Method and system for evaluating resolution index in naked eye stereoscopic display
A naked-eye stereo and evaluation method technology, applied in stereo systems, televisions, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of impracticality and increase the difficulty of determining the minimum resolution test target.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The principle of 3D display is the principle of binocular parallax, that is, the image is divided into two channels by using a light-splitting element, so that different images are sent to different eyes, and then the brain produces a concave-convex visual effect through the fusion of the images, so there is stereo vision. The most critical element in this process is the light splitting element, which is also the biggest difference between the display in 2D mode and 3D mode. In glasses-type 3D displays, polarizers or shutter glasses are used to split light, while in naked-eye 3D displays, grating arrays or lens arrays are used to split light.
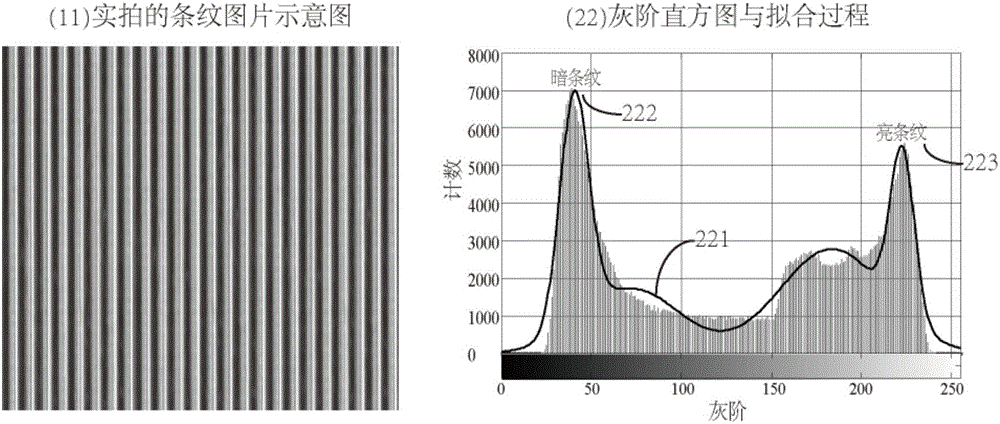
[0041] Secondly, the spectroscopic element is a linear optical system. When the object light passes through the spectroscopic element for imaging, its spatial spectrum will be modulated. The modulation behavior is as follows: the imaging contrast and phase will be modulated, and the imaging quality will be affected accordingly. ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The evaluation method provided in Embodiment 1 can only determine whether the resolution of the naked-eye stereoscopic display device is lost in 3D mode, but cannot evaluate its actual resolution. In order to solve this technical defect, this embodiment provides another evaluation method. On the basis of the method in Embodiment 1, this method adds a step, and the specific content is as follows:
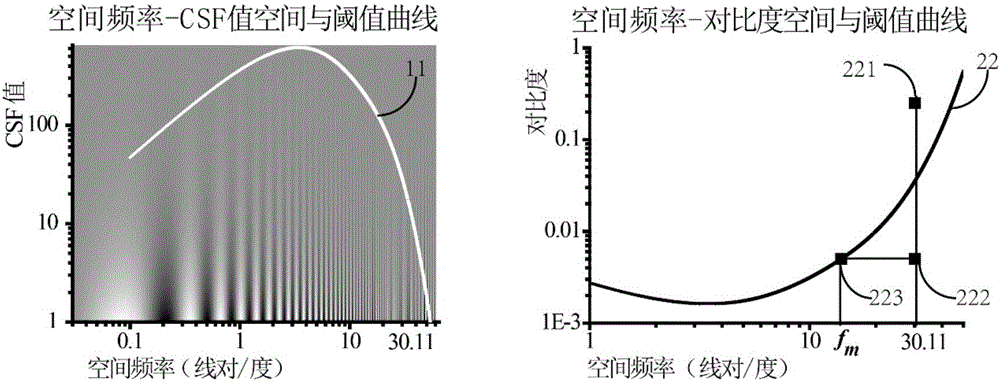
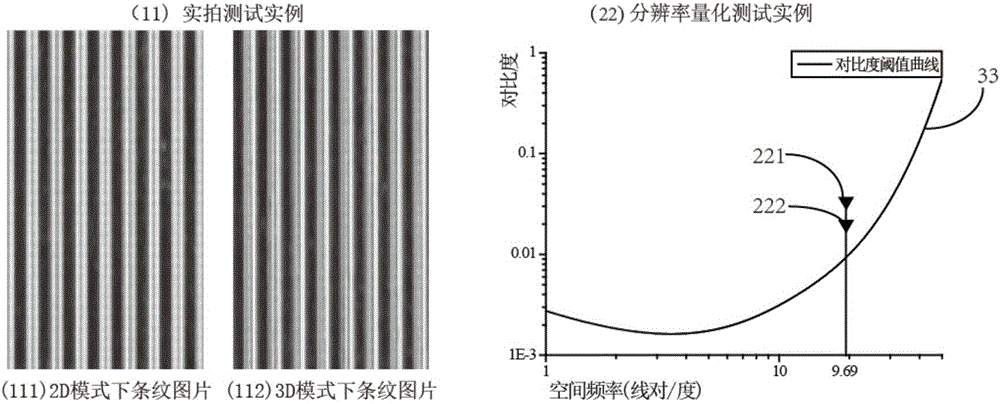
[0065] In the case that it is determined that the resolution has been lost, the evaluation method also includes the step of determining the actual resolution of the naked-eye stereoscopic display device in 3D mode, specifically shifting the determined point to the left so that it falls on the spatial frequency-contrast threshold curve On C(f), then determine the spatial frequency corresponding to this contrast, and then solve the actual resolution of the naked-eye stereoscopic display device in 3D mode according to the spatial frequency.
Embodiment 3
[0067] This embodiment further explains the quantization process through two examples.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com