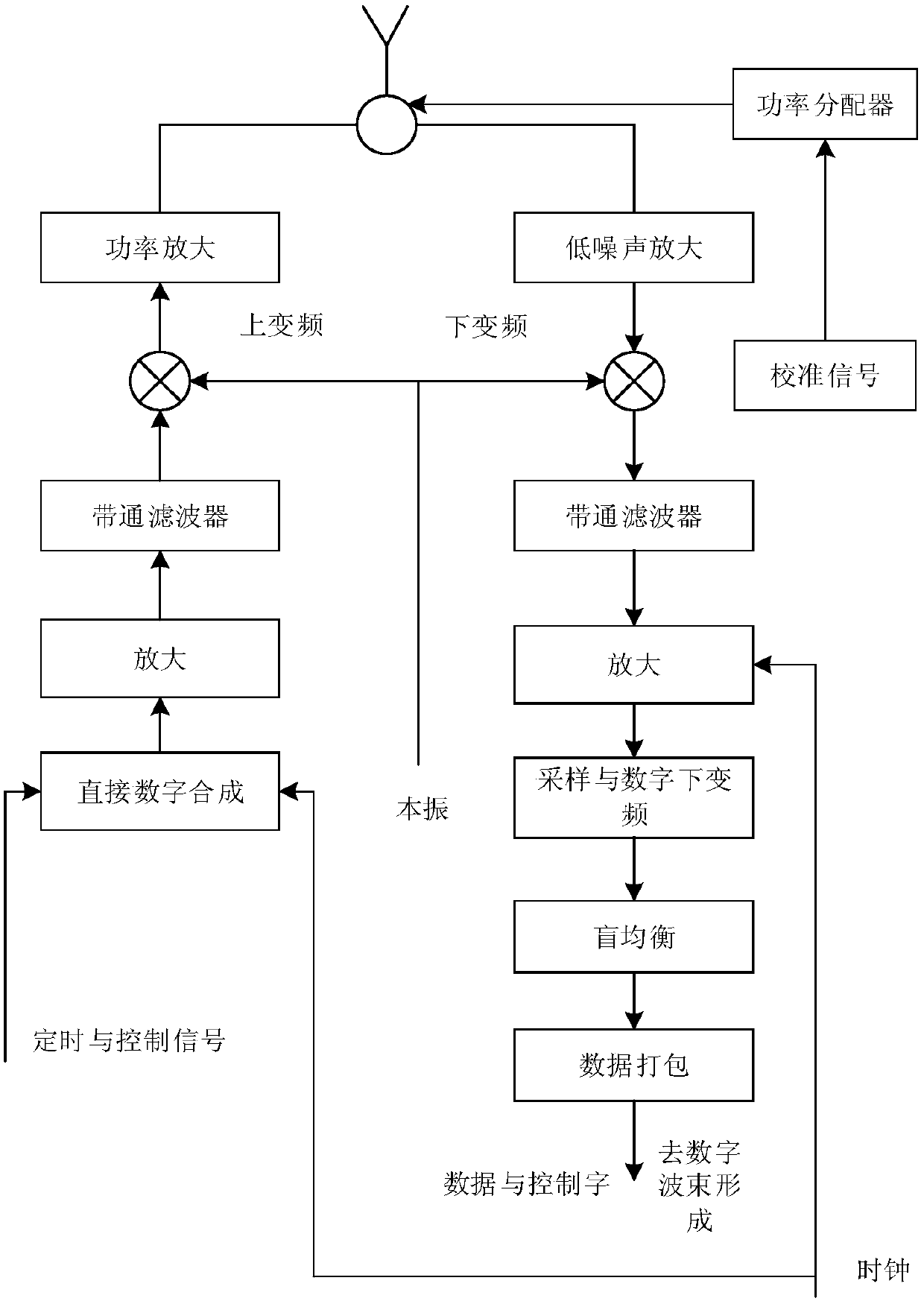
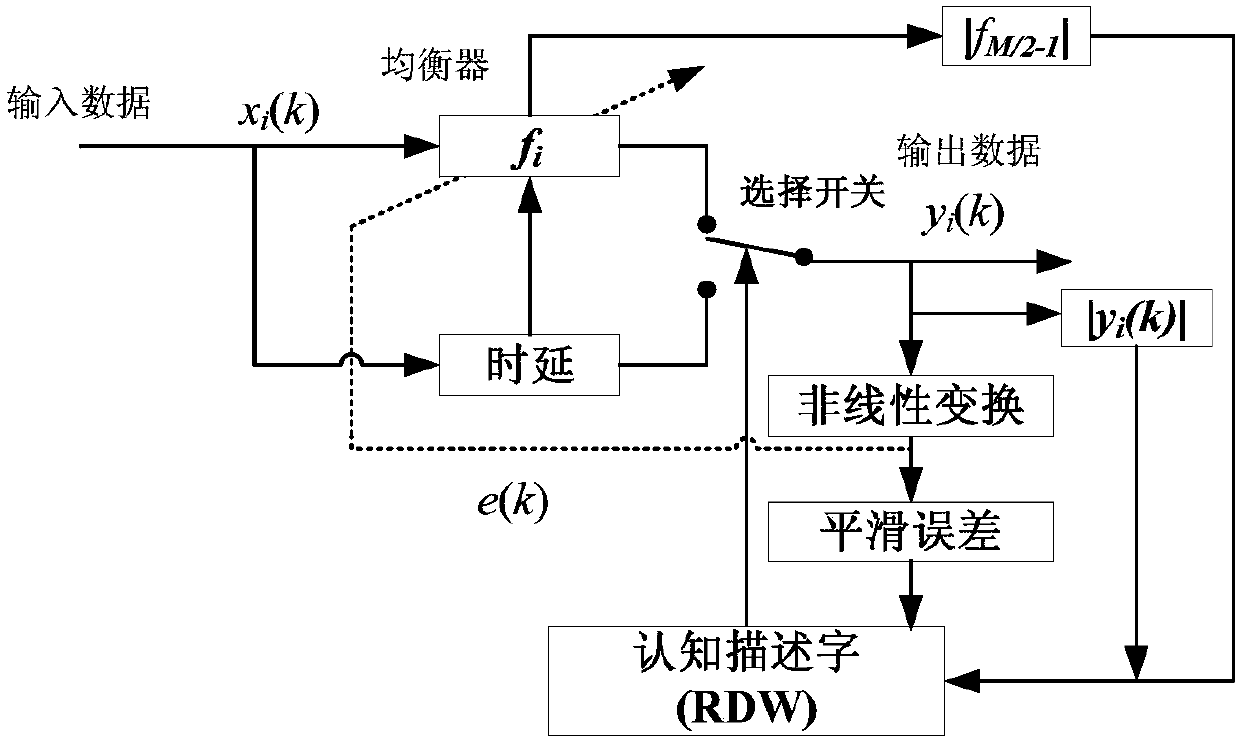
A Cognitive Blind Equalization Method for Radar Channel Amplitude and Phase Correction
A phase correction and blind equalization technology, applied in the field of digital array radar, which can solve the problems of complex data transmission links and complex system implementation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0119] First define the following simulation model to generate the data required for channel constant modular blind equalization verification:
[0120] The input signal of the cognitive equalizer is represented by the following formula:
[0121]
[0122] In the formula: k is discrete time sampling, x i (k) is the i-th channel equalizer input data; p(k) is the calibration signal input, which is a random phase modulation signal; is the discrete channel response of the i-th channel, Q is the number of channel response coefficients, ξ i (k) is the Gaussian noise of the i-th channel, Indicates convolution;
[0123] In the simulation, the simulation conditions of the constant blind equalization algorithm are shown in Table 1:
[0124] Table 1
[0125]
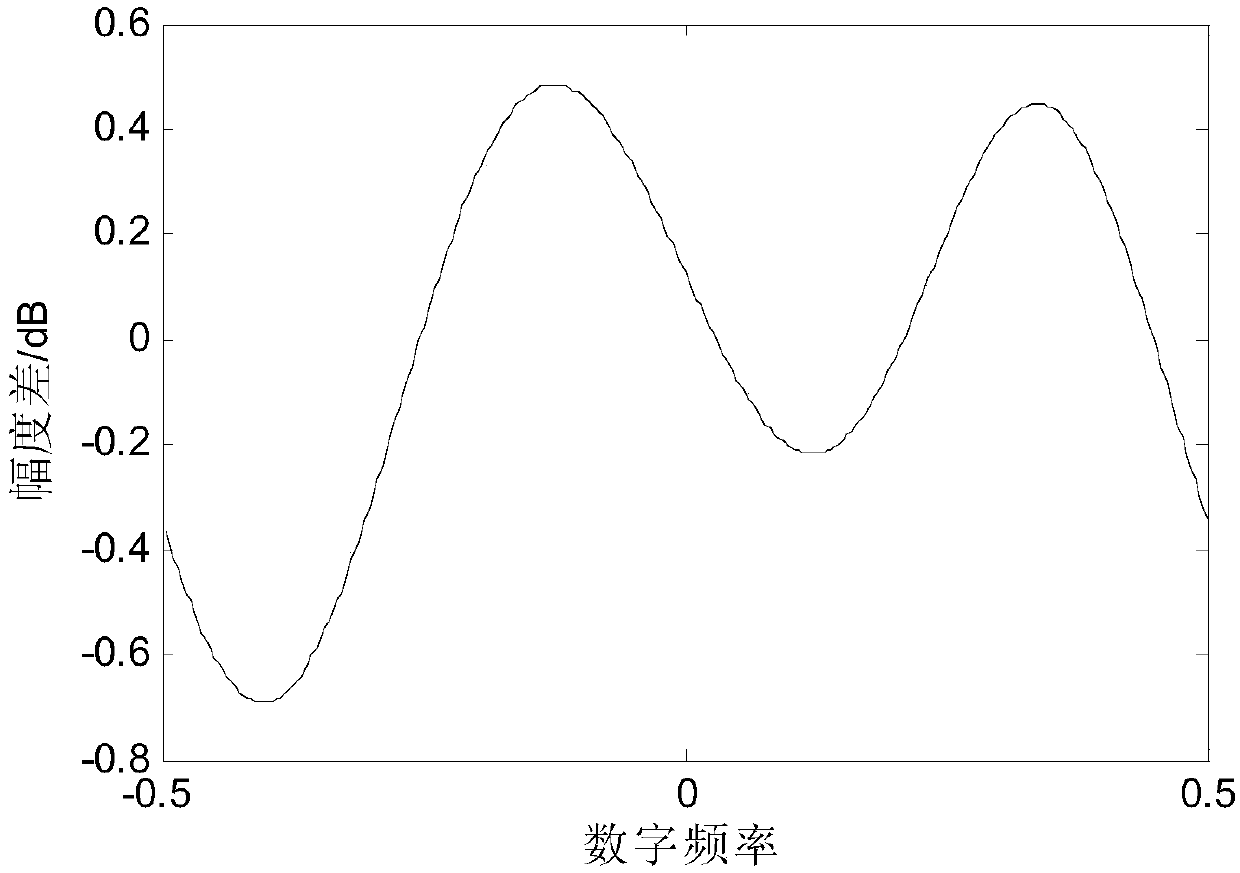
[0126] As shown in Figure 3(a)-(b), two channels with large gaps in amplitude and phase are used to verify the channel correction capability of the blind equalization method. The amplitude error between channels is 2dB (...
Embodiment 2
[0135] When there are errors such as bit errors in the input data, it will affect the convergence ability of the cognitive blind equalizer, thus making the equalizer unusable. In this embodiment, data with bit errors is used to verify the cognitive ability of blind equalization, and a bit error exists at the 4000th point of the data in simulation.
[0136] Figure 6(a)-(d) shows the change of parameters in cognitive descriptor RDW. It can be seen that the equalizer diverges at the position where the bit error occurs, so that the equalizer has not yet converged to a steady state at the sampling point at the end of the data. At this time, RDW=[0,1,0,1]. Therefore, this equalizer fails. The equalizer switches to pure delay mode. Otherwise, with the obtained equalizer equalization, more harsh channel characteristics will be obtained, such as Figure 7 As shown, compared with the situation before equalization in Fig. 3(a), the performance is worse.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com