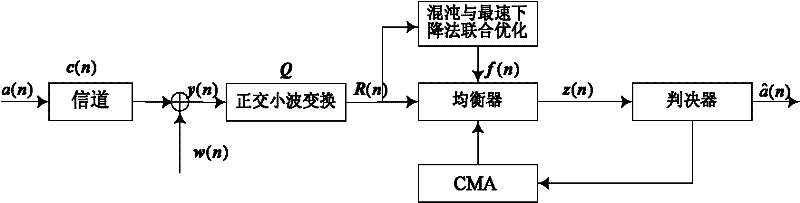
Orthogonal wavelet transform constant modulus blind equalization algorithm based on chaos and steepest descent joint optimization
A technique of steepest descent method and orthogonal wavelet, which is applied to the shaping network and baseband system components in the transmitter/receiver, and can solve the problems of slow convergence speed and large mean square error.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0110] In order to verify the effectiveness of the CWTCMA of the present invention, a simulation study of the underwater acoustic channel is carried out and compared with CMA and WT-CMA.
[0111] In the simulation experiment, the underwater acoustic channel [0.3132, -0.104, 0.8908, 0.3134] is used, the signal-to-noise ratio is 25dB, and the weight length of the equalizer is 16.
Embodiment 1
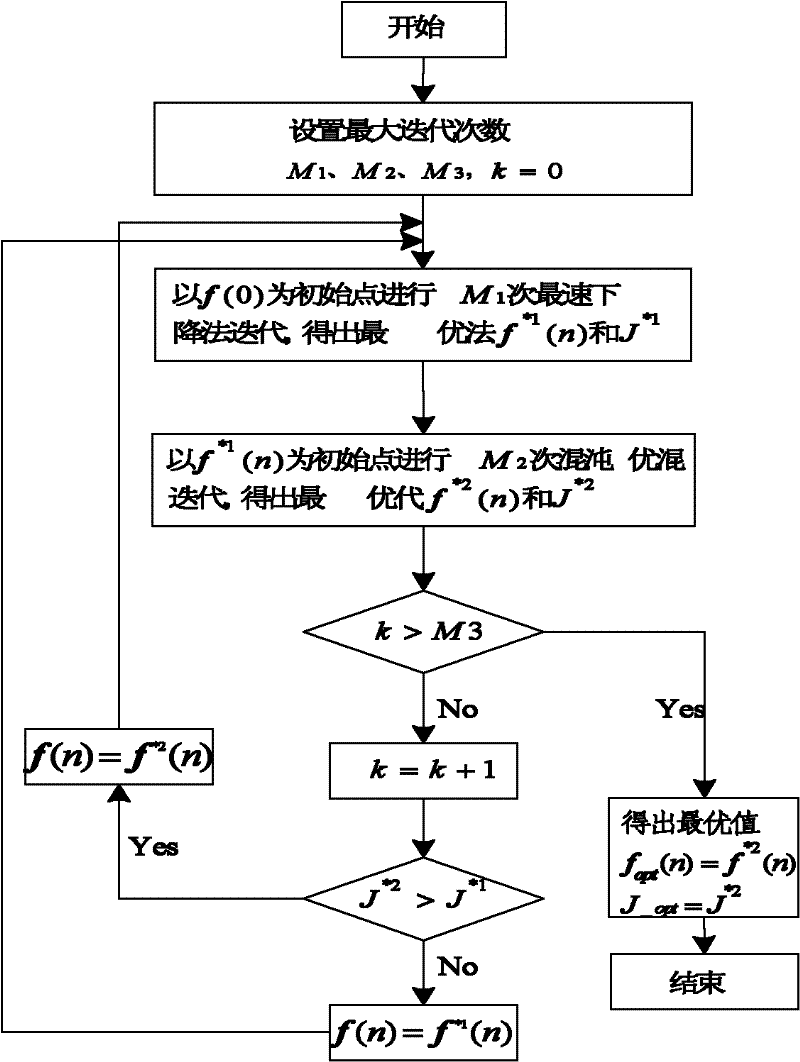
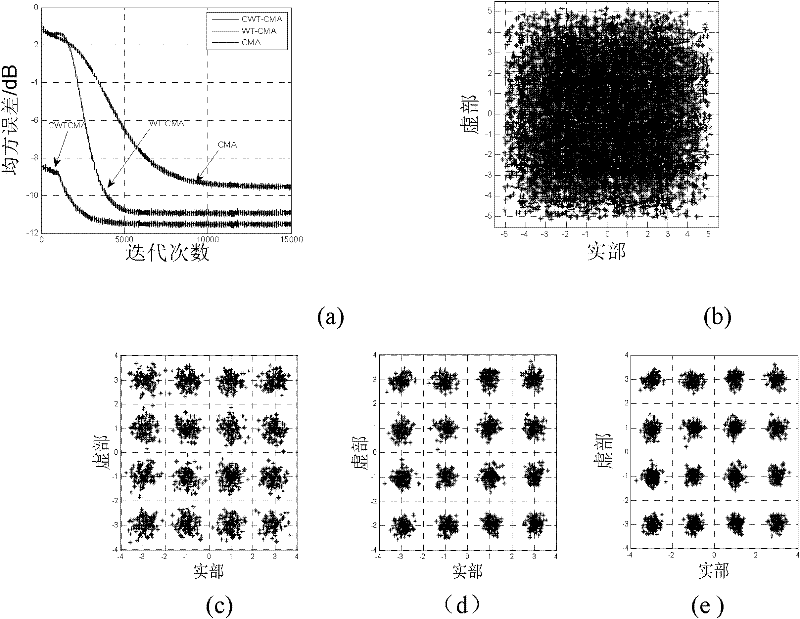
[0112] [Example 1] The transmission signal is 16QAM, and the step factor μ in CMA, WT-CMA, and CWTCMA is 0.00001, 0.0002, and 0.0001, respectively, M 1 , M 2 , M 3 The values are 500, 800, 20 respectively, and N is 20; all adopt the fourth tap coefficient as 1, and the rest are all 0; c i The values are all 0, d i The values of ζ are all 1; the first 500 points of the equalizer input data are used to initialize the weight vector when the chaos is initialized, and the initialization switching condition ζ is 10 -5 ; The simulation result of Monte Carlo simulation times is 5000 times, such as image 3 shown.
[0113] Depend on image 3 (a) It can be seen that the mean square error of CWTCMA of the present invention after convergence is about 2dB smaller than CMA, and about 0.5dB smaller than WT-CMA; the convergence speed of CWTCMA of the present invention is about 5000 steps faster than CMA, and about 1000 steps faster than WT-CMA ;Depend on image 3 From (c) to (e),...
Embodiment 2
[0114] [Example 2] The transmission signal is 16PSK, and the step factor μ in CMA, WT-CMA, and CWTCMA is 0.001, 0.002, and 0.001, respectively, M 1 , M 2 , M 3 The values are 300, 800, 20 respectively, and N is 20; all adopt the fourth tap coefficient as 1, and the rest are all 0; c i The values are all 0, d i The values of are all 1; the weight vector is initialized with the first 300 points of the equalizer input data during the chaos initialization, and the initialization switching condition ζ is 10 -5 ; The simulation result of Monte Carlo simulation times is 5000 times, such as Figure 4 shown. Figure 4 (a) shows that, on steady-state error, CWTCMA of the present invention reduces about 5dB than CMA, is basically the same with WT-CMA; On convergence speed, CWTCMA of the present invention is faster than CMA by nearly 4200 steps faster than WT-CMA About 1500 steps; by Figure 4 From (c) to (e), it can be seen that the equalized constellation diagram of CWTCMA i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com