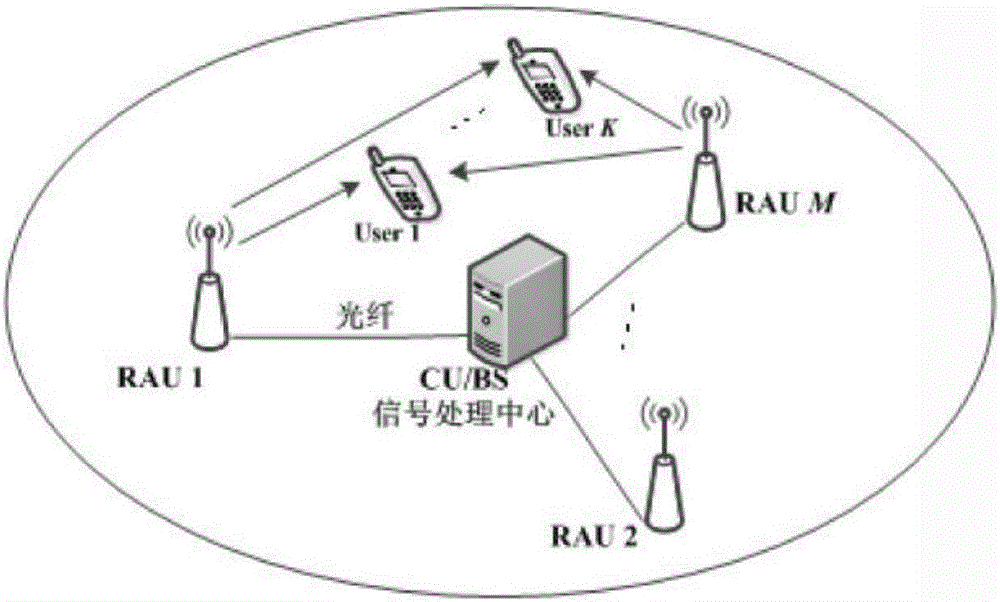
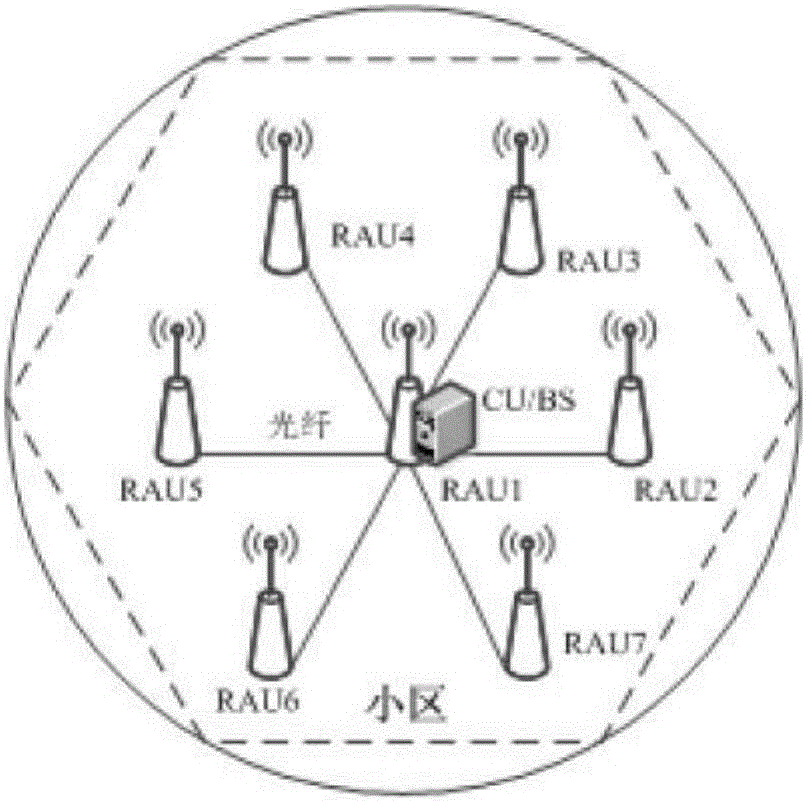
[0098] For the distributed MIMO multi-antenna system, the cell radius is set to 1km, and the system bandwidth is in Hz. like image 3 As shown, it is assumed that there are 7 RAUs in the cell, and each RAU is equipped with 4 antennas. One of the RAUs is located in the center of the cell, and the remaining 6 RAUs are evenly distributed on a circle with a radius of R / 2 at an angle of 60°. Each RAU passes through Optical fiber is connected to CU / BS. For BD precoding and the precoding proposed in the present invention, the receiving end adopts the maximum SINR to carry out receiving combination design. Since BD precoding requires that the total number of transmitting antennas is not less than the total number of receiving antennas, the actual total number of transmitting antennas is selected to be equal to the total number of receiving antennas. The number of receiving antennas. The number of transmitting an...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Embodiment 2 A centralized MIMO multi-antenna system scenario
[0100] As a comparison, the average data rate and average symbol error rate performance of the precoding joint optimization method proposed in the present invention in a centralized MIMO multi-antenna system (C-MIMO) are also given by simulation. For a centralized MIMO multi-antenna system, the radius of the cell is set to 1 km, the system bandwidth is in Hz, there is a base station in the cell, located in the center of the cell, and the number of antennas of the base station is equal to that of all RAUs in the distributed MIMO multi-antenna system (D-MIMO) The sum of the number of antennas is 28, and 16 antennas are selected from the base station antennas to transmit data for the user. In a centralized MIMO multi-antenna system, the system average data rate and average symbol error rate of the joint optimization method based on SLNR precoding, the joint optimization method based on weighted SLNR precoding,...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Embodiment 3 A scenario where the number of transmit antennas changes in a distributed MIMO multi-antenna system
[0102] Same as the distributed MIMO multi-antenna system in Embodiment 1, the cell radius is set to 1km, the system bandwidth is in Hz, there are 7 RAUs in the cell, each RAU is equipped with 4 antennas, one RAU is located in the center of the cell, and the remaining 6 Each RAU is evenly distributed on a circle with a radius of R / 2 at an angle of 60°. Each RAU is connected to the CU / BS through an optical fiber. The transmission signal-to-noise ratio is 20dB. The principle of minimum path loss selects the required number of transmit antennas from the antennas of all RAUs. Variation curves of the system average data rate with the number of transmitting antennas for the joint optimization method based on SLNR precoding, the joint optimization method based on weighted SLNR precoding, the iterative joint optimization method based on weighted SLNR precoding, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com