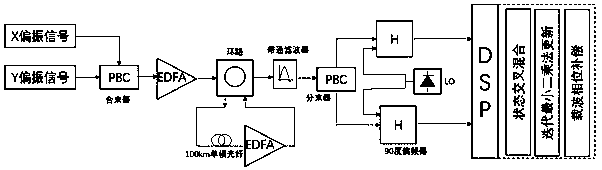
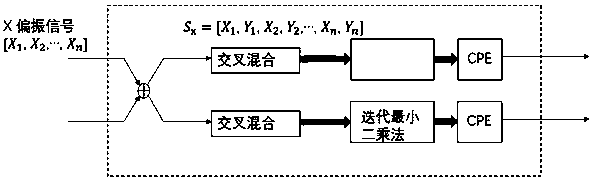
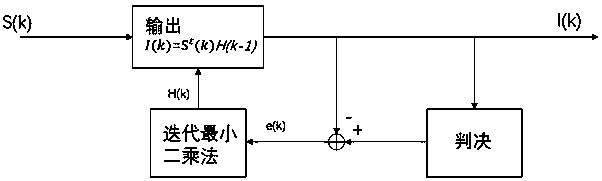
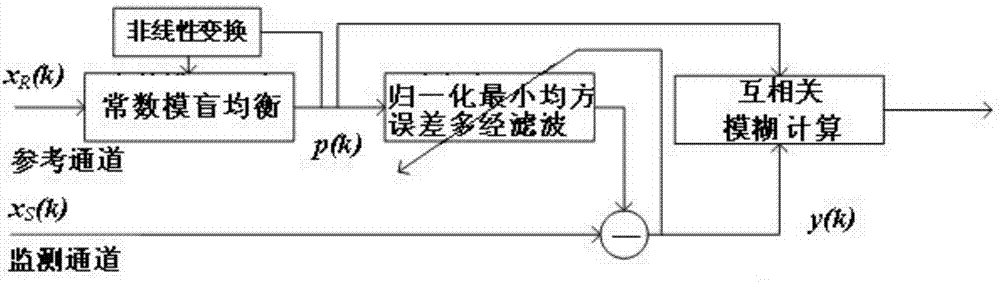
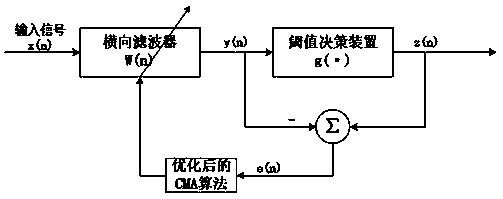
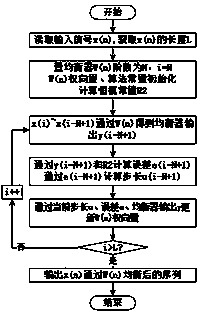
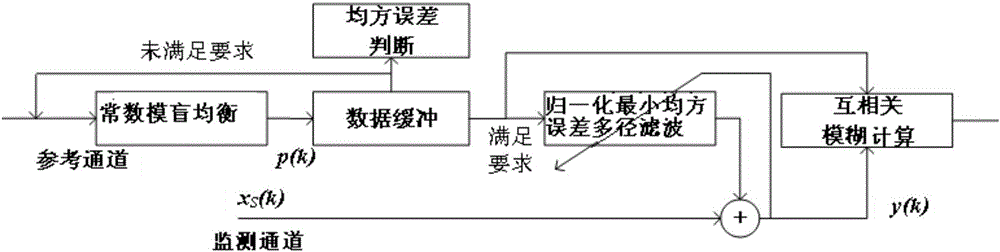
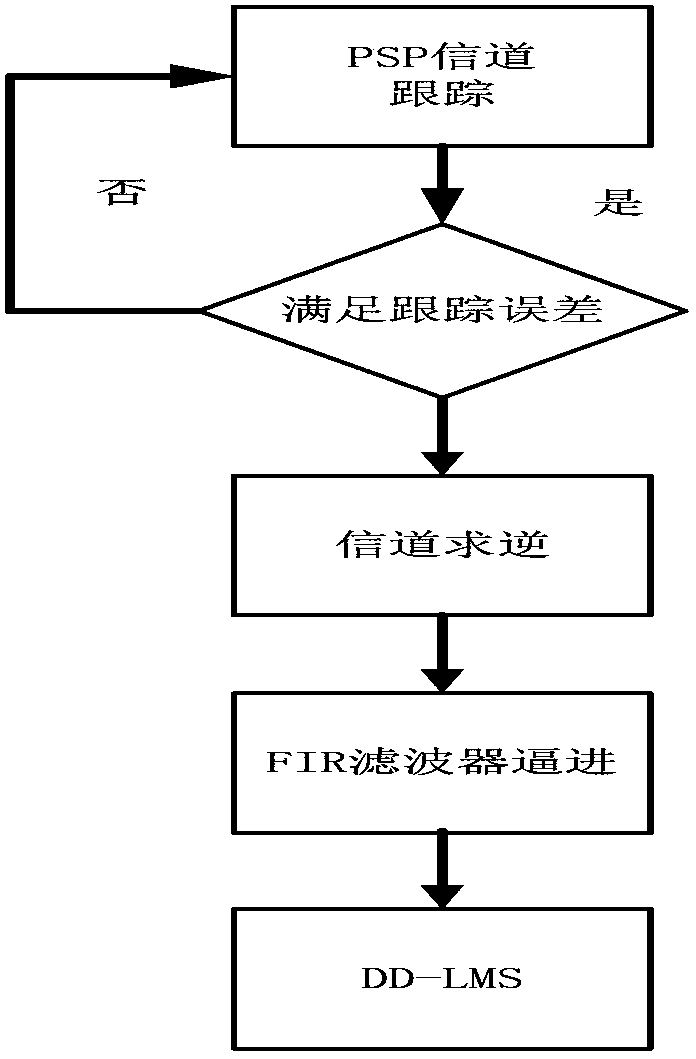
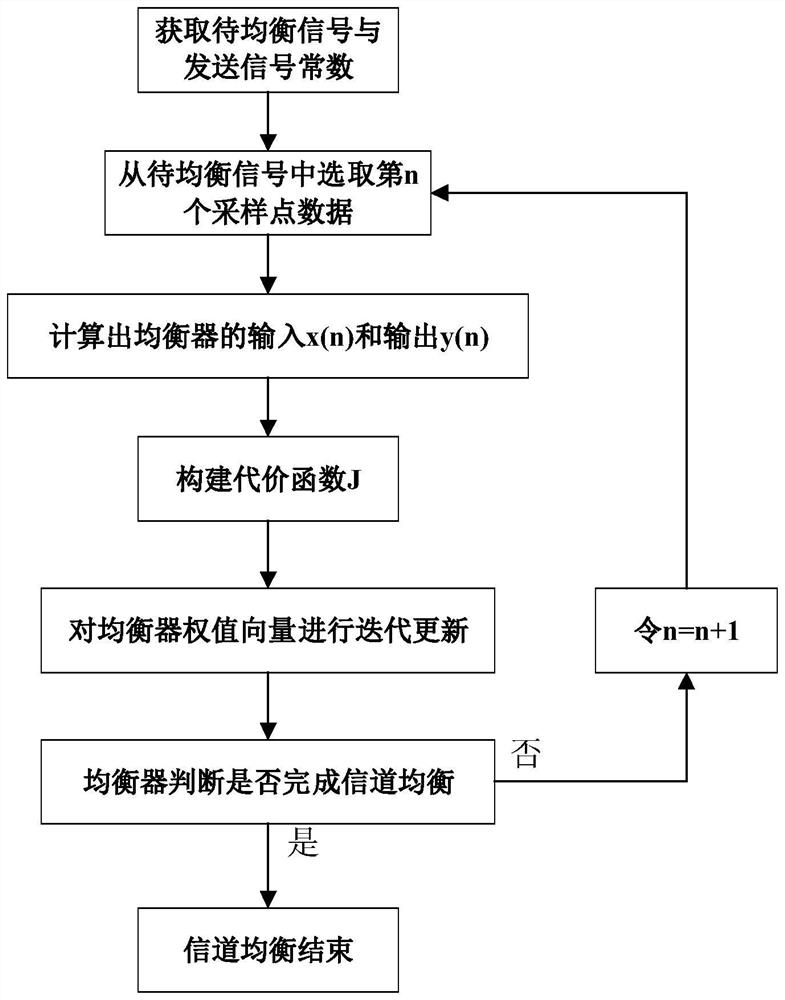
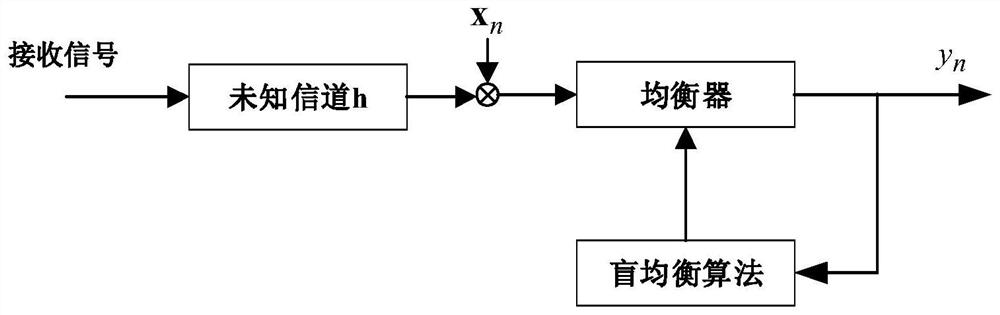
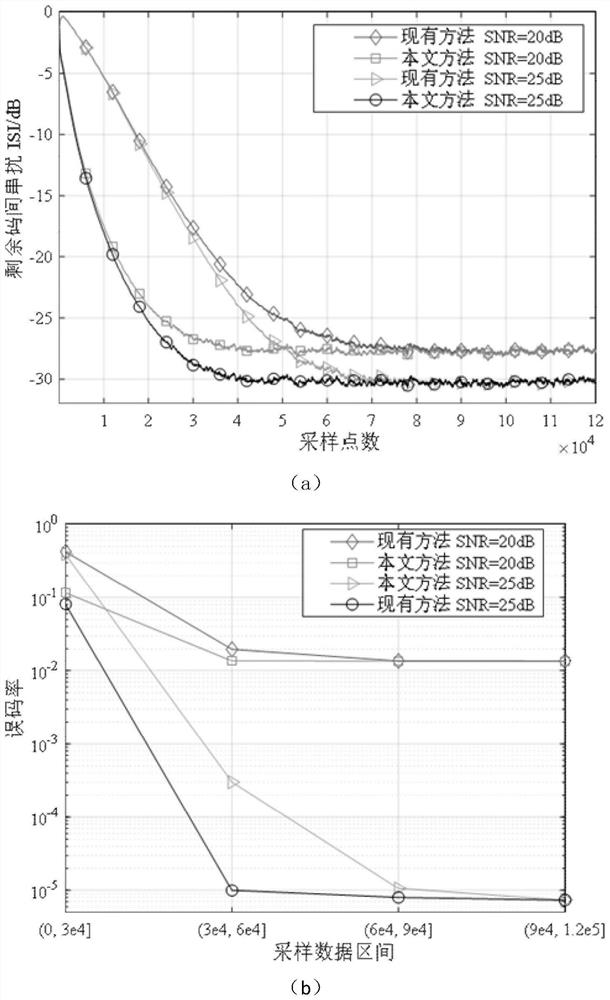
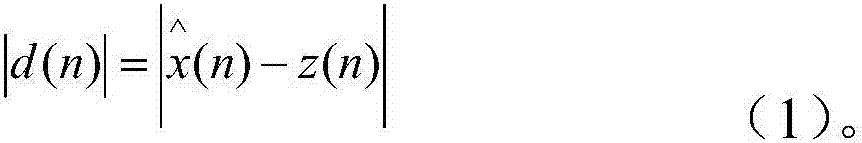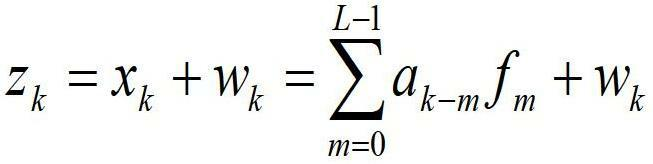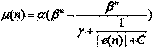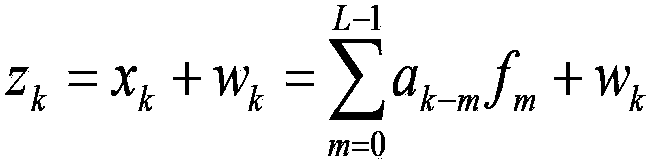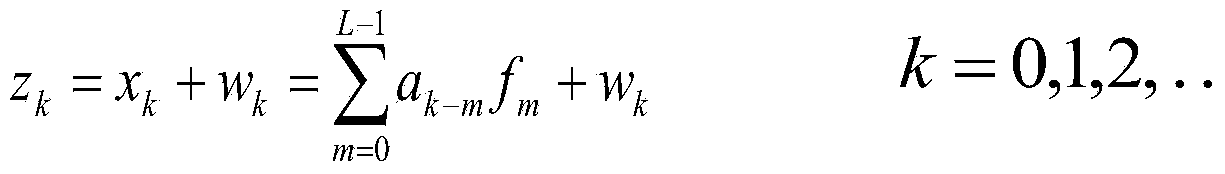Patents
Literature
52 results about "Blind equalization algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
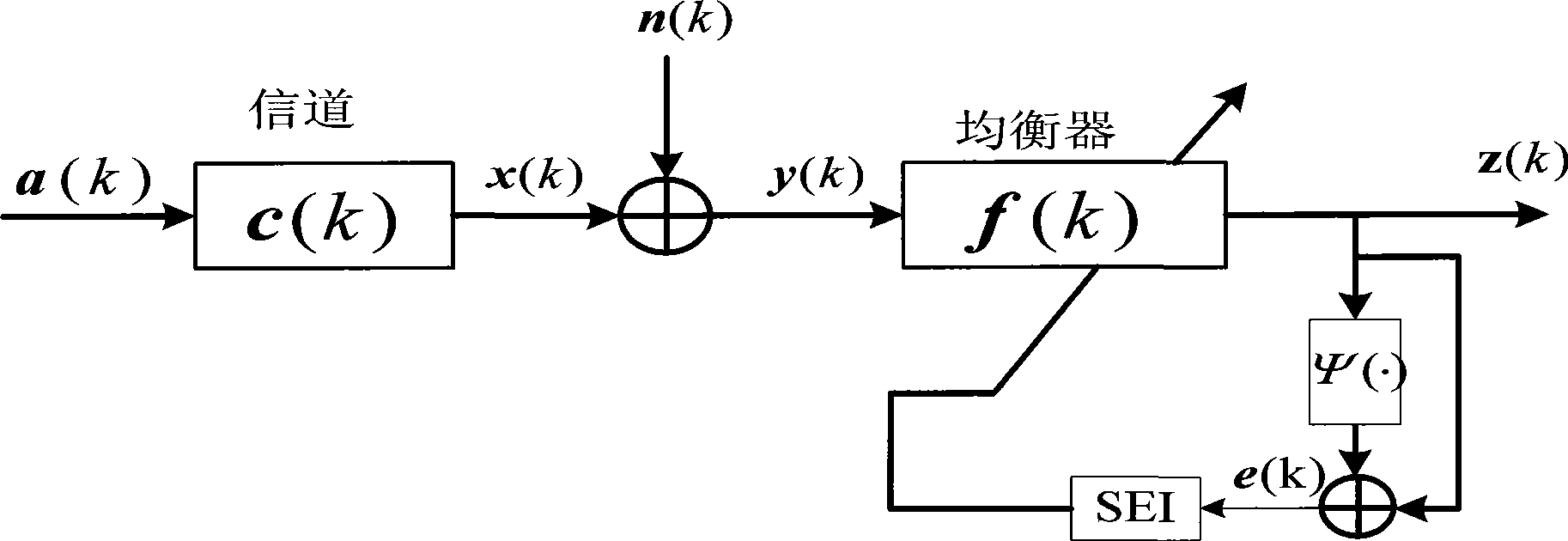
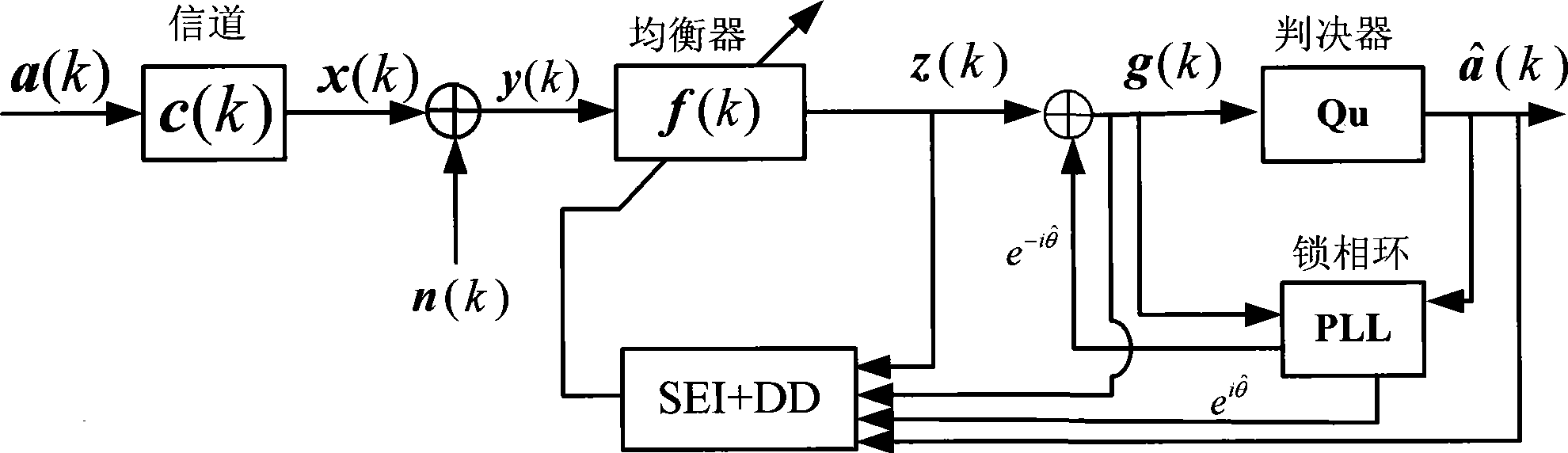
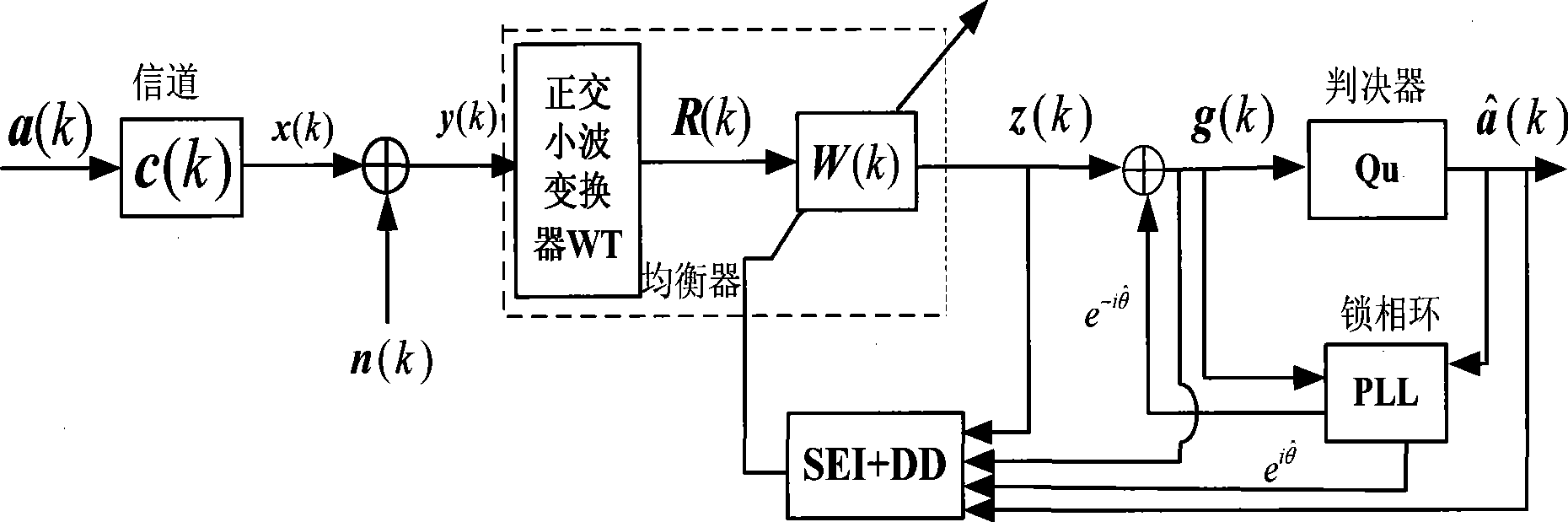
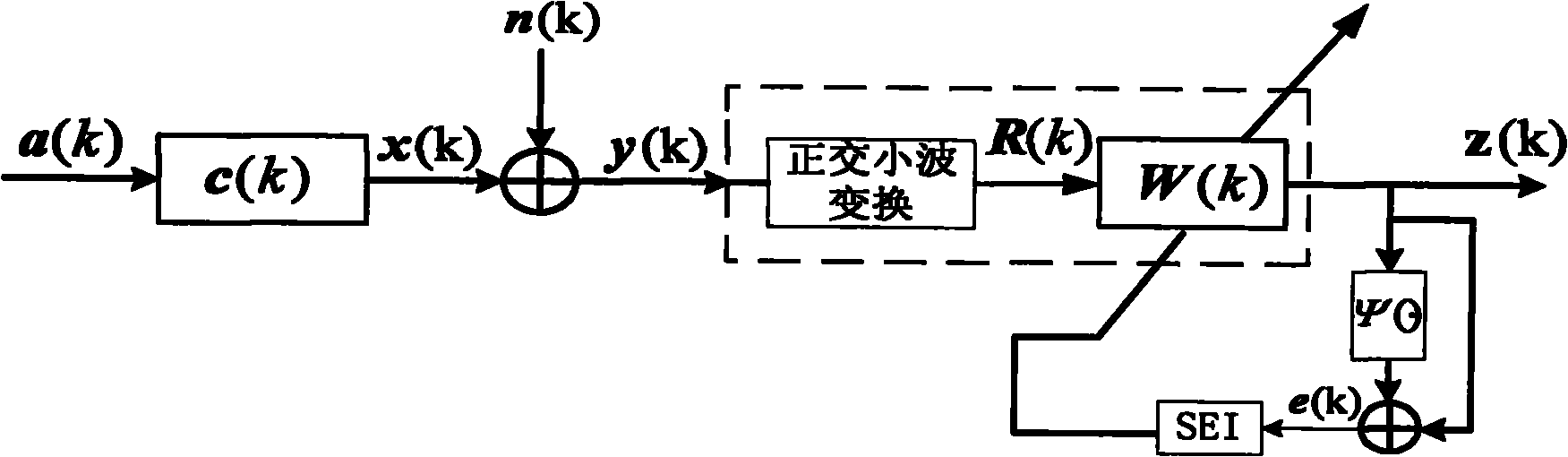
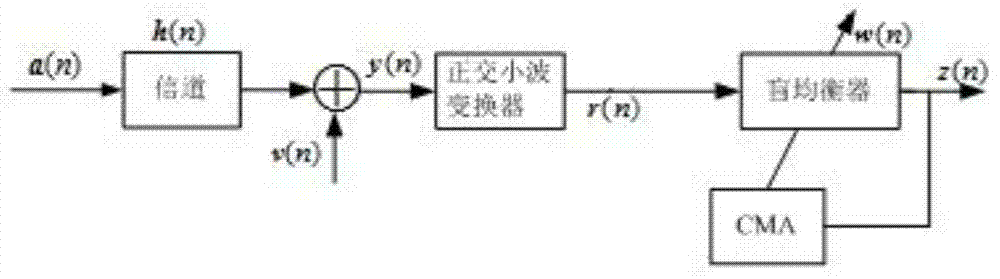
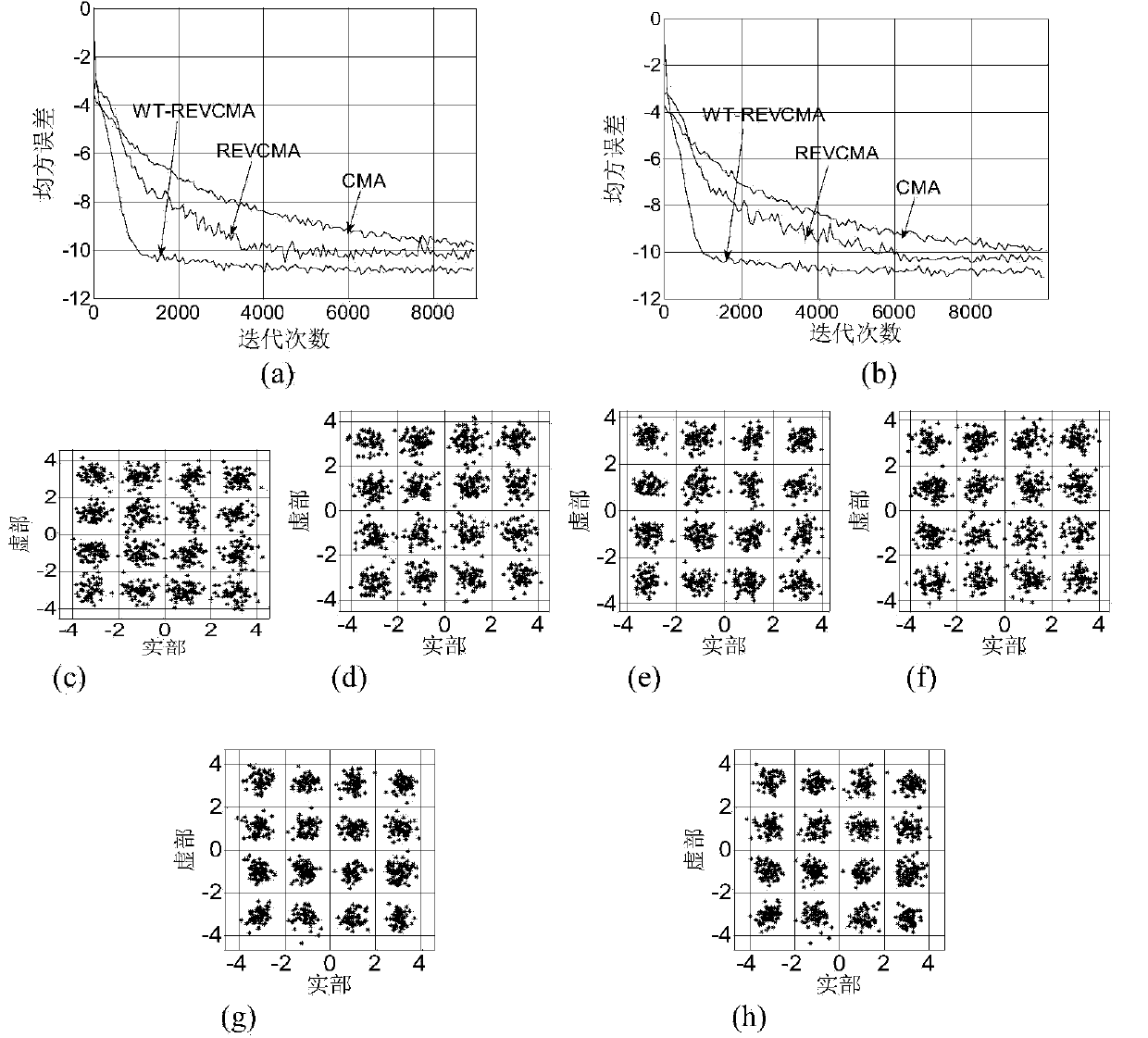
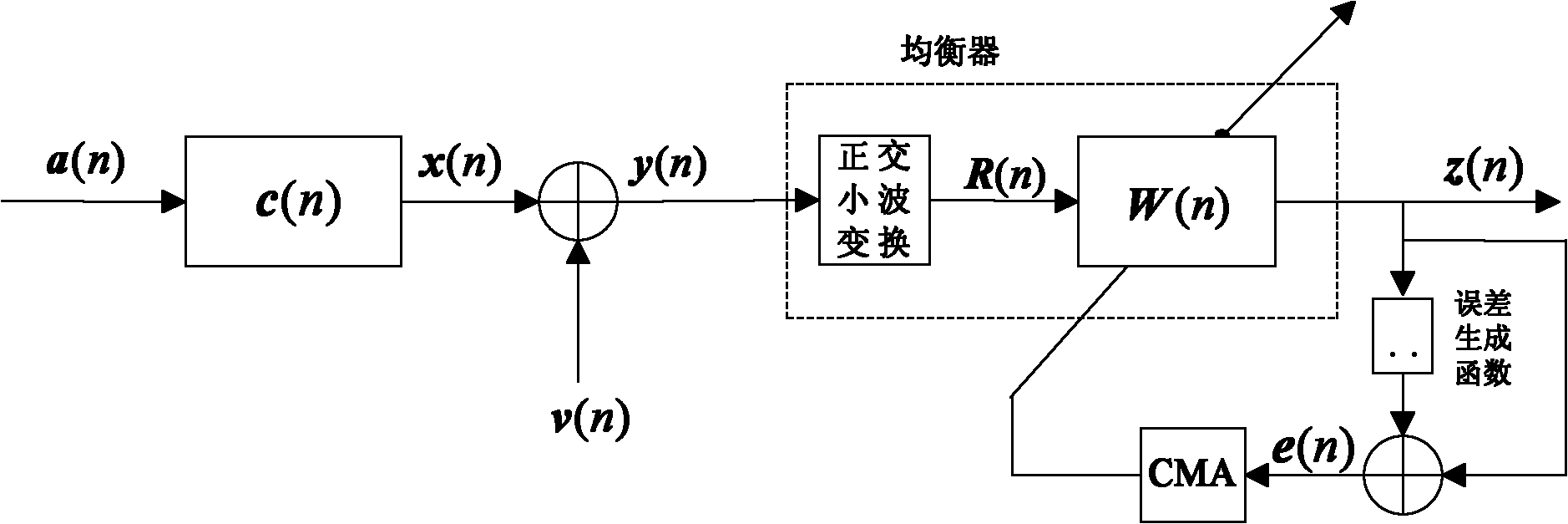
Combined super-exponential iteration blind equalization algorithm based on orthogonal wavelet transform
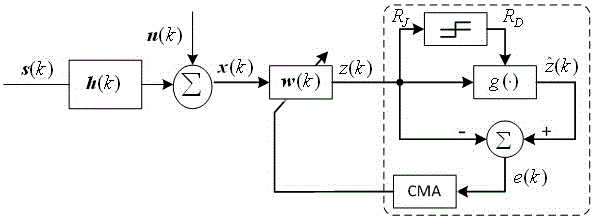
The invention discloses a super-exponential interative combined blind equalization method based on orthogonal wavelet transformation (WT-CSEI). The WT-CSEI algorithm is implemented by incorporating the orthogonal wavelet transformation in the super-exponential interative (SEI) algorithm, correcting by use of the weight vector iterative formula of the orthogonal wavelet transformation relative to the SEI algorithm, simultaneously combining the decision directed (DD) algorithm with the soft-switching method, and introducing a phase-locked loop (PLL) technique with regard to the characteristics of time-variable Doppler frequency shift of under acoustic channel. The WT-CSEI algorithm corrects the phase rotation by means of the PLL technique, accelerates the convergence rate by means of the orthogonal wavelet transformation, reduces the steady-state error by means of the combination of the soft switching method and the DD algorithm, can effectively track the time varying characteristics of the channel, and is applied to the blind equalization of the time-variable multipath fading underwater acoustic channel.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
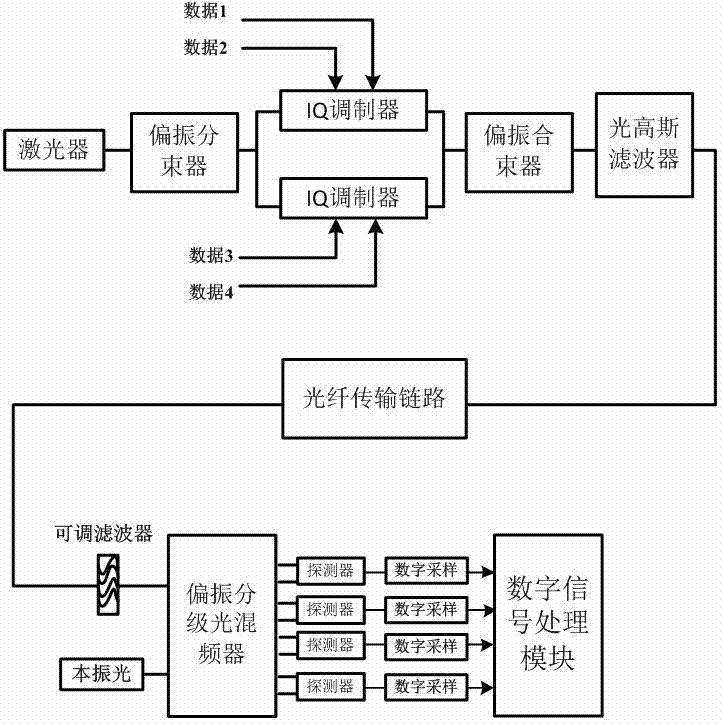
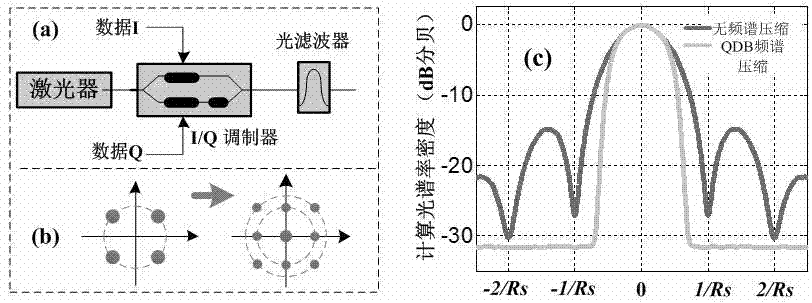
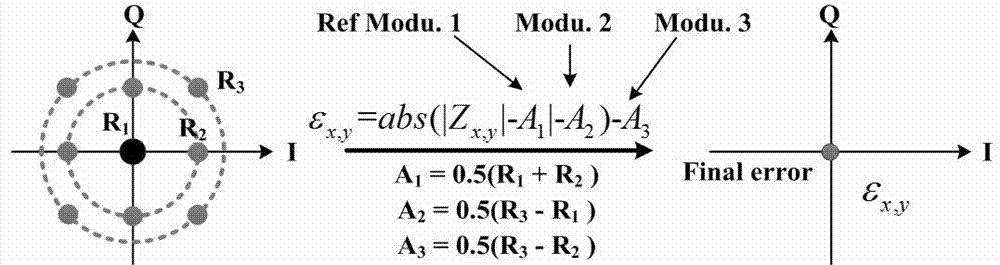
Multimode blind equalization algorithm applied to quadrature duobinary (QDB) frequency-spectrum-compressed polarization multiplexing signal
ActiveCN102904643AImprove spectral efficiencyImprove transmission qualityPolarisation multiplex systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumBlind equalization algorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical fiber communication, in particular to a multimode blind equalization digital signal processing algorithm applied to a quadrature duobinary (QDB) frequency-spectrum-compressed polarization multiplexing signal. According to the invention, in a coherent optical communication system, the multimode-blind-equalization-based digital signal processing algorithm is adopted to realize equalization compensation and demodulation of an optical signal which is subjected to QDB frequency spectrum compression; suitable filters are adopted in an electric field or an optical field to realize the QDB frequency spectrum compression of a polarization multiplexing signal; the polarization demultiplexing of a transmitted optical signal is realized by using a cascade multimode algorithm (CMMA); frequency offset estimation is realized by using a multimode quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) partition method; and phase retrieval is realized by using the multimode QPSK partition method and maximum likelihood estimation. By the algorithm, the frequency spectrum efficiency of the signal can be effectively improved, the transmission quality of the signal can be improved, and high-spectral-efficiency coherent optical transmission can be realized.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
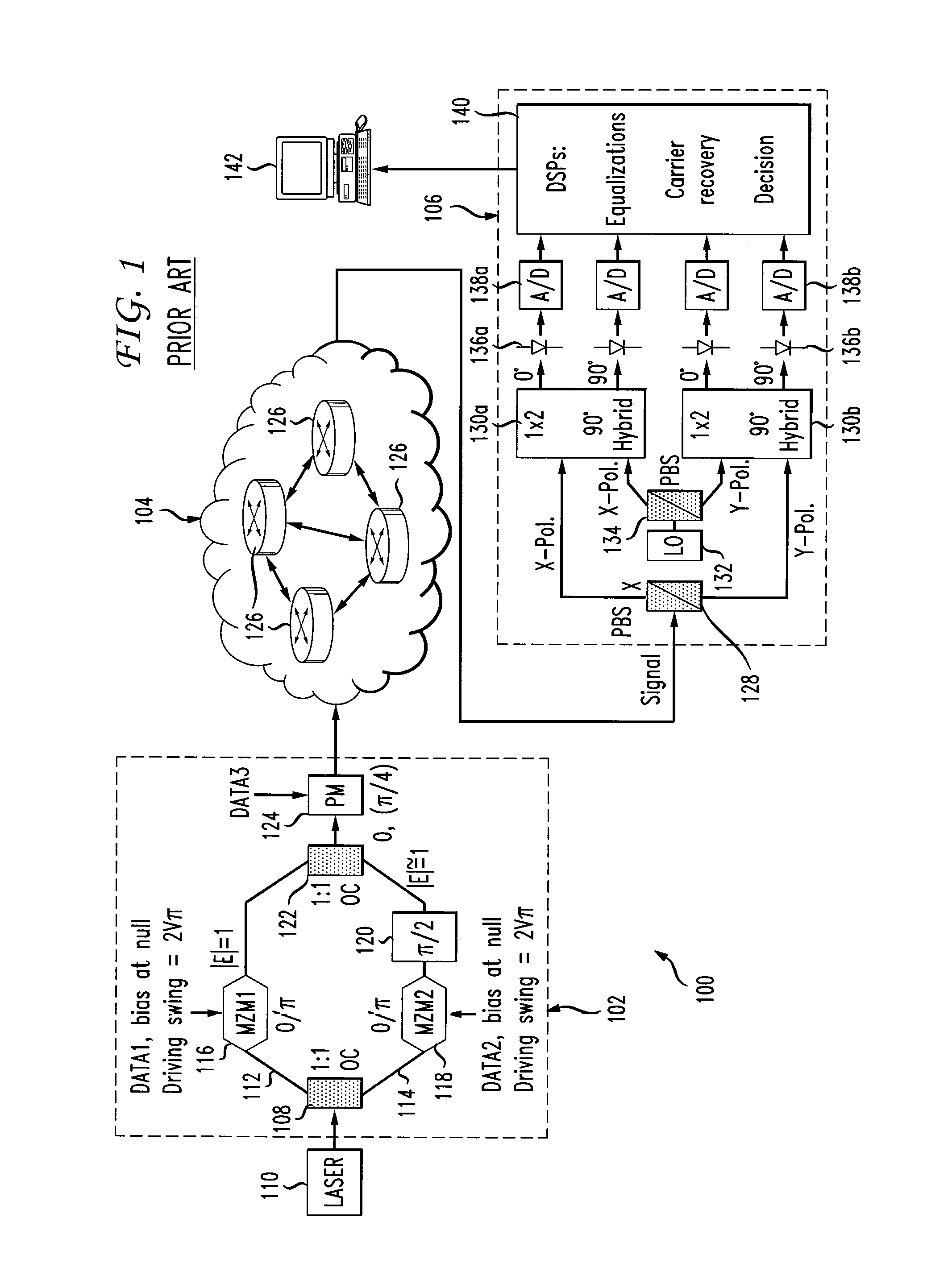
Blind Equalization Algorithms for Adaptive Polarization Recovery and PMD Compensation
ActiveUS20110052215A1Electromagnetic receiversOptical transmissionCommunications systemBlind equalization algorithm
A device and method are disclosed for blind equalization of an optical signal to implement adaptive polarization recovery, Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) compensation, and residual Chromatic Dispersion (CD) compensation in a digital coherent optical communication system.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
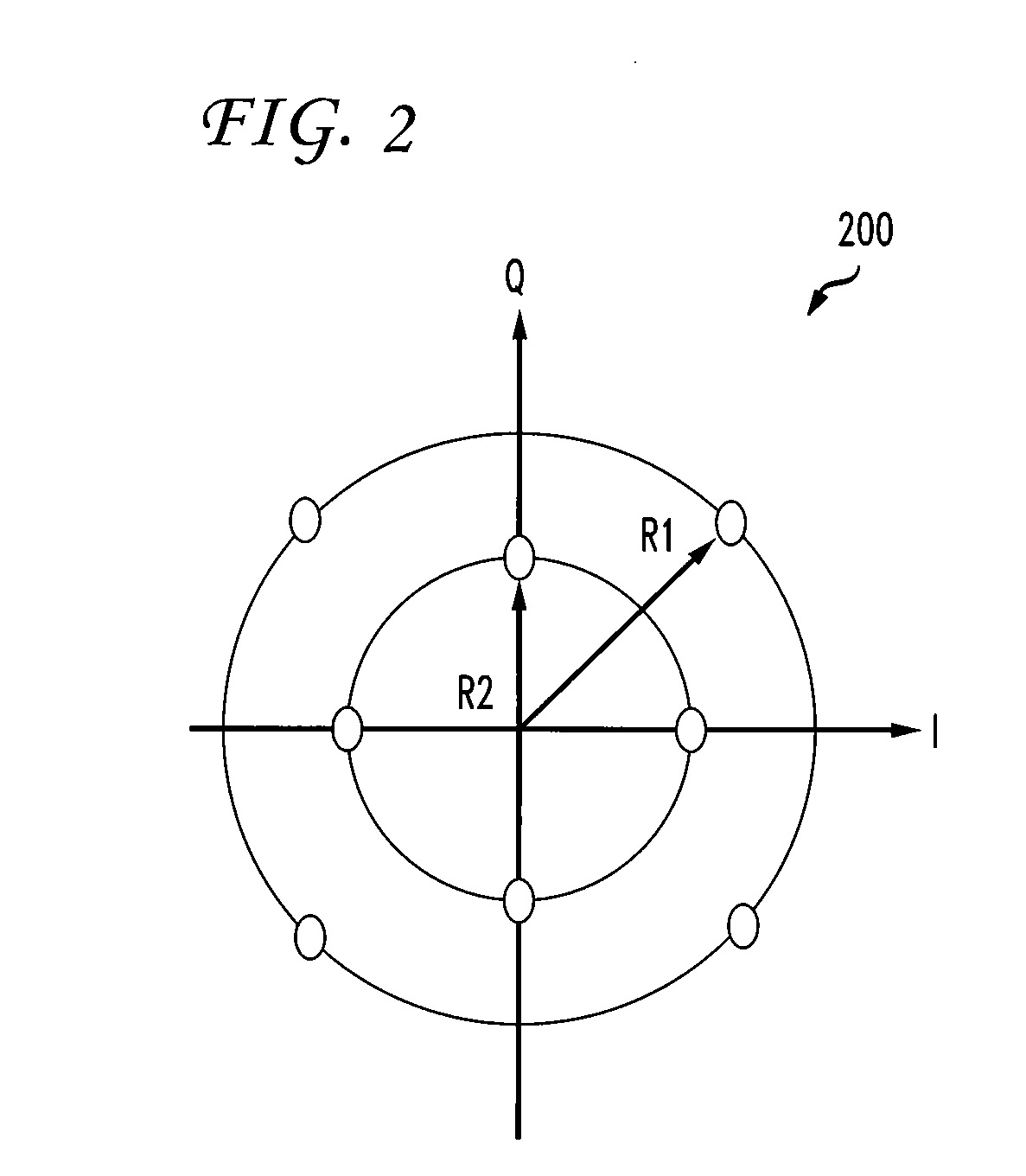
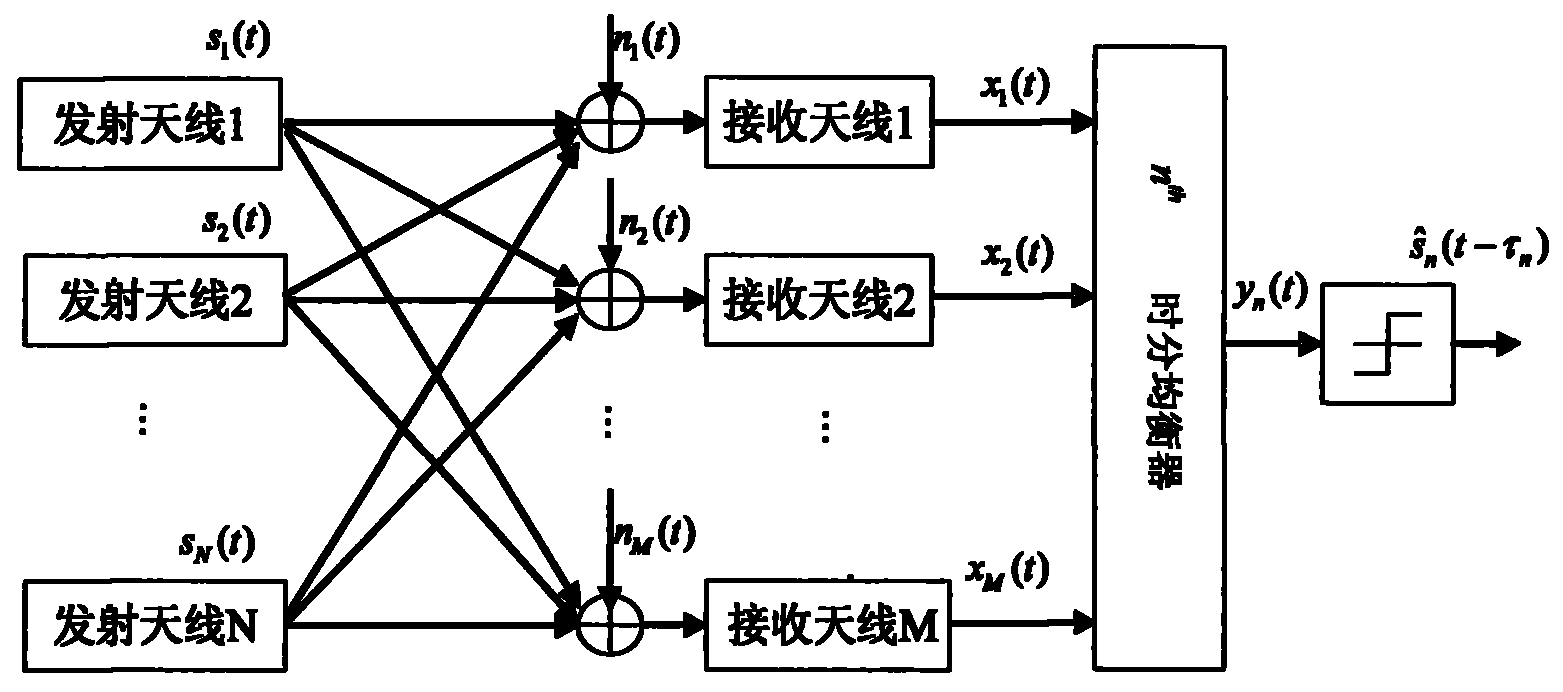
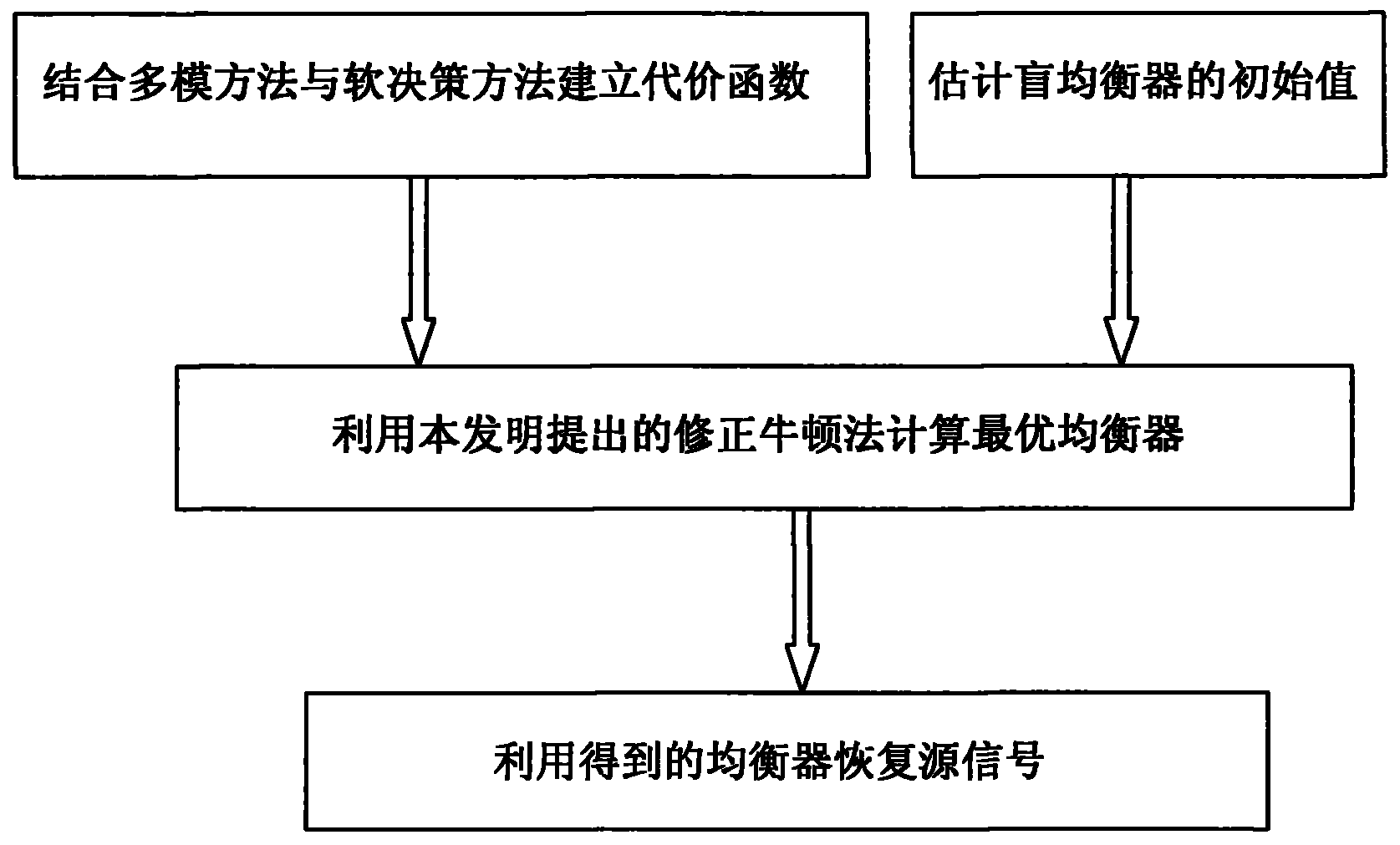
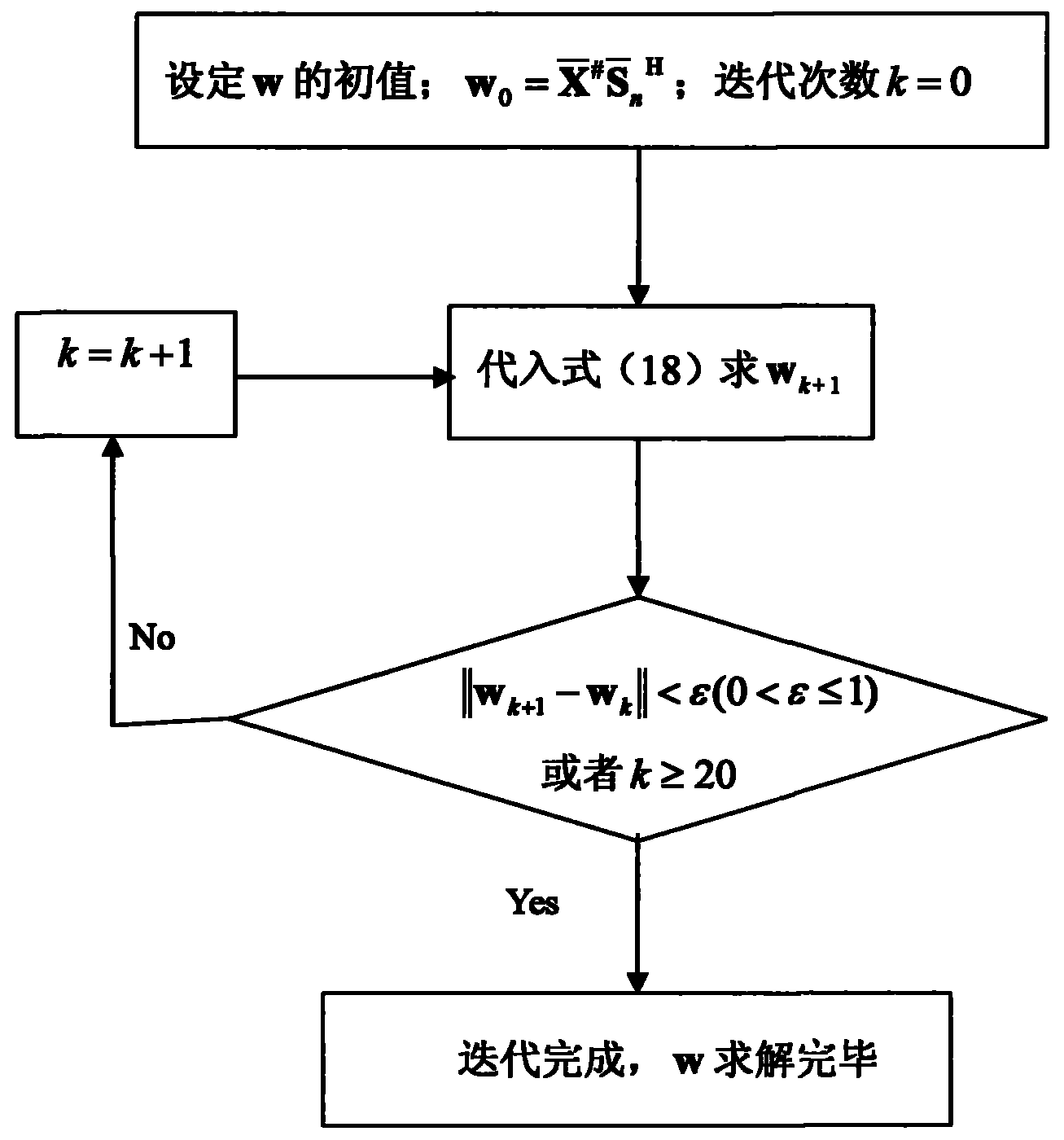
Frequency selectivity MIMO (multiple input multiple output) system space-time blind equalizer method based on MNM (modified Newton method)
InactiveCN103401824AReduce the number of samplesGuaranteed to workTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError prevention/detection by diversity receptionBlind equalizerBatch processing
The invention discloses a frequency selectivity MIMO (multiple input multiple output) system space-time blind equalizer method based on a MNM (modified Newton method). The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a multimode method and a soft decision guide method are combined for building a cost function; then, a batch processing mode is adopted, the training sequence length is selected, and the initial value of the blind equalizer is estimated from the known emitted data and the corresponding observing data by a least square method; a newly provided MNM is utilized for calculating the optimal equalizer from observing samples; and finally, the equalizer is utilized for evenly receiving signals, the interference among signals and the interference among codes are eliminated, and resources signals are recovered. The method overcomes the defects that when the exiting MNM is applied to a MIMO system, the calculation quantity is great, and the equalization precision of the existing blind equalization algorithm is low. Compared with the exiting method, the method has the advantages that MNM, MMA and SDD only need little training sample data, and the equalizer can be enabled to be correctly converged to the optimum MMSE (minimum mean square error) equalizer.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
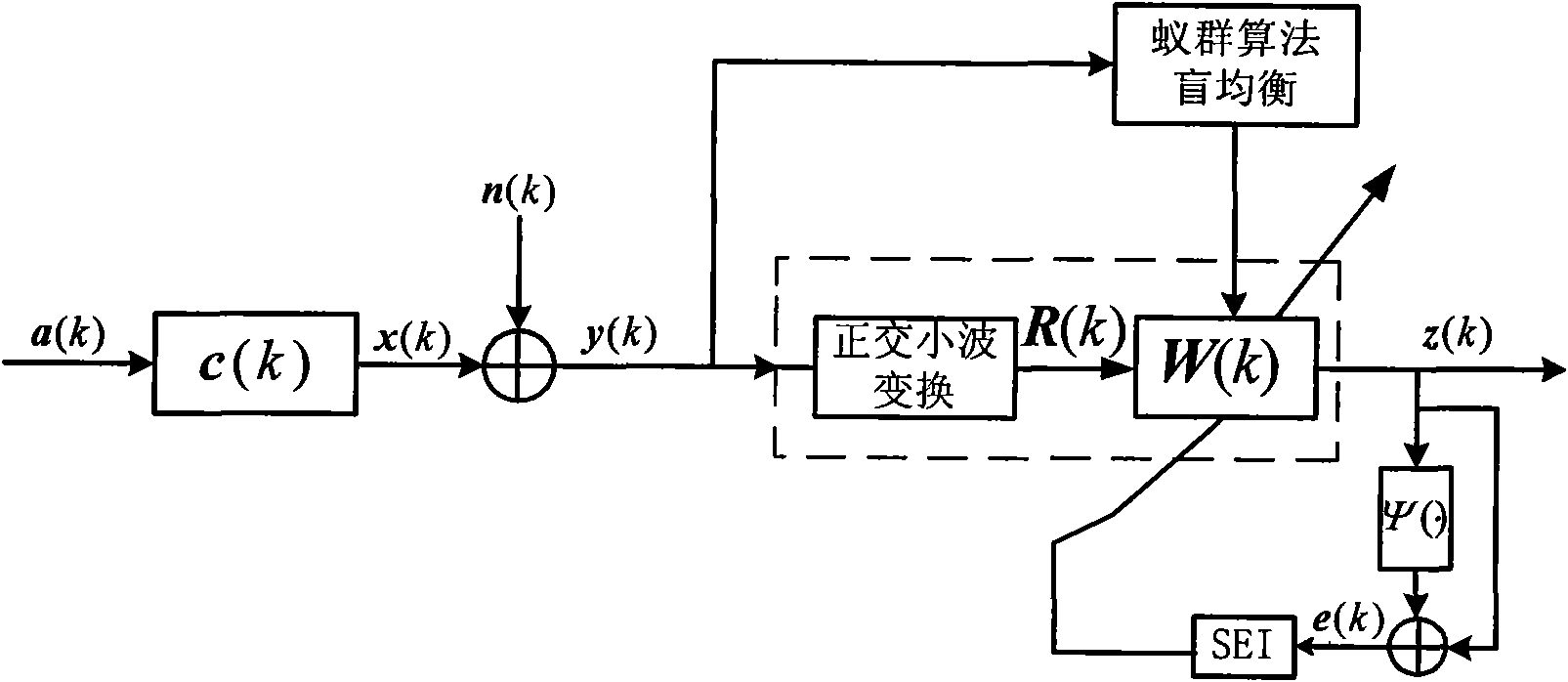
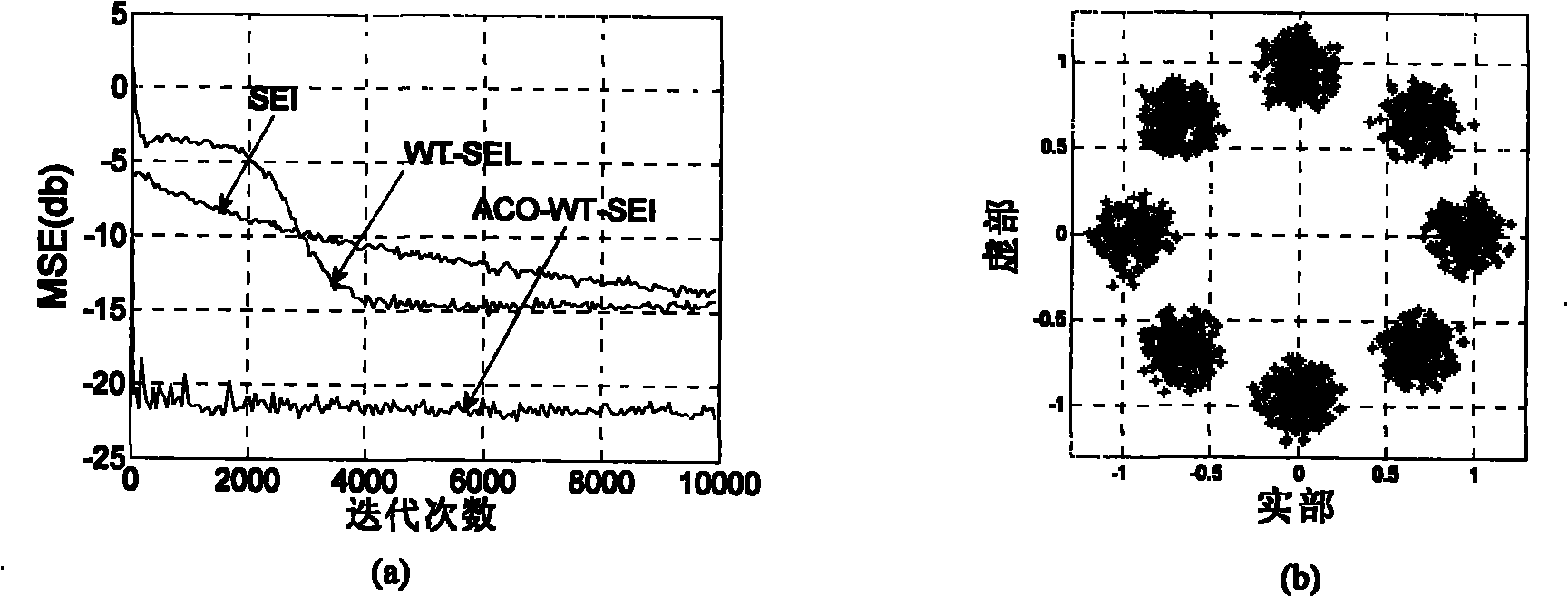
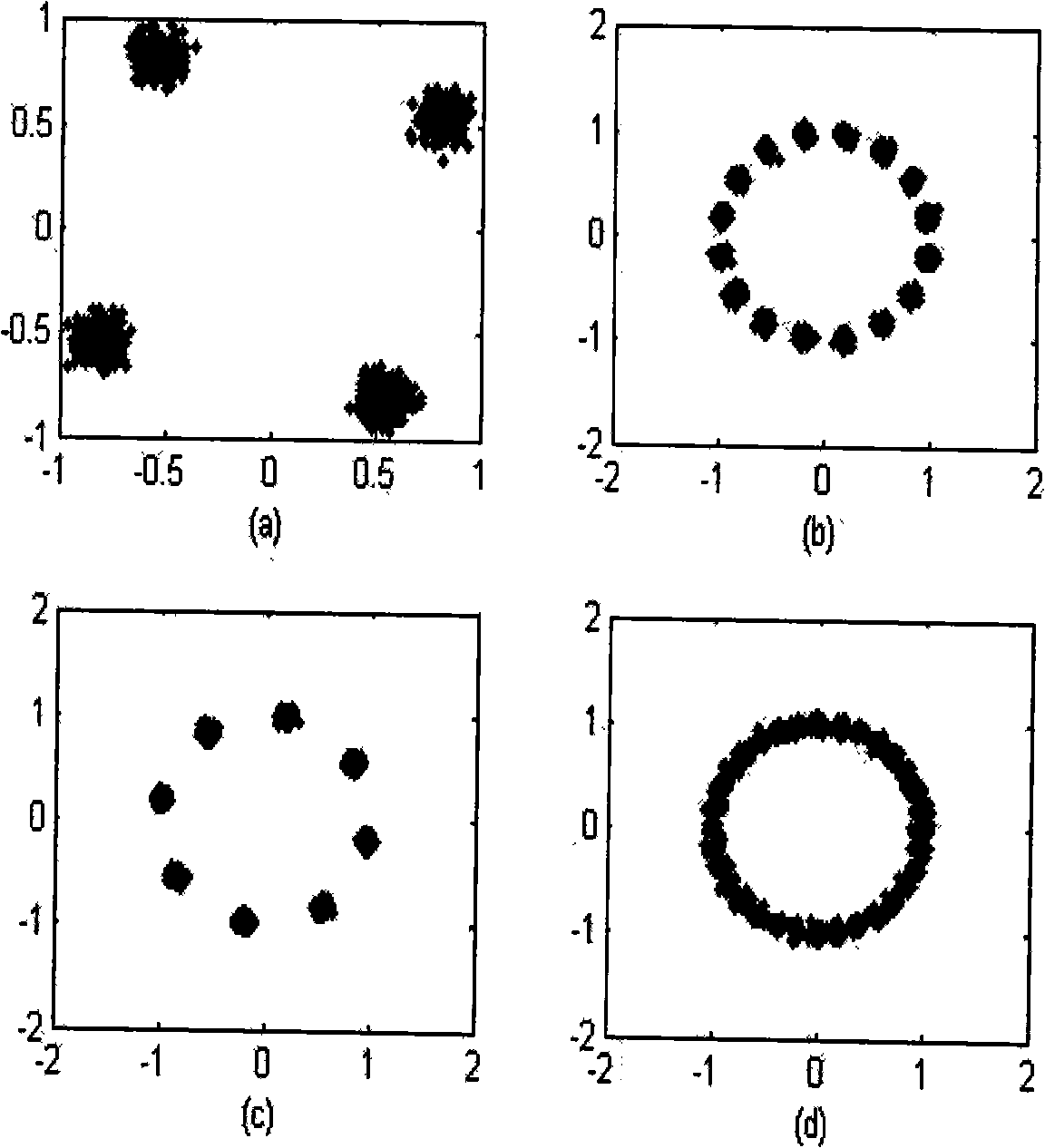
Orthogonal wavelet transformation super-exponential iteration (SEI) blind equalization algorithm based on ant colony optimization
InactiveCN101902417AAvoid cases of local convergenceTake advantage of global convergenceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalization algorithmOptimal weight
The invention discloses an orthogonal wavelet transformation super-exponential iteration (SEI) blind equalization method based on ant colony optimization. The method utilizes ant colony optimization to search the optimal weight vector as an initial weight vector value inputted by an equalizer so as to avoid local convergence of the algorithm. The method utilizes a positive feedback mechanism to increase convergence rate, utilizes the whitening action of the super-exponential iteration (SEI) method on data, utilizes orthogonal wavelet transformation to perform decorrelation on signals and fully utilizes the global convergence of ant colony optimization. Underwater acoustic channel simulation results show that compared with the orthogonal wavelet transformation super-exponential iteration constant modulus algorithm (WT-SEI-CMA), the method has higher convergence rate and smaller state error, and an equalized eye pattern is clearer and compacter. Thus, the method has certain practical valve.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
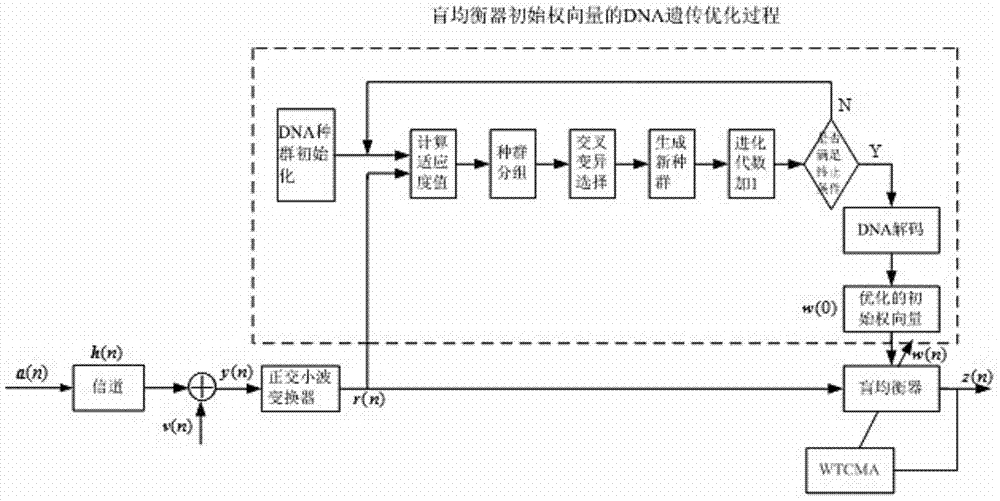
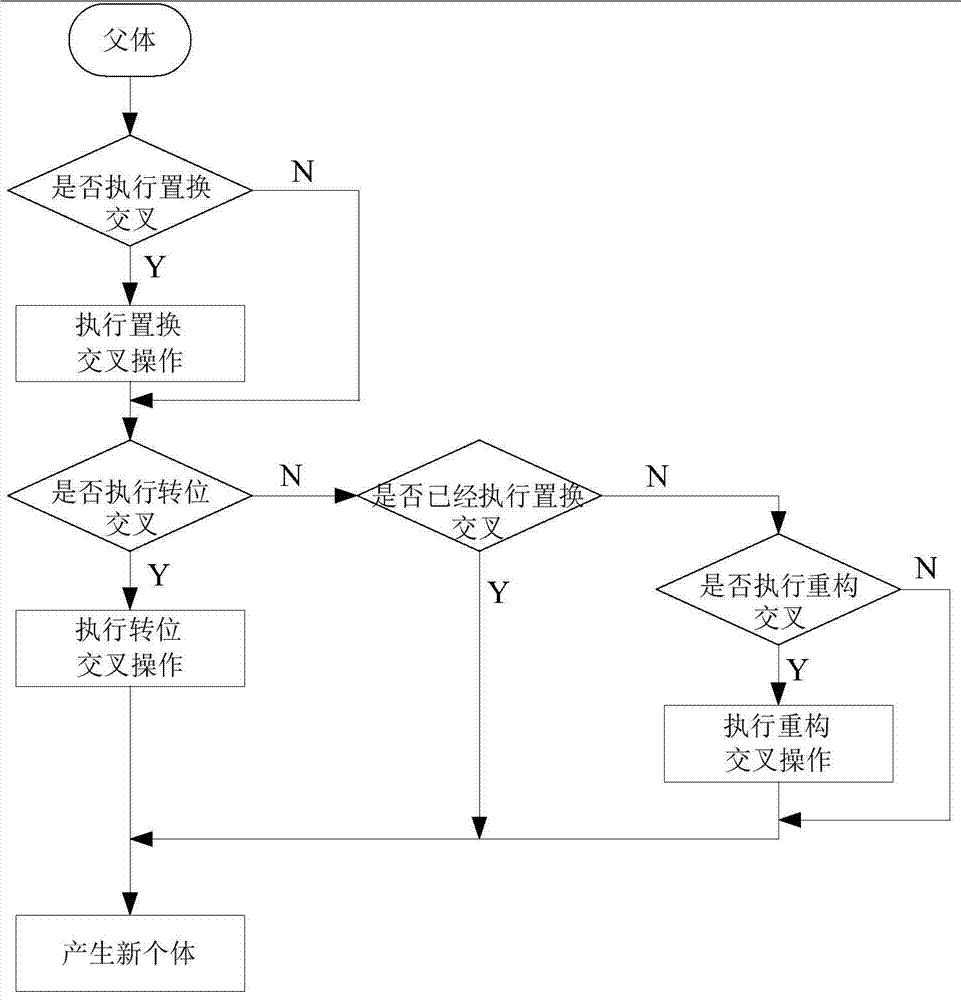
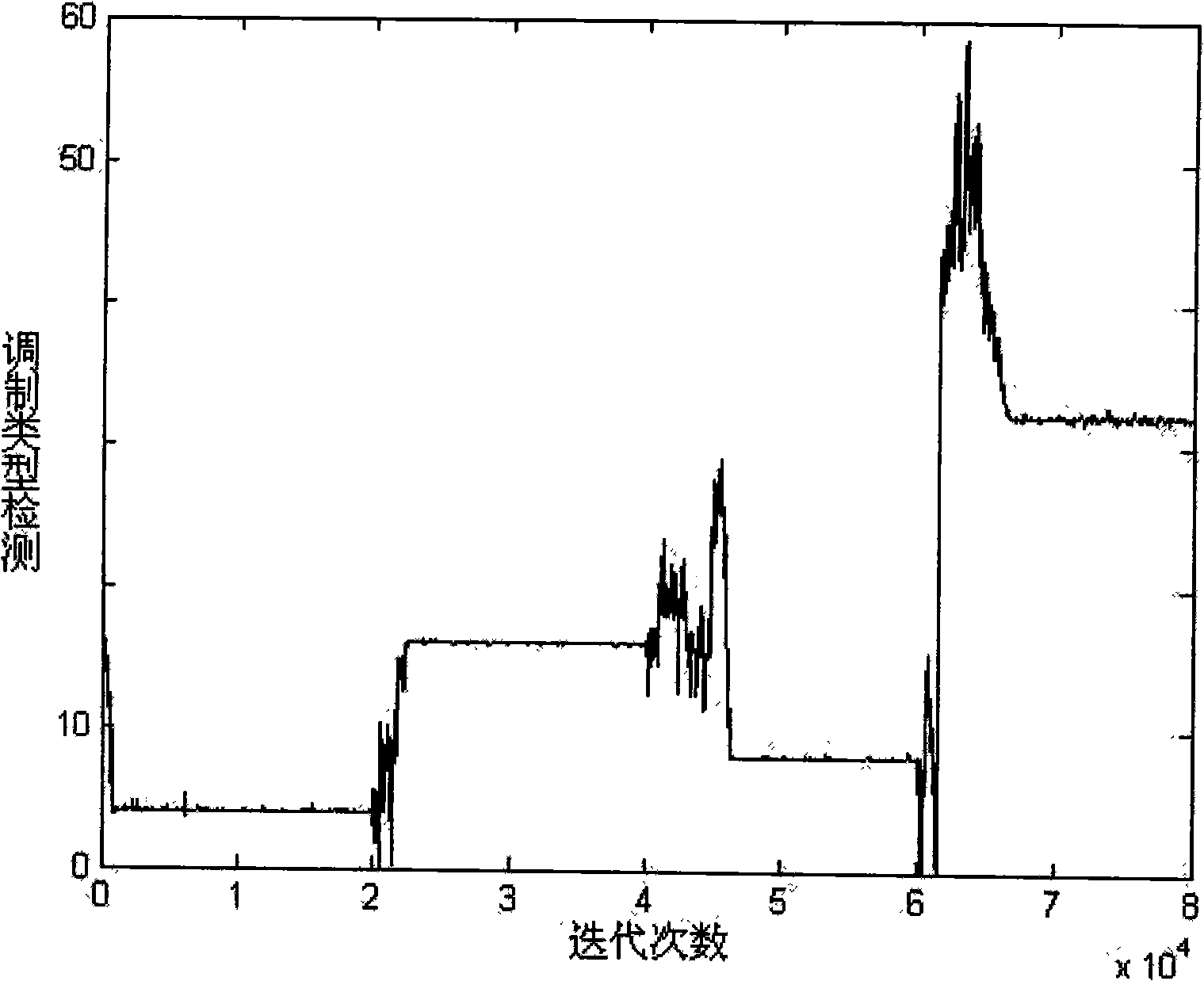
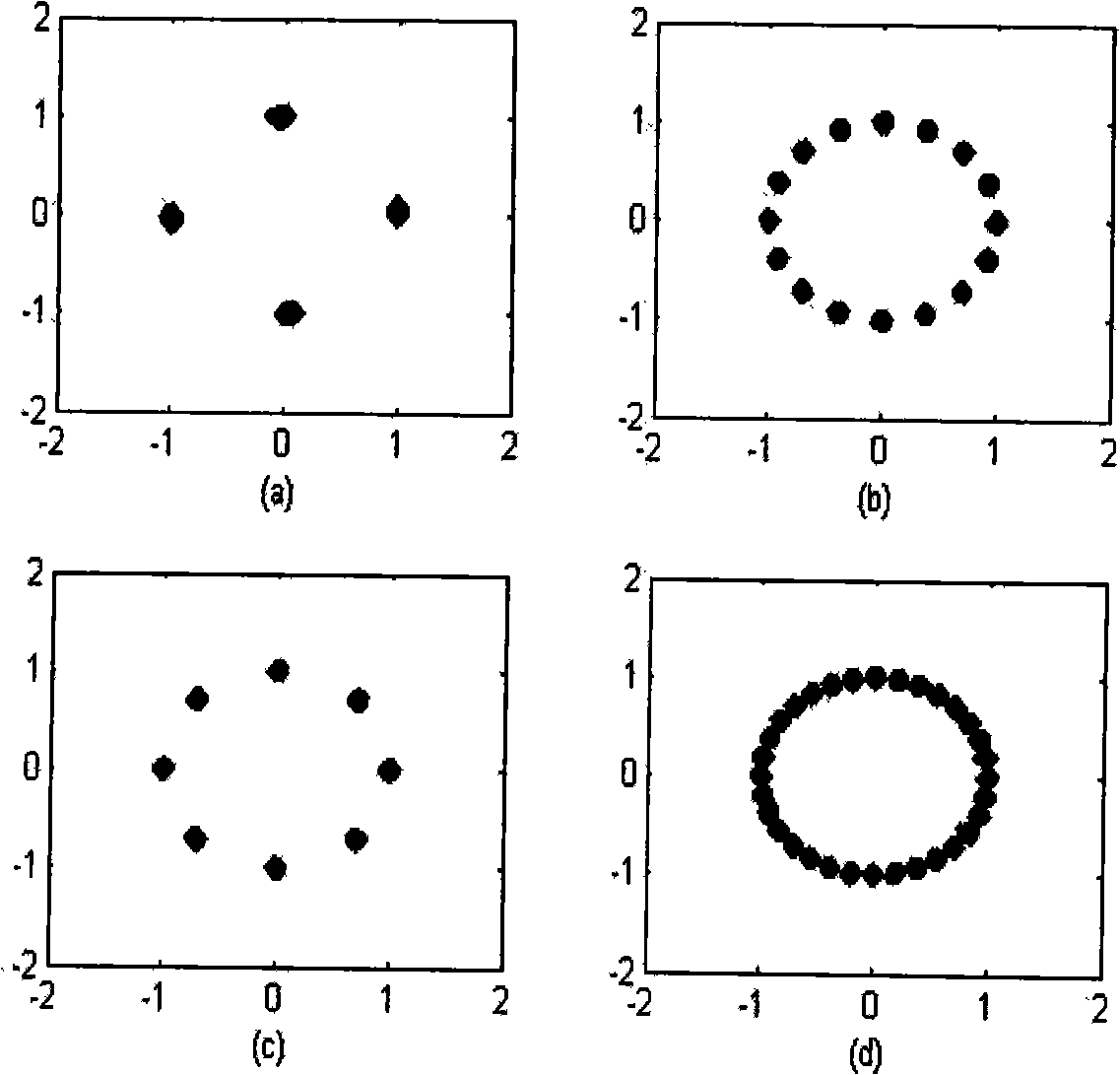
Orthogonal wavelet transform constant modulus blind equalization algorithm based on optimization of DAN genetic algorithm
InactiveCN103888392AFast convergenceExcellent global performanceGenetic modelsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalization algorithmNucleotide
The invention discloses an orthogonal wavelet transform constant modulus blind equalization algorithm based on optimization of the DAN genetic algorithm (DNA-GA-WTCMA). According to the algorithm, the DNA genetic algorithm is combined with the WTCMA and the advantages of the WT-CMA and the advantages of the DNA genetic algorithm are thoroughly utilized. According to the orthogonal wavelet transform constant modulus blind equalization algorithm, a weight vector of the blind equalization algorithm is shown according to a coding method based on a DNA nucleotide chain and interlace operation and mutation operation are conducted on the coded DNA chain to find an optimal individual in a DAN group, the decoded optimal individual serves as an optimal initial weight vector of a blind equalization device, and the shortages that the WTCMA is low in convergence rate, large in mean square error and prone to getting into local minimum are overcome. Compared with the WTCMA and the GA-WTCMA, the DNA-GA-WTCMA is the highest in convergence rate, the smallest in mean square error, globally optimal in performance and high in practical value in the communication technical field.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Constant modular complete blind detection equalizing method for phase modulation signal
InactiveCN101309244AUniqueness guaranteedEliminate Phase Offset IssuesPhase-modulated carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDifferential phaseBlind equalization algorithm
Disclosed is a phase modulation signal constant modulus full-blind detection equalization method which is a solution in the MPSK (multiple phase shift keying) modulation system that the receiver end adopts the CMA (constant modulus algorithm) to process the full-blind equalization; the full-blind detection equalization method mainly solves the problem that in the MPSK modulation system, the phase ambiguity exists in the signal which is equalized by the receiver end through the CMA; in the full-blind environment, the CMA is adopted to trace and detect the modulation mode of the MPSK. The full-blind detection equalization method extracts the difference phase information of the common constant modulus output signal and uses the trigonometric function relation to process self-adopting towards the detection phase modulation mode; meanwhile, the detected phase modulation mode is substituted in the improved constant modulus equalizer so that the common phase deviation problem in the blind equalization algorithm is further eliminated; with the aim of eliminating the error periodically caused by the trigonometric function, the full-blind detection equalization method adds restrictive conditions to the trigonometric function so that the uniqueness of the detection of the phase modulation mode is guaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
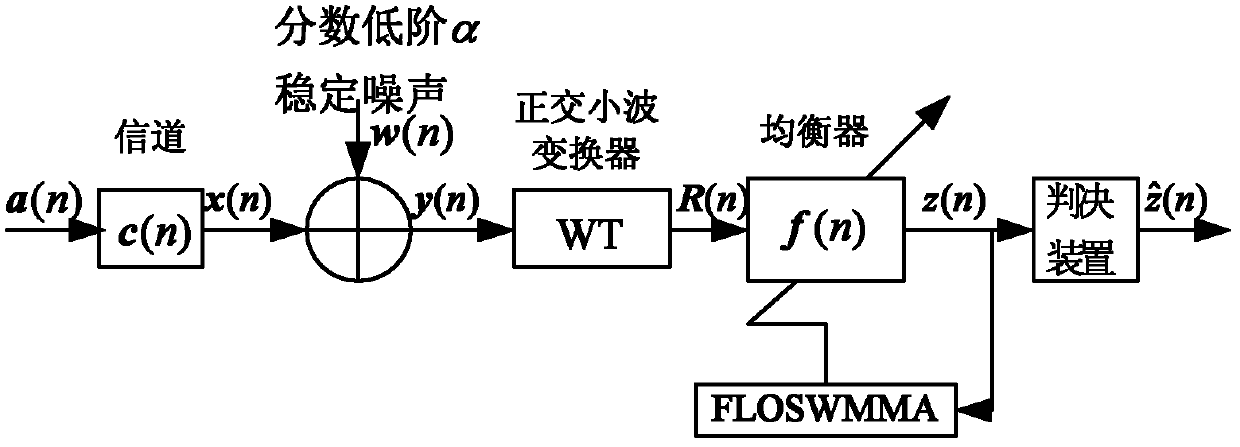
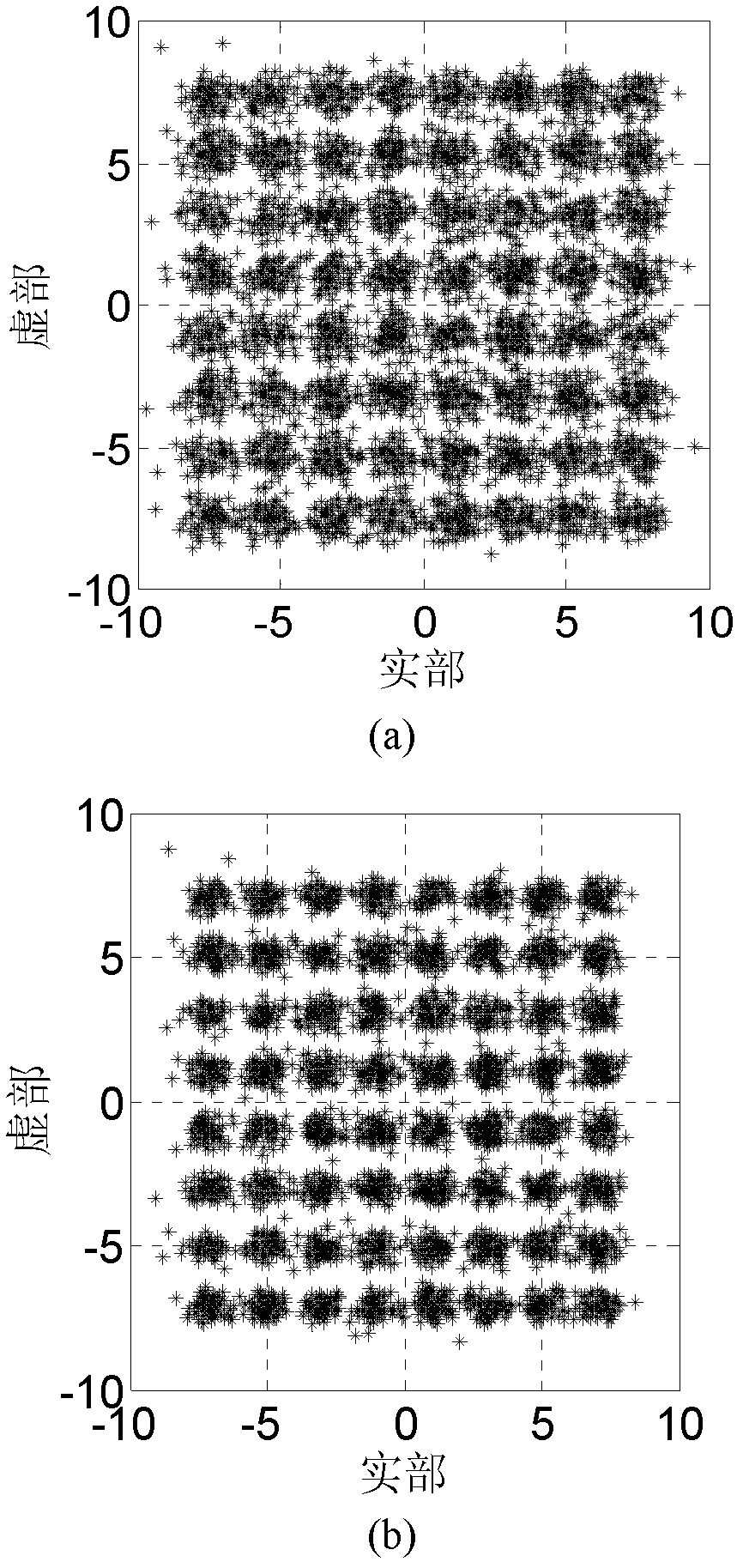
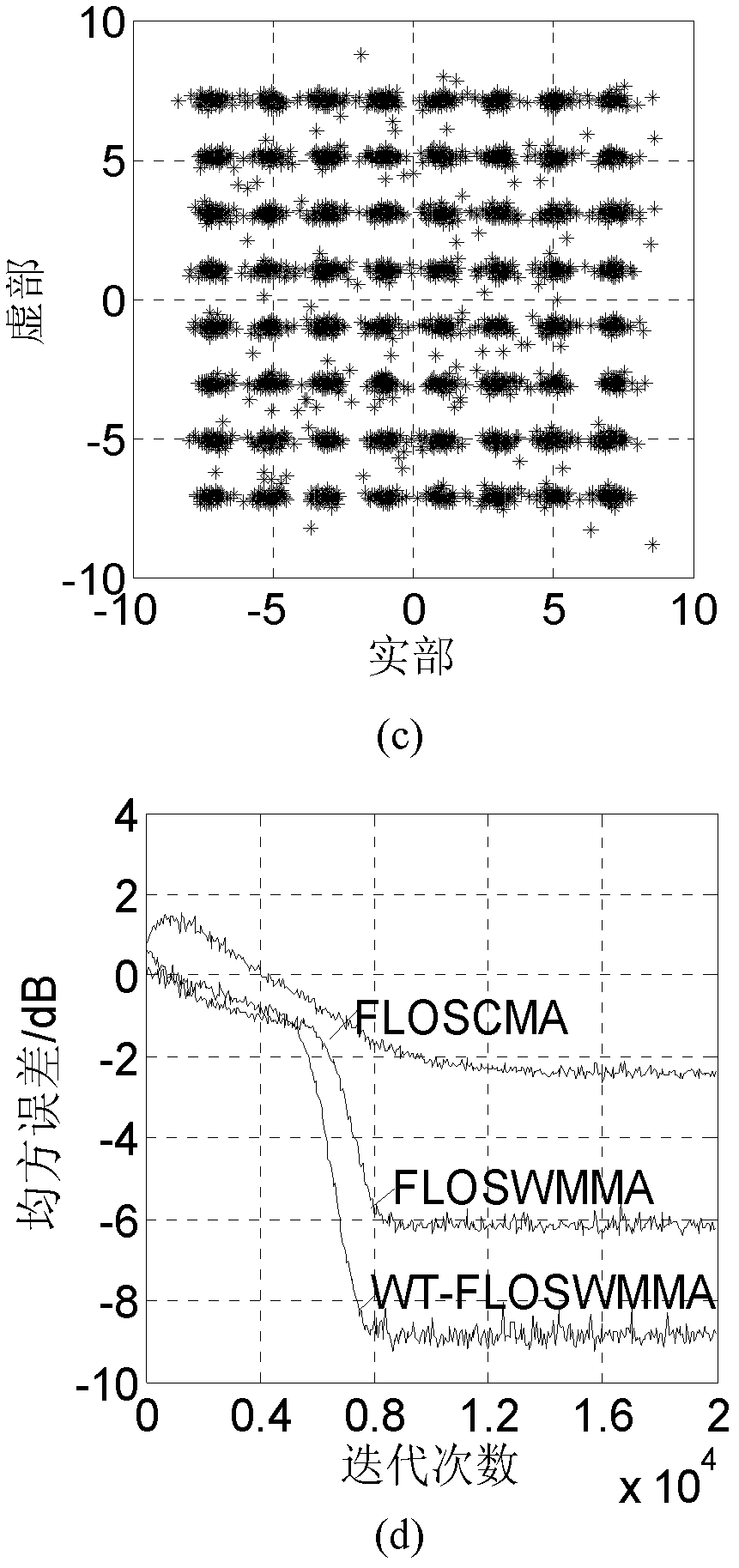
Wavelet weighted multi-modulus blind equalization algorithm based on fractional lower order statistics (WT-FLOSWMMA)
InactiveCN102355435AReduce autocorrelationDecreased convergenceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMultiple carrier systemsBlind equalization algorithmAlgorithm
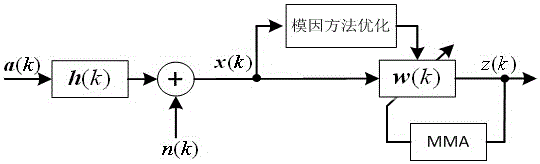
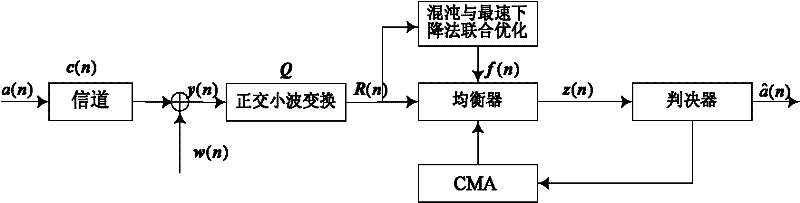
The invention discloses a wavelet weighted multi-modulus blind equalization algorithm based on fractional lower order statistics (WT-FLOSWMMA), which comprises the following steps of: obtaining a channel output vector x(n) from a transmitted signal a(n) through a pulse response channel c(n); obtaining an input signal y(n) of an orthogonal wavelet transformer (WT) by using [alpha] stable distribution channel noise w(n) and the channel output vector x(n); and processing y(n) by the orthogonal WT to obtain the input R(n) of an equalizer f(n), wherein the output of the equalizer f(n) is z(n), and meantime the WT-FLOSWMMA error and the iterative formula of a weight vector are as shown in the specification. In the invention, the [alpha] stable noise is suppressed by use of the fractional lower order statistics, the prior information of the signal source is sufficiently used, and the modulus is corrected adaptively in the iteration process; and moreover, orthogonal wavelet transformation is performed on the input signal of the equalizer, self correlation of the input signal is recued, and the equalizing performance is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Multi-modulus blind equalization algorithm (MMA) optimized by Memetic algorithm (MA)
ActiveCN105007246ASlow convergenceFast convergenceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMemetic algorithmBlind equalization algorithm
The invention discloses a multi-modulus blind equalization algorithm (MMA) optimized by a Memetic algorithm (MA). The concepts of individual evolution, social behaviors among individuals and the like are introduced into a blind equalization technology; the reciprocal of an MMA cost function is defined as a fitness function of the MA; individual optimal vectors are searched in a global scope by means of the population optimization mechanism and local area deep-searching capability of the MA and are taken as the initial optimization weight vectors of the MMA. Iteration is performed through the MMA to obtain an optimal weight vector of the MMA. Compared with a constant modulus blind equalization algorithm (CMA), the MMA and a genetic algorithm-based multi-modulus blind equalization algorithm (GA-MMA), the algorithm disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high convergence speed during equalization of high-order multi-modulus signals, smallest steady-state errors and clearest output signal constellation map.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
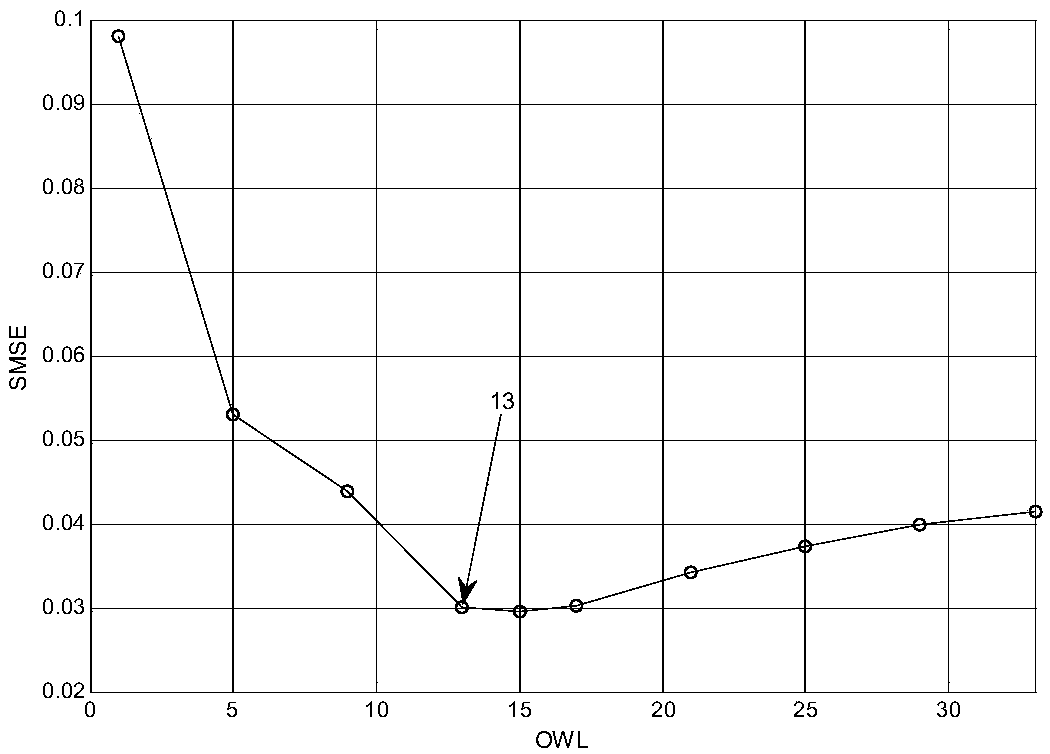
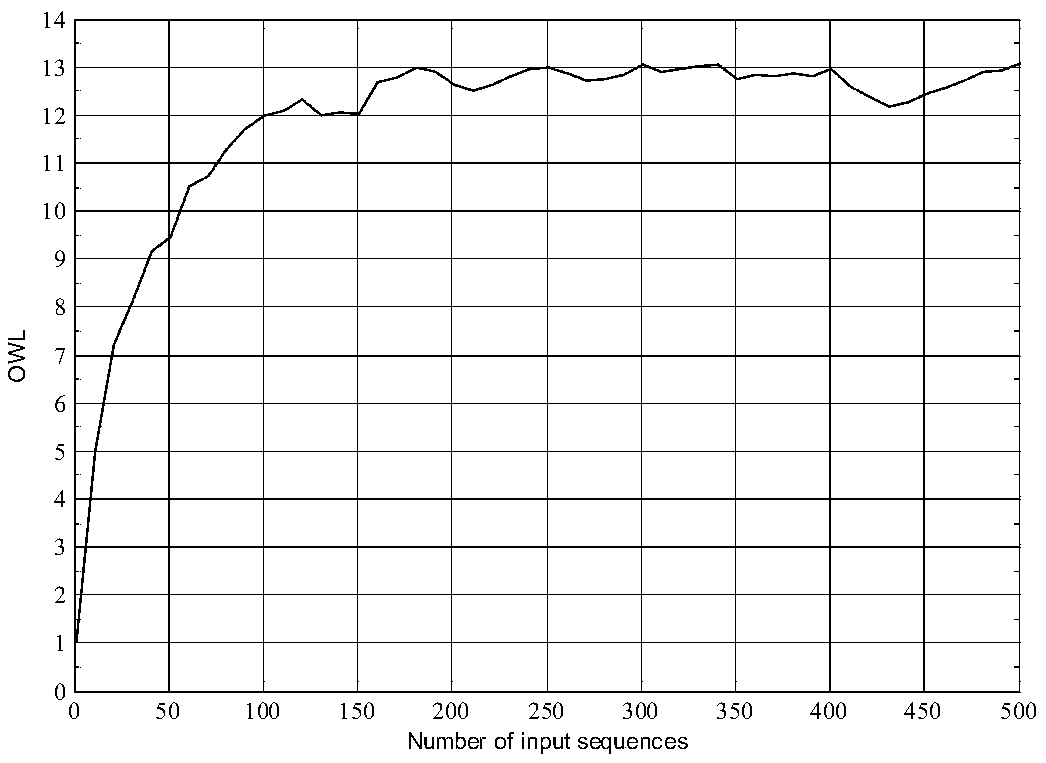
Blind equalization detector with adjustable observation window length applied to underwater acoustic communication
ActiveCN108696466AImprove transmission efficiencySonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalization algorithmSelf adaptive
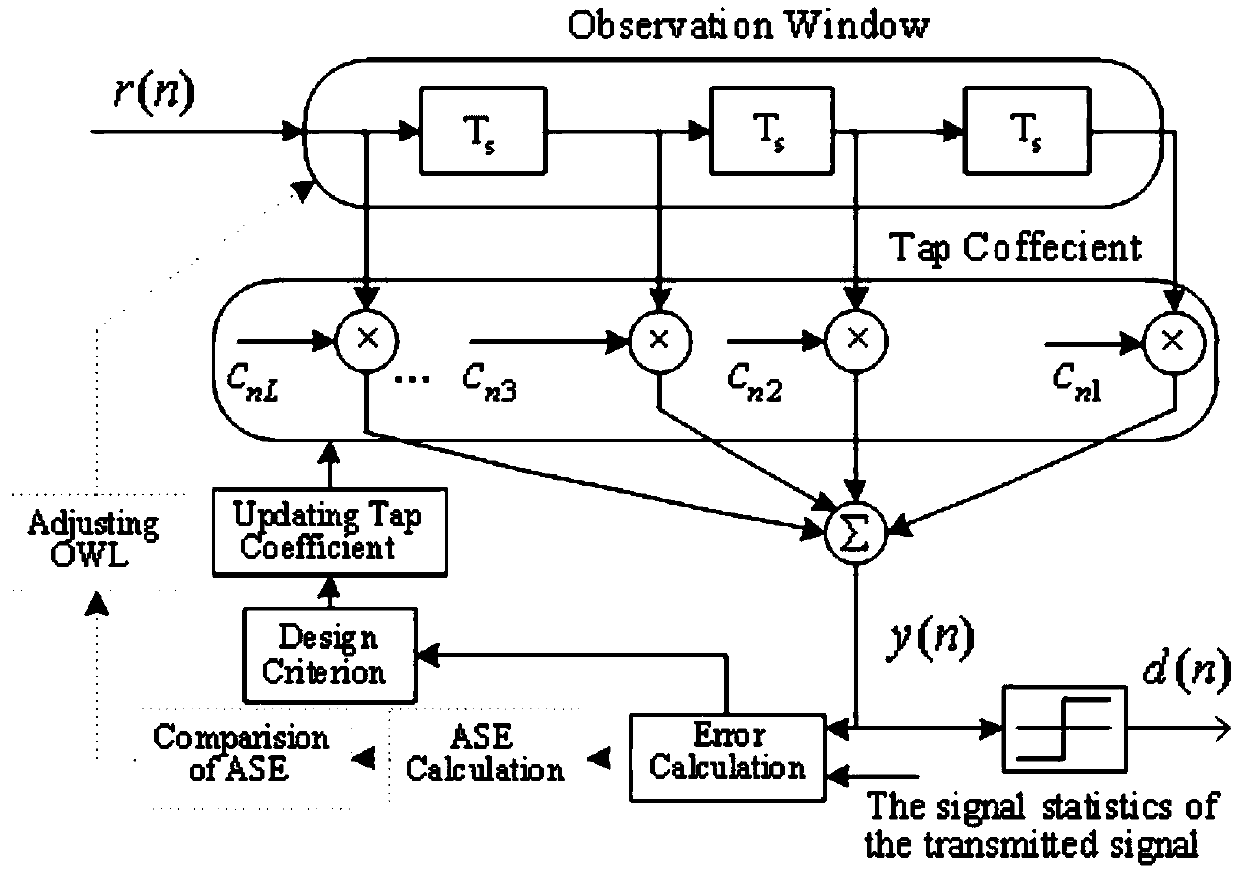
The invention relates to the technical field of underwater acoustic communication, and in particular relates to a blind equalization detector with an adjustable observation window length (OWL) appliedto underwater acoustic communication, which can adaptively adjust the length of an observation window according to specific underwater acoustic channel envelope. Compared with the prior art, the blind equalization detector can adaptively adjust the OWL according to the specific underwater acoustic channel; in addition, the detector provided by the invention is achieved based on a blind equalization algorithm without a training sequence, so that the transmission efficiency can be improved, and the blind equalization detector is more applicable to the actual underwater acoustic communication system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Blind equalization algorithms for adaptive polarization recovery and PMD compensation
ActiveUS8320778B2Electromagnetic receiversOptical transmissionCommunications systemBlind equalization algorithm
A device and method are disclosed for blind equalization of an optical signal to implement adaptive polarization recovery, Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) compensation, and residual Chromatic Dispersion (CD) compensation in a digital coherent optical communication system.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
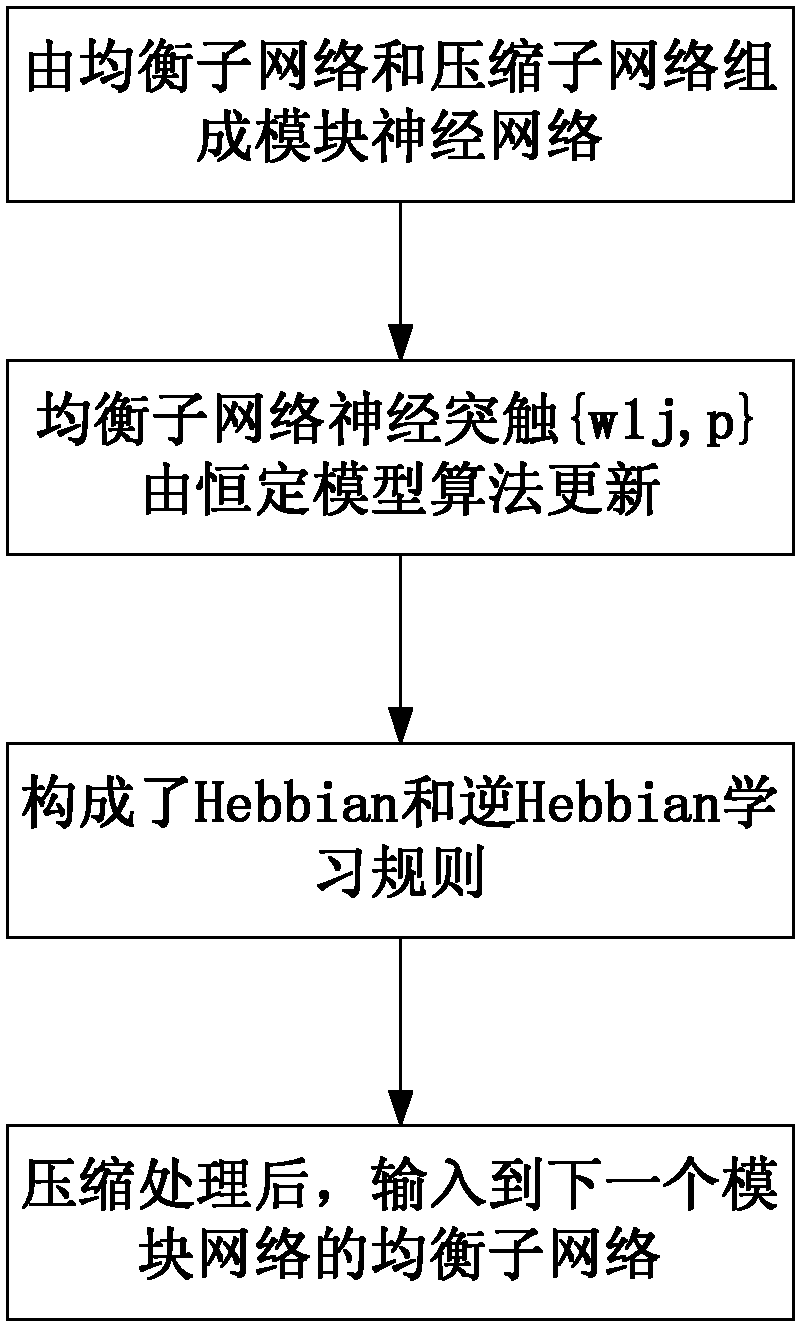
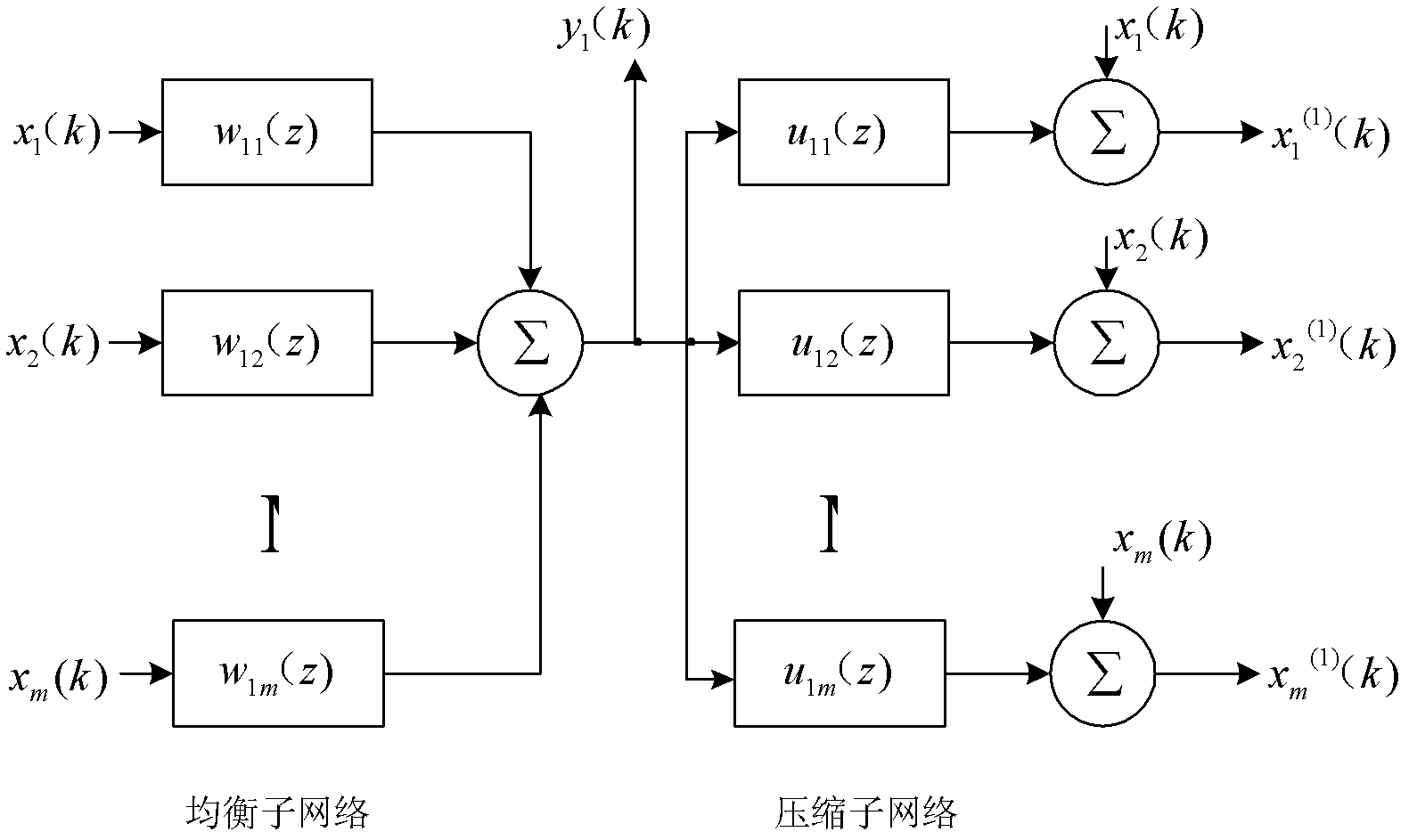
Method for multi-channel blind deconvolution on cascaded neural network
InactiveCN102546128AEasy extractionSimple methodTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError prevention/detection by diversity receptionSynapseBlind equalization algorithm
The invention provides a method for multi-channel blind deconvolution on a cascaded neural network. The method comprises the following steps: (1) forming a module neural network by a balanced sub-network and a compressed sub-network; (2) updating a nerve synapse {wlj,p} of the balanced sub-network by using a constant model algorithm; (3) constituting Hebbian and inverse Hebbian learning rules; and (4) after compression, inputting to the balanced sub-network of a next module network. The method disclosed by the invention is an expansion of a method which is novel, simple and individually effective, and can be used for effectively extracting a plurality of source signals online from unknown and staggered mixed signals, namely each module of the cascaded neural network is composed of the balanced sub-network and the compressed sub-network. The method disclosed by the invention can be applicable to any blind equalization algorithm (an extension of signal channel equalization) and further can be applied to a condition that the quantity of the source signals is unknown in advance. The method disclosed by the invention is easy to realize and can be widely applied to aspects of wireless communication, array processing, biomedical signal processing and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG BAIYUN UNIV
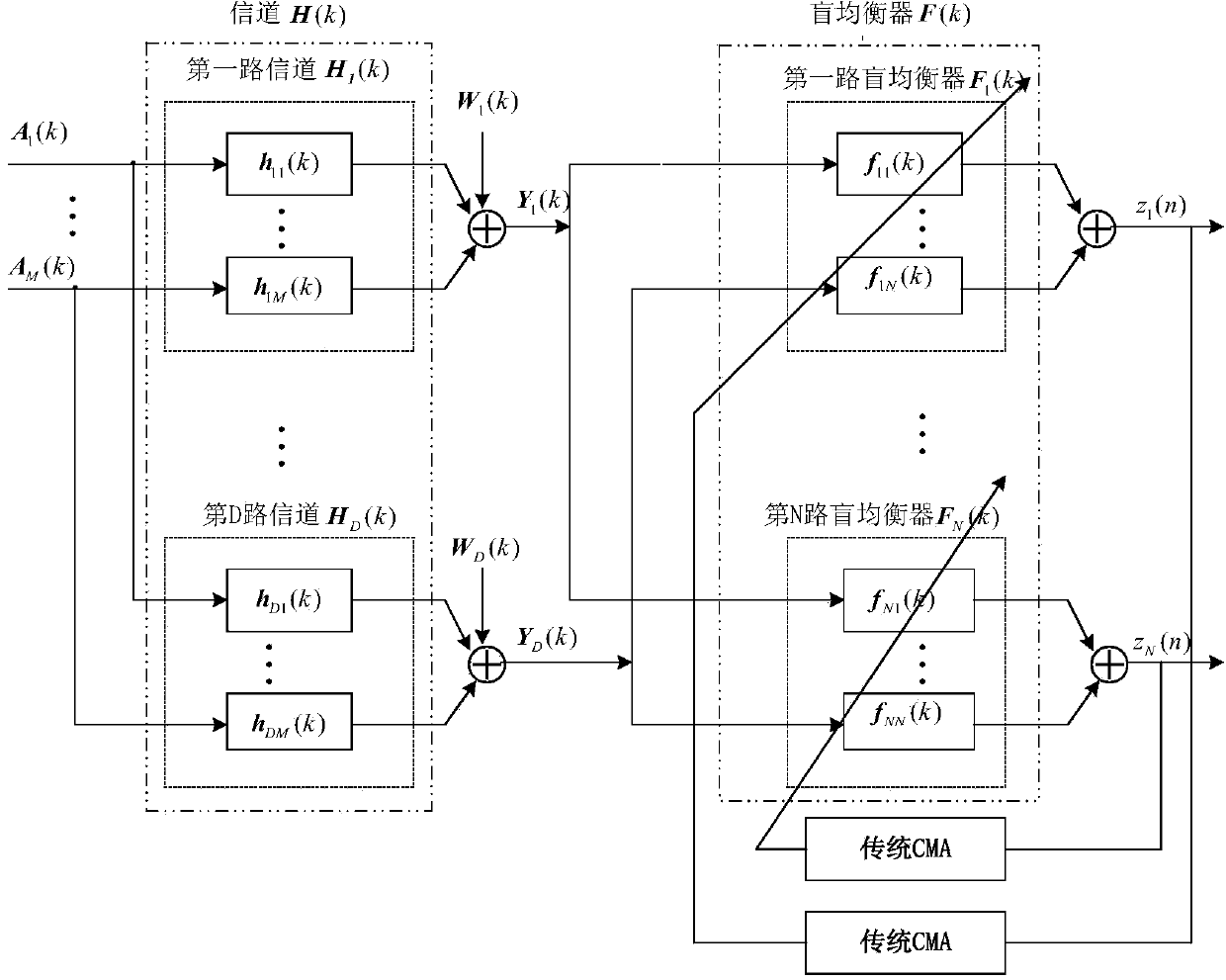
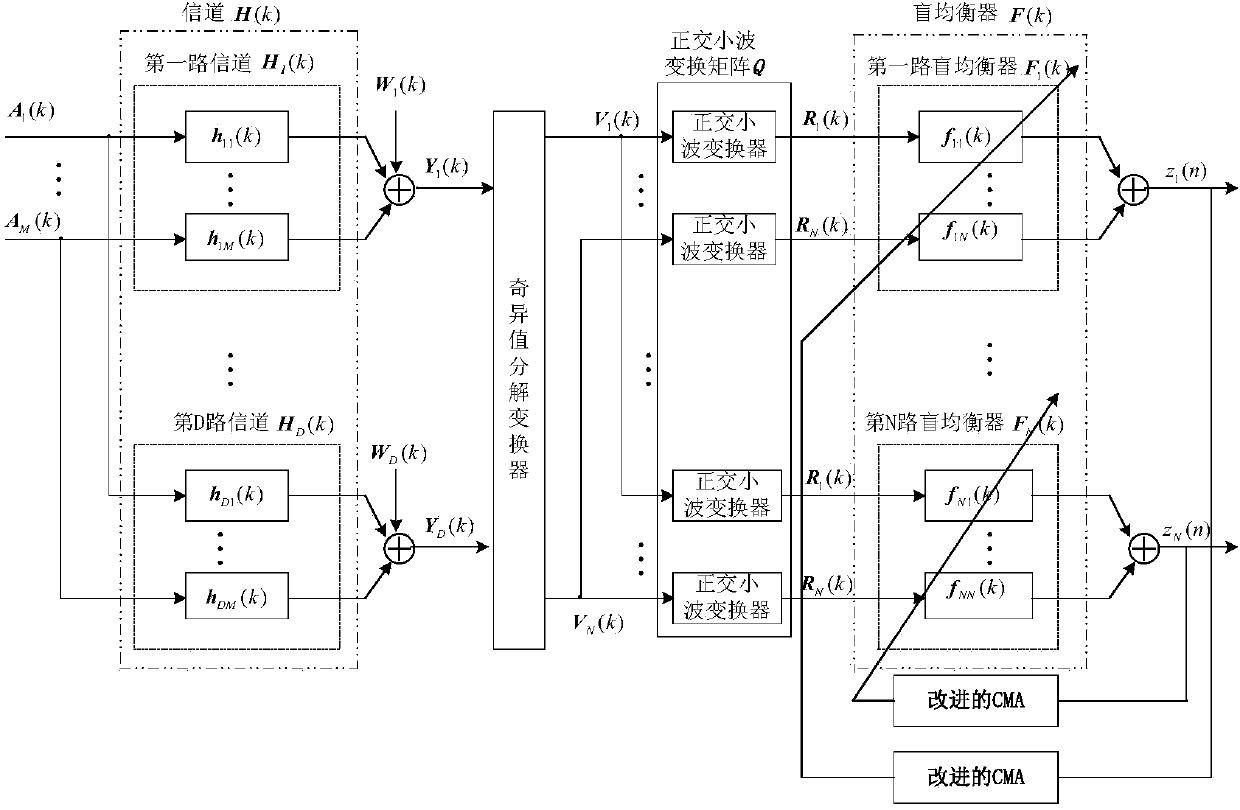
Wavelet constant modulus blind equalization method in MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system
ActiveCN103825851AReduce correlationReduce autocorrelationSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSingular value decompositionBlind equalization algorithm
The invention discloses a wavelet constant modulus blind equalization method in a MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system from the aspect of reducing?inter channel?and inter signal?correlation, so as to overcome defects that the traditional constant modulus blind equalization method in the MIMO system is weak in inter channel interference inhibition ability, slow in the convergence rate and large in steady-state errors. According to the method, singular value decomposition is used for reducing the correlation of channel output signals; an orthogonal wavelet base function is used for carrying out orthogonal wavelet transformation on MIMO channel output signals and autocorrelation of input signals of a blind equalizer is reduced; on the basis of fully considering the inter channel correlation, a cost function of MIMO system constant modulus blind equalization algorithm is redefined, and cross-correlation of output signals of the blind equalizer is reduced; and a variable step size function is used for controlling a blind equalization?weight vector?updating process, the convergence rate quickened, and the steady-state errors are reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
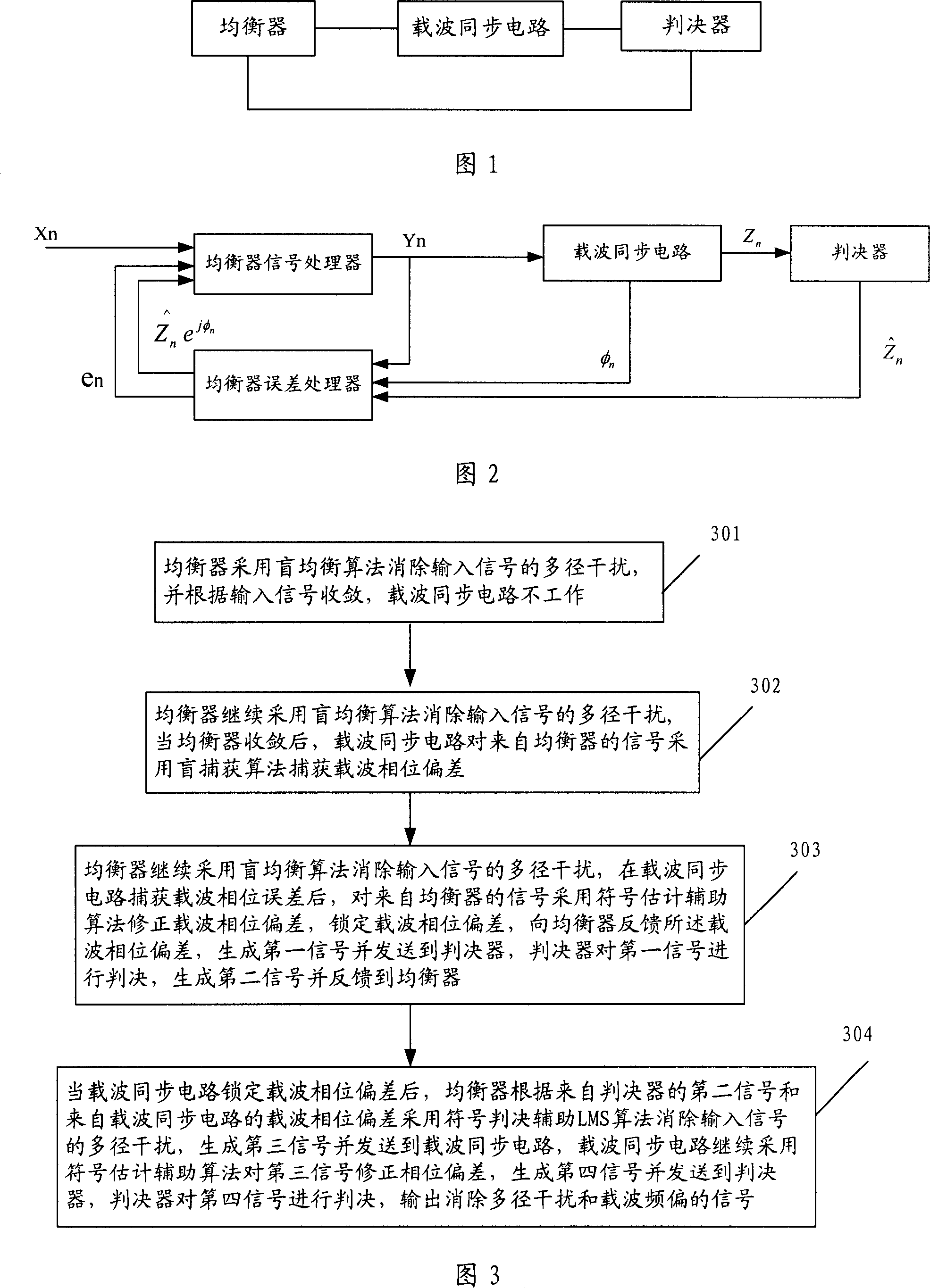
A method and system for elimination of the multi-path interference and carry frequency deviation
ActiveCN1996976AEliminate multipath interference signalsReduce bit error rateTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalization algorithmMultipath interference
This invention discloses one method to delete multi-radium interference load wave bias frequency, which comprises the following steps: a, even device adopts blind even formula method to remove input signal of its interference data for collecting signals; b, after getting even part to capture formula load wave phase bias by use of blind formula; c, after capturing load wave phase bias, using character estimation aid formula to locking load wave phase bias; d, after locking, even part adopts characters to judge aid LMS formula to delete input signal multi-radium interference.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
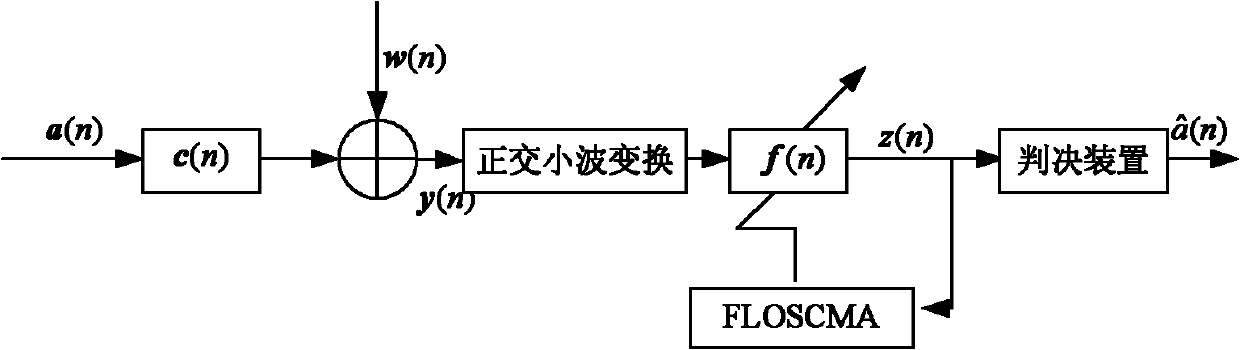
WT-FLOSCMA (Orthogonal Wavelet Transform and Fraction Lower Order Statistics Based Constant Modulus Algorithm)
InactiveCN102223329AFast convergencePoor environmental adaptabilityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMean squareBlind equalization algorithm
The invention discloses a WT-FLOSCMA (Orthogonal Wavelet Transform and Fraction Lower Order Statistics Based Constant Modulus Algorithm), which comprises the following steps that a transmitting signal a (n) passes through an impulse response channel c (n) to obtain a channel output vector x (n); stable distributed alpha channel noise w (n) and the channel output vector x (n) are adopted to obtain an input signal y (n) of an orthogonal wavelet transformer (WT); after the input signal y (n) of a balancer is subject to orthogonal wavelet transformation, the input of the balancer is R (n), and the output of the balancer is z (n); and at the moment, a mean-square error of the WT-FLOSCMA is e(n) equals to / z(n) / minus Rcm square root (Rcm equals to E { / a(n) / <4>} dividing E { / a(n) / <2>}, and the iterative format of a weight vector is f(n+1) equals to f(n) plus muR <-1>(n) / e (n) / <p-1> sgn (e(n))z (n) R (n) / / z(n) / . In the invention, the fractional lower order statistics is utilized to suppress the stable alpha noise, the weight vector of blind equalization algorithm is optimized according to the minimum dispersion coefficient rule, orthogonal wavelet transformation is carried out on the input signal o the balancer, and the autocorrelation of the input signal of the balancer is reduced to quicken the convergency rate. The water sound channel simulation result shows that the performance of the method disclosed by the invention is obviously superior to that of the constant modulus algorithm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Blind equalization algorithm-based PCM/FM anti-multipath interference telemetry receiving method
InactiveCN106253922ACompensating for Frequency Selective FadingTransmitter/receiver shaping networksPerformance functionBlind equalization algorithm
The present invention relates to an adaptive blind equalization method for PCM / FM telemetry links. According to the method, frequency selective fading caused by multipath channels is compensated, so that ISI (inter-symbol interference) will not be generated on the time domain of PCM (pulse-code modulation) / FM (frequency modulation) signals; analog modulation signals are sampled, so that digital signals can be obtained; and the digital signals are sent to a tap coefficient-adjustable digital filter, so that the frequency selective fading of the channel can be compensated, and influence on PCM / FM constant-mode signals caused by the frequency selective fading of the channel can be eliminated; and the digital FIR filter operates a simple adaptive algorithm through using the gradient search of a performance function.
Owner:HUAIHUA UNIV
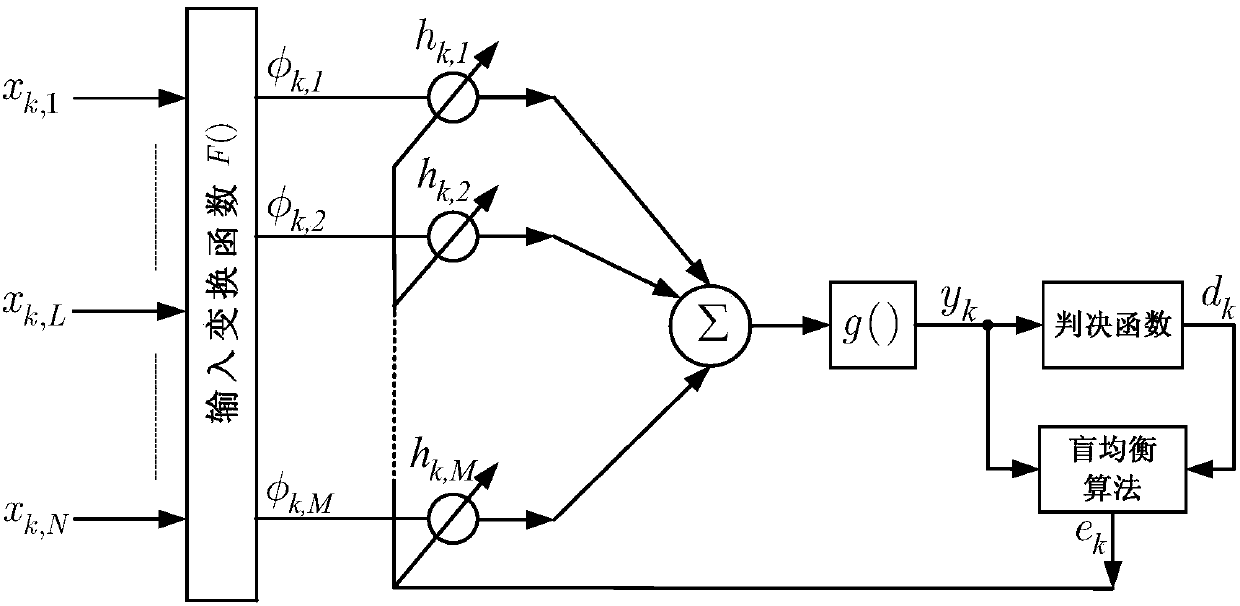
Blind equalization method and blind equalization system
InactiveCN104883330AGuaranteed performanceConvergent and robustTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalization algorithmNetwork structure
The invention provides a blind equalization method and a blind equalization system. The method comprises the following steps of performing input transformation on input signals and generating input vectors after transformation; acquiring output signals through a feedforward network by means of the input vectors after transformation and recursive updating parameters; when desired signals are uncertain, acquiring input decision information through input signals and acquiring output decision information through output signals; designing blind equalization algorithm by using both the input decision information and the output decision information to acquire a feedback error; and updating the recursive updating parameters through the feedback process through the feedback error and the input vectors after transformation. By additionally using the input decision information to assist the feedback process, the method can effectively prevent common local convergence problems generated during blind equalization due to the influence of the feedforward network structure and the recursive updating parameters. Robust convergence of blind equalization results is guaranteed. Meanwhile, the blind equalization performance is also ensured.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
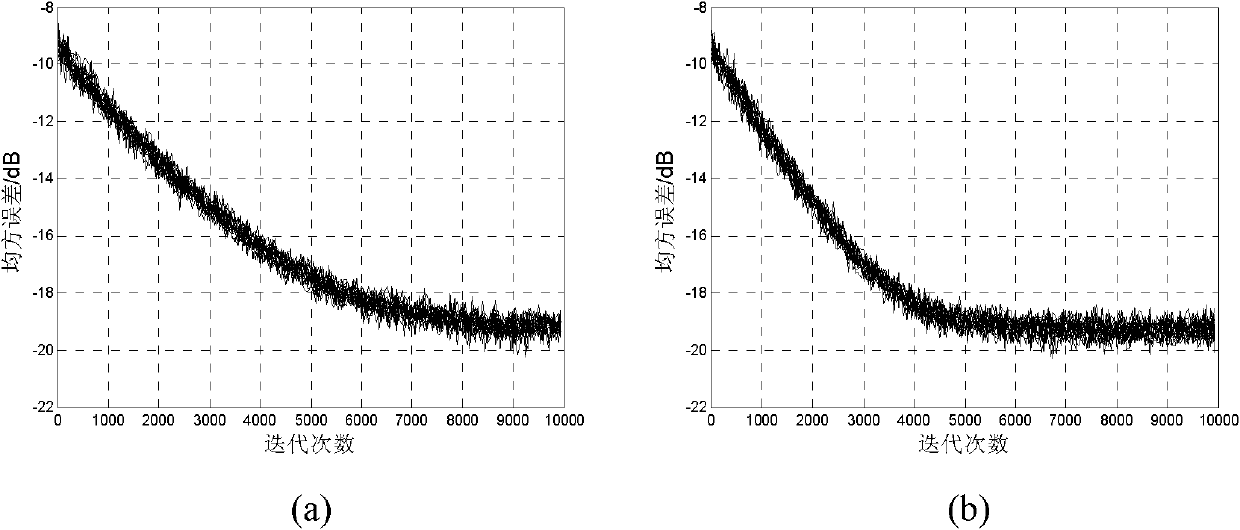
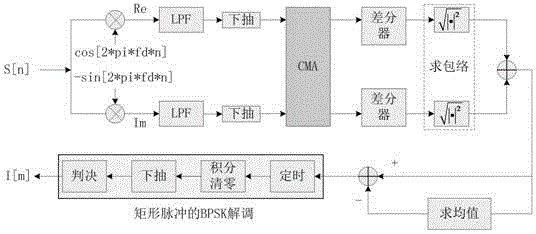
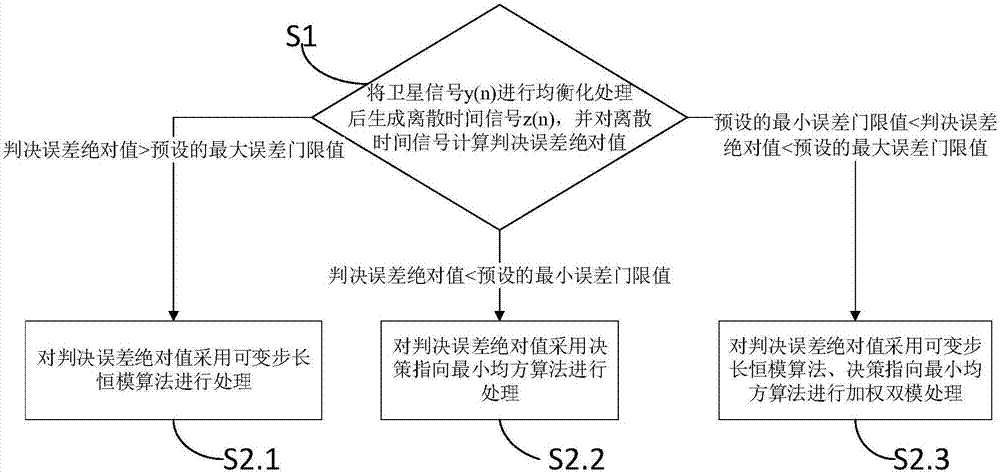
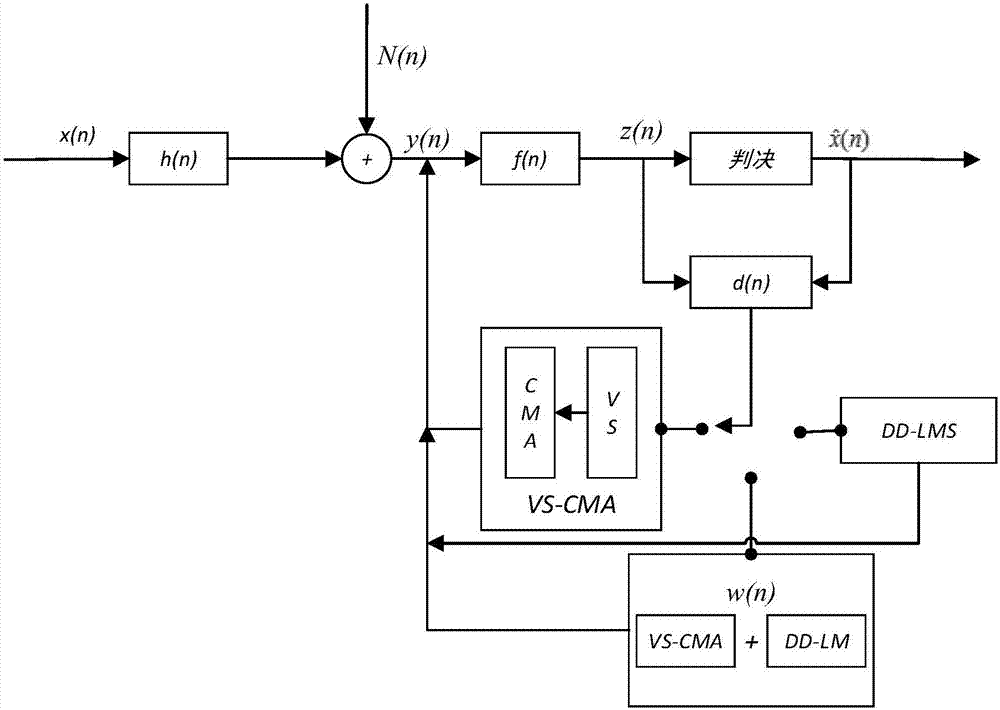
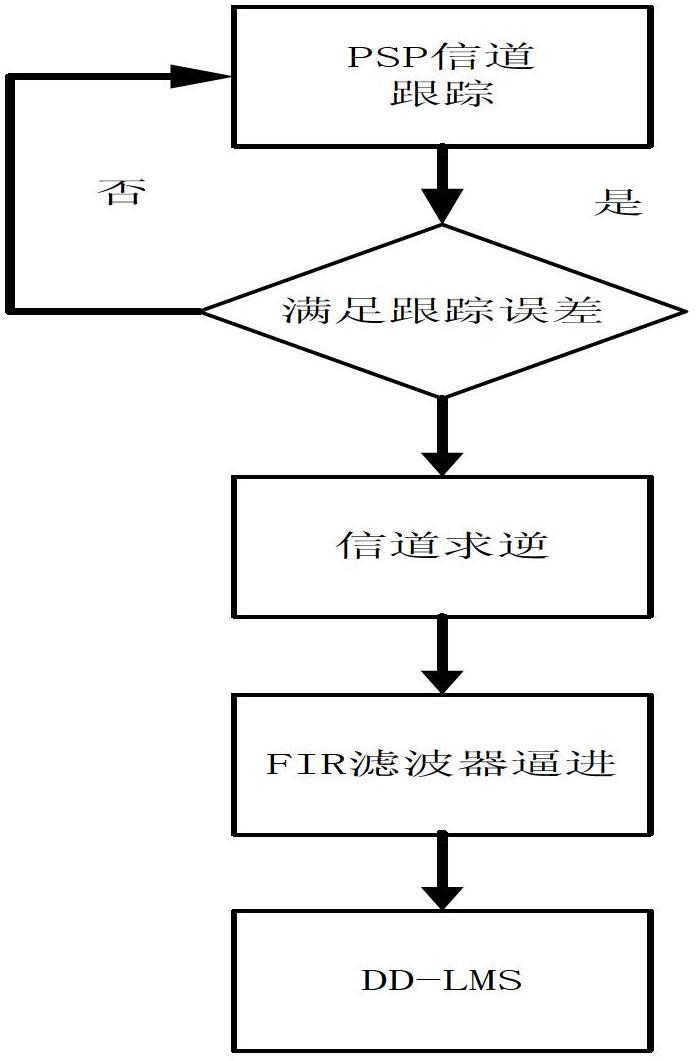
Satellite channel multi-mode blind equalization algorithm
InactiveCN106878211AReduce distractionsAchieve traceabilityRadio transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalization algorithmDiscrete-time signal
The invention discloses a satellite channel multi-mode blind equalization algorithm, and the algorithm comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the equalization of a satellite signal, generating a discrete time signal, and calculating a judgment error absolute value of the discrete time signal; secondly processing the judgment error absolute value through employing a VS-CMA algorithm when the judgment error absolute value is greater than a preset maximum judgment error threshold value; thirdly carrying out the processing of the judgment error absolute value through employing a DD-LMS algorithm when the judgment error absolute value is less than a preset minimum judgment error threshold value; finally carrying out the processing of the judgment error absolute value through employing the VS-CMA algorithm and the DD-LMS algorithm when the judgment error absolute value is greater than the preset minimum judgment error threshold value and less than the preset maximum judgment error threshold value. The method introduces a nonlinear residual error function to control the step of the CMA algorithm, so as to achieve the variable-step CMA algorithm. The method provided by the invention is smaller in residual error, is higher in convergence speed, enables intersymbol interference to be smaller, and is strong in tracking capability of time-variable channel.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Blind equalization algorithm for burst signal
InactiveCN102685048AReduce complexityGuaranteed real-time processing performanceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMean squareBlind equalization algorithm
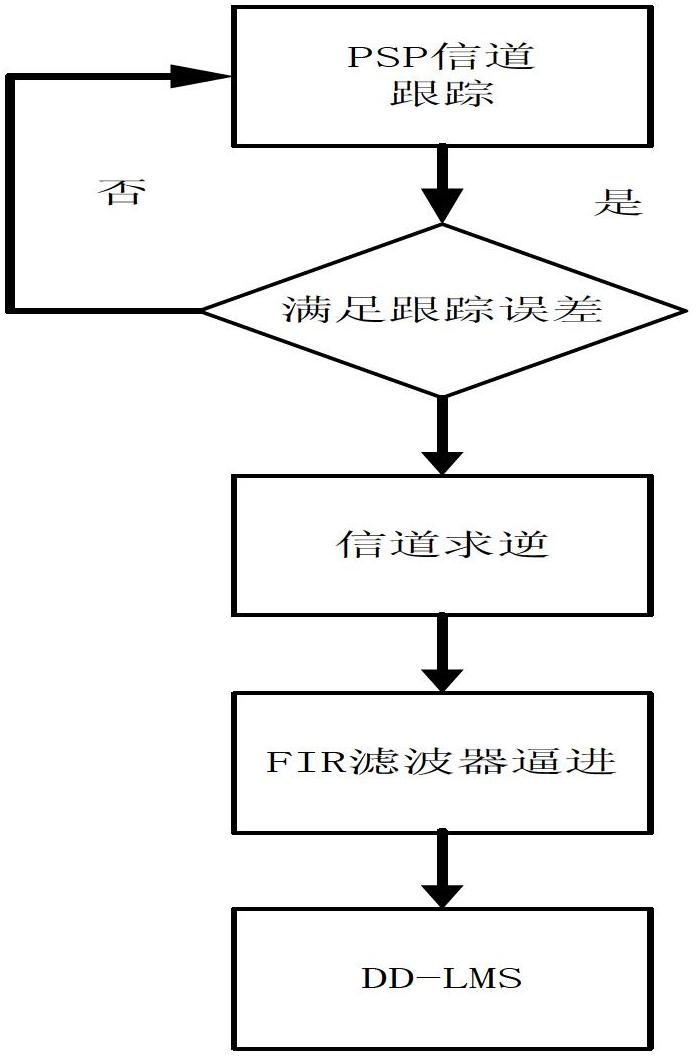
The invention discloses a blind equalization method for a burst signal. The blind equalization method comprises the following steps of: first performing rapid channel estimation on a wireless channel by adopting a per-survivor sequence algorithm to obtain a forward estimated channel parameter; then decomposing the forward estimated channel parameter into a system consisting of a minimum phase system and a maximum phase system, which are connected in series, when the mean square error of the forward estimated channel parameter is less than 0.05 and the forward estimated channel parameter is not a minimum phase, and inverting the minimum phase system and the maximum phase system respectively to obtain a linear equalizer initialization coefficient; and finally substituting the linear equalizer initialization coefficient into a decision directed minimum mean square error algorithm to realize rapid blind equalization. According to the blind equalization algorithm for the burst signal, the rapid blind equalization of the burst signal is realized, the complexity of the algorithm is lowered, and the real-time processing performance of the algorithm is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
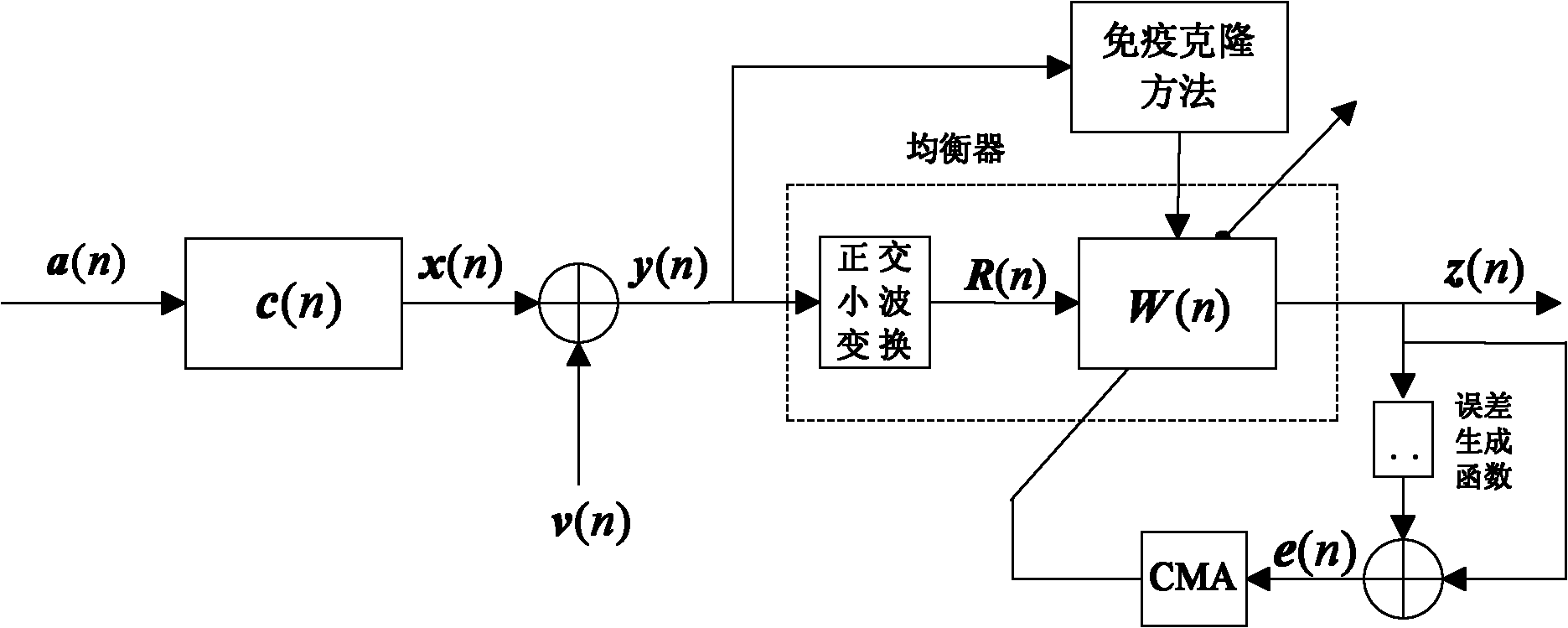
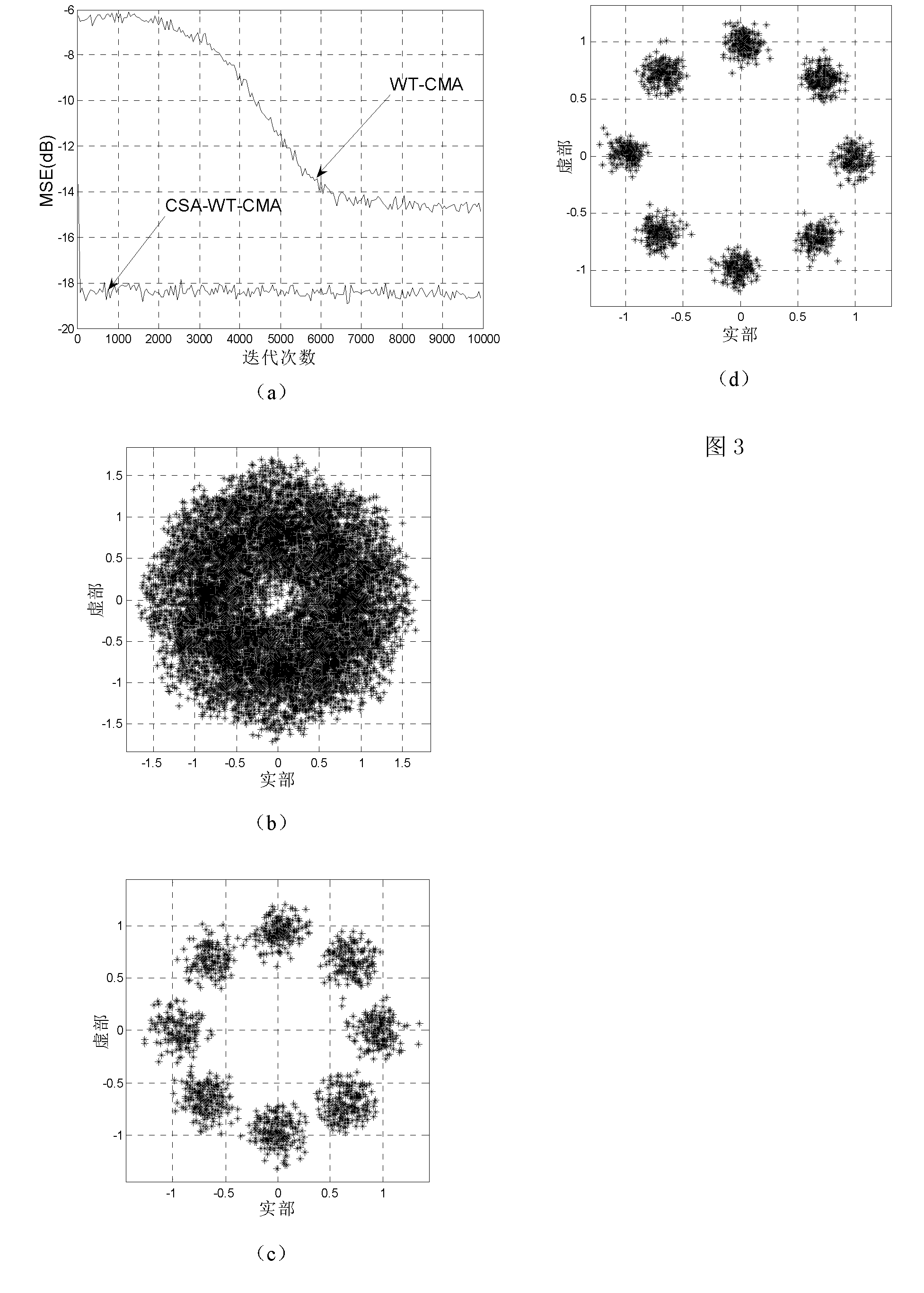
Rapidly-convergent immune-clone-based orthogonal wavelet transform constant modulus blind equalization algorithm
InactiveCN102185808AFast convergenceSmall steady state errorTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalization algorithmImmune clonal selection algorithm
The invention discloses a rapidly-convergent immune-clone-based orthogonal wavelet transform constant modulus blind equalization algorithm, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: initializing a population; calculating an affinity value; performing clonal selection; implementing a king-crossover method; performing high frequency variation; calculating the affinity value; performing selection; judging whether to perform termination or not; and selecting an optimal weight vector individual. In the invention, an immune clonal selection algorithm is introduced into an orthogonal wavelet transform based constant modulus blind equalization algorithm (WT-CMA), the characteristics of multi-modal function optimization of a clonal selection method are utilized, weight vectors of an equalizer serve as antibodies, and the autocorrelation of signals is reduced by adopting orthogonal wavelet transform. Compared with the WT-CMA, the algorithm provided by the invention is high in the rate of convergence and relatively lower in steady state error.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Coherent light communication equalization method by using intersection mixed state
ActiveCN108521385AAchieving Signal ConvergenceHigh Speed Polarization TrackingTransmitter/receiver shaping networksElectromagnetic receiversRound complexityBlind equalization algorithm
The invention relates to the technical field of communications and particularly relates to a coherent light communication equalization method by using an intersection mixed state. The method is basedon an iterative least square method and comprises the following steps: mixing two paths of signals received by a receiving end of a filter into one path of signals by intersection; filtering the signals by the filter to obtain an output value; taking a point on a circle formed by rotating an ideal constellation point and nearest to the output value on a constellation diagram as a judgment value; taking a difference between the judgment value and the output value as an error coefficient to add to an update process of the iterative least square method; and enabling an updated system state to enter next iteration. According to the coherent light communication equalization method, effective equalization can be performed on signals affected by SOP effect in a coherent light communication transmission process; compared with a blind equalization algorithm, the coherent light communication equalization method can track a higher RSOP and has a quicker convergent speed; and meanwhile, compared with Kalman filtering, the coherent light communication equalization method has lower complexity and calculated amount, and the signals do not need to be decomposed into a real part and an imaginary part to input. Therefore, the coherent light communication equalization method is applied to each order of PSK and QAM PDM signals.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
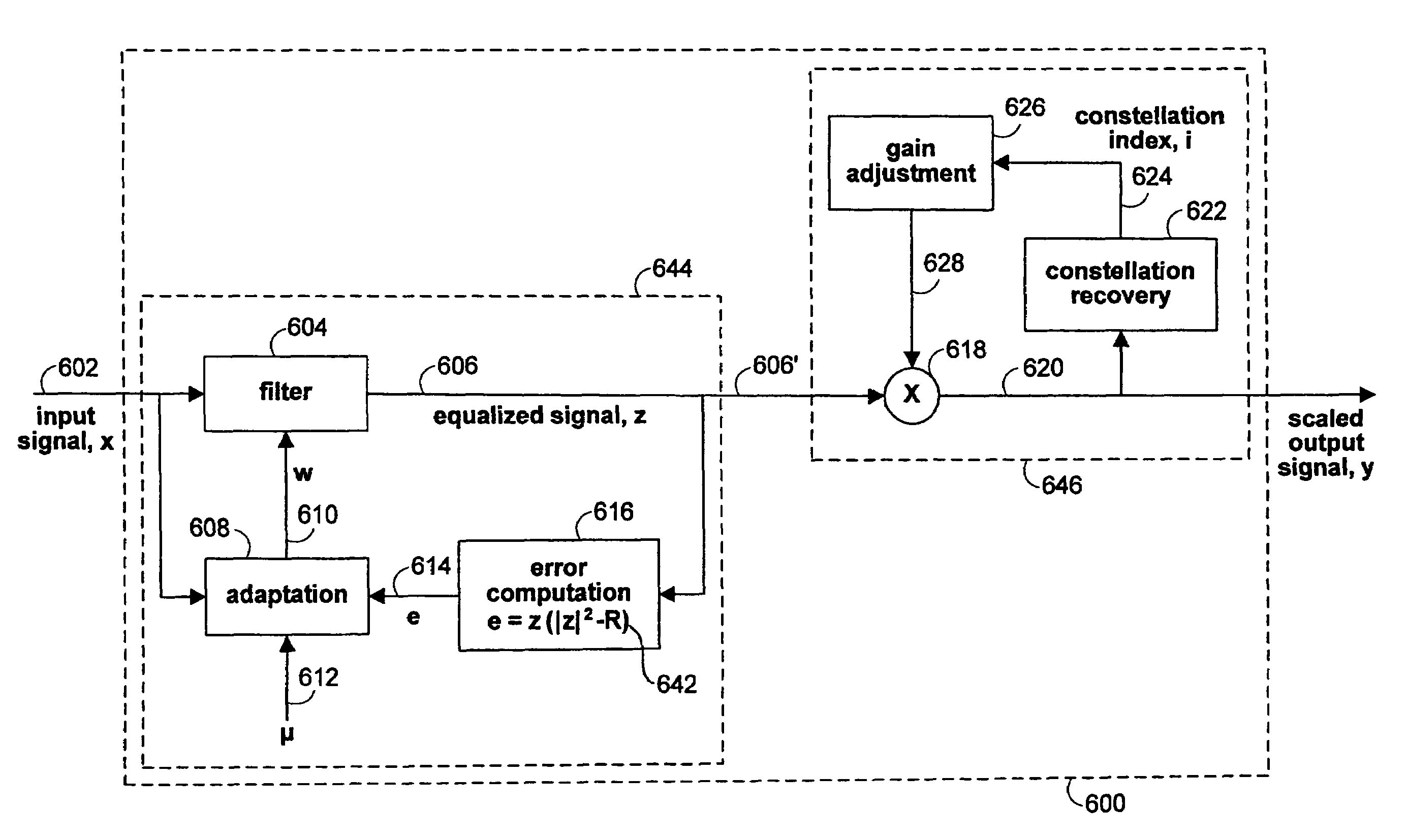
Efficient blind equalization for quadrature amplitude modulation
InactiveUS7688885B1Effectively equalizedEnsure correct executionMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsQuadrature modulationBlind equalization algorithm
Methods and apparatus are provided for receiving a signal transmitted with a quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) constellation. In an embodiment of the invention, a blind equalization algorithm can be performed to equalize the signal, and a constellation recovery algorithm can be performed to identify a constellation index corresponding to the QAM constellation. The blind equalization algorithm can be altered based on the identified constellation index. The invention advantageously allows for relatively efficient and relatively reliable equalization of signals transmitted with an unknown QAM constellation.
Owner:MARVELL INT LTD
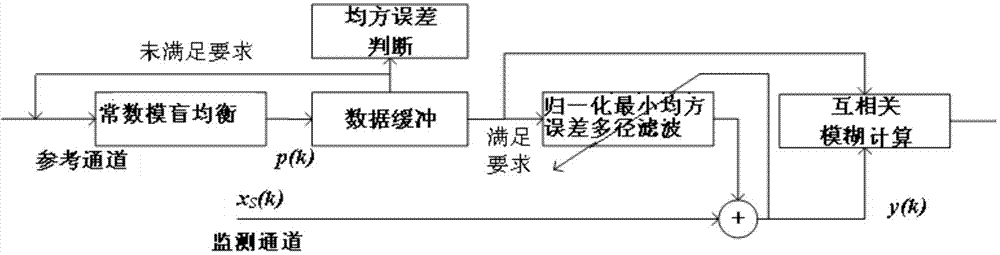
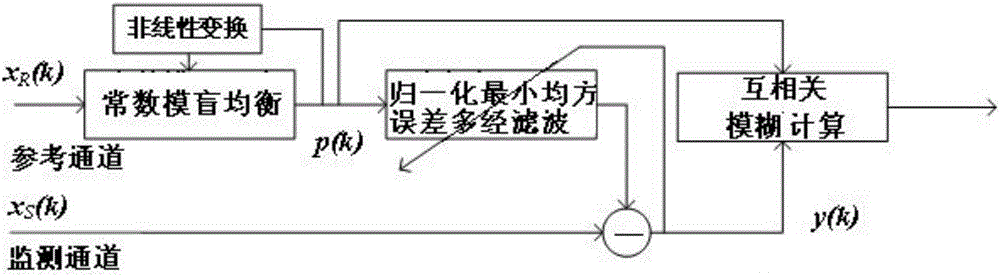
Passive bistatic radar signal processing method based on blind equalization of cyclic constant modulus
InactiveCN104749562AFast convergenceImprove Adaptive Convergence PerformanceWave based measurement systemsVIT signalsBlind equalization algorithm
The invention discloses a passive bistatic radar signal processing method based on the blind equalization of a cyclic constant modulus. The method comprises the steps: S101: restoring a direct wave signal in a signal received by a reference channel of passive bistatic radar by adopting a blind equalization method of cyclic constant modulus; S102: carrying out multi-diameter self-adapting filtering processing on the direct radar signal by adopting a normalized minimum mean square error according to a signal received by a monitoring channel of the passive bistatic radar; S103: carrying out cross-correlation fuzzy function calculation after the Doppler revision to the signal processed by the multi-diameter self-adapting filtering processing and the direct radar signal, so as to obtain a cross-ambiguity function, and detecting an objective. According to the method provided by the invention, the mean square error of a constant blind equalization load-balancing algorithm can be reduced, and the self-adapting convergence performance can be improved, so as to improve the target detection capability of an entire signal processing flow.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
CMA blind equalization variable step size optimization method for MPSK signals
InactiveCN110581816AReduce time overheadFast convergencePhase-modulated carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalization algorithmAlgorithm
The invention discloses a CMA blind equalization variable step size optimization method for MPSK signals, and belongs to the field of digital communication signal processing. The method is characterized in that the convergence step length of a blind equalization algorithm is controlled through a blind equalization convergence error; the step length of the optimized CMA blind equalization algorithmis cooperatively controlled by an inverse proportional function and an exponential function, and the fractal property is utilized, so that the step length of the equalization algorithm is quickly reduced at the early stage of the algorithm, the convergence speed is increased, the step length of the algorithm changes slowly at the later stage of the algorithm, and residual errors are reduced. Compared with a traditional fixed-step-length CMA algorithm, the optimized CMA blind equalization algorithm has the advantages of being high in convergence speed, small in residual error and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A Signal Processing Method for Passive Bistatic Radar Based on Circular Constant Blind Equalization
InactiveCN104749562BFast convergenceImprove Adaptive Convergence PerformanceWave based measurement systemsBlind equalization algorithmMean square
The invention discloses a passive bistatic radar signal processing method based on the blind equalization of a cyclic constant modulus. The method comprises the steps: S101: restoring a direct wave signal in a signal received by a reference channel of passive bistatic radar by adopting a blind equalization method of cyclic constant modulus; S102: carrying out multi-diameter self-adapting filtering processing on the direct radar signal by adopting a normalized minimum mean square error according to a signal received by a monitoring channel of the passive bistatic radar; S103: carrying out cross-correlation fuzzy function calculation after the Doppler revision to the signal processed by the multi-diameter self-adapting filtering processing and the direct radar signal, so as to obtain a cross-ambiguity function, and detecting an objective. According to the method provided by the invention, the mean square error of a constant blind equalization load-balancing algorithm can be reduced, and the self-adapting convergence performance can be improved, so as to improve the target detection capability of an entire signal processing flow.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
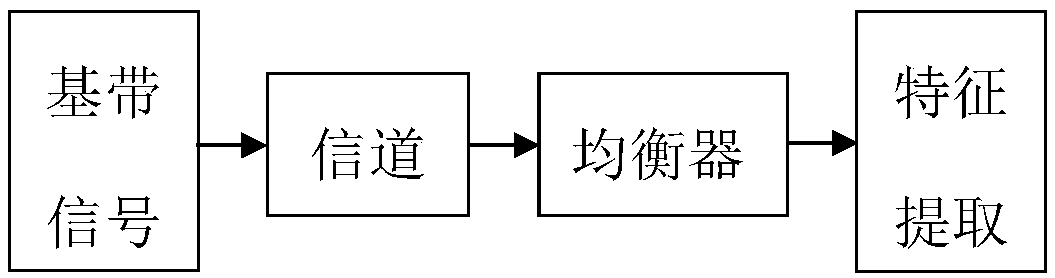
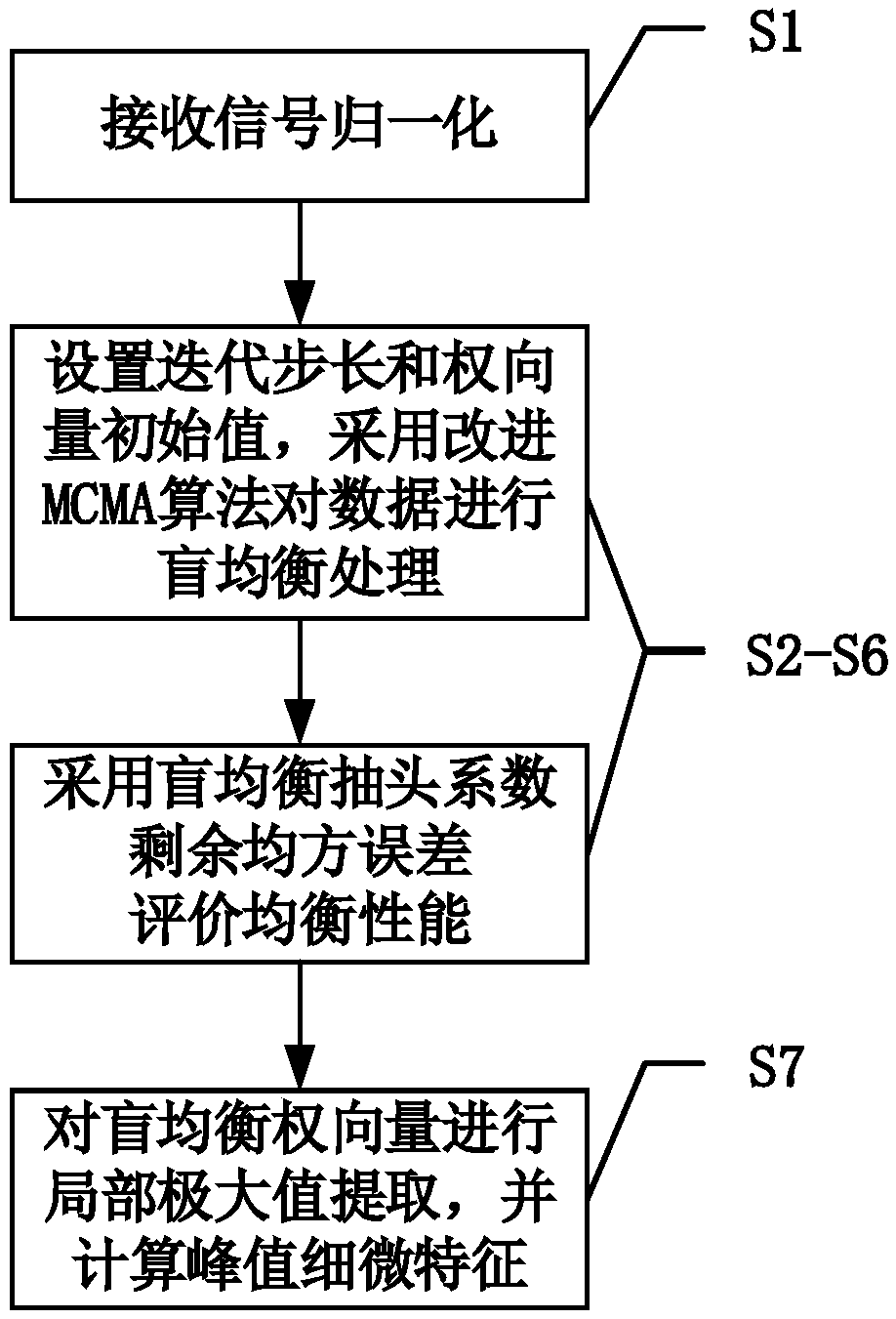
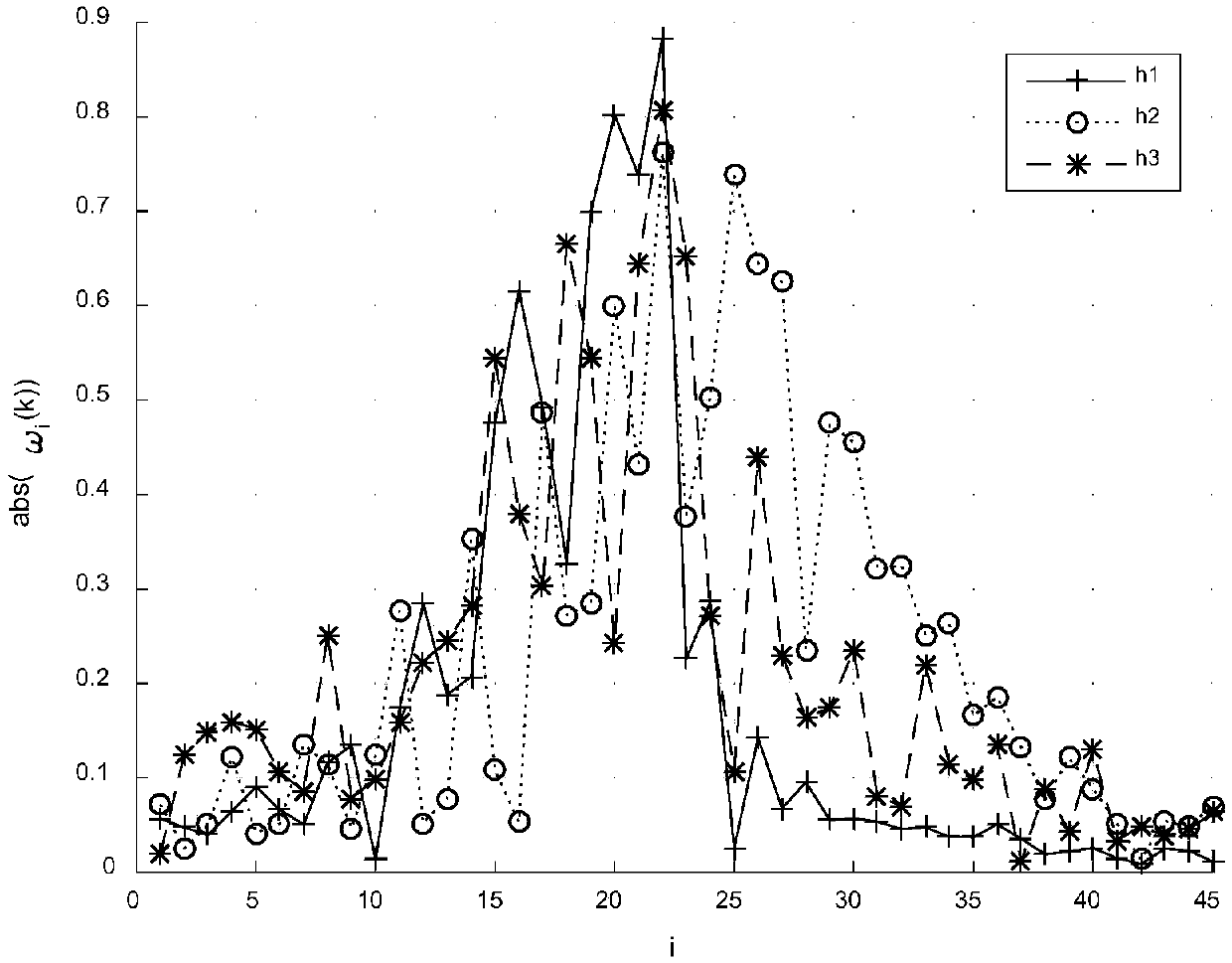
Method for extracting fine feature of channel
InactiveCN108848044ASmall amount of calculationEasy to implementTransmission monitoringChannel estimationFeature extractionBlind equalization algorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of signal sorting, and specifically relates to a method for extracting a fine feature of a channel. A transmitted signal is subjected to the action of thechannel in a transmission process, and a received signal can implicitly characterize the fine feature of channel information. In the method provided by the invention, the transmitted signal is restored from the received signal by using a blind equalization algorithm, and a peak value is extracted from a blind equalization weight vector to serve as the fine feature of the channel for the description and differentiation of the channel. Through simulation experiments, an embodiment 1 verifies the feasibility of the method for extracting the fine feature of the channel.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Orthogonal wavelet transform constant modulus blind equalization algorithm based on chaos and steepest descent joint optimization
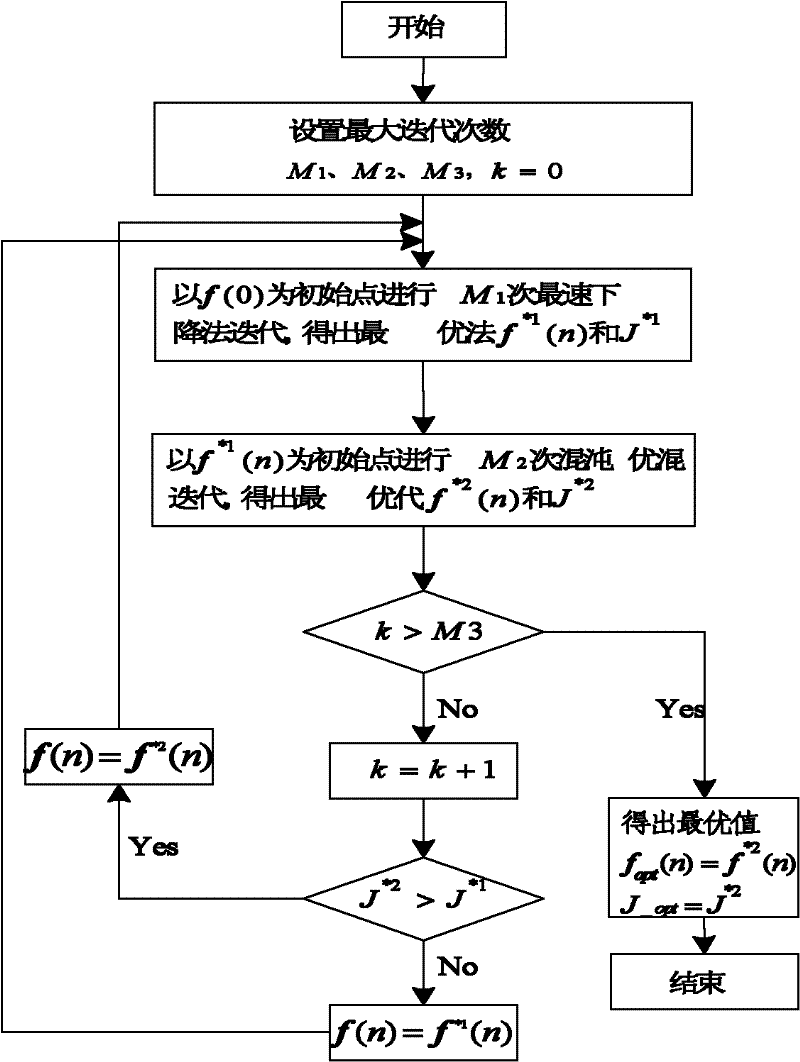
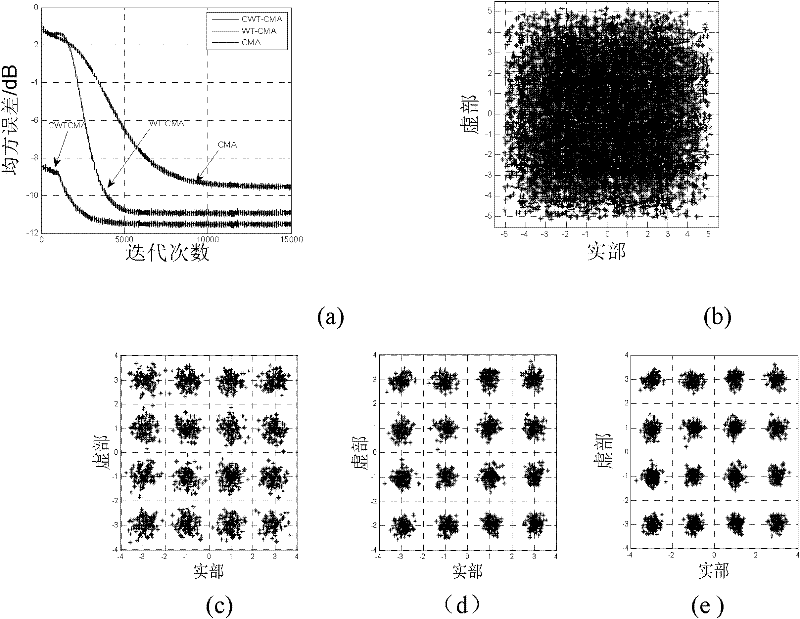
The invention discloses an orthogonal wavelet transform constant modulus blind equalization algorithm based on chaos and steepest descent joint optimization. The algorithm comprises the following steps of: causing a transmitted signal a(n) to pass through a pulse response channel c(n) to obtain a channel output vector x(n); obtaining an input signal y(n) of an orthogonal wavelet transformer (WT) by adopting channel noises w(n) and the channel output vector x(n); causing the y(n) to pass through the orthogonal WT to obtain equalizer input R(n) and equalizer output z(n); combining a chaos optimization algorithm and a steepest descent method by adopting a short segment of initial data to optimize a weight vector to make the optimized weight vector hop from a local optimal point and approach a global optimal point; and preprocessing an input signal of an equalizer by utilizing the high decorrelation of orthogonal wavelet transform to reduce the autocorrelation of the input signal and accelerate convergence. Simulation results of an underwater acoustic channel show that the orthogonal wavelet transform constant modulus blind equalization algorithm based on the chaos and steepest descent joint optimization is relatively faster in convergence, relatively higher in convergence accuracy and relatively lower in remainder error.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
A pcm/fm anti-multipath interference telemetry receiving method based on blind equalization algorithm
InactiveCN106253922BCompensating for Frequency Selective FadingTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalization algorithmMultipath interference
Owner:HUAIHUA UNIV
A Blind Equalization Algorithm for Burst Signals
InactiveCN102685048BReduce complexityGuaranteed real-time processing performanceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMean squareBlind equalization algorithm
The invention discloses a blind equalization method for a burst signal. The blind equalization method comprises the following steps of: first performing rapid channel estimation on a wireless channel by adopting a per-survivor sequence algorithm to obtain a forward estimated channel parameter; then decomposing the forward estimated channel parameter into a system consisting of a minimum phase system and a maximum phase system, which are connected in series, when the mean square error of the forward estimated channel parameter is less than 0.05 and the forward estimated channel parameter is not a minimum phase, and inverting the minimum phase system and the maximum phase system respectively to obtain a linear equalizer initialization coefficient; and finally substituting the linear equalizer initialization coefficient into a decision directed minimum mean square error algorithm to realize rapid blind equalization. According to the blind equalization algorithm for the burst signal, the rapid blind equalization of the burst signal is realized, the complexity of the algorithm is lowered, and the real-time processing performance of the algorithm is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Channel equalization method based on momentum fractional order multimode blind equalization algorithm
ActiveCN114095320ALow costOvercoming structural complexityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksHigh level techniquesBlind equalization algorithmAlgorithm
The invention provides a channel equalization method based on a momentum fractional order multimode blind equalization algorithm, and the method comprises the steps of introducing the concept of fractional order gradient, momentum information and the like into a blind equalization technology, and constructing a cost function by utilizing the expectation of an output signal and an input signal of an equalizer, and iteratively updating the tap weighted vector of the equalizer by using fractional order gradient information and momentum information of the cost function, thereby increasing the convergence rate while ensuring low residual intersymbol interference and low bit error rate. Compared with a traditional multimode algorithm, the method has lower residual inter-symbol interference and bit error rate at the initial stage of equalization, can quickly compensate and correct a channel, and is simple in structure and easy to implement.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com