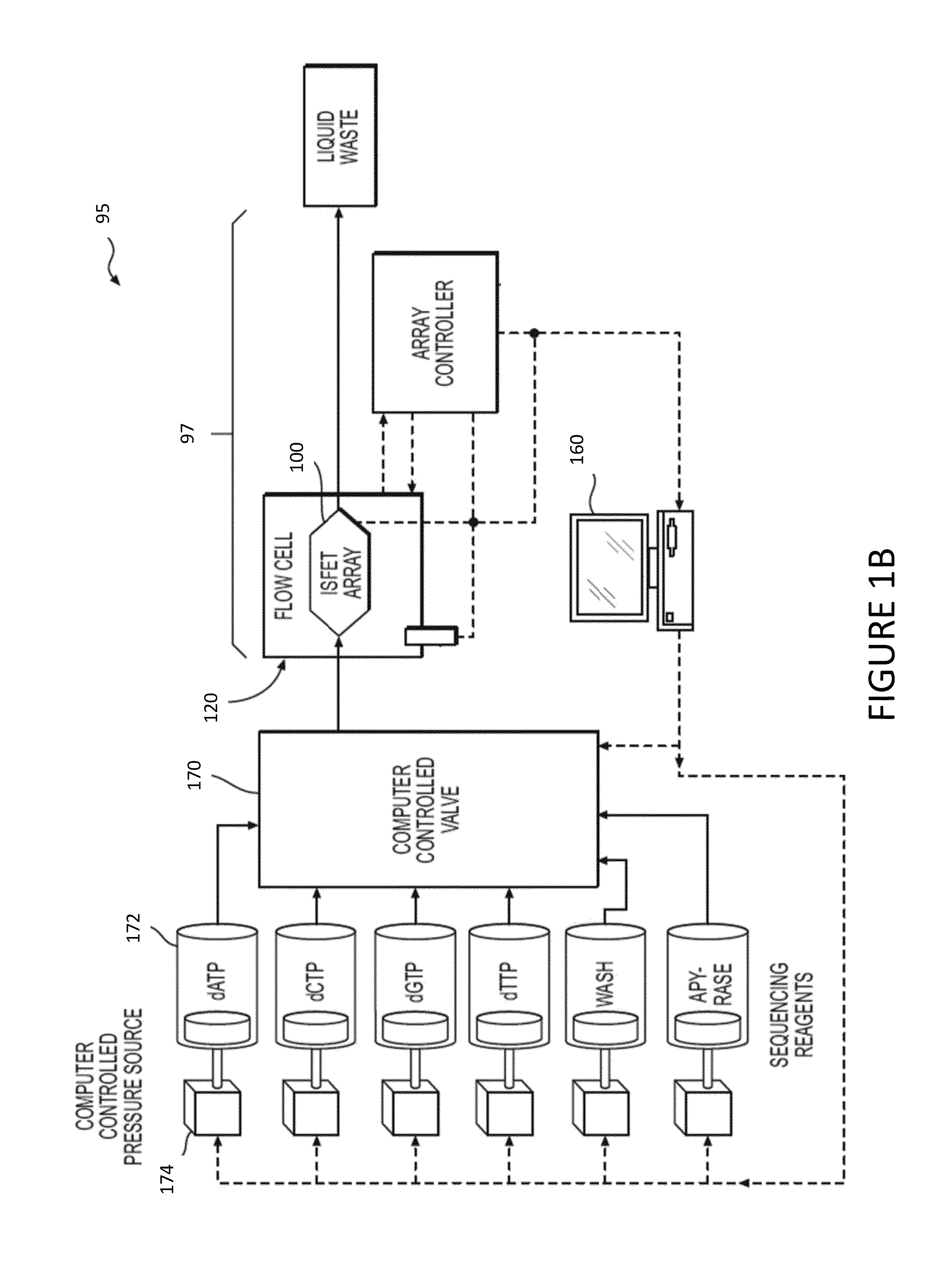
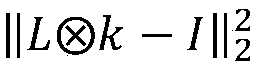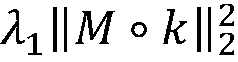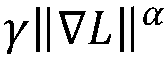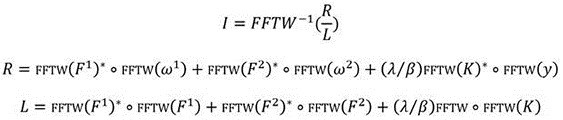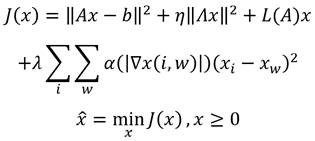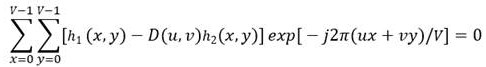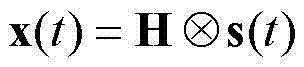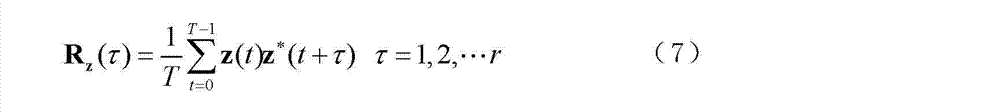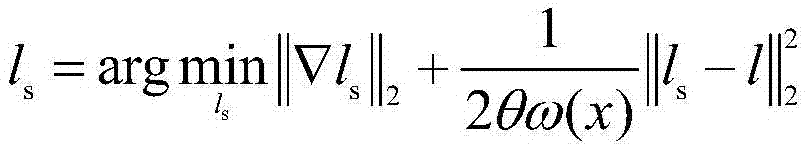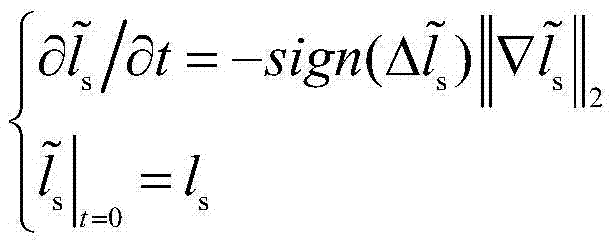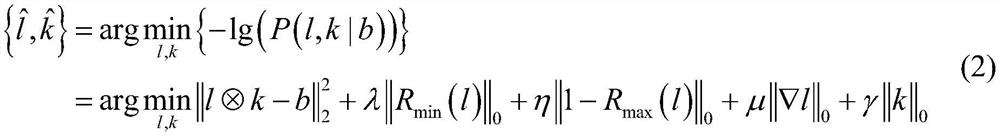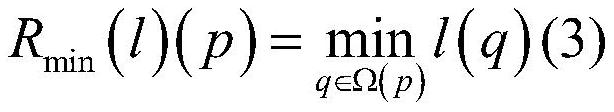Patents
Literature
121 results about "Blind deconvolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
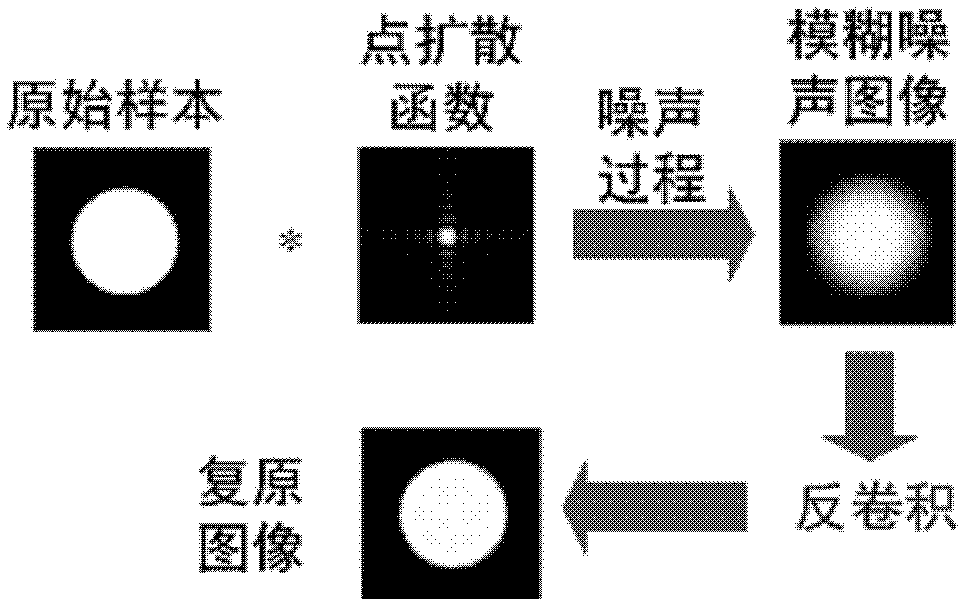
In electrical engineering and applied mathematics, blind deconvolution is deconvolution without explicit knowledge of the impulse response function used in the convolution. This is usually achieved by making appropriate assumptions of the input to estimate the impulse response by analyzing the output. Blind deconvolution is not solvable without making assumptions on input and impulse response. Most of the algorithms to solve this problem are based on assumption that both input and impulse response live in respective known subspaces. However, blind deconvolution remains a very challenging non-convex optimization problem even with this assumption.
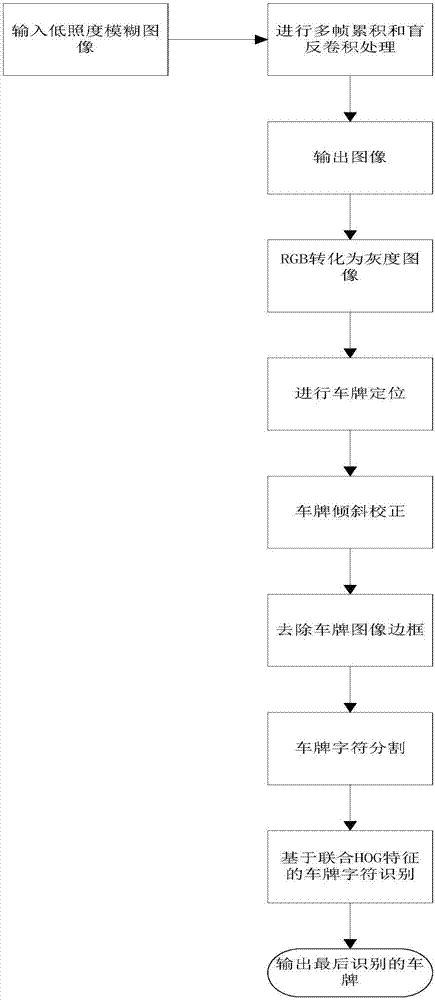
Blurred license plate image identification algorithm based on image fusion and blind deconvolution
InactiveCN107103317AImprove read reliabilityEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual perceptionImage based
The present invention relates to the computer vision field, especially to a blurred license plate image identification algorithm based on image fusion and blind deconvolution. The algorithm comprises 5 steps: 1, multi-frame image fusion for enhancement of distinguishing degree of low-illumination images of a license plate; 2, blurred image processing based on the blind deconvolution algorithm; 3, license plate location and inclination estimation; 4, segmentation of license plate characters; and 5, character identification and output after segmentation of the license plate characters. The blurred license plate image identification algorithm based on the image fusion and the blind deconvolution is high in reading reliability of license plate characters, good in identification degree and good in robustness in the condition of blurred license plate and low-quality imaging of license plate images caused by low illumination at night or vehicle overspeed and the like; and moreover, the step calculation is simple, the high efficiency is maintained, and the timeliness can satisfy the requirement.
Owner:HUNAN VISION SPLEND PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
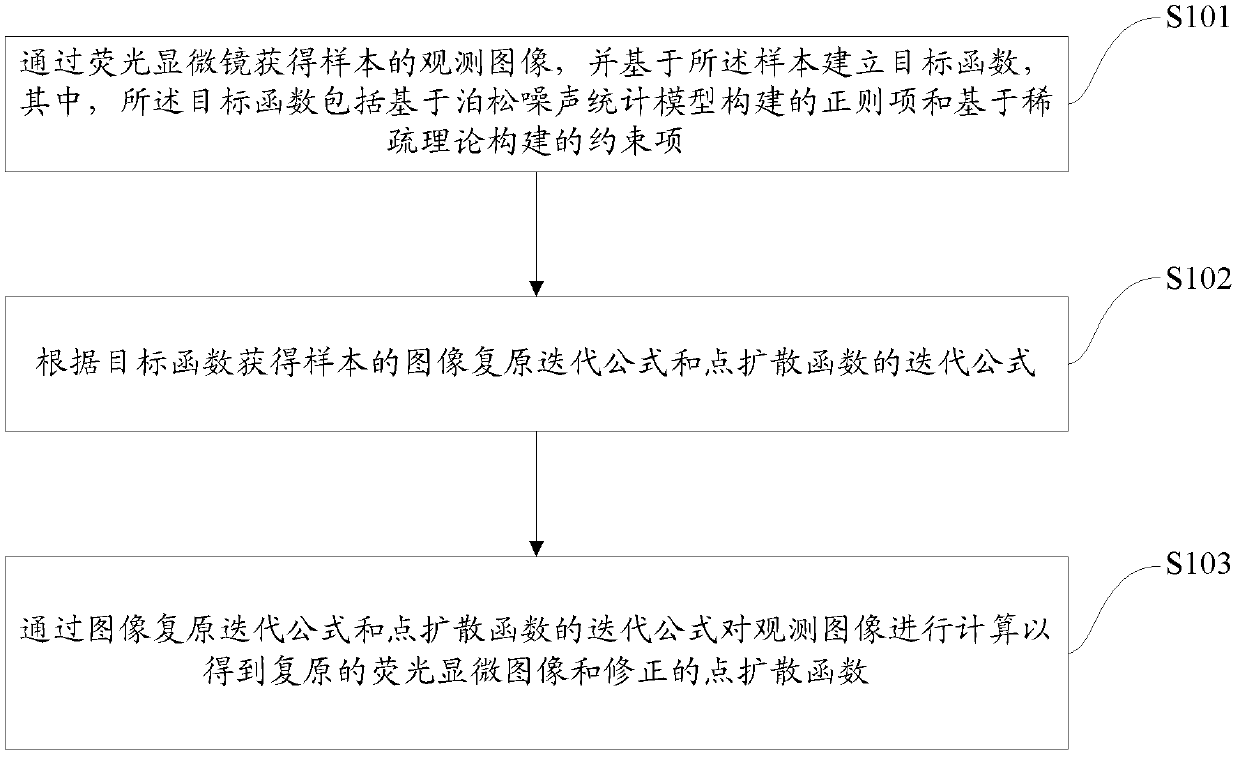
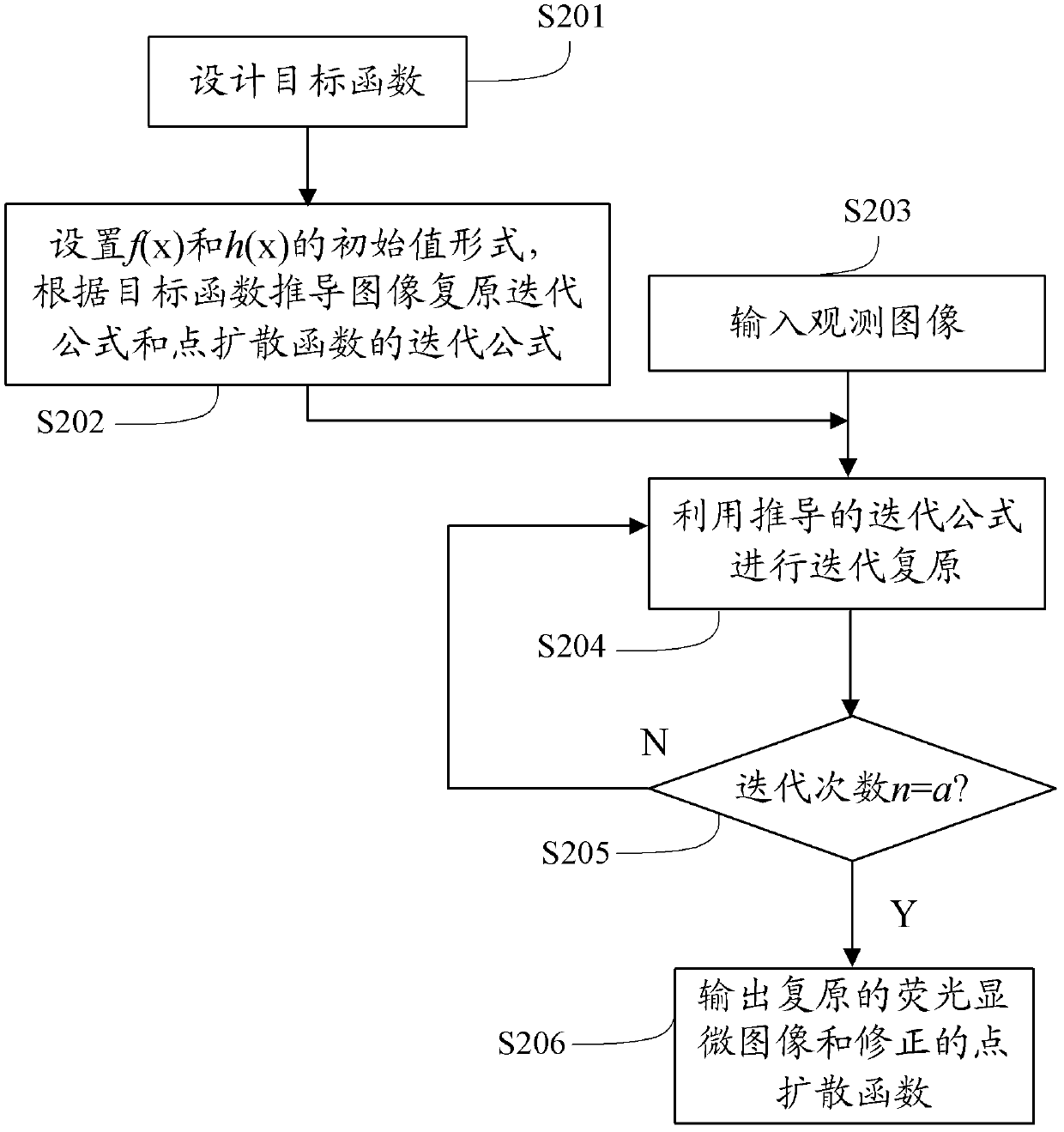
Fluorescent microscopic image restoring method based on blind deconvolution and sparse representation and device thereof
InactiveCN102708543AImprove accuracyKeep detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionMicroscopic image
The invention provides a fluorescent microscopic image restoring method based on the blind deconvolution and the sparse representation and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining an observing image of a sample through a fluorescence microscope, and building an objective function based on the sample, wherein the objective function comprises a regular item and a constraint item; obtaining an image restoring iteration formula and a point spreading function iteration formula of the sample according to the objective function; and calculating the observed image through the image restoring iteration formula and the point spreading function iteration formula in order to obtain the restored fluorescent microscopic image and the corrected point spreading function. By using the embodiment of the invention, the contrast ratio and the definition of the restored image are high; the texture details are effectively maintained; the image visual effect is more clear; and naturally, the point spreading function obtained after restoring also has very high degree of accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
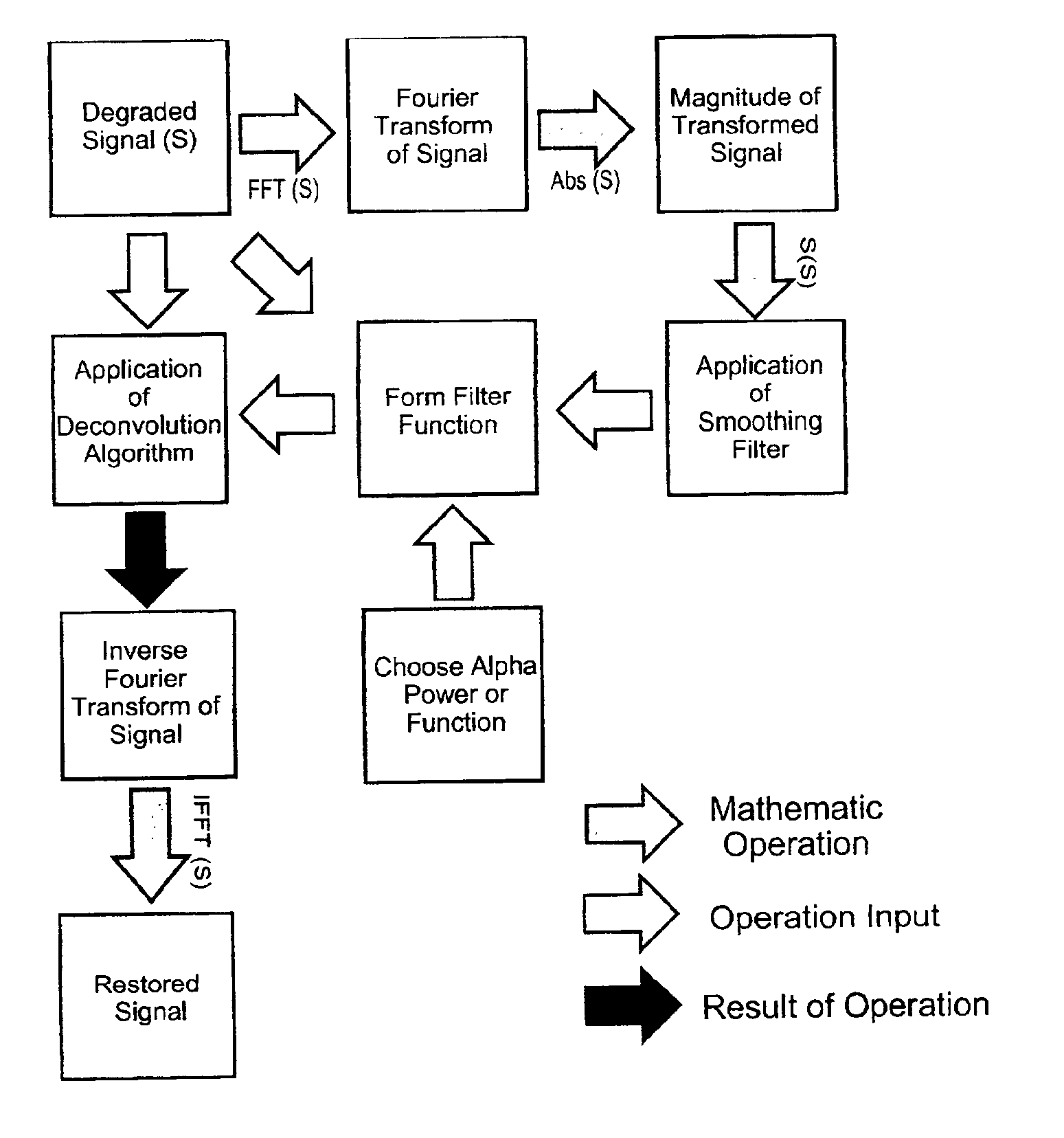
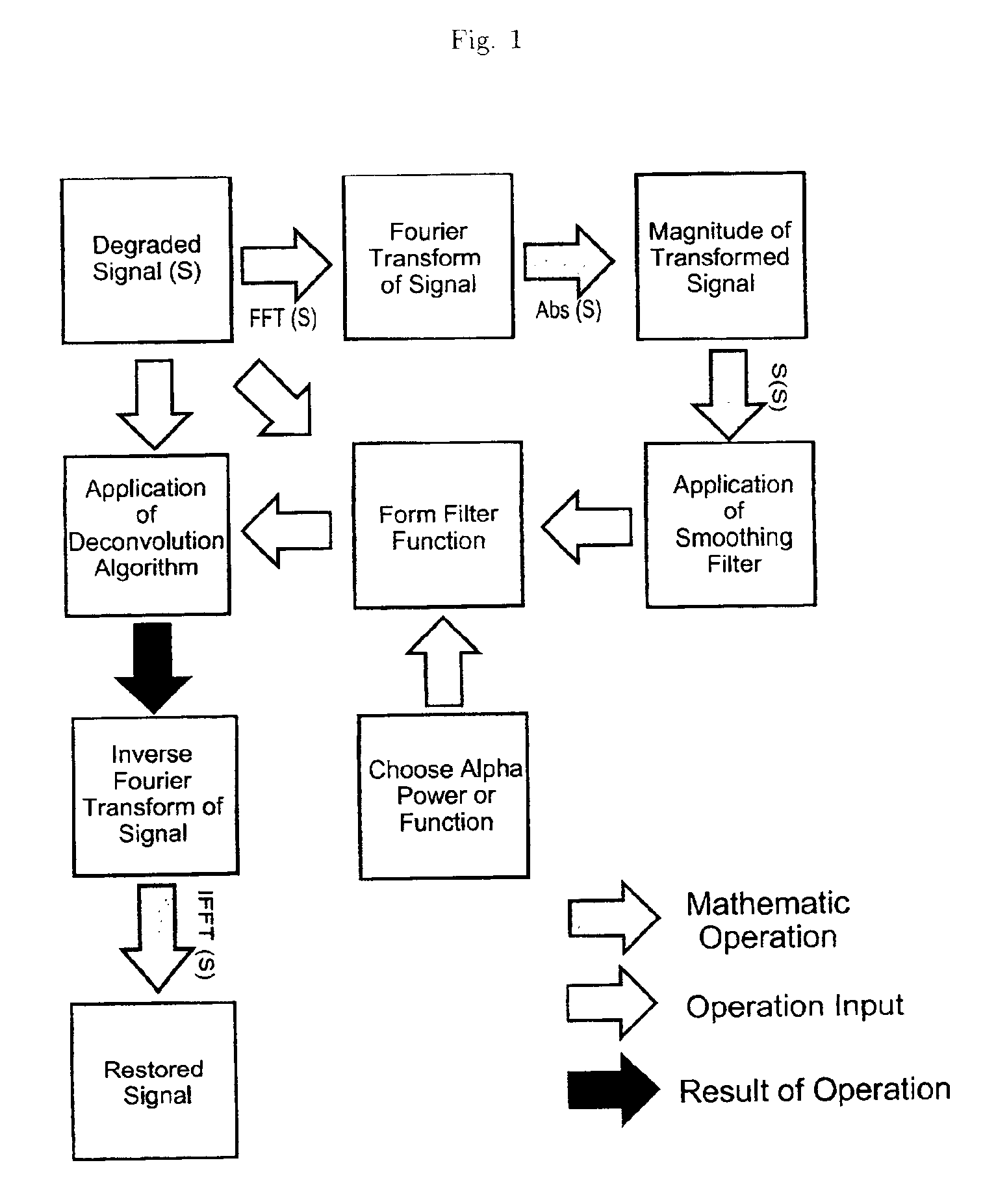
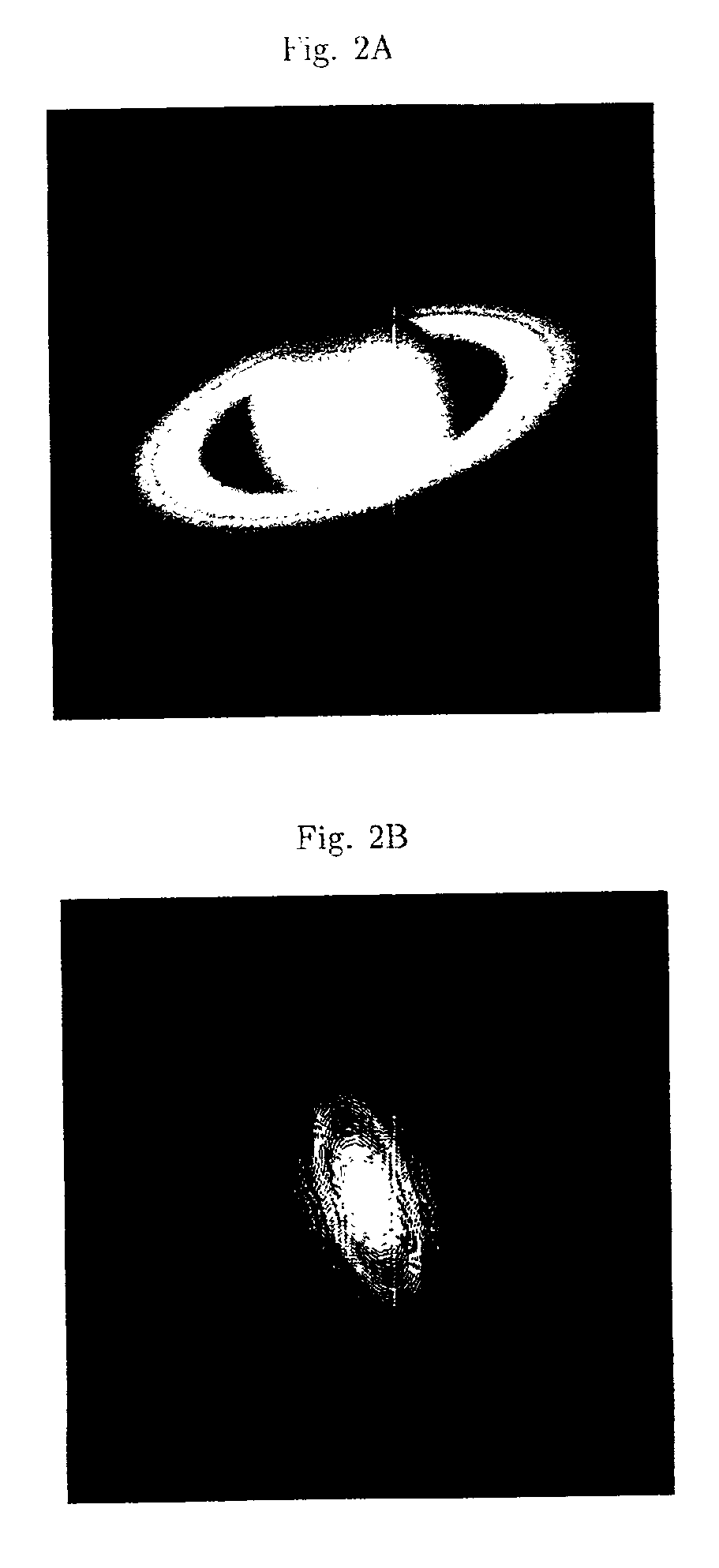
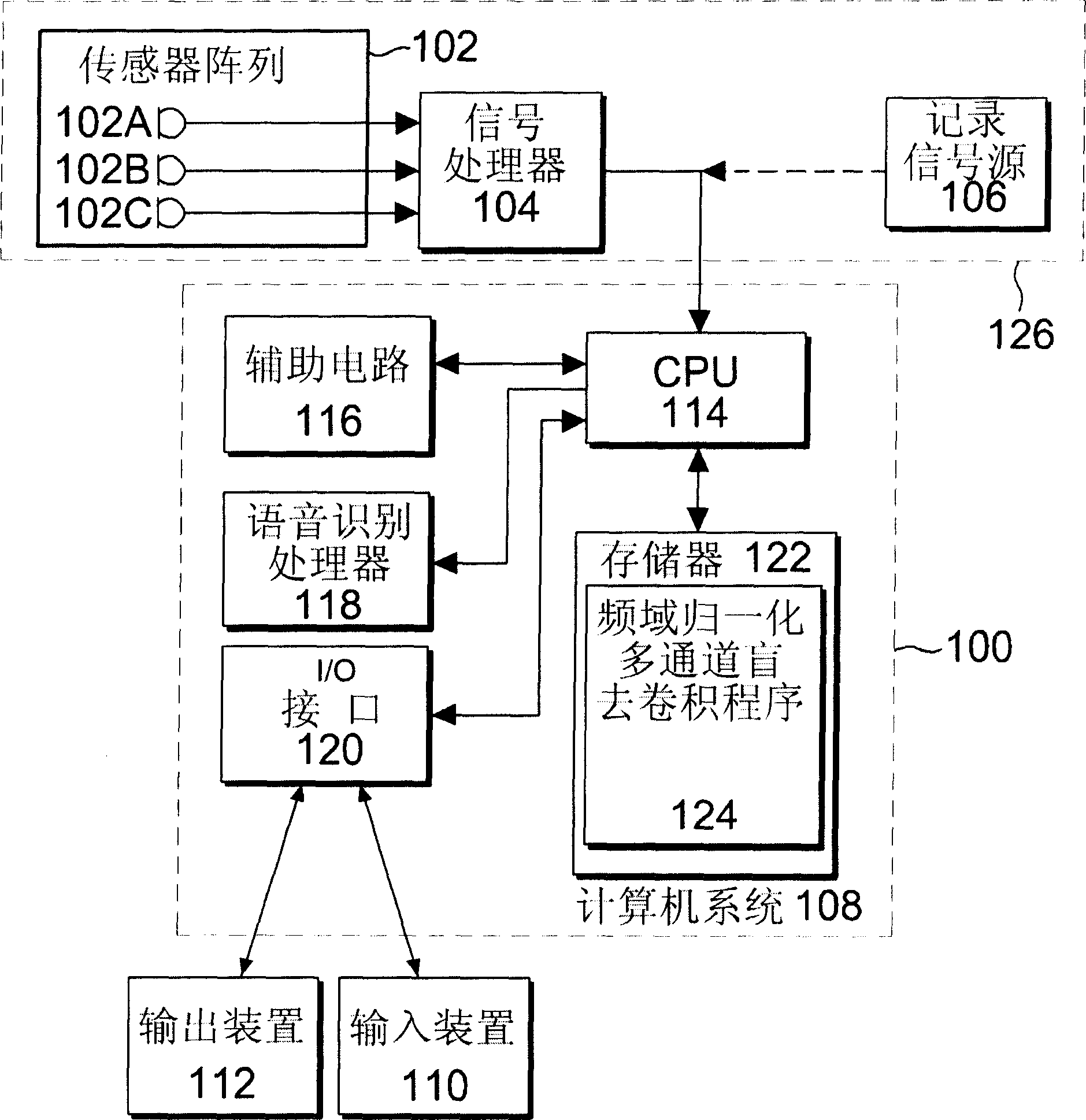
Signal processing using the self-deconvolving data reconstruction algorithm
InactiveUS6859564B2Easy to implementEasy to handleImage enhancementImage analysisFrequency spectrumOriginal data
A signal processing algorithm has been developed in which a filter function is extracted from degraded data through mathematical operations. The filter function can then be used to restore much of the degraded content of the data through use of any deconvolution algorithm. This process can be performed without prior knowledge of the detection system, a technique known as blind deconvolution. The extraction process, designated Self-deconvolving Data Reconstruction Algorithm (SeDDaRA), has been used successfully to restore digitized photographs, digitized acoustic waveforms, and other forms of data. The process is non-iterative, computationally efficient, and requires little user input. Implementation is straight-forward, allowing inclusion into all types of signal processing software and hardware.The novelty of the invention is the application of a power law and smoothing function to the degraded data in frequency space. Two methods for determining the value of the power law are discussed. The first method is by educated guess where the value is deemed a constant of frequency that ranges between zero and one. This approach requires no knowledge of the original data or the degradation and is quite effective. The second method compares the frequency spectrum of the degraded data to the spectrum of a signal with the desired frequency response. This approach produces a superior result, but requires additional processing.
Owner:CARON JAMES N
Image de-blurring method based on bright stripe information in image
ActiveCN105976332AQuality improvementAccurate estimateImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention discloses an image de-blurring method based on bright stripe information in an image. Bright stripes existing in a motion blurred image are applied, information of the shape of a blurred kernel is obtained, image restoration is restrained through combining the image and the blurred kernel, and an accurate blurred kernel and a high-quality restoration image are obtained. The method particularly comprises steps: the optimal image block containing the optimal bright stripes is selected; the blurred kernel shape information is obtained through extraction; blurred kernel estimation is carried out to obtain the final blurred kernel; and non-blind deconvolution is carried out, and a distinct restoration image is obtained through restoration to serve as the final de-blurring image. An actually-photographed bright stripe-containing blurred image testing set is built; and by adopting the technical scheme of the invention, the accurate blurred kernel and the high-quality restoration image can be obtained, and the application value in the image processing field is high.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
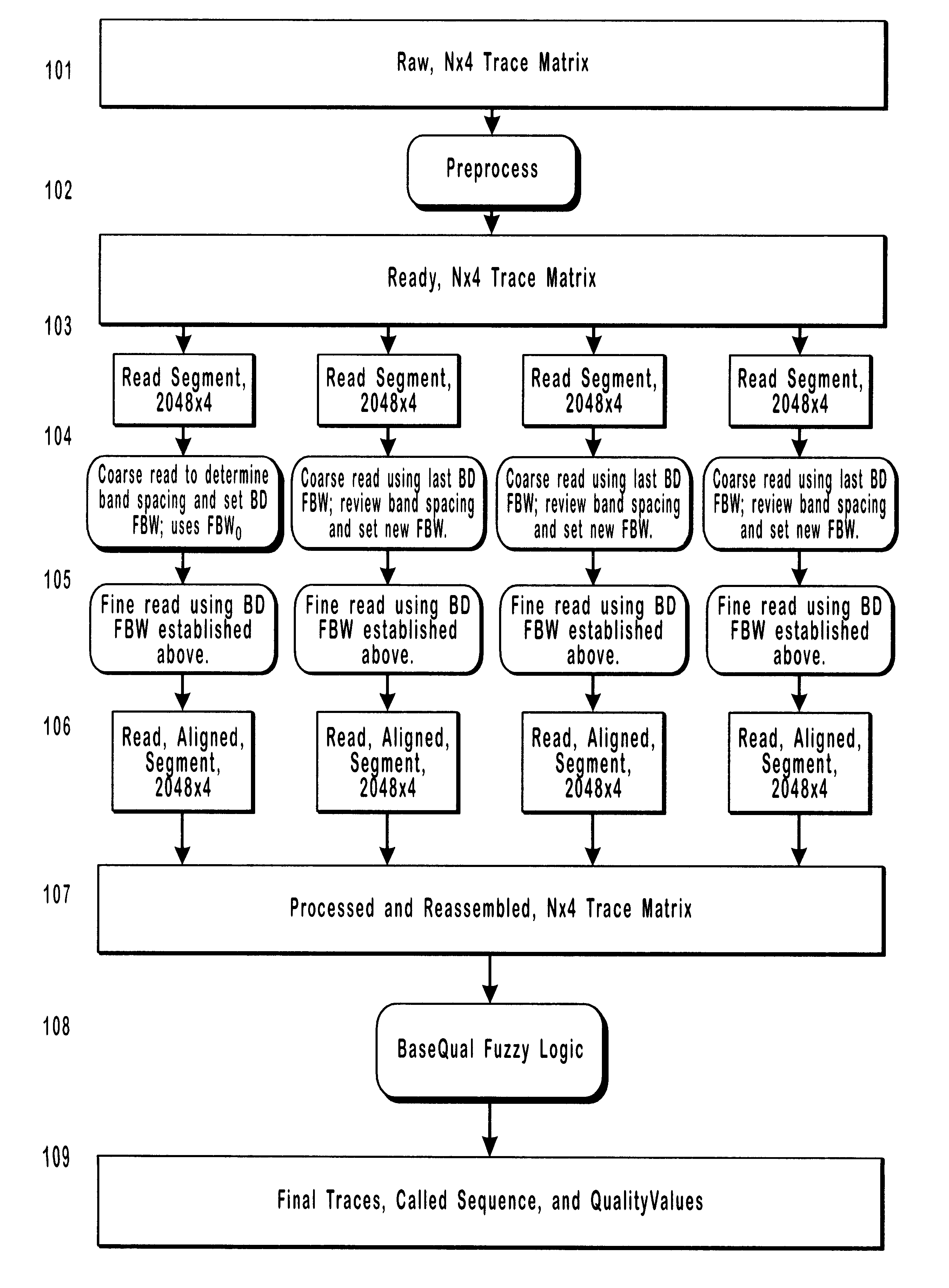
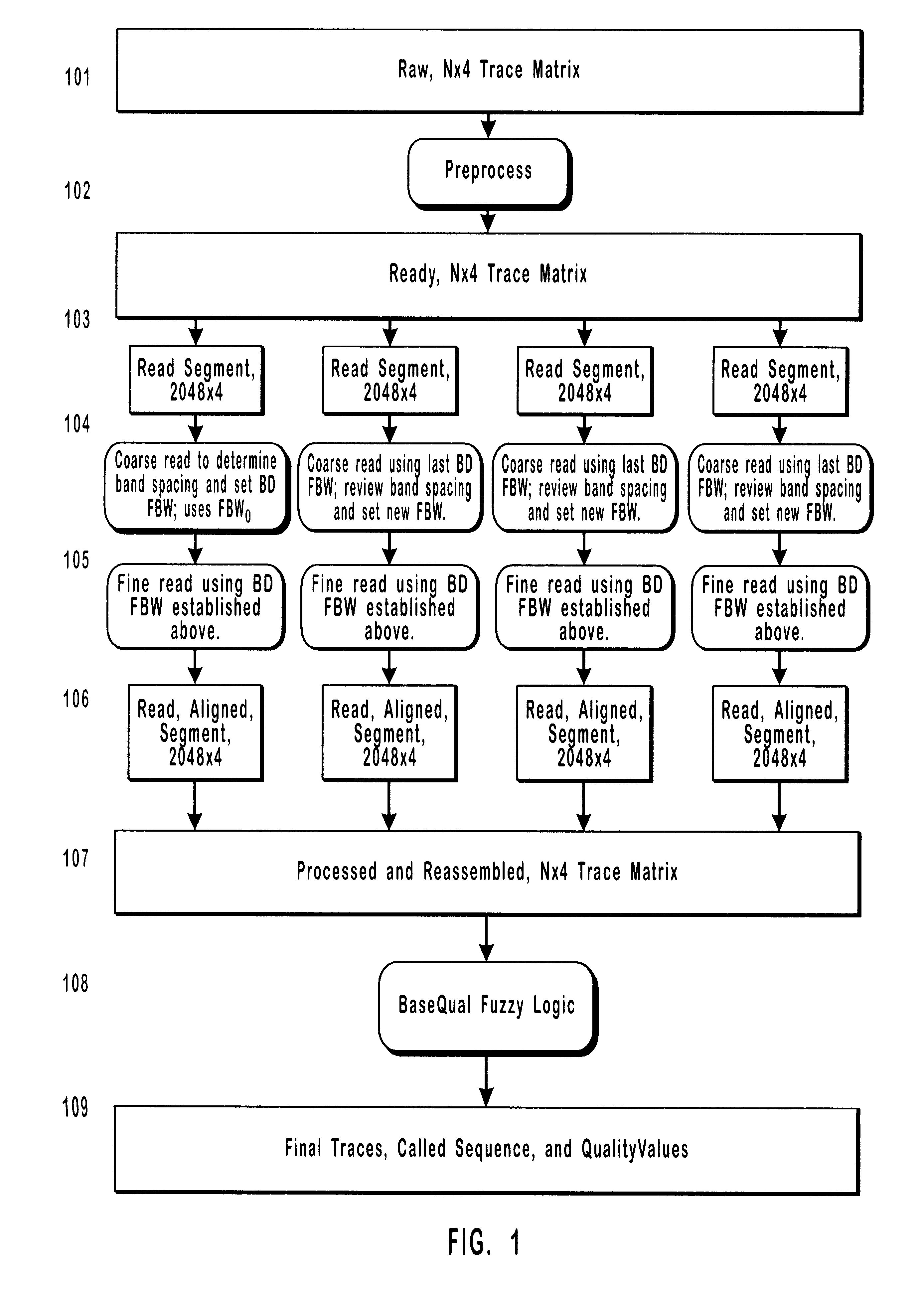
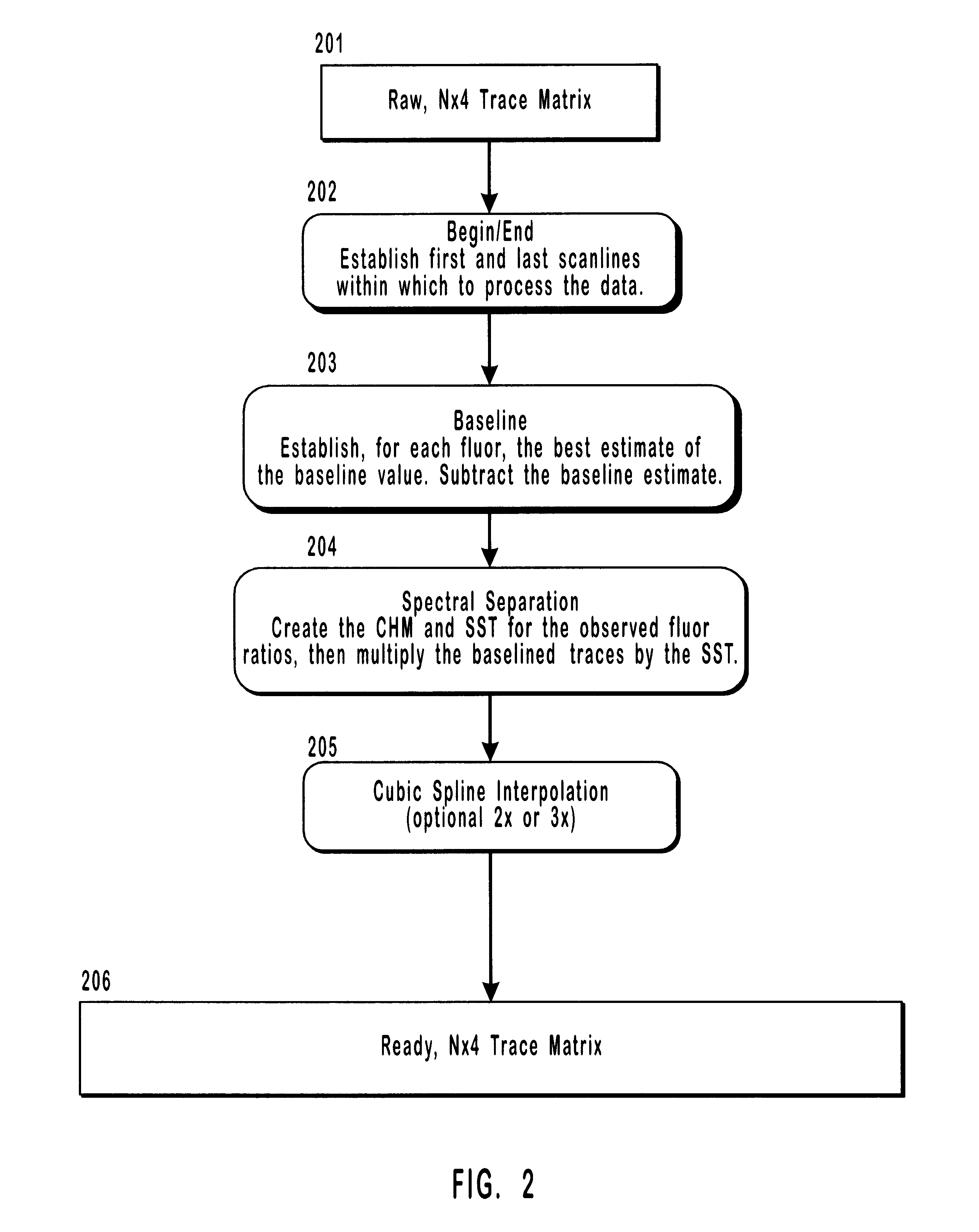
Method and apparatus for analysis of chromatographic migration patterns
InactiveUS6208941B1Rapid and efficient signal analysisLarge segment sizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapillary electrophoresisBase calling
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for the detection and analysis of information-containing signals in chromatographic data using iterative blind deconvolution and fuzzy logic algorithms. The invented method analyzes chromatographic data from a wide variety of sources of DNA sequencing information, including gel and capillary electrophoresis. Autoradiograms, single-fluor, four-lane and four fluor, single lane fluorescent chromatographic data are suitable sources of unprocessed input data. The output from the invented base calling method includes called (identified) sequence data and quality values for the called bases.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
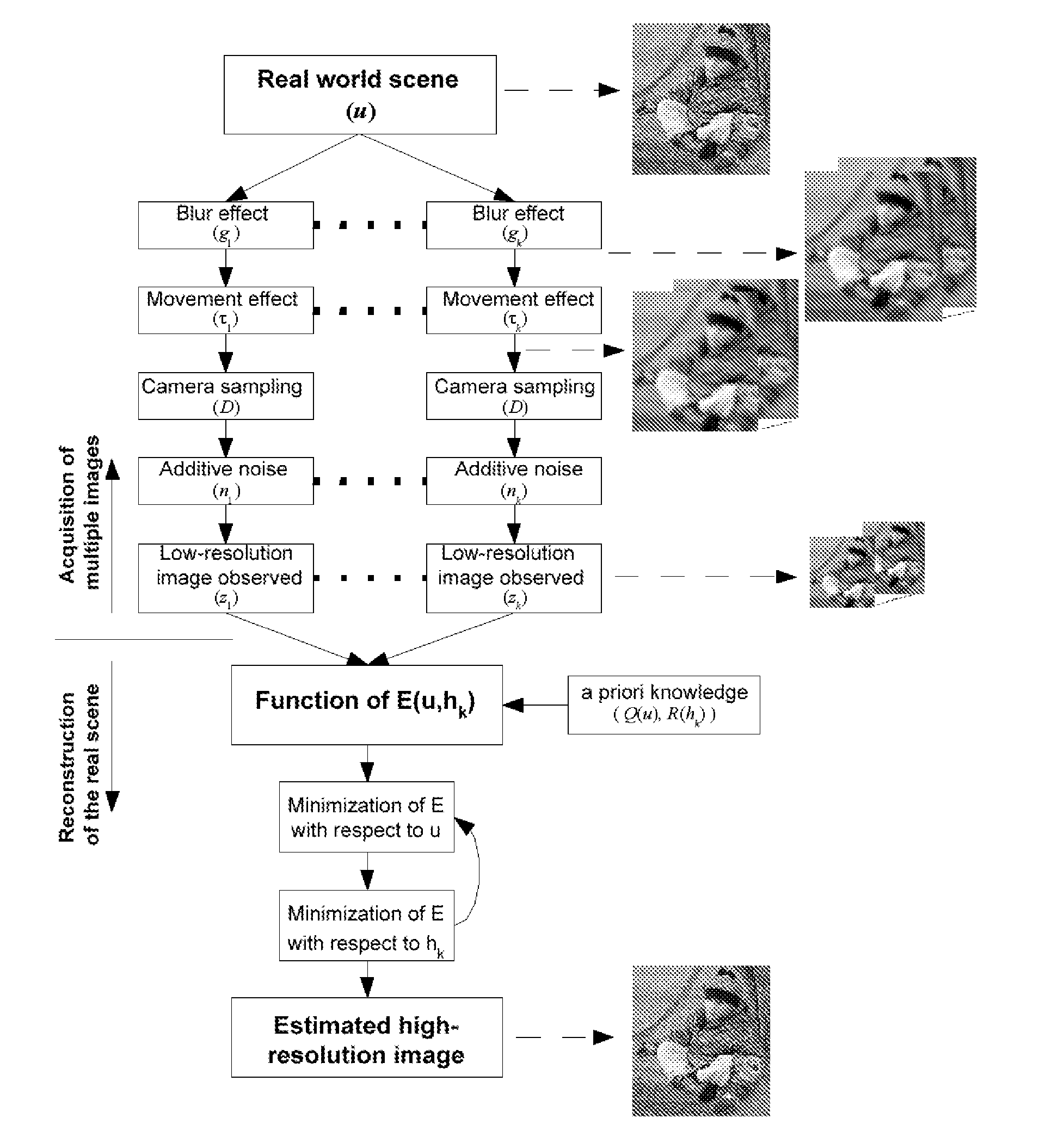
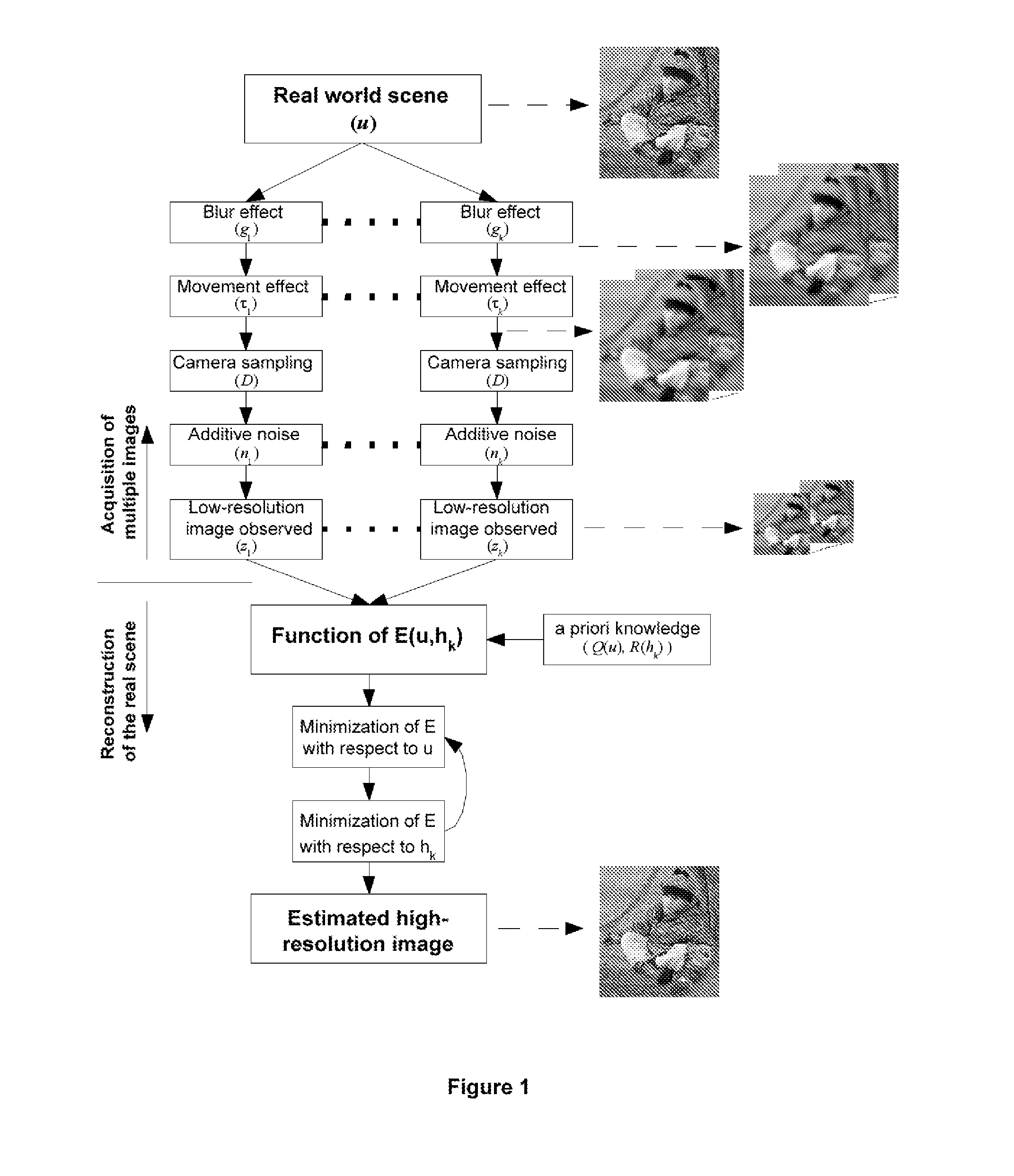
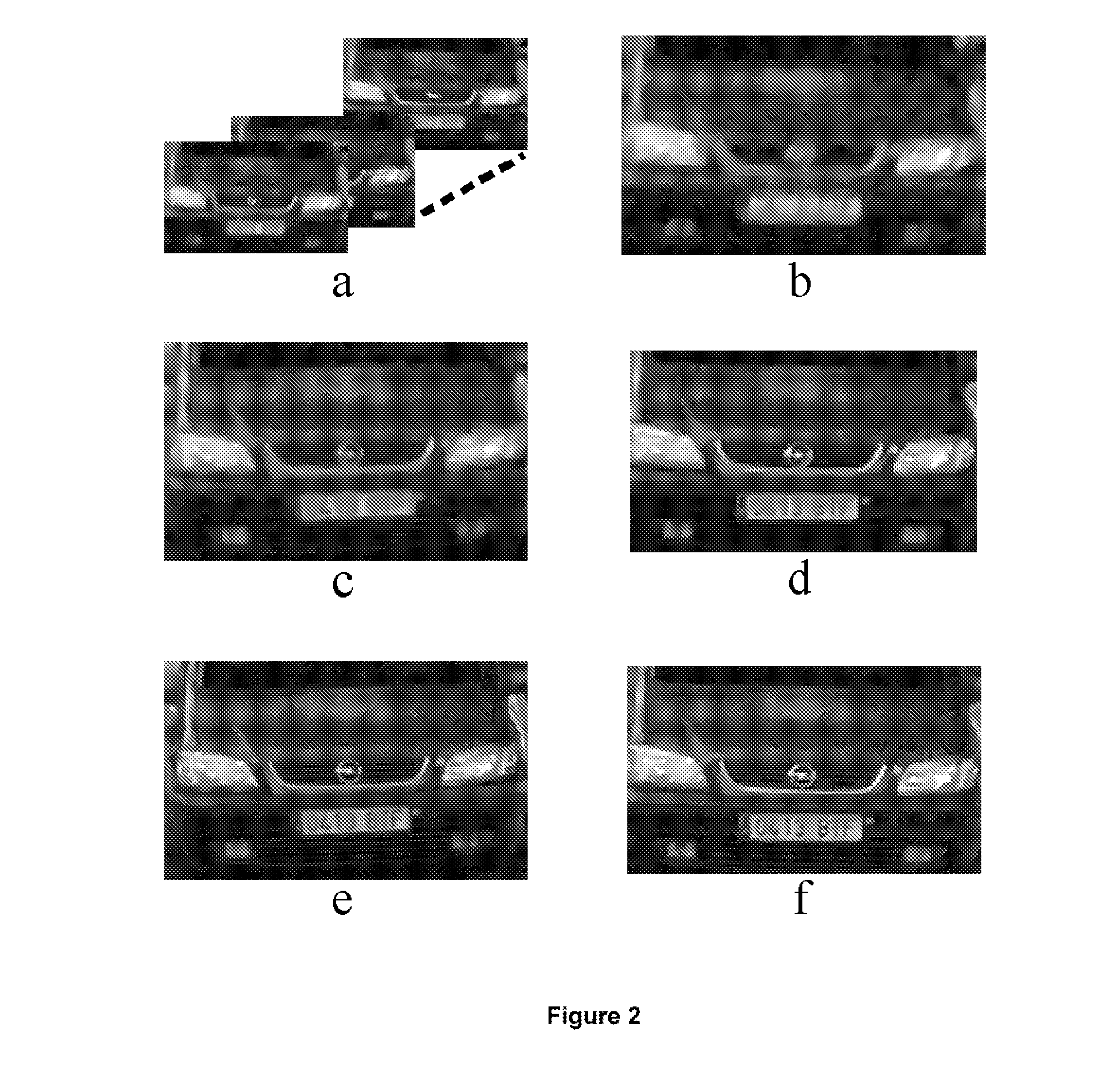
Blind deconvolution and super-resolution method for sequences and sets of images and applications thereof
InactiveUS20090263043A1Remove blurHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisDigital videoSecurity system
The present invention relates to the image achieved by any conventional method of capture and their subsequent computer processing. The process of the invention presented is based on the simultaneous processing of the input images and their restoration (deconvolution) pixel by pixel by means of a new mathematical method. Furthermore, and in the case of having more than one image of the scene in question, the system is capable of providing superresolution of the input images. It has direct application in digital photographic cameras, digital video cameras, mobile phones, video and photography edition programmes, image analysis programmes for microscopy and astronomy, analysis of medical images, forensic image, image-based security systems, aerial image and in the restoration of works of art, among others.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
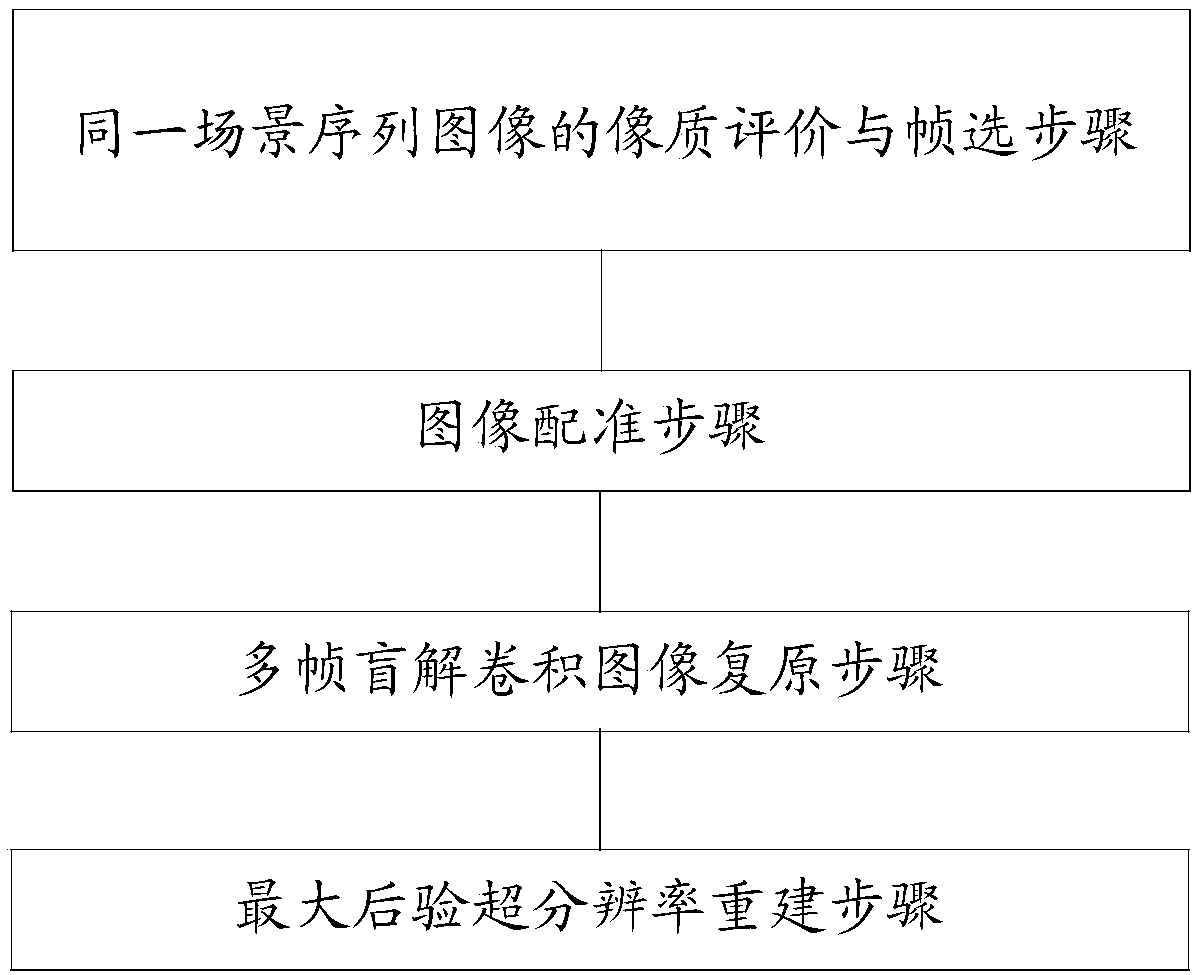
Bayes' rule based multi-frame blind convolution super-resolution reconstruction method and device
InactiveCN107680040AImprove spatial resolutionSolving the Simultaneous Estimation ProblemImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityDiffusion function
The invention discloses a Bayes' rule based multi-frame blind convolution super-resolution reconstruction method and device. The method includes steps of acquiring an interest area of a reference image and a matching area of a target image subjected to radiation correction through an image quality evaluation and frame selection algorithm for an image sequence of one scene; acquiring the radiancy and an accurate geometric distortion parameter through an image registration algorithm executed on the matching area of the target area subjected to radiation correction; acquiring a point diffusion function of image super-resolution restoration through execution of a multi-frame blind deconvolution image restoration algorithm on the accurate geometric distortion parameter; acquiring a super-resolution reconstruction image through execution of a maximum posterior super-resolution reconstruction algorithm on the radiancy and the point diffusion function of image super-resolution restoration. According to the invention, problems of insufficient consideration of point diffusion function, motion blur, image structure information, sparsity and the like of a traditional general algorithm are solved, automatic estimation on the system point diffusion function and multi-frame image registration parameters is performed, and the image resolution is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
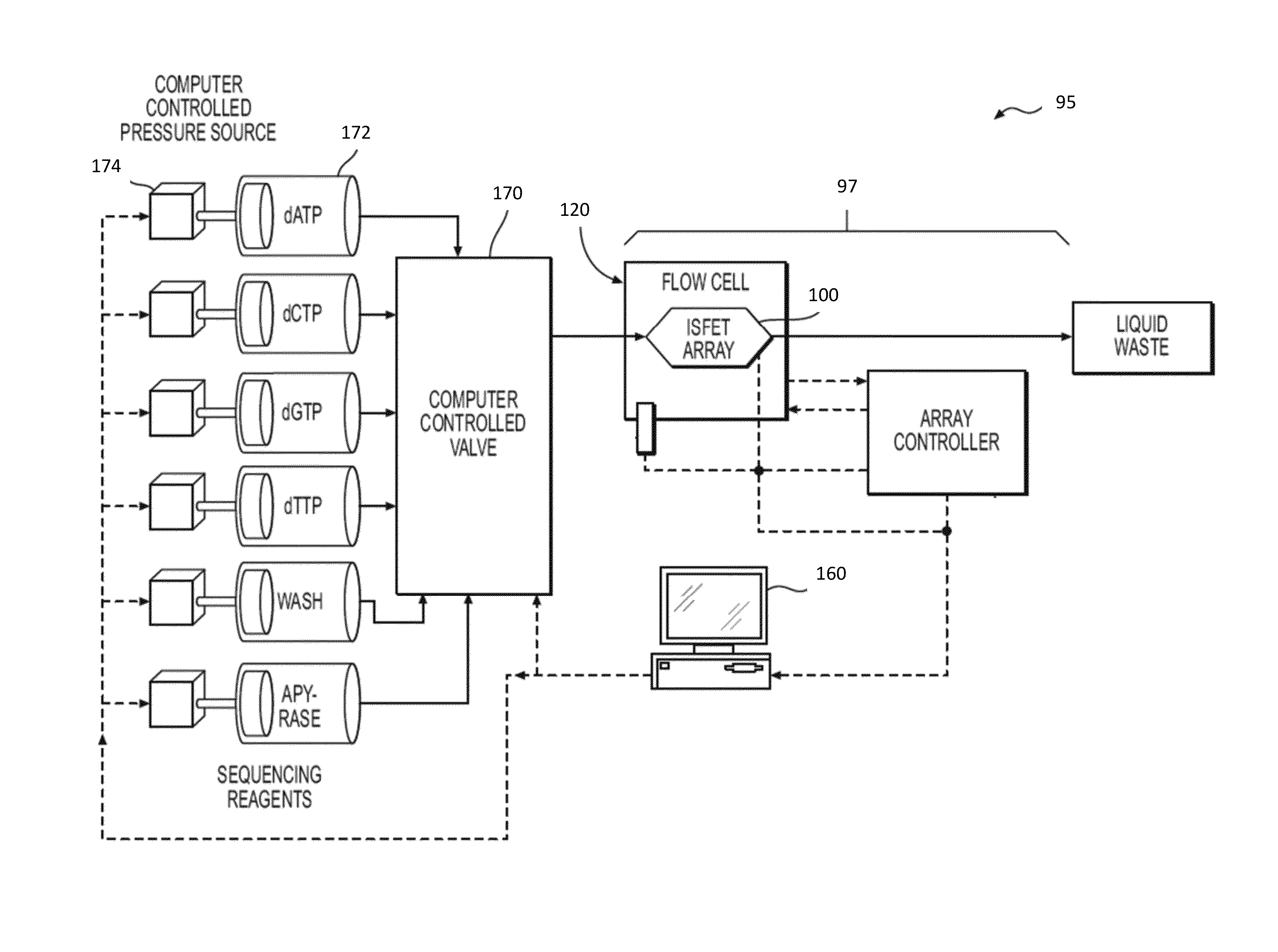
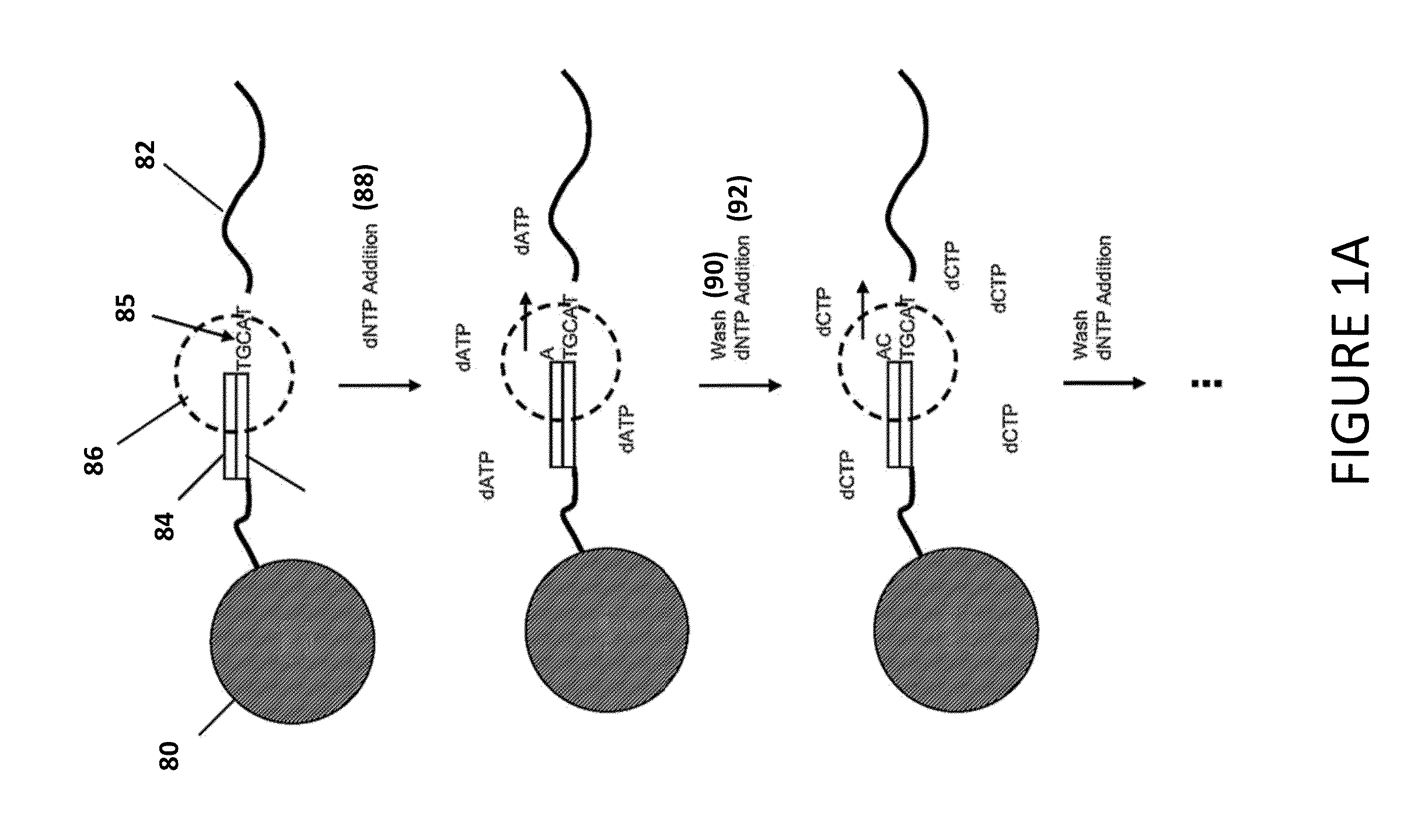
Methods, systems, and computer-readable media for blind deconvolution dephasing of nucleic acid sequencing data
InactiveUS20160110499A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBase callingNucleic acid sequencing
Embodiments disclose methods, systems, and computer-readable media for base-calling of sequencing data in the presence of systematic or phasic synchrony errors. These techniques may be adapted to rapidly and accurately resolve signal data arising from a variety of different nucleic acid sequencing platforms. In various embodiments, techniques for blind deconvolution dephasing of nucleic acid sequencing data may be adapted to perform raw signal processing, basecalling, and / or sequence determination.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
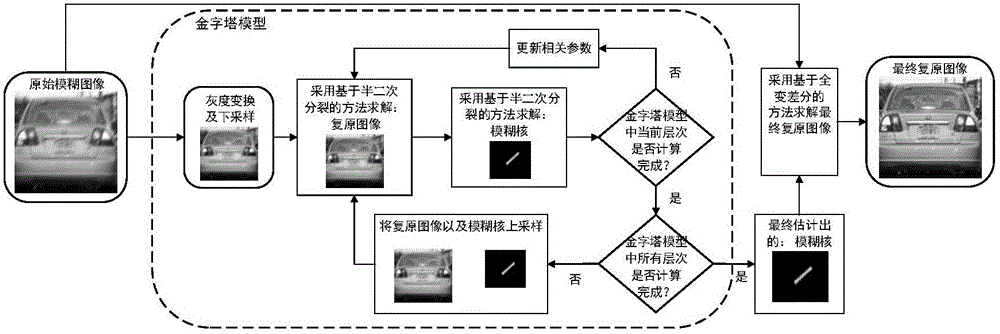
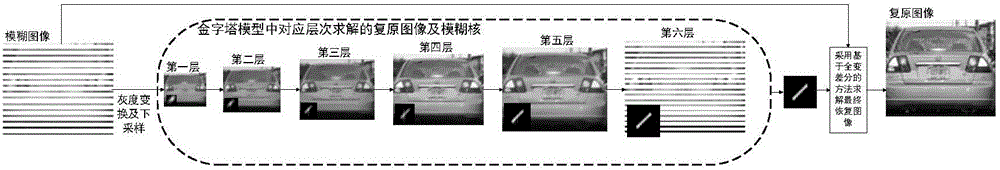
Natural image blind motion blur elimination method based on L0 regularization
The invention provides a natural image blind motion blur elimination method based on L0 regularization. Gradient information of a natural image and the sparse characteristic of a motion blur core are utilized, and corresponding L0 regular terms are respectively introduced into a solving model of the blur core. In the model solving process, a half-quadratic splitting method is firstly utilized to respectively solve a middle recovered image and the blur core, a pyramid model is utilized in the solving process for carrying out solving layer by layer so as to increase the robustness, only the gradient information of the image is utilized for the estimation of the blur core, and by means of Fourier transform, the solving process is transformed to frequency domain, so that the deconvolution operation carried out directly on a space domain is avoided, and a rapid solving purpose is achieved; in addition, the obtained blur core is utilized, and a final recovered image is obtained by a non-blind deconvolution method based on the total-variable difference. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the solving speed is high, the robustness is high, and the final recovered image has a good visual effect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
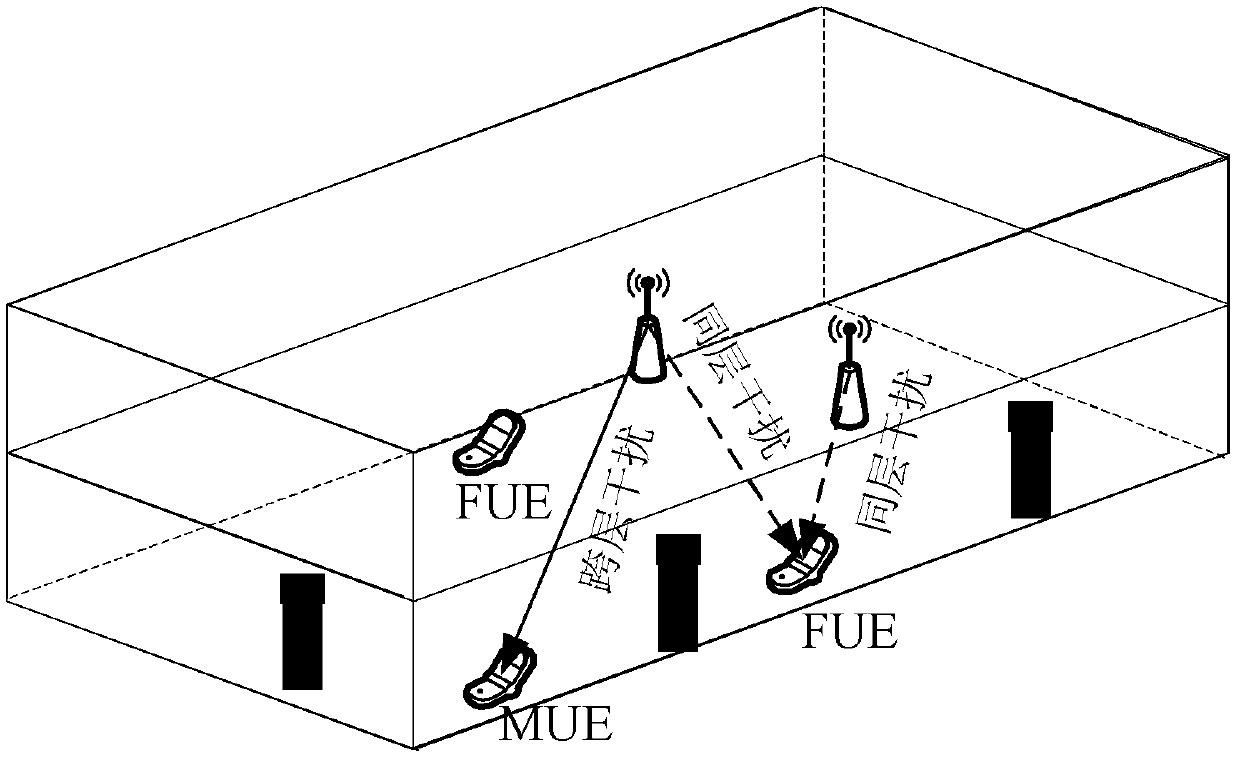
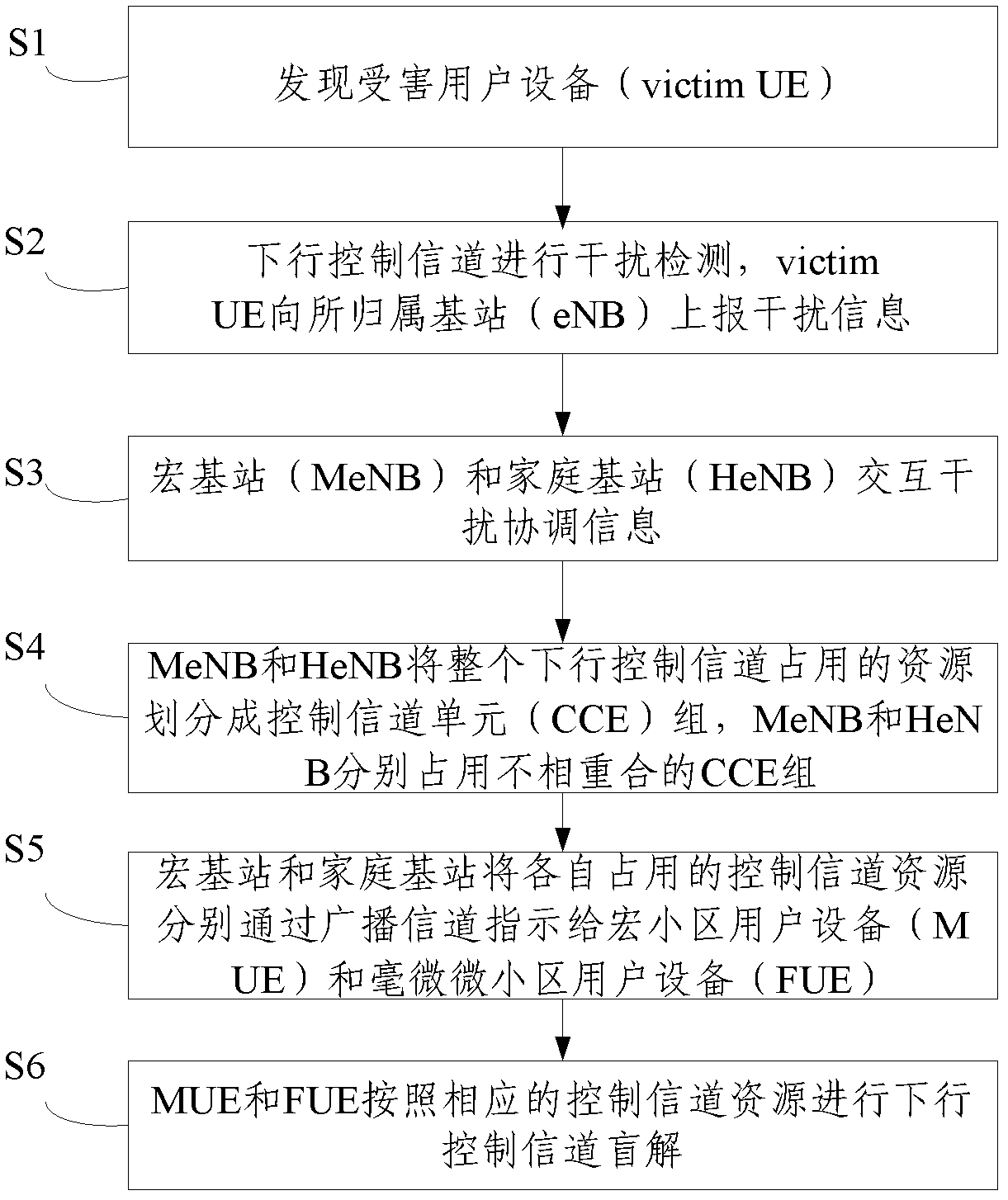
Method for downlink control channel interference coordination in layered heterogeneous network
InactiveCN102711252AAvoid interferenceDynamic AdjustmentTransmission path multiple useWireless communicationBroadcast channelsControl channel
The invention discloses a method for downlink control channel interference coordination in a layered heterogeneous network. The method comprises steps of S101, discovering victim user equipment (UE); S102, performing interference detection for a downlink control channel and enabling the victim UE to report interference information to evolved node B (eNB) which the victim UE belongs to; S103 enabling macro evolved node B (MeNB) and home evolved node B (HeNB) to perform interaction of interference coordination information; S104, enabling the MeNB and the HeNB to divide resources occupied by the whole downlink control channel into control channel element (CCE) groups, wherein the MeNB and the HeNB occupy respectively CCE groups which are not overlapped; S105, enabling control channel resources which are respectively occupied by the MeNB and the HeNB to be respectively instructed to macrocell user equipment (MUE) and femtocell user equipment (FUE) through broadcast channels; and S106, enabling the MUE and the FUE to perform blind deconvolution of the downlink control channel in accordance with corresponding control channel resources. The method can avoid cross-layer interference and same-layer interference.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
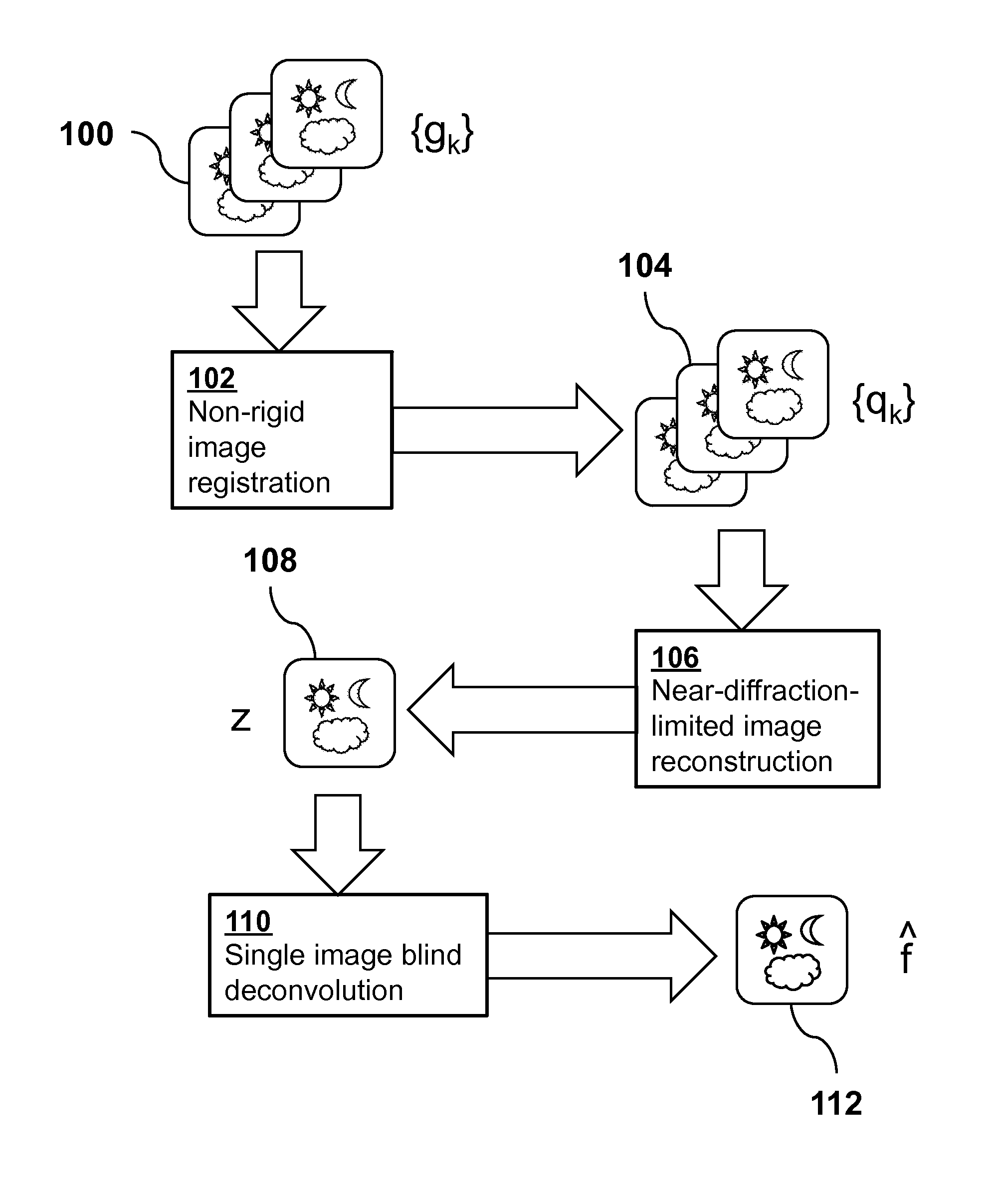
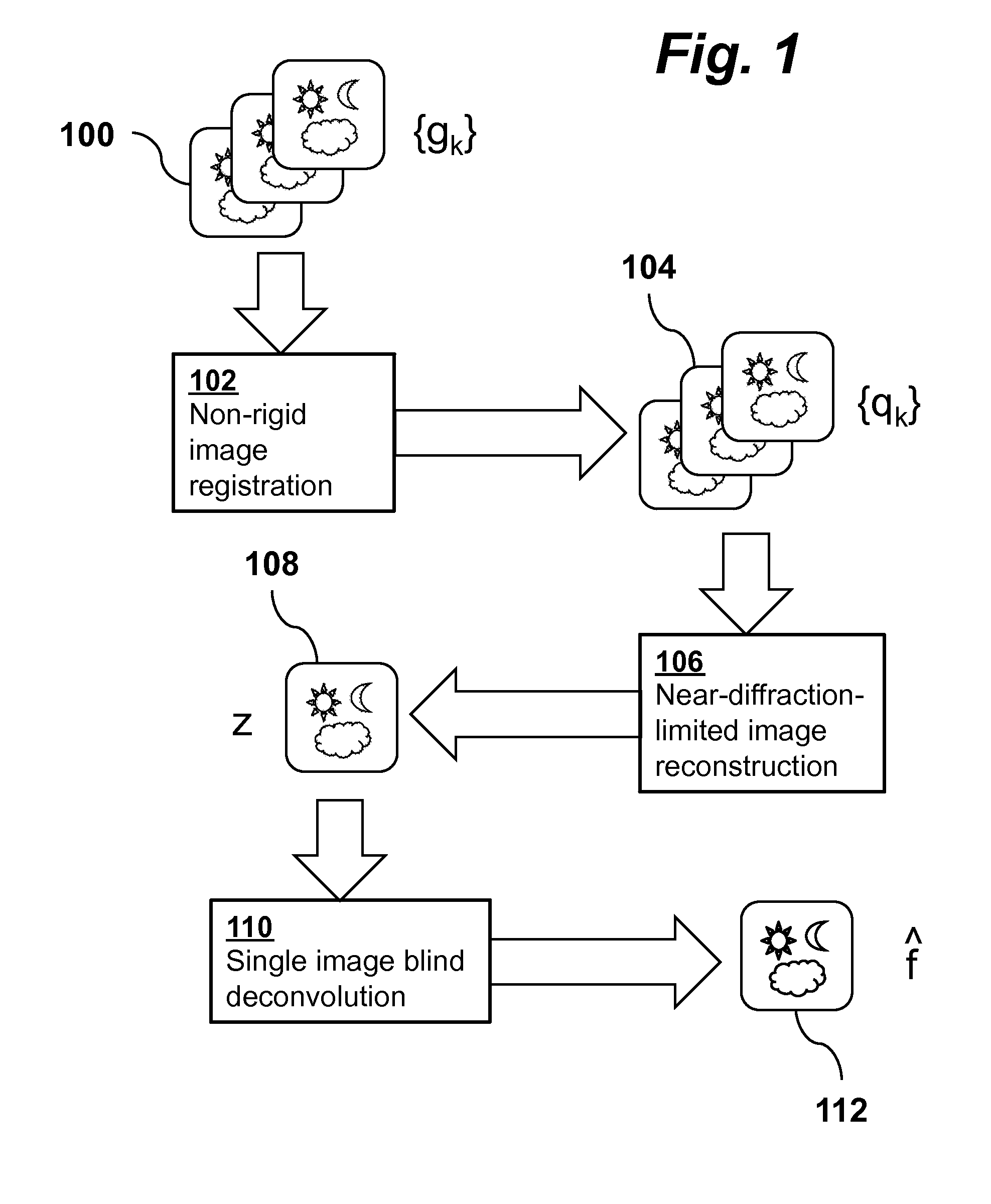
Stabilizing and Deblurring Atmospheric Turbulence
InactiveUS20140105515A1Reduce spatial variationAlleviating geometric deformationImage enhancementImage analysisSingle imageImage restoration
A method for image restoration and reconstruction registers each frame of an observed image sequence to suppress geometric deformation through B-spline based non-rigid registration, producing a registered sequence, then performs a temporal regression process on the registered sequence to produce a near-diffraction-limited image, and performs a single-image blind deconvolution of thenear-diffraction-limited image to deblur it, generating a final output image.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
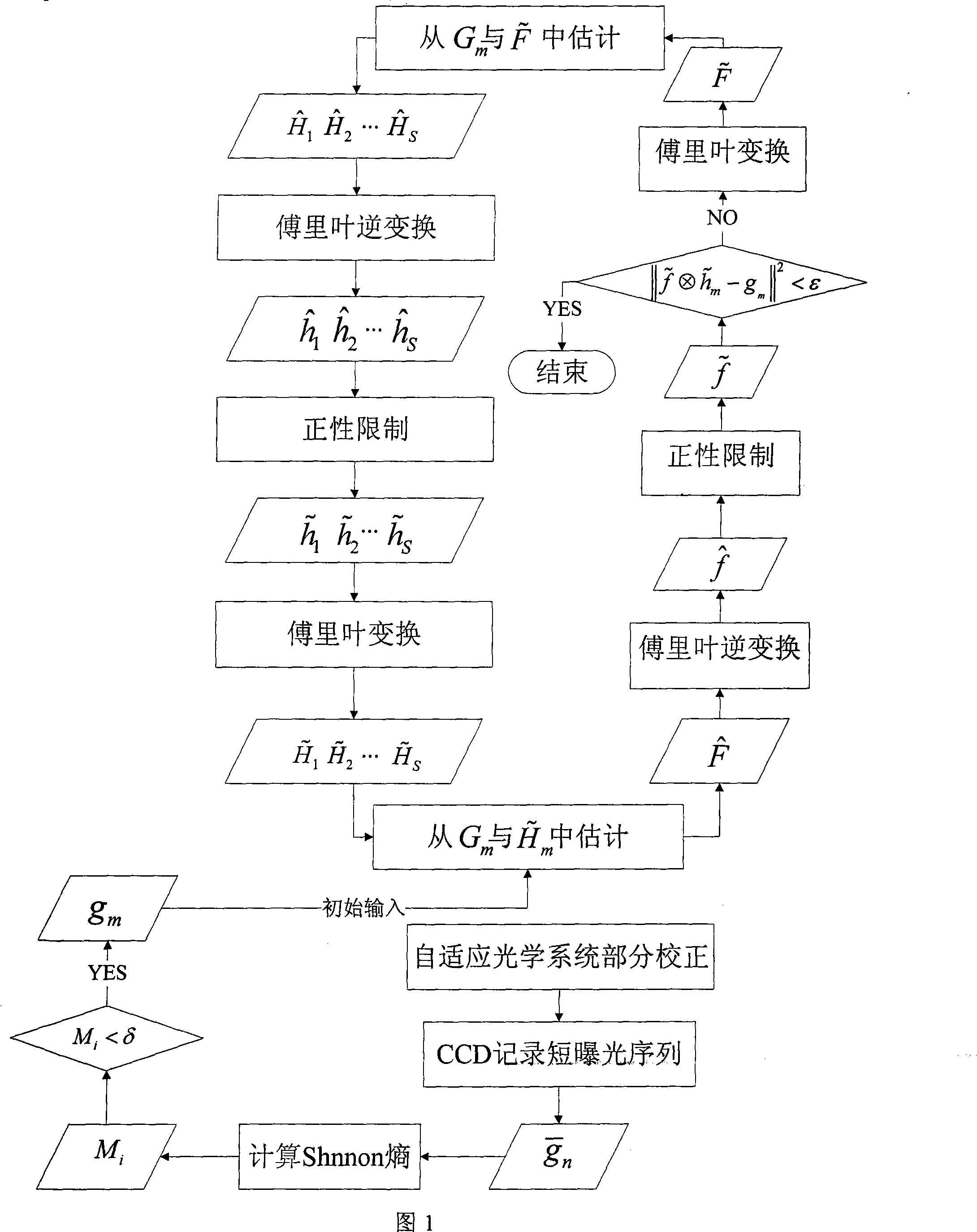
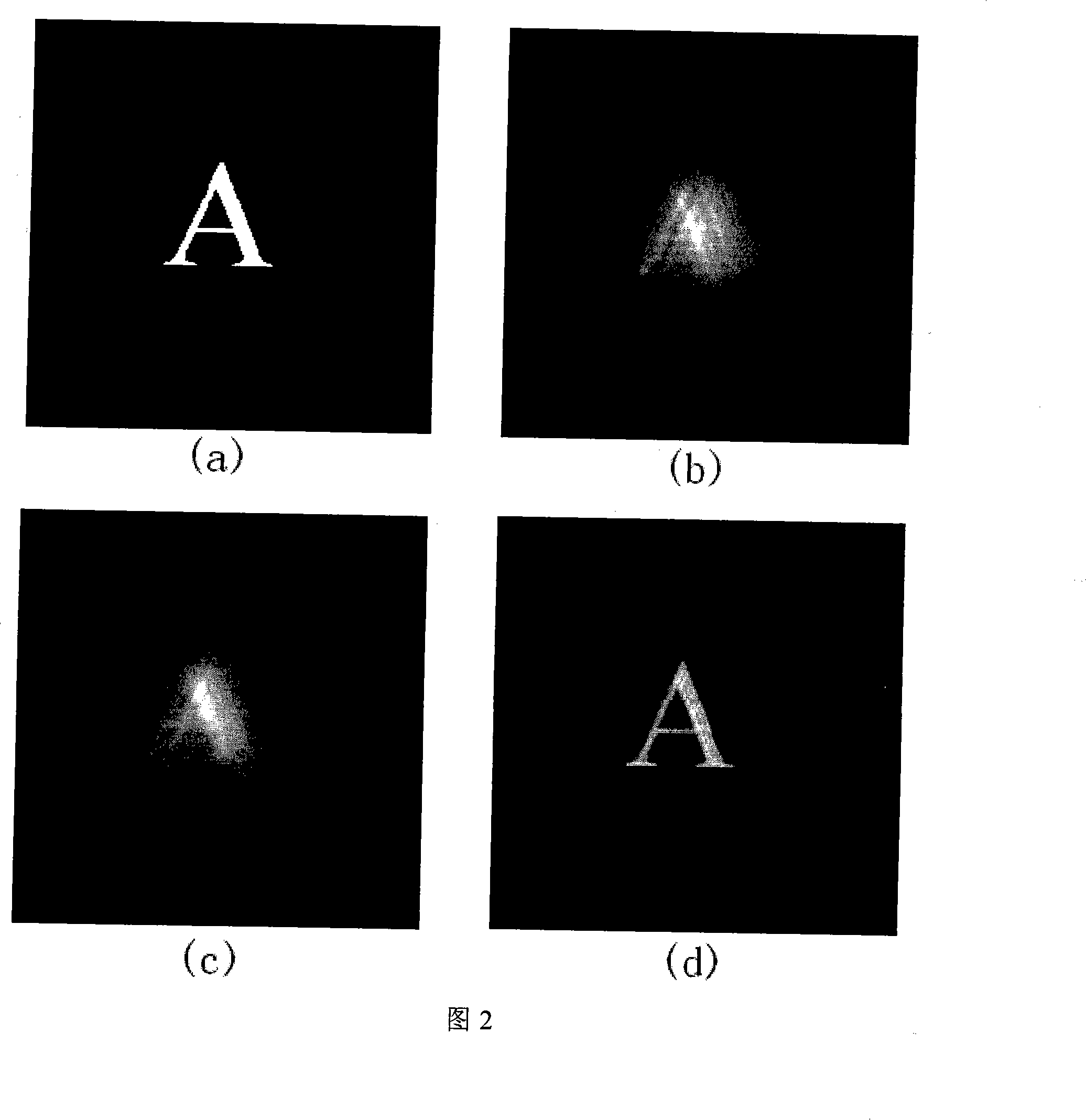
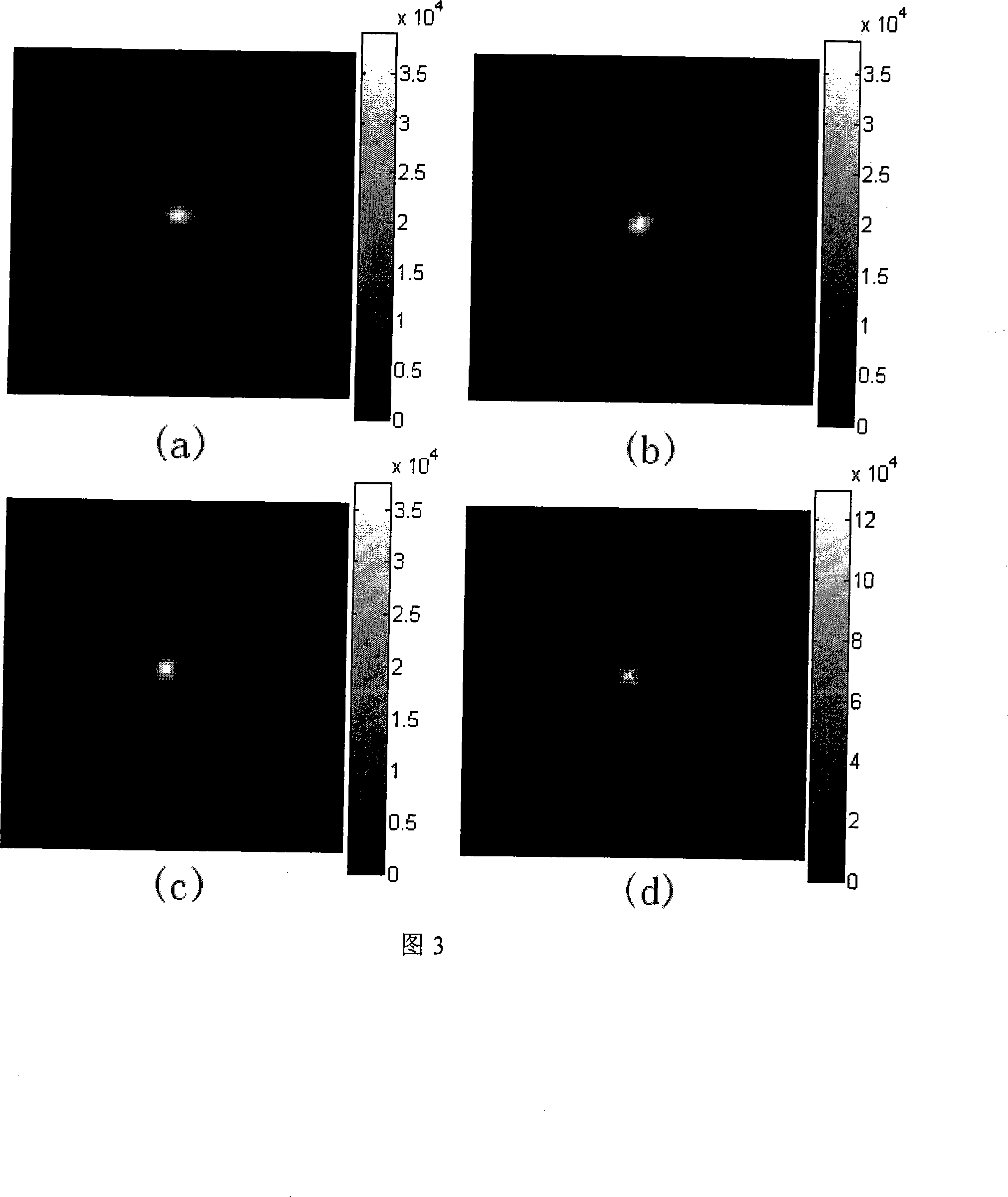
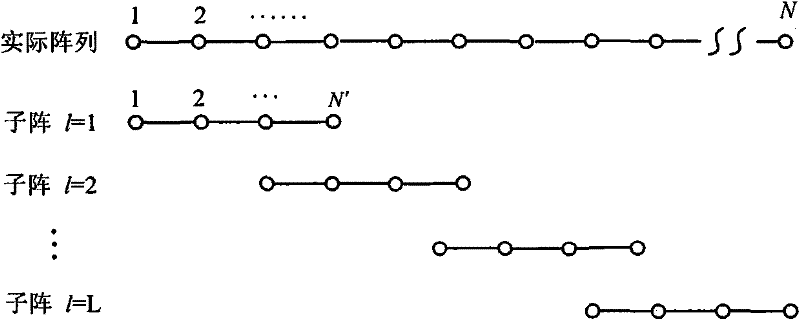
Self-adaption optical image high resolution restoration method combining frame selection and blind deconvohtion
InactiveCN101206762AFast convergenceAvoid the effects of true target restorationImage enhancementOptical measurementsImaging qualityDiffusion function
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Underwater sound signal blind deconvolution method suitable for shallow sea low-frequency conditions
InactiveCN102333052AEfficient extractionEfficient decompositionBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsDecompositionOptimal weight
The invention relates to an underwater sound signal blind deconvolution method suitable for shallow sea low-frequency conditions, which is technically characterized by comprising the steps of: estimating a horizontal wave number in a normal vibration mode from a horizontal array receiving signal by using a wave number estimation method, wherein the horizontal wave number is propagated in a waveguide; and then constructing one group of weight vectors according to the information of the estimated horizontal wave number in the normal vibration mode, and carrying out mode decomposition processing on the horizontal array receiving signal by using the weight vectors for recovering a source signal waveform. The restrain optimal weight vector in the invention can also be used for further improving deconvolution performance of the horizontal array manual time reversal blind deconvolution method provided by Sabra and the like.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Reconstruction method of atmospheric turbulence degraded images
The invention discloses a reconstruction method of atmospheric turbulence degraded images and aims to solve the technical problem that the image reconstructed and restored by the existing turbulence image reconstruction and restoration method is poor in sharpness. According to the technical scheme, the method includes firstly, performing multi-frame registration to eliminate distorted images; secondly, reconstructing a diffraction blurred image based on space-time neighborhood combination; and thirdly, performing globally uniform blind deconvolution to eliminate diffraction blur. According to the method, the influence upon artificial derivatives caused by registration errors and registration interpolation and the action upon the reconstructed observation object caused by space-dimensional and time-dimensional redundant structure information are fully considered, statistical dependency relationship of space-time similar image blocks and intra-block pixels to potential high-quality image content is established, corresponding sampling strategies are designed and used to select structurally similar high-quality image blocks, the diffraction blurred image is obtained by means of neighborhood combination, the diffraction blurred image is finally deblurred by the universal globally-uniform deconvolution, and accordingly a sharp reconstructed image is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Intelligent time-varying blind deconvolution broadband processing method and device
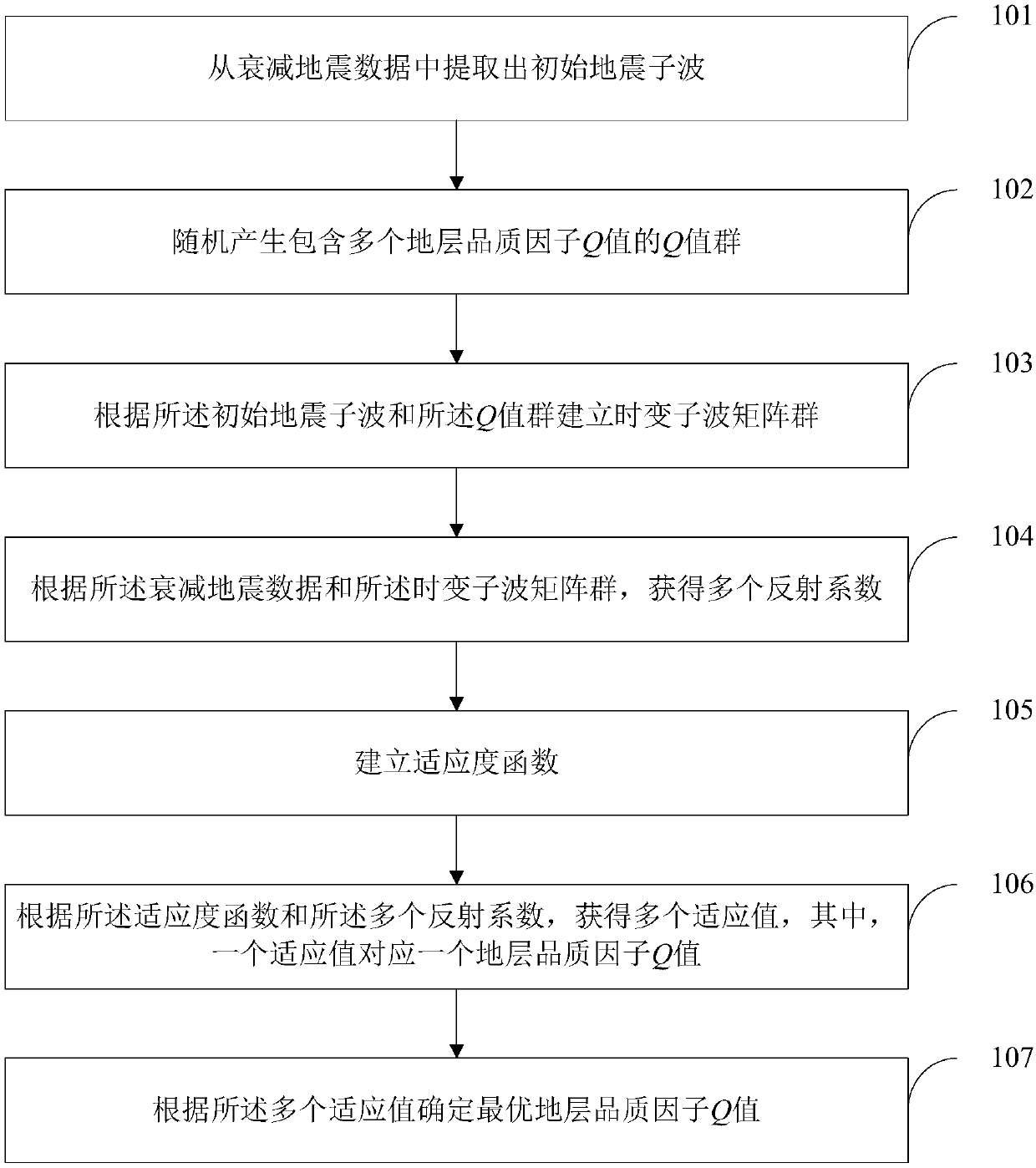
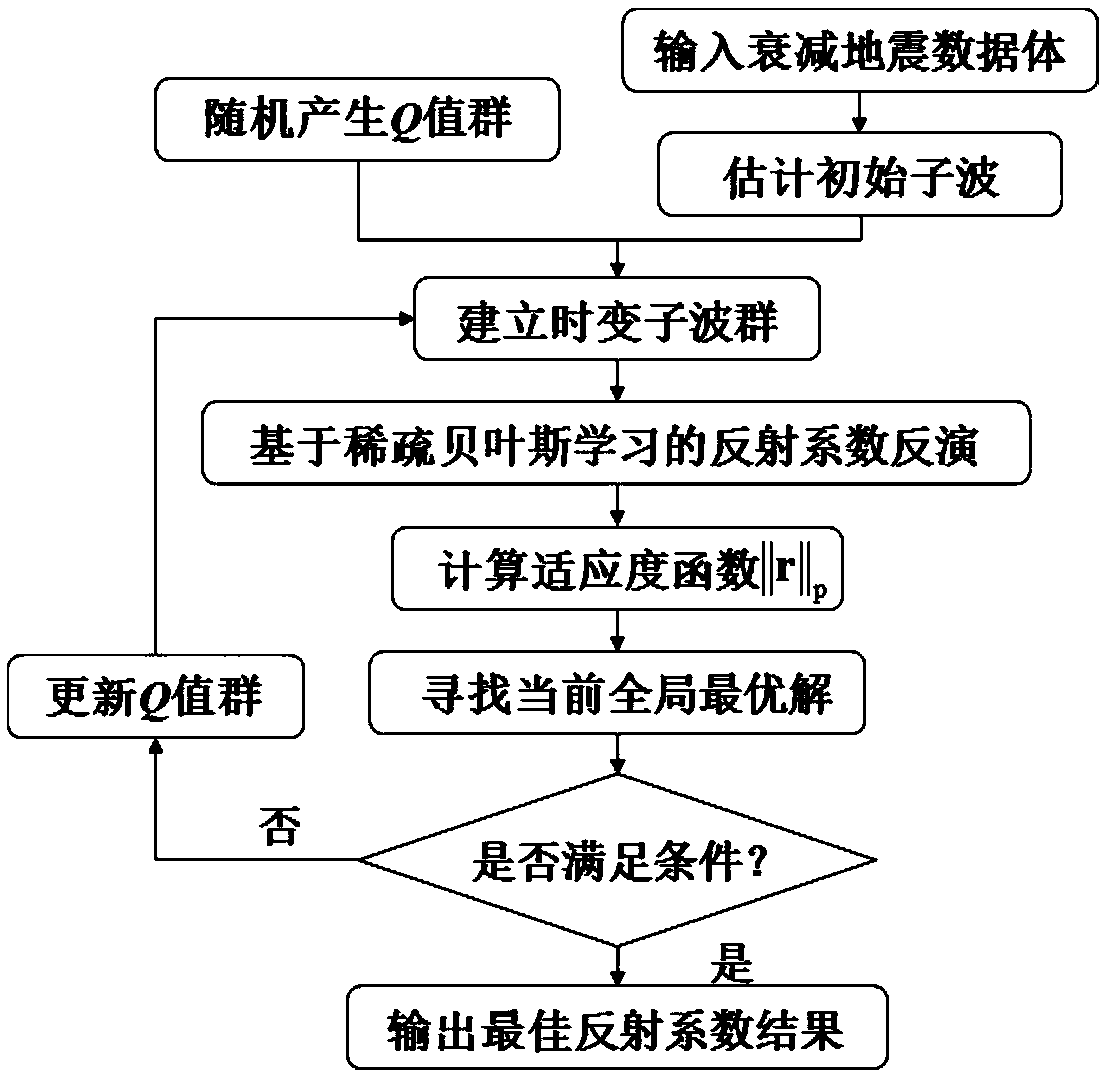
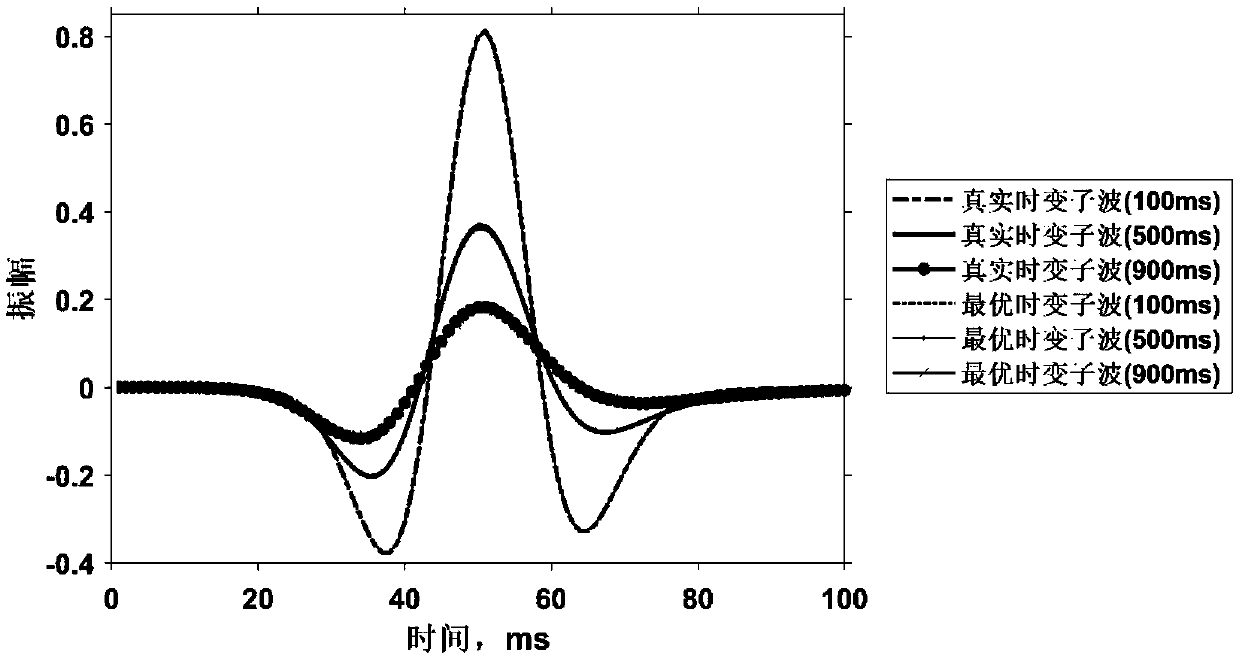
ActiveCN108693555AOptimal time-varying waveletUT blinded deconvolution resultsSeismic signal processingAlgorithmMatrix group
The invention provides an intelligent time-varying blind deconvolution broadband processing method and device. The method comprises: extracting an initial seismic wavelet from an attenuated seismic data; generating a Q value group including a plurality of stratum quality factors Q values randomly; according to the initial seismic wavelet and the Q value group, establishing a time-varying wavelet matrix group; acquiring a plurality of reflection coefficients according to the attenuated seismic data and the time-varying wavelet matrix group; establishing a fitness function; on the basis of the fitness function and the multiple reflection coefficients, acquiring a plurality of fitness values corresponding to the stratum quality factors Q values one by one; according to the multiple fitness values, determining an optimal stratum quality factors Q value. Because the optimal Q value is obtained by intelligent searching instead of manual determination, the work load and error occurrence are reduced, so that an optimal time-varying wavelet is estimated from unsteady data; and an optimal time-varying blind deconvolution result is obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Blind detection method for tampered image based on deconvolution
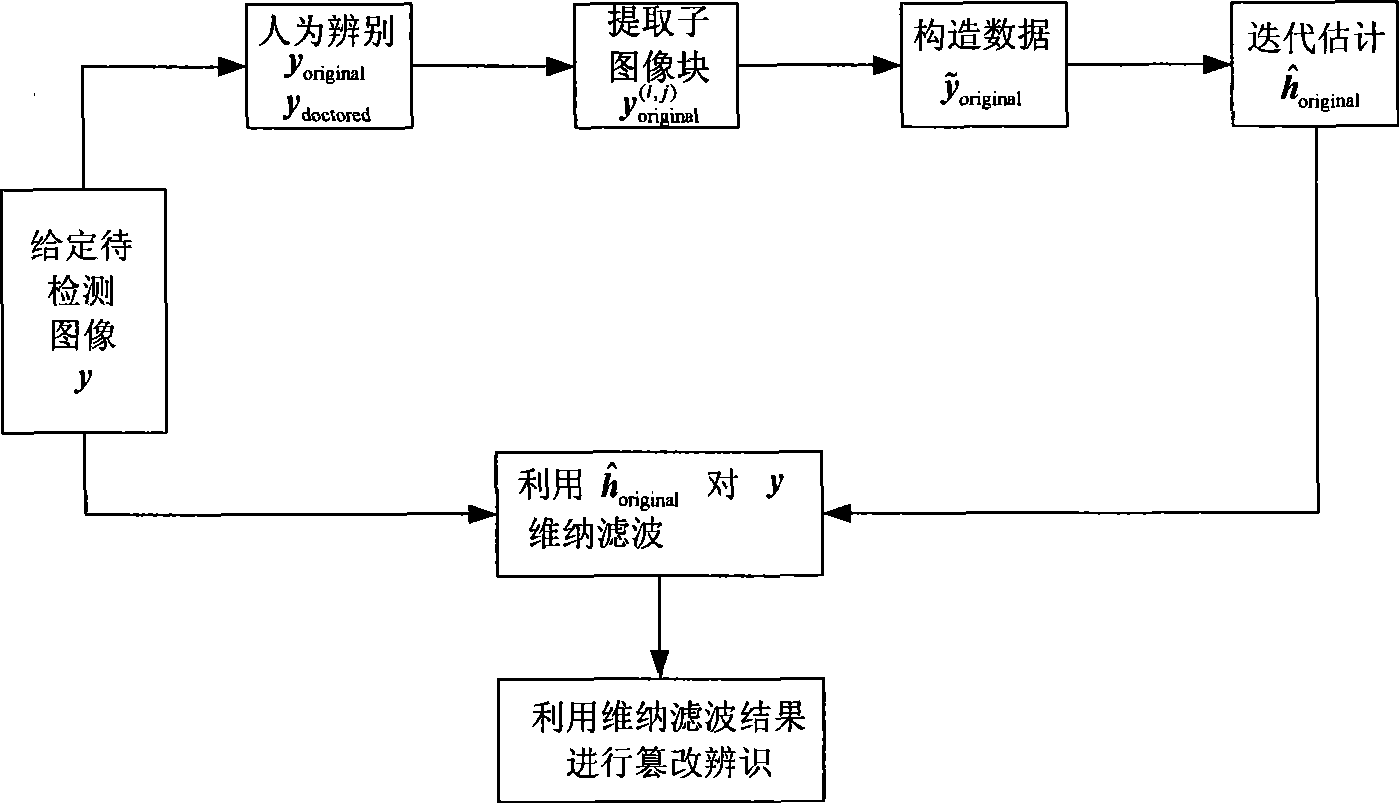
InactiveCN101452568AHighlight the tampered partSimple methodImage data processing detailsInformation securityWiener filter
The invention discloses a deconvolution-based tampered image blind detection method and belongs to the field of image information safety. The method uses deconvolution and Wiener filtering techniques to realize the blind detection of blurred and tampered images. The method comprises: firstly, manually and initially determining the position of the tampered region of an image to be detected; secondly, extracting a plurality of subimages of the rest region which is not tampered and building a data block approximately meeting a complete convolution relation by using the plurality of subimages; estimating a blurring function of the region which is not tampered from the data block by an alternant interactive blind deconvolution method; and finally, using the estimated blurring function to carry out Wiener filtering to the whole image and using the filtering results to identify whether or not the image to be detected is tampered and the concrete tampered region. The method is simple and effective and has certain application prospect in the field of image information safety.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
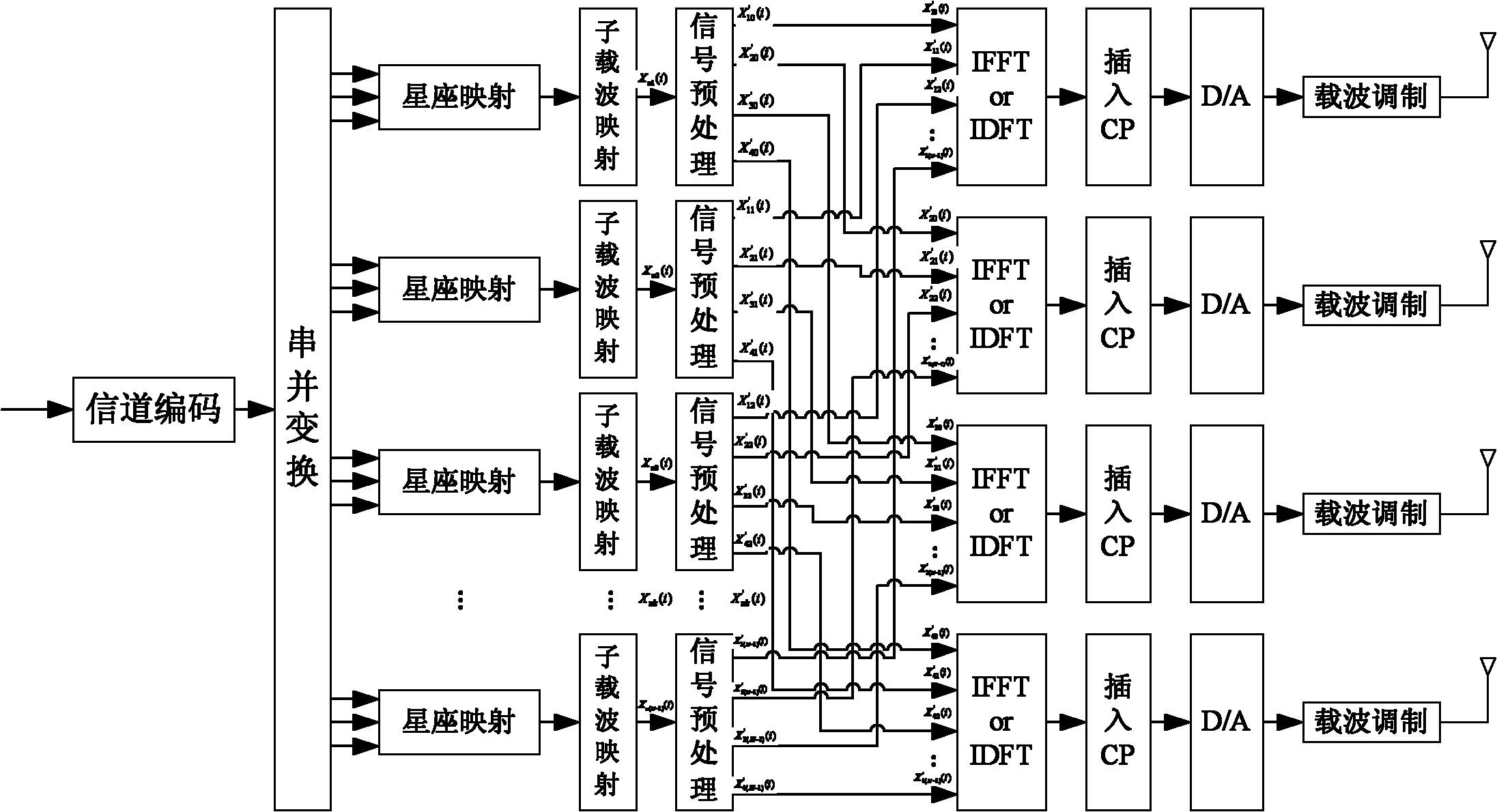
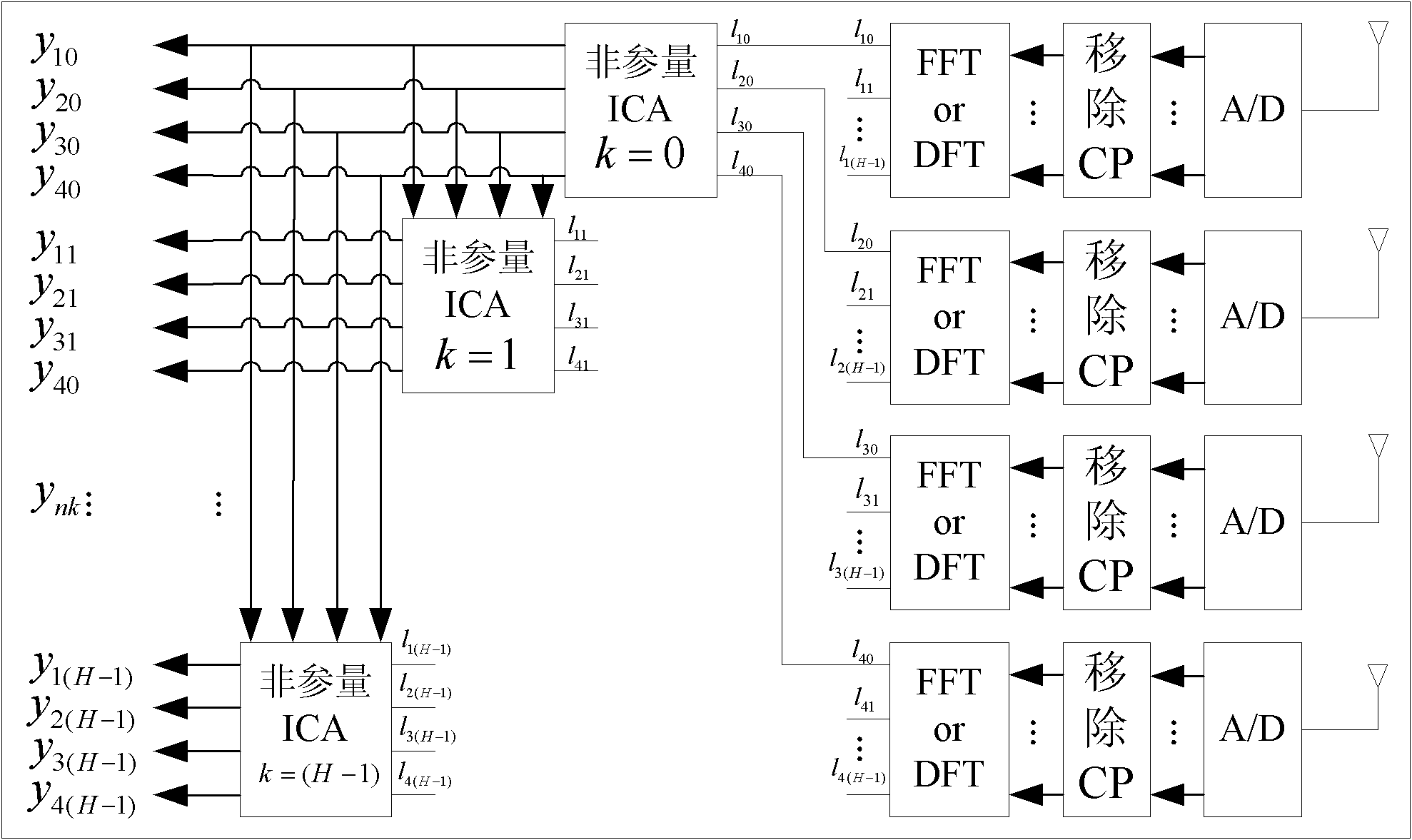
Nonparametric estimation ICA-based MIMO-OFDM system blind deconvolution method
InactiveCN102025459ASave Spectrum ResourcesSmall amount of calculationBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumComputer science
The invention discloses a nonparametric estimation independent component analysis (ICA)-based multiple input multiple output-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM) system blind deconvolution method. The method comprises the following steps of: combining nonparametric estimation ICA and MIMO-OFDM; arranging a signal preprocessing module at a transmitting end of the MIMO-OFDM system to perform non-redundant linear precoding on a frequency domain signal mapped to a subcarrier so as to eliminate fuzziness of an independent component analysis algorithm in reconstructed signal sorting and energy; and arranging a nonparametric ICA module at a receiving end of the system to perform channel estimation so as to restore a source signal. By the method, frequency spectrum resource is saved, the amount of calculation is reduced, the operational speed is increased and a time-varying channel can be estimated well.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
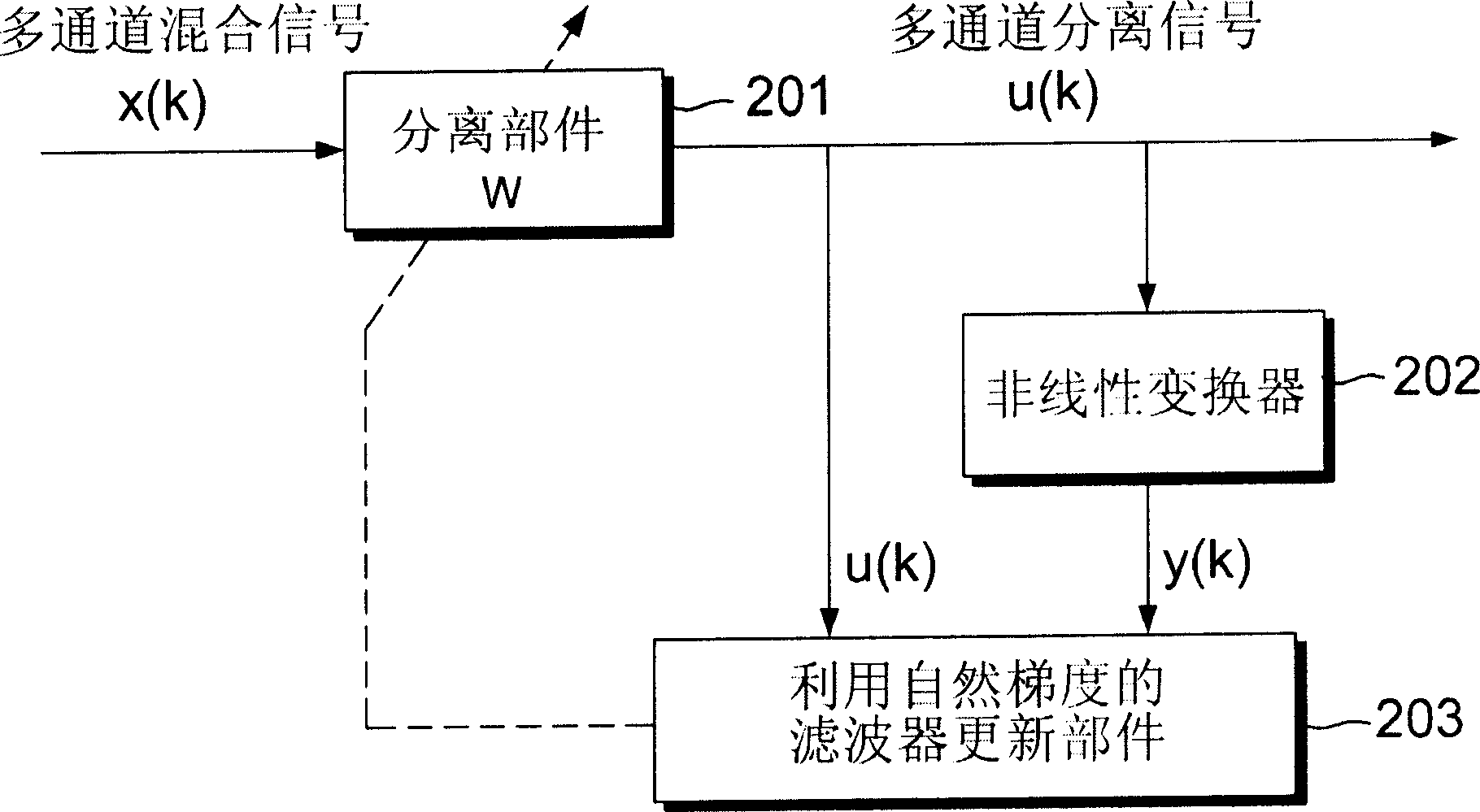
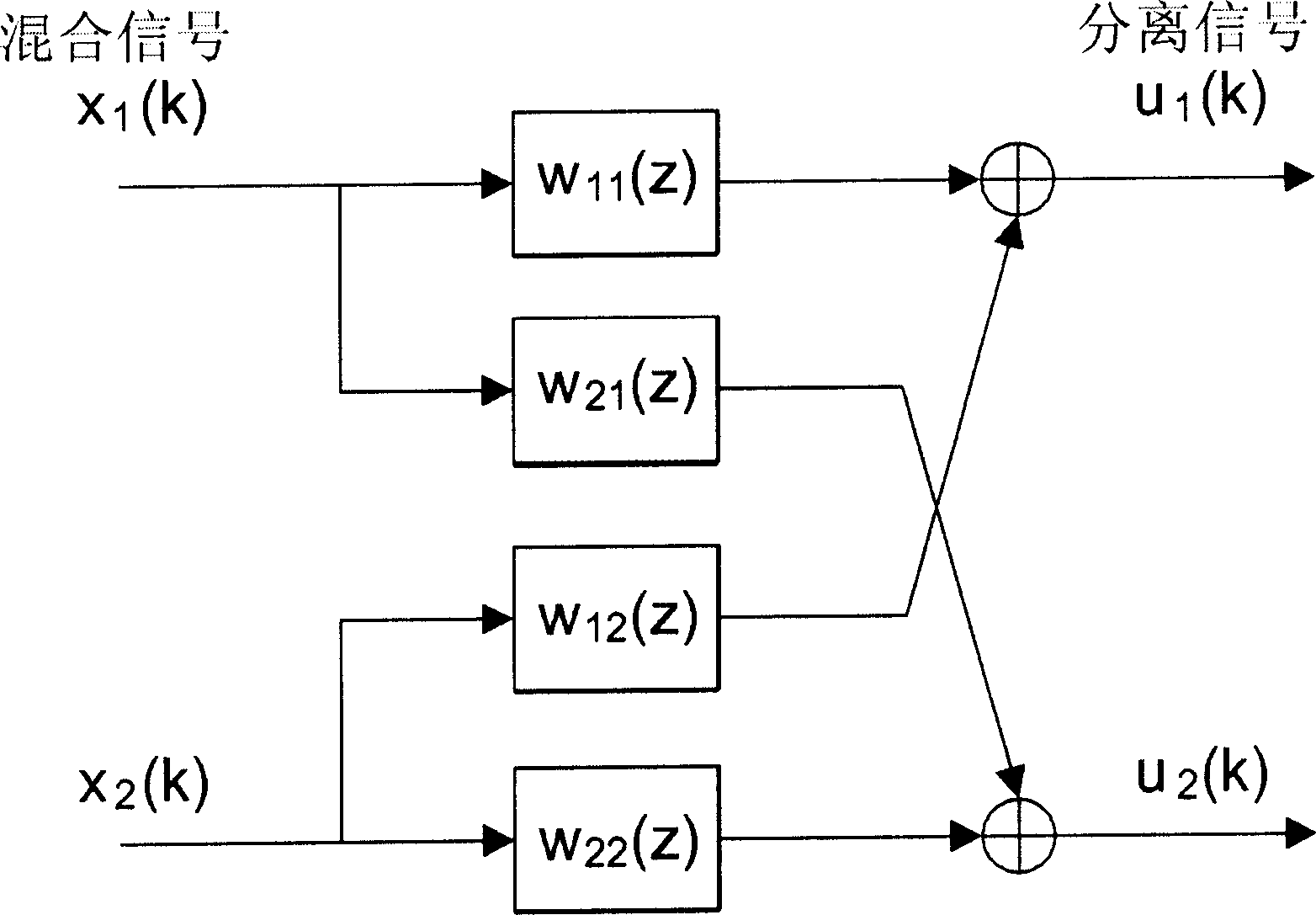
Methods and apparatus for blind separation of multichannel convolutive mixtures in the frequency domain
A method and apparatus is disclosed for performing blind source separation using frequency-domain normalized multichannel blind deconvolution. The multichannel mixed signals are formed as frames of N samples, which consist of r consecutive blocks of M samples. The frames of mixed signals are separated using separating filters in the frequency domain in an overlap-save manner using a discrete Fourier transform(DFT). The separated signals are then converted back into the time domain using the inverse DFT to be applied to a nonlinear function. The cross-power spectra between separated signals and nonlinear-transformed signals are computed and are normalized by the power spectra of separated signals and the power spectra of nonlinear-transformed signals to have flat spectra. The invention then applies the time domain constraint to preserve the first L cross-correlations. These alias-free normalized cross-power spectra are further constrained by nonholonomic constraints. The invention then computes natural gradient by convolving alias-free normalized cross-power spectra with separating filters. After the length of separating filters is constrained to L, separating filters are updated using the natural gradient and normalized to have unit norm. The terminating conditions are checked to see if separating filters converged.
Owner:南 承铉
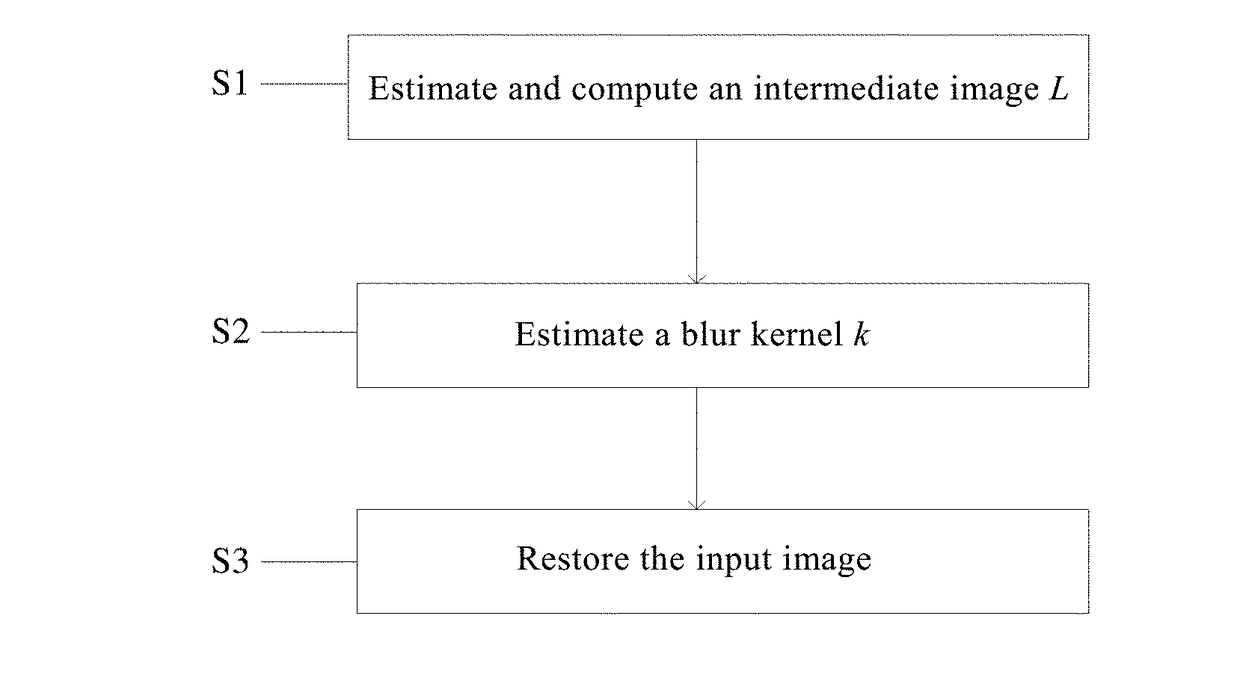
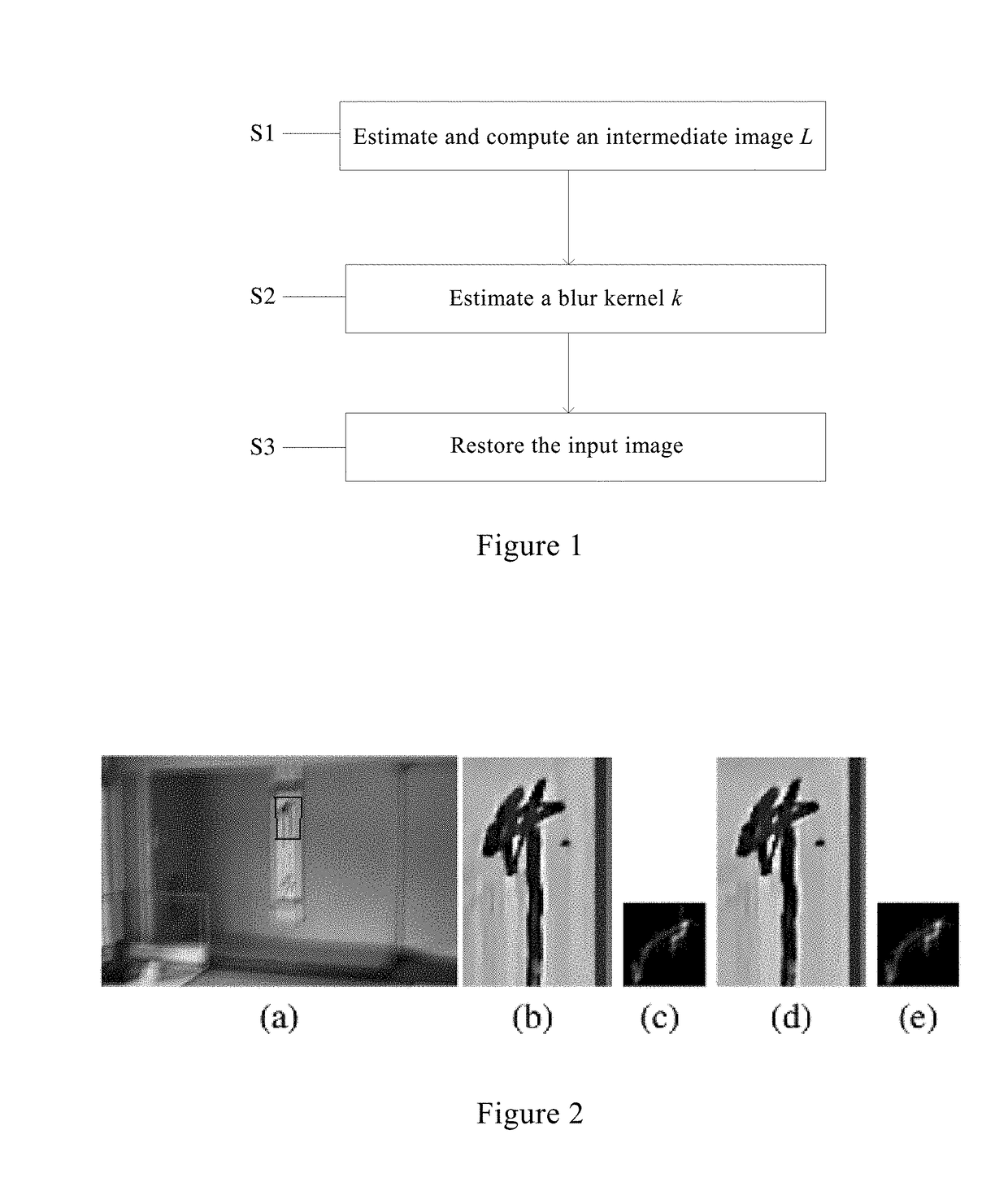
Method and system for image de-blurring
ActiveUS20180137606A1Effectively removing noiseAccurate estimateImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionIntermediate image
A method for image de-blurring includes estimating an intermediate image L by marking and constraining an edge region and a smooth region in an input image; estimating a blur kernel k by extracting salient edges from the intermediate image L, wherein the salient edges have scales greater than those of the blur kernel k; and restoring the input image to a clear image by performing non-blind deconvolution on the input image and the estimated blur kernel k. Imposing constraints on the edge region and the smooth region allows the intermediate image to maintain the edge while effectively removing noise and ringing artifacts in the smooth region. The use of the salient edges in the intermediate image L enables more accurate blur kernel estimation. Performing non-blind deconvolution on the input image and the estimated blur kernel k restores the input image to a clear image achieving desired de-blurring effect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
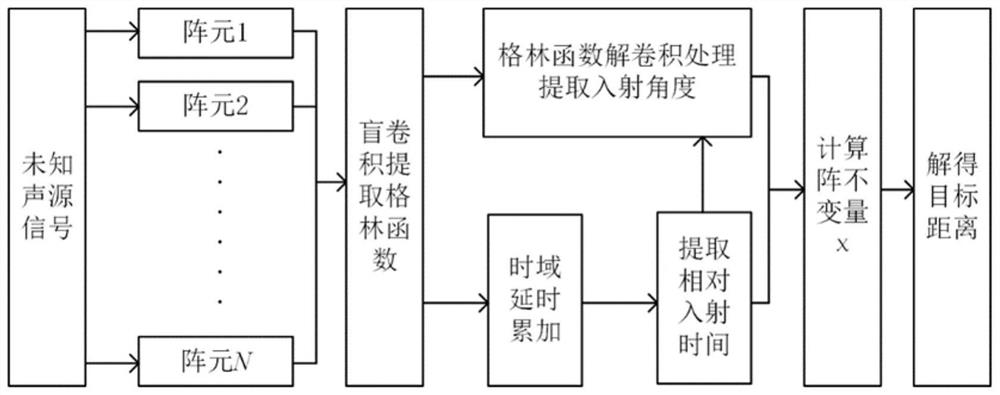
Shallow sea horizontal array passive positioning method and system based on spatial domain deconvolution processing
PendingCN112098983AHigh passive positioning accuracyHigh passive target positioning accuracyWave based measurement systemsSound sourcesFrequency spectrum
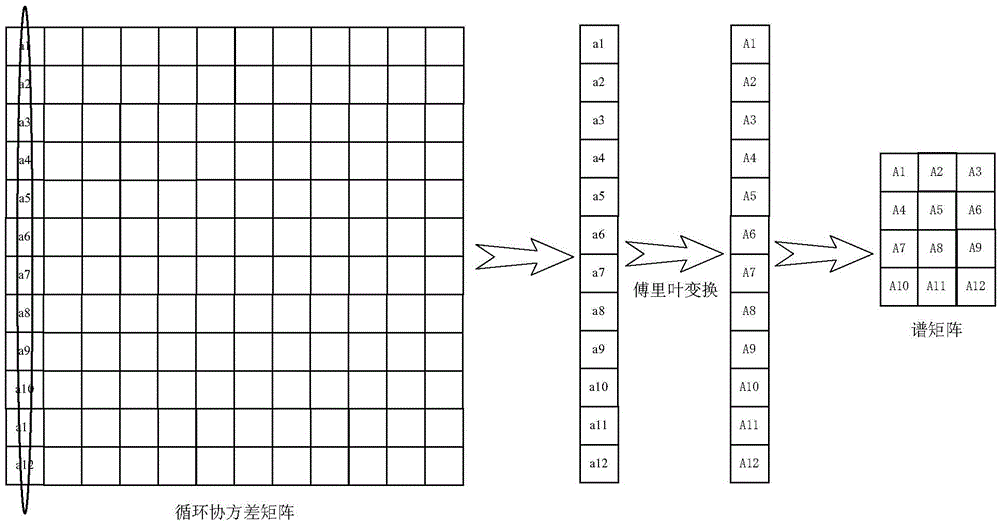
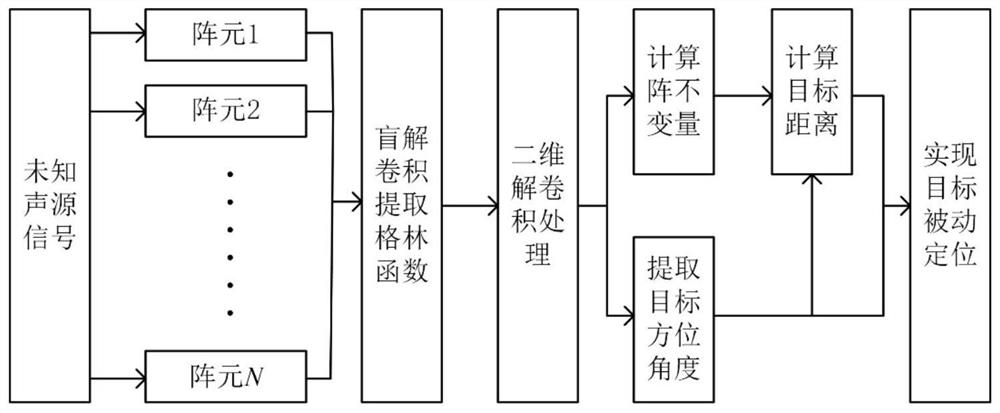
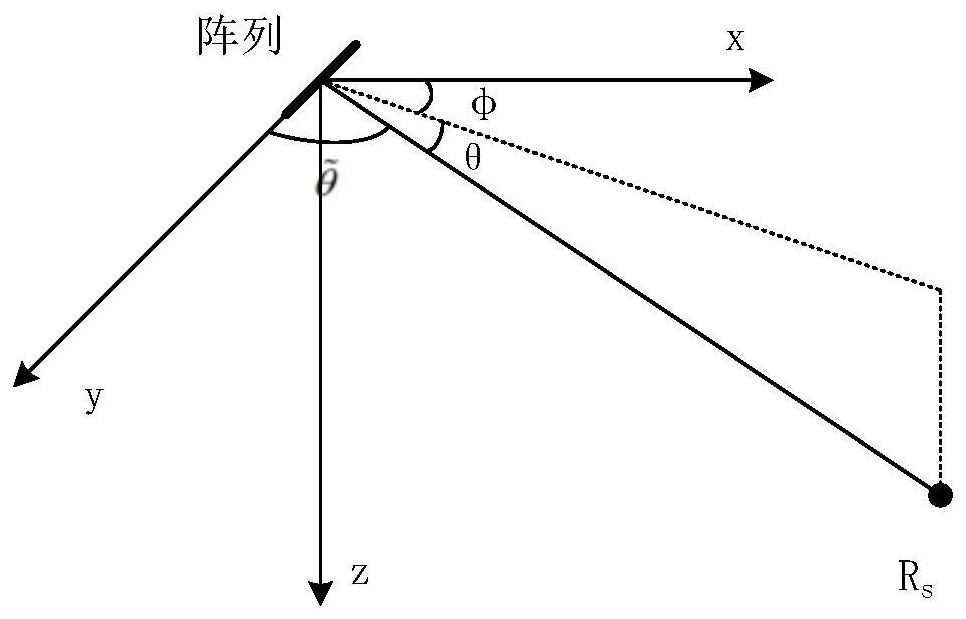
The invention discloses a shallow sea horizontal array passive positioning method and system based on spatial domain deconvolution processing, and the method comprises the steps: receiving a radiationsignal of a target sound source in an underwater sound field through an N-element horizontal uniform linear array, and obtaining a received signal frequency spectrum of each array element through thefrequency spectrum analysis of a sound pressure signal collected by a hydrophone; obtaining an estimated value of a frequency domain Green function through blind deconvolution calculation according to the frequency spectrum of the received signal; carrying out inverse Fourier transform on the estimated value of the frequency domain Green function, extracting target multipath relative incident time from the obtained array element time domain Green function, and then calculating a target multipath incident angle through a deconvolution processing method; calculating to obtain an array invariantaccording to the target multipath incident angle; and calculating the distance of the target sound source according to the array invariant, thereby realizing positioning of the target sound source. According to the method, steady passive positioning under the shallow sea small-aperture horizontal array condition is realized, and higher passive positioning precision is obtained under the conditionthat the calculated amount is not remarkably increased.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Removing Blur from an Image
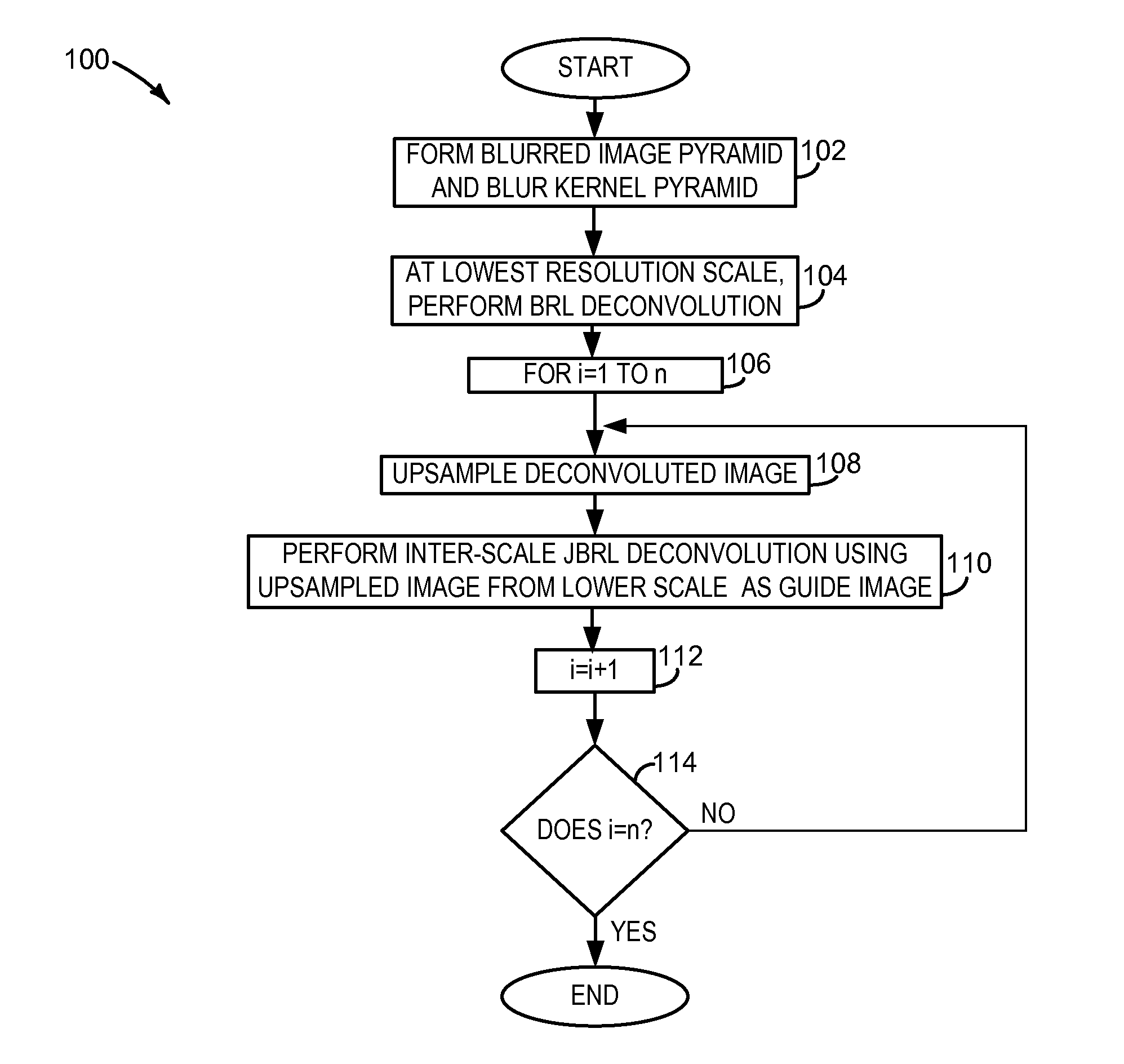
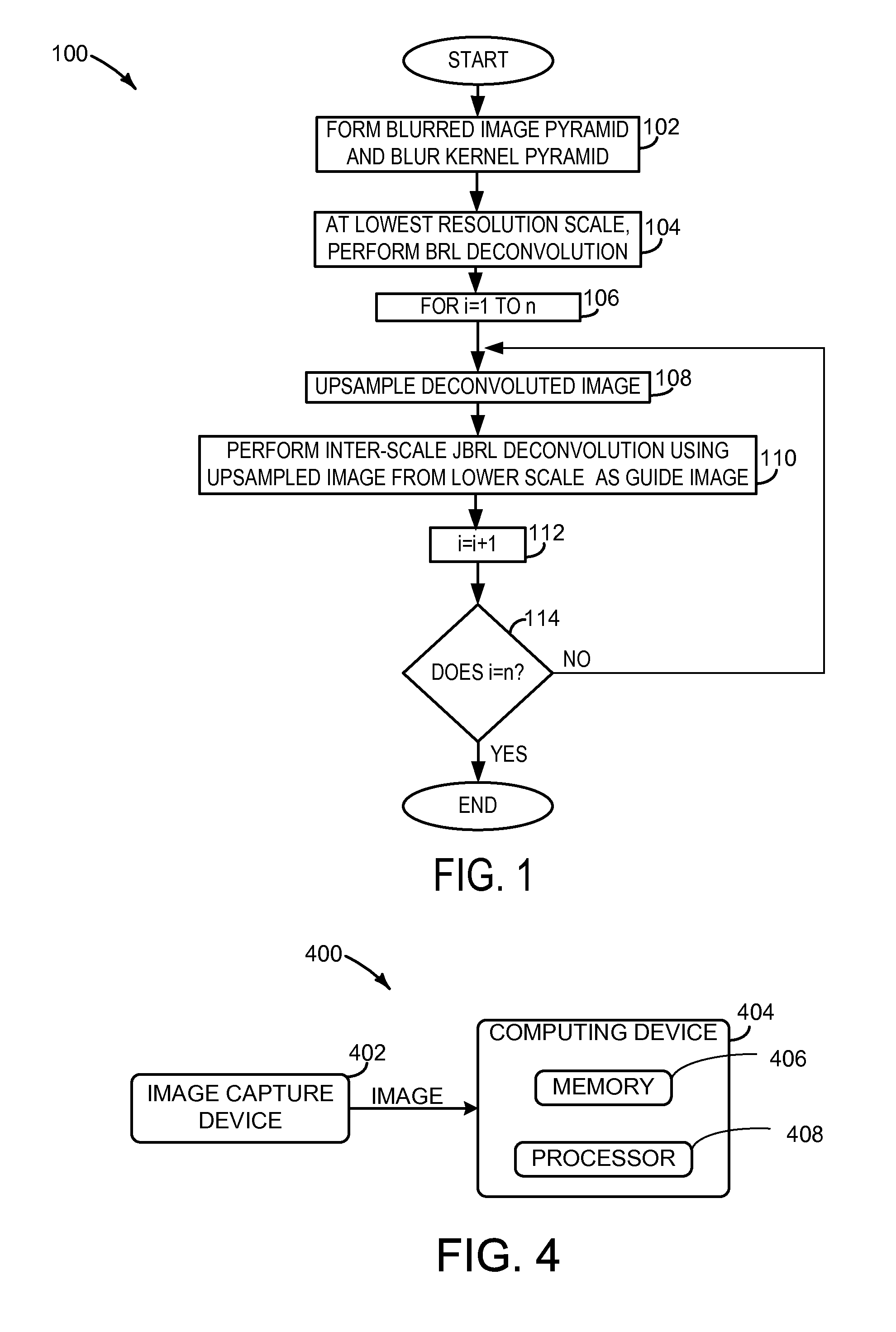
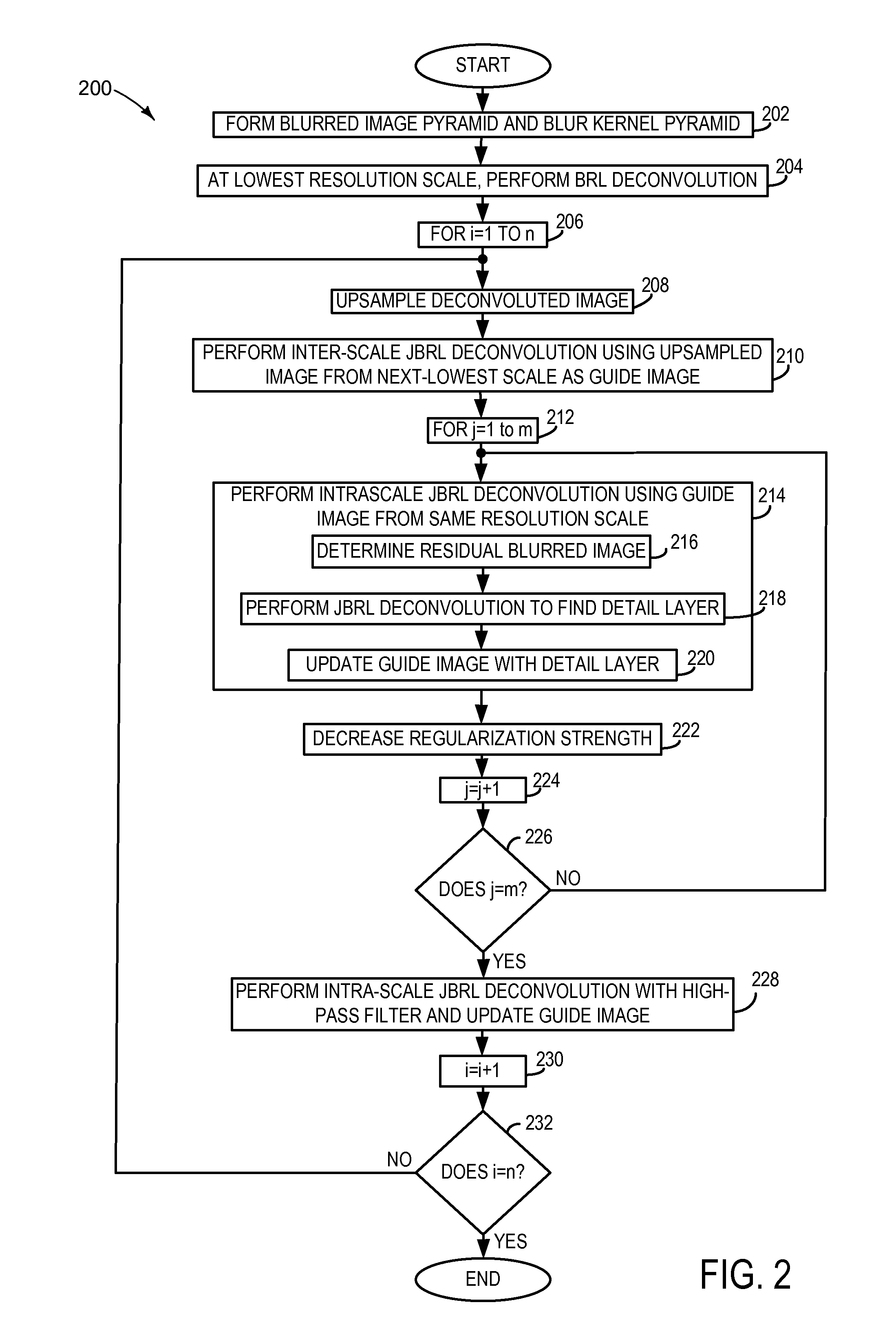
ActiveUS20130223754A1Well formedImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionRichardson–Lucy deconvolution
Embodiments related to the removal of blur from an image are disclosed. One disclosed embodiment provides a method of performing an iterative non-blind deconvolution of a blurred image to form an updated image. The method comprises downsampling the blurred image to form a blurred image pyramid comprising images of two or more different resolution scales, downsampling a blur kernel to form a blur kernel pyramid comprising kernels of two or more different sizes, and deconvoluting a selected image in the blurred image pyramid according to a Richardson-Lucy deconvolution process in which a bilateral range / spatial filter is employed.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
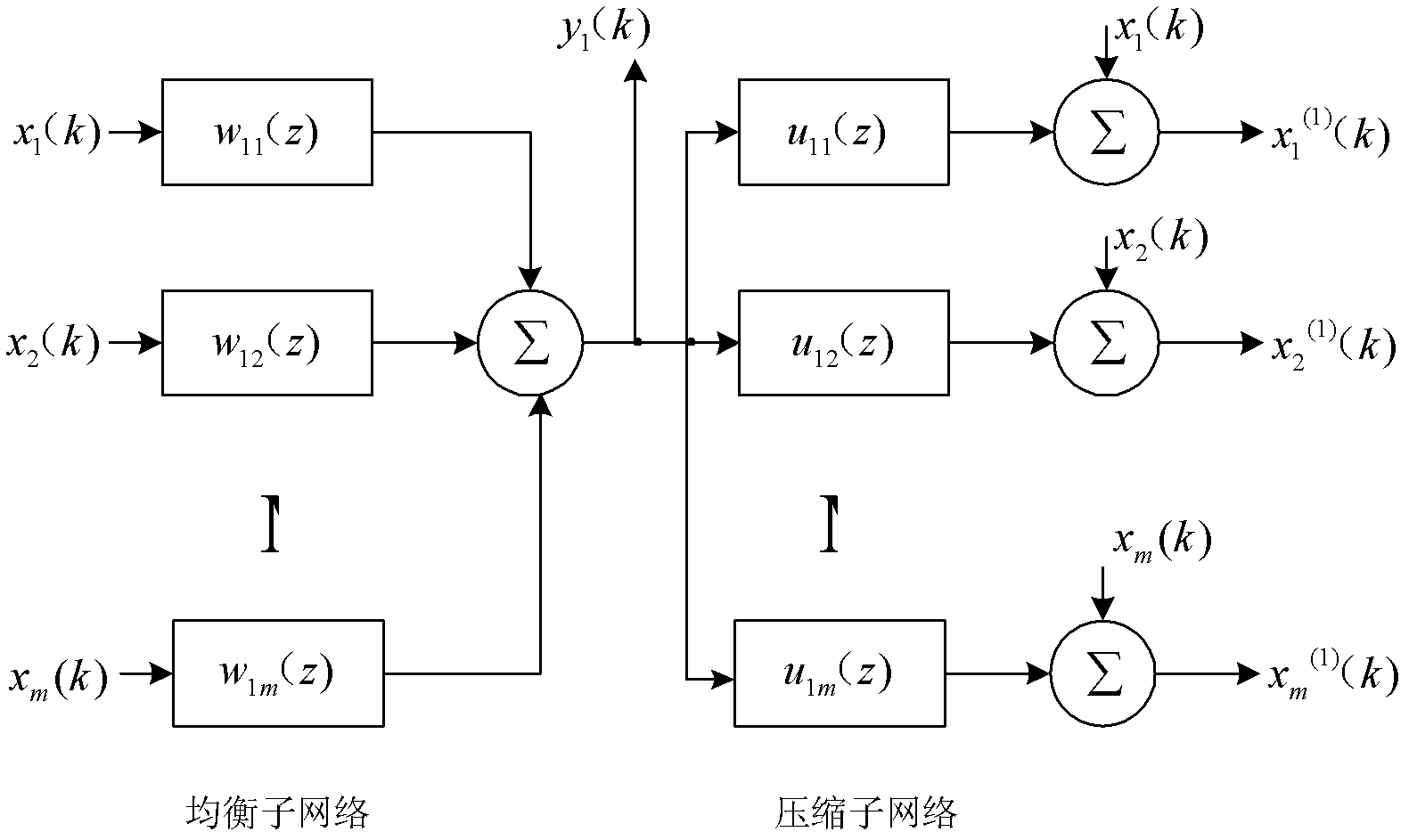
Method for multi-channel blind deconvolution on cascaded neural network
InactiveCN102546128AEasy extractionSimple methodTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError prevention/detection by diversity receptionSynapseBlind equalization algorithm
The invention provides a method for multi-channel blind deconvolution on a cascaded neural network. The method comprises the following steps: (1) forming a module neural network by a balanced sub-network and a compressed sub-network; (2) updating a nerve synapse {wlj,p} of the balanced sub-network by using a constant model algorithm; (3) constituting Hebbian and inverse Hebbian learning rules; and (4) after compression, inputting to the balanced sub-network of a next module network. The method disclosed by the invention is an expansion of a method which is novel, simple and individually effective, and can be used for effectively extracting a plurality of source signals online from unknown and staggered mixed signals, namely each module of the cascaded neural network is composed of the balanced sub-network and the compressed sub-network. The method disclosed by the invention can be applicable to any blind equalization algorithm (an extension of signal channel equalization) and further can be applied to a condition that the quantity of the source signals is unknown in advance. The method disclosed by the invention is easy to realize and can be widely applied to aspects of wireless communication, array processing, biomedical signal processing and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG BAIYUN UNIV
Ultrafast recovery method and system for twin image of pneumatic optical effect target
ActiveCN113793285AFast recoveryDesensitizationImage enhancementDiscrete Fourier transformRinging effect
The invention discloses an ultrafast restoration method for a target twin image based on an aerodynamic optical effect, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, rapidly generating two frames of target twin images through a camera in a high-speed flow field; S2, carrying out fast discrete Fourier transform on the two frames of target twin images, and establishing image turbulence fuzzy degradation models respectively; S3, merging and calculating the two image turbulence fuzzy degradation models, eliminating the same noise item and the same item in the degradation model, adding a non-negative constraint item and a spatial correlation constraint item, and solving to obtain a fuzzy kernel of each frame of target twin image; S4, respectively carrying out differential continuous continuation on the boundaries of the two frames of target twin images, and inhibiting a boundary ringing effect; S5, according to the solved blurring kernel, carrying out the restoration of two frames of target twin images through a fast non-blind deconvolution method of super-Laplacian prior; and S6, normalizing the restored images to obtain clear images. According to the method, ultrafast restoration can be carried out on the aerodynamic optical effect degraded image with the target twin image.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Frequency-domain blind deconvolution method for voice signal
InactiveCN102760435AEasy to separateImprove the accuracy of speech signal recognitionSpeech recognitionTime domainInteraction systems
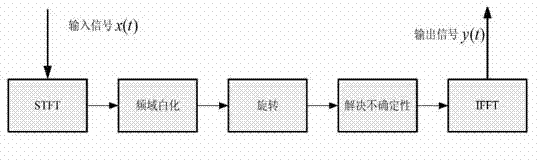
The invention discloses a frequency-domain blind deconvolution method for a voice signal, comprising the following steps of: converting a time-domain convolution mixed voice signal to a frequency domain and then performing blind separation; converting and transforming the time-domain convolution mixed voice signal to a frequency-domain linear instantaneous mixture model via windowed Fourier transform according to the short-time stability of the voice signal; after performing pre-processing such as filtering and whitening in the frequency domain, realizing segmented blind separation for the voice signal by adopting a method of the approximate joint diagonalization of correlation matrices under different time delays; and after solving the problem of the fuzziness of the blind separation for the signal, performing segmented recombination for the separated signals in the time domain via inverse Fourier transform. Via the frequency-domain blind deconvolution method disclosed by the invention, a good separation effect is realized for 2*2 real-time recoded mixed voice signal, and the recognition accuracy of the voice signal of a human-computer interaction system in an environment with the speech interference of other people can be efficiently improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
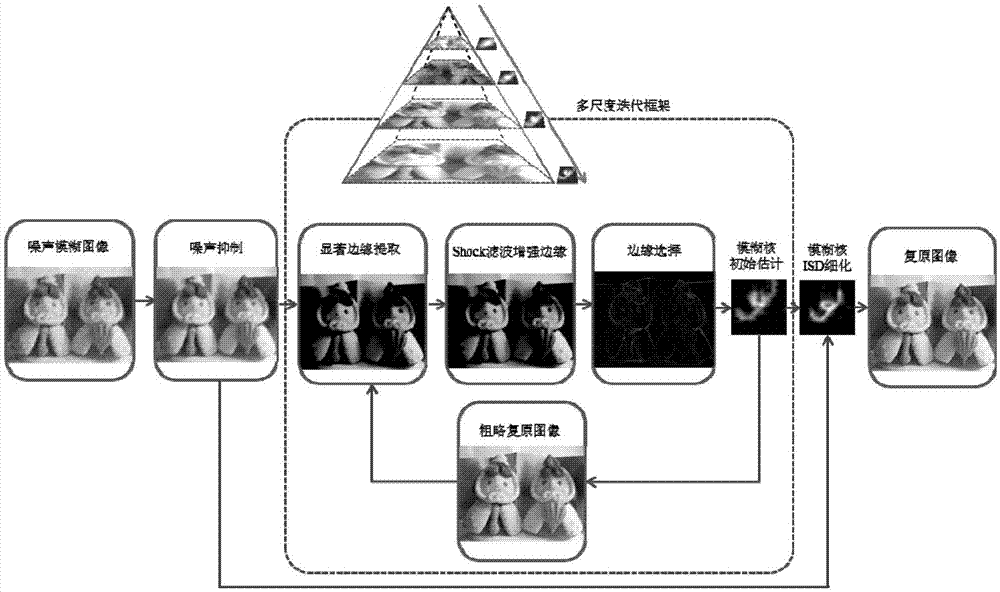
Noise blurred image blind deconvolution method based on image significant structure
InactiveCN106960417AEasy to handleAccurate estimateImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionEdge extraction
The invention discloses a noise blurred image blind deconvolution method based on an image significant structure. The noise blurred image blind deconvolution method comprises steps that to-be-deblurred image data is input; the denoising pre-treatment of the input image data is carried out; the significant edge extraction of the image after the denoising pre-treatment is carried out; an image strong edge is reconstructed by carrying out the Shock filtering of the image after the significant edge extraction; the image significant edge used for blurred kernel estimation is calculated by using the image strong edge; an initial blurred kernel is estimated; the rough image restoration is carried out by using the estimated initial blurred kernel; the blurred kernel based on ISD after the rough image restoration is corrected; and the image is restored. The problem of the image deblurring sensitive to noises is solved, and the blurred kernel of the noise blurred image is estimated accurately, and high quality restored image is provided.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image resampling operation detection method
ActiveCN106709915ALow dimensionality of detection featuresReduce training timeImage analysisGeometric image transformationSupport vector machineEuclidean vector
The invention relates to an image resampling operation detection method. The method comprises the steps of representing image resampling operation by using a model; carrying out initial blind deconvolution operation on a resampled image to obtain an initial kernel; working out initial kernels with different sizes so as to obtain a group of convolution kernel sets with multiple scales and different sizes; comparing a result, obtained by carrying out convolution on one convolution kernel in the convolution kernel sets and an original image corresponding to the convolution kernel, with the resampled image, wherein the convolution kernel with the minimum mass difference is an optimal kernel, namely, system output; unfolding the optimal kernel to obtain a column vector; putting the obtained column vector into in a classifier for training a model to obtain a classification model; repeating the step 2 to the step 5 for the image to be detected, and putting the obtained column vector into the classification model obtained in the step 6 for testing so as to obtain a final detection result. The image resampling operation detection method can effectively reduce the training time of the support vector machine (SVM) classifier. Furthermore, the method in high in compression resistance, and has excellent detection accuracy rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Multilayer Bayes blind deconvolution method for SAR image based on frequency domain and spectrum matrix
InactiveCN105551007AImprove processing efficiencyFast operationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionPoint spread function
The invention discloses a multilayer Bayes blind deconvolution method for an SAR image based on a frequency domain and spectrum matrix, and the method comprises the steps: inputting and observing the SAR image g, and giving an observation model; initializing an original SAR image f and a point spread function h as f<0> and h<0>, and giving a prior model; initializing hyper-parameters of the model, setting a confidence value, and giving a prior model; carrying out the zero extending and cyclic shift of a mask, h and h<0> of the prior model as c<es>, h<es>, and h<0><es>, and carrying out the conversion of c<es>, h<es>, and h<0><es> and the image into the frequency domain; constructing and initializing a spectrum matrix through the spectrums of cycle covariance matrixes of f and h<es>; optimizing random distribution to iterate and estimate hyper-parameters, frequency domain h<es> and frequency domain f; converting the frequency domain to a spatial domain, carrying out shifting and zero removing, and outputting the final result of blind deconvolution. The method saves a process of vectoring and matrixing, so as to avoid high-cost superlarge matrix operation. The method employs the frequency domain to represent the vectors and matrixes, employs the spectrums of the matrixes to construct the spectrum matrix, achieves the deconvolution at low operation cost, and effectively improves the operation efficiency of blind deconvolution of the SAR image.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
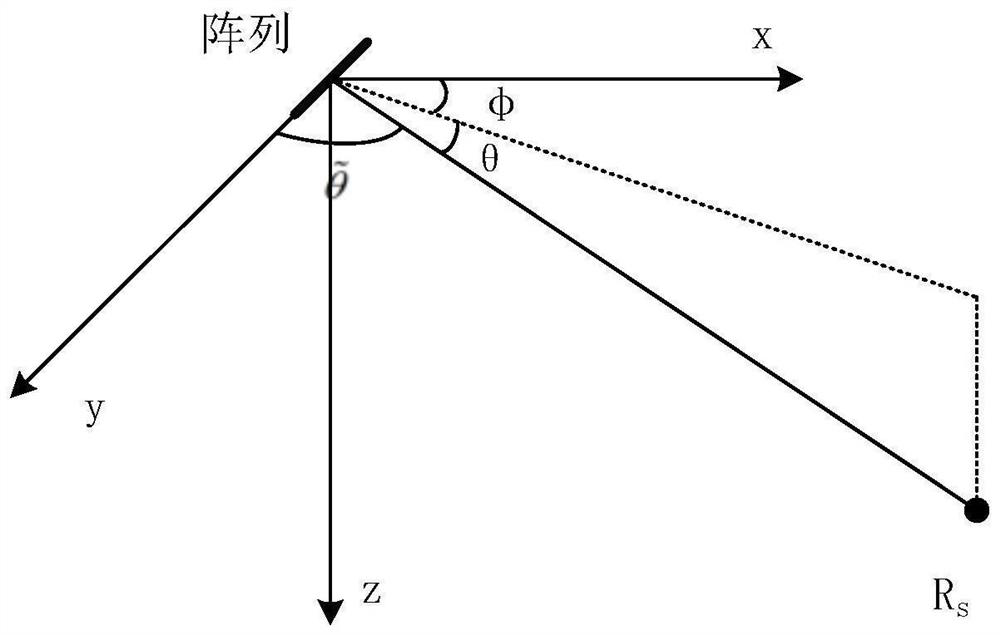
Array invariant passive positioning method and system based on Green function two-dimensional deconvolution
PendingCN112034441AAdvantages highlightedHigh passive target positioning accuracyAcoustic wave reradiationHigh level techniquesSound sourcesFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an array invariant passive positioning method and system based on Green function two-dimensional deconvolution. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a radiationsignal of a target sound source in an underwater sound field through an N-element horizontal uniform linear array, and obtaining a received signal frequency spectrum of each array element through thefrequency spectrum analysis of a sound pressure signal collected by a hydrophone; obtaining an estimated value of a frequency domain Green function through blind deconvolution calculation according tothe frequency spectrum of the received signal; performing two-dimensional deconvolution processing on the estimated value of the frequency domain Green function to obtain an incident angle and relative incident time of each oblique line of the time domain Green function; calculating to obtain an array invariant according to the incident angle and the relative incident time of each oblique line ofthe time domain Green function; and calculating the distance of the target sound source through the array invariant to realize the positioning of the target sound source. According to the method, thepassive target positioning precision is remarkably improved, the method can be used for a horizontal array and a vertical array, and the advantages are more prominent under the condition that the horizontal array is moved through a small aperture.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Iterative heavy weighted blind deconvolution method of passive millimeter wave radar image
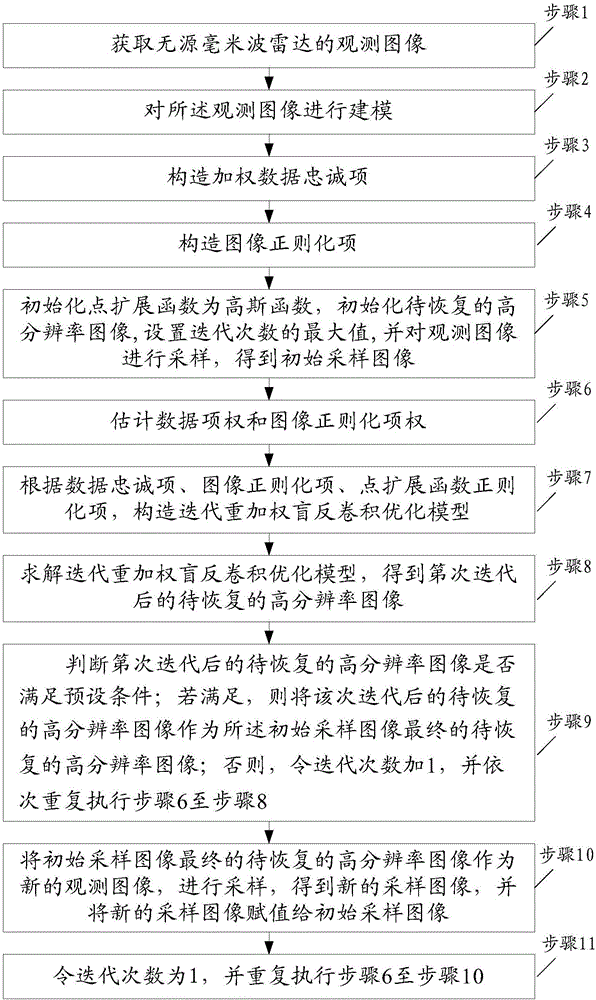
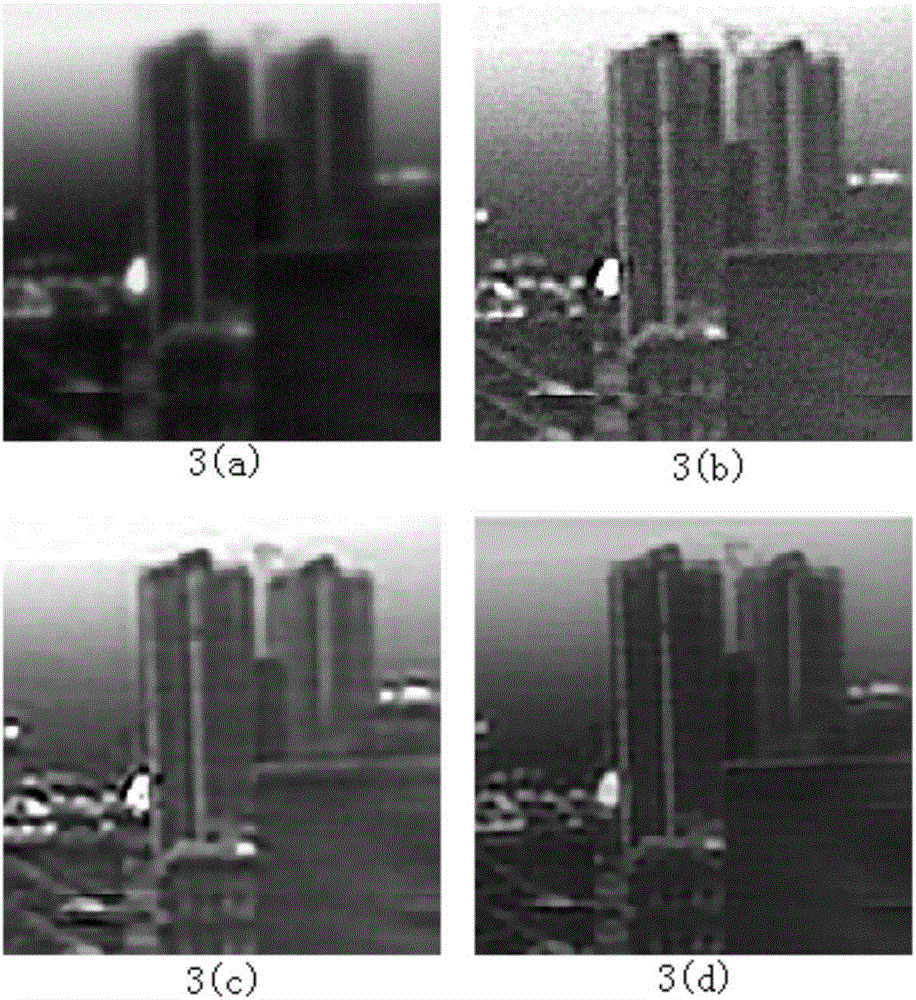
InactiveCN106504209AImprove stabilityEasy to storeImage enhancementImage analysisMixed noiseImaging processing
The invention belongs to the radar image processing technology field and discloses an iterative heavy weighted blind deconvolution method of a passive millimeter wave radar image. The method comprises the following steps of (1) integrating an adaptive weight constructed based on a residual error into a data item; (2) integrating a spatial adaptive weight of a coefficient of an image under a bilateral total variational operator effect into an image regularization item; (3) applying a smoothness constraint under a Laplace operator effect on a passive millimeter wave imaging system point expansion function; (4) realizing image and point expansion function combination iteration blind deconvolution under a multi-scale coarse-to-fine framework; and (5) deriving an adaptive estimation formula of a model regularization parameter. In the prior art, during passive millimeter wave image blind deconvolution, a radar is sensitive to a loud noise and a mixing noise and can not recover image edge and detail information. By using the heavy weighted blind deconvolution method of the invention, the above problems are solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High-energy X-ray image blind restoration method and system
ActiveCN112819723AQuality improvementFuzzy accurateImage enhancementImage analysisFast Fourier transformComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a high-energy X-ray image blind restoration method and system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, proposing definition of an image region extreme value according to the characteristic that high-energy X-ray image gray level distribution is concentrated and continuous; then, constraining the regional extreme value and the blurring kernel of the image by using an l0 norm, and constructing an image blind restoration model on an MAP framework in combination with the gradient prior of the image; thirdly, alternately solving a clear image and a fuzzy kernel through a semi-quadratic splitting method and fast Fourier transform, and accelerating the solving of sub-problems by using linear approximation and an acceleration conjugate gradient method; and finally, obtaining the main structure information of the preliminarily estimated blurring kernel through a skeleton extraction and traversal method, constructing a continuous function in a blurring kernel cross sliding window for optimization, and performing non-blind deconvolution on the blurring image by using the optimized blurring kernel k, to obtain a clear image. According to the method, the system blurring in the high-energy X-ray image is better removed, the quality of the image is improved, and a more accurate blurring kernel is estimated for nonlinear reconstruction of the image.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com